1991 FORD FESTIVA brake sensor
[x] Cancel search: brake sensorPage 169 of 454

memory. Intermittent failures may be caused by a sensor, connector, or wiring. See INTERMITTENTS in TESTS W/O CODES article in the
ENGINE PERFORMANCE Section.
VISUAL CHECK & VEHICLE PREPARATION
Before connecting any equipment to diagnose EEC system, perform following preparatory procedures:
Verify condition of air cleaner and air ducts.
Check all vacuum hoses for leaks, restrictions, or improper routing.
Check EEC system wiring harness electrical connections for corrosion, bent or broken pins, loose wires or terminals, or improper
routing.
Check ECA, sensors, and actuators for physical damage.
Check engine oil and coolant level.
Perform all necessary safety precautions to prevent personal injury or vehicle damage.
Set parking brake. Place shift lever in Park for automatic transmissions, or Neutral for manual transmissions. DO NOT move shift lever
during test unless specifically directed.
Turn off all lights and accessories. Ensure vehicle doors are closed when measuring voltage or resistance.
Start engine. Run at idle until upper radiator hose is hot and pressurized and engine is off fast idle. Check for leaks around exhaust
manifold, exhaust gas oxygen sensor, and vacuum hose connections.
Turn ignition off. Service items as required. Go to EQUIPMENT HOOK-UP .
EQUIPMENT HOOK-UP
VOM
1. Turn ignition off. Connect a jumper wire from STI connector to ground. Refer to SELF-TEST CONNECTOR LOCATION and
SELF
-TEST CONNECTOR WIRE COLORS tables. See Fig. 1 .
2. Connect VOM between STO terminal and engine ground. Set VOM to measure 0-20 volts DC.
CHECK ENGINE Light (MIL)
Connect a jumper wire between STI connector and ground.
SUPER STAR II Tester
Turn ignition off. Connect adapter cable leads to diagnostic tester. Connect service adapter cables to vehicle self-test connectors. Ground
adapter cable.
SELF-TEST CONNECTOR LOCATION
SELF-TEST CONNECTOR WIRE COLORS
Fig. 1: Self
-Test Connector Terminal ID
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
RETRIEVING CODES
Reading Service Codes
ApplicationLocation
1.3LLeft Rear Corner Of Engine Compartment
1.6LRight Rear Corner Of Engine Compartment
CircuitWire Color
1.3L
SMLBlue/Green
STIYellow/Green
STOYellow/White
1.6L
SMLBlack/Blue
STIYellow
STOGreen/Black
Page 2 of 20 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - G - TESTS W/CODES 1991-92 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford Motor Co. Self-Diagnostics
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 170 of 454
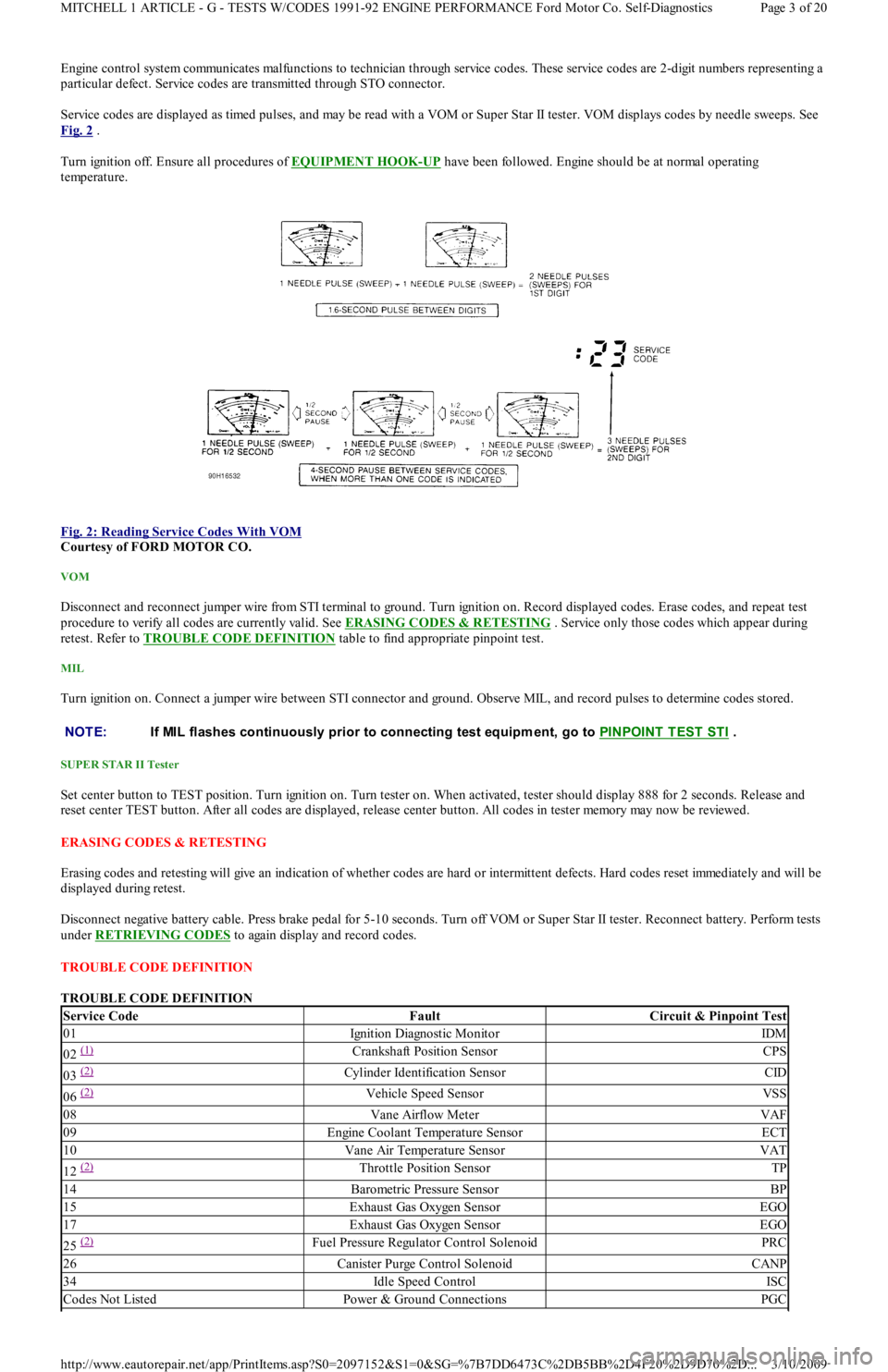
Engine control system communicates malfunctions to technician through service codes. These service codes are 2-digit numbers representing a
particular defect. Service codes are transmitted through STO connector.
Service codes are displayed as timed pulses, and may be read with a VOM or Super Star II tester. VOM displays codes by needle sweeps. See
Fig. 2
.
Turn ignition off. Ensure all procedures of EQUIPMENT HOOK
-UP have been followed. Engine should be at normal operating
temperature.
Fig. 2: Reading Service Codes With VOM
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
VOM
Disconnect and reconnect jumper wire from STI terminal to ground. Turn ignition on. Record displayed codes. Erase codes, and repeat test
procedure to verify all codes are currently valid. See ERASING CODES & RETESTING . Service only those codes which appear during
retest. Refer to TROUBLE CODE DEFINITION
table to find appropriate pinpoint test.
MIL
Turn ignition on. Connect a jumper wire between STI connector and ground. Observe MIL, and record pulses to determine codes stored.
SUPER STAR II Tester
Set center button to TEST position. Turn ignition on. Turn tester on. When activated, tester should display 888 for 2 seconds. Release and
reset center TEST button. After all codes are displayed, release center button. All codes in tester memory may now be reviewed.
ERASING CODES & RETESTING
Erasing codes and retesting will give an indication of whether codes are hard or intermittent defects. Hard codes reset immediately and will be
displayed during retest.
Disconnect negative battery cable. Press brake pedal for 5-10 seconds. Turn off VOM or Super Star II tester. Reconnect battery. Perform tests
under RETRIEVING CODES
to again display and record codes.
TROUBLE CODE DEFINITION
TROUBLE CODE DEFINITION
NOTE:If MIL flashes continuously prior to connecting test equipm ent, go to PINPOINT T EST ST I .
Service CodeFaultCircuit & Pinpoint Test
01Ignition Diagnostic MonitorIDM
02 (1) Crankshaft Position SensorCPS
03 (2) Cylinder Identification SensorCID
06 (2) Vehicle Speed SensorVSS
08Vane Airflow MeterVAF
09Engine Coolant Temperature SensorECT
10Vane Air Temperature SensorVAT
12 (2) Throttle Position SensorTP
14Barometric Pressure SensorBP
15Exhaust Gas Oxygen SensorEGO
17Exhaust Gas Oxygen SensorEGO
25 (2) Fuel Pressure Regulator Control SolenoidPRC
26Canister Purge Control SolenoidCANP
34Idle Speed ControlISC
Codes Not ListedPower & Ground ConnectionsPGC
Page 3 of 20 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - G - TESTS W/CODES 1991-92 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford Motor Co. Self-Diagnostics
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 171 of 454

CLEARING CODES
Clearing Codes Procedure
Disconnect negative battery cable. Press brake pedal for 5-10 seconds. Turn off VOM or Super Star II tester. Reconnect battery.
ECA LOCATION
ECA is located on center console behind kick panel on Capri, and under instrument panel on driver side of Festiva.
QUICK TESTS
KEY ON, ENGINE OFF (KOEO) SELF-TEST
KOEO
1. This is a test of electronic engine control system, conducted with power (voltage) applied and engine not running. Activate self-test, and
record all codes displayed.
2. Erase codes, and repeat self-test. Diagnose only codes occurring during repeat self-test. See TROUBLE CODE DEFINITION
table. If
no codes are present, proceed to KEY ON, ENGINE RUNNING (KOER) SELF
-TEST .
KEY ON, ENGINE RUNNING (KOER) SELF-TEST
KOER
1. Deactivate self-test. Start and run engine at 2000 RPM for 2 minutes to warm up EGO sensor. Turn off engine and wait 10 seconds.
2. Restart engine, and activate self-test. Record all service codes displayed. See TROUBLE CODE DEFINITION
table. If no codes are
present, proceed to SWITCH MONITOR TEST
.
SWITCH MONITOR TEST
This test procedure checks input signals received by ECA from individual switches. Use following procedure to perform switch monitor test:
Turn engine off and allow it to cool.
Ensure all accessories are turned off.
Deactivate self-test.
Ensure transmission is in Neutral or Park.
Turn ignition on.
SUPER STAR II Tester
Connect Super Star II tester adapter cable. Turn on tester. Latch center button. Operate each switch listed in SWITCH MONITOR TEST
table. Note output of LED on adapter cable as each switch operates. Record test results.
VOM
1. Ground STI connector. Connect VOM positive lead to SML terminal on self-test connector. Connect negative lead to ground. See Fig.
1 .
2. Operate each switch listed in SWITCH MONITOR TEST
table. Note output on VOM as each switch is operated. Go to specified
PINPOINT TEST if any switch does not meet specification.
SWITCH MONITOR TEST
(1)Festiva only.
(2)Capri only.
NOTE:DO NOT m ove throttle during KOEO self-test.
NOTE:It is necessary to clear codes in m em ory before perform ing this test. DO NOT m ove throttle during test.
NOTE:All switches m ust be tested individually. Allowing a switch to rem ain on while testing another will lead
to false test results.
NOTE:DO NOT m ove throttle, clutch, or transm ission lever unless so directed.
SwitchVOM Indication/Condition(1) Pinpoint Test
A/C SwitchLess Than 1.5 Volts; A/C & Blower Switch OnSTG
Blower Motor SwitchLess Than 1.5 Volts; Switch Set To "2" Or HigherSTG
Brake On/Off SwitchLess Than 1.5 Volts; Brake Pedal Partially
PressedSTP
Clutch Engage/Neutral Gear Switch (2) Less Than 1.5 Volts; In Gear, Clutch ReleasedSTG
Coolant Temperature SwitchLess Than 1.5 Volts; Cooling Fan OnSTP
Defrost SwitchLess Than 1.5 Volts; Defrost Switch OnSTP
Headlight SwitchLess Than 1.5 Volts; Headlight Switch OnSTP
Id l e Swit chLess Than 1.5 Volts; Accelerator Pedal PressedSTG
Page 4 of 20 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - G - TESTS W/CODES 1991-92 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford Motor Co. Self-Diagnostics
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 191 of 454

Back To Article
E - T HEORY/OPERAT ION
1991 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford/Mercury T heory & Operation
INTRODUCTION
This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related systems and components. Read this article before attempting
to diagnose systems with which you are not completely familiar.
COMPUTERIZED ENGINE CONTROLS
An electronic Control Assembly (ECA) receives and processes signals from various sensors and switches. See Fig. 1 . It then generates signals
which control ignition timing, fuel injection functions and various emission control devices. The ECA has system diagnostic capabilities and
will store trouble codes for use by service technicians.
Fig. 1: Identifying Input Devices & Output Signals (Not All Shown)
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL ASSEMBLY (ECA)
The ECA is located under the instrument panel on the driver side. It receives and processes data from sensors, switches and other components.
The ECA generates output signals to control fuel injection, spark timing, other engine functions and emission systems.
CEC INPUT DEVICES
Vehicles are equipped with different combinations of input devices. Not all devices are used on all models. To determine input device usage of
a specific model, see appropriate wiring diagram in WIRING DIAGRAMS article. The available input devices include the following:
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR (BP)
This device senses changes in barometric pressure. The ECA uses this information in calculating fuel metering, ignition timing and idle speed.
On Festiva, BP is incorporated into the ECA. On Capri, BP is located on the passenger-side cowl.
BRAKE ON-OFF (BOO) SWITCH
This switch, located at the brake pedal, senses brake operation. The ECA uses this information in calculating fuel metering.
NOTE:Com ponents are grouped into 2 categories. T he first category is CEC INPUT DEVICES, which control or
produce voltage signals m onitored by the control unit. T he second category is CEC OUT PUT SIGNALS,
which are com ponents controlled by the control unit.
Page 1 of 6 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - E - THEORY/OPERATION 1991 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford/Mercury Theory & Operation
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 195 of 454

IDLE SPEED
While the engine is cold, the Idle Speed Control By-Pass Air (ISC-BPA) Valve increases idle speed to warm the engine quickly. At engine
temperatures less than 140°F (60°C), the valve is open. As the engine warms, the valve begins to close. The valve is fully closed at engine
temperatures higher than 140°F (60°C). Idle speed is also affected by various switches, sensors and load on the engine.
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
CAPRI
A pick-up coil within the distributor sends a signal to a Distributor-Mounted Ignition Module With Vacuum Advance (DMIVA) within the
distributor. The DMIVA then sends a signal which fires the coil. When the coil fires, the distributor directs high voltage current to the spark
plugs. The DMIVA system operates independently of the ECA.
FESTIVA
A pick-up coil within the distributor sends a signal to a transistorized ignition module on the coil bracket. A timing signal also goes from the
ECA to the ignition module. The ignition module then sends a signal which fires the coil. When the coil fires, the distributor directs high
voltage current to the spark plugs.
IGNITION TIMING CONTROL SYSTEM
CAPRI
Spark timing is controlled by vacuum and centrifugal advance mechanisms and by a signal from the ECA. The ECA does not affect ignition
timing on turbo models. On turbo models, a knock sensor and control unit retard ignition timing when knock occurs.
FESTIVA
The ECA generates a spark timing signal from data received from the BP, CPS and VAF. This signal goes to the ignition module. The ignition
module then sends a signal to fire the coil.
HIGH ALTITUDE SPARK ADVANCE CORRECTION
A barometric pressure sensor is incorporated into the ECA on Festiva and is a separate component on Capri. At high altitudes, the ECA sends
a signal to the ignition module to advance ignition timing. This feature is not used on turbo models.
KNOCK SENSOR (CAPRI)
A Knock Sensor (KS) generates a signal when knock occurs. A control unit processes this signal and then sends it to the ignition module to
retard spark timing. The KS is located in the engine block, near the oil pressure switch. This device is only used on 1.6L turbo engines.
KNOCK CONTROL UNIT (CAPRI)
The Knock Control Unit filters normal engine vibration signals from the KS, then sends a signal to the ignition module to retard spark timing.
This unit, used only on 1.6L turbo engines, is located on right side of engine compartment.
EMISSION SYSTEMS
DECELERATION SYSTEM (DASHPOT)
The deceleration control system closes the throttle plate gradually during deceleration. The dashpot prevents engine stalling on deceleration
and provides a smooth transition from deceleration to sudden acceleration.
EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM
CARBON CANISTER
The carbon canister stores vapors from the fuel tank until they are purged and burned in the engine. On Festiva, carbon canister is
located under the brake booster. On Capri, carbon canister is located on the right side of the engine compartment near the cowl panel.
CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID
This component is connected between the carbon canister and intake manifold. When the ECA sends a signal to the solenoid to open,
fuel vapors in the carbon canister are drawn into the engine.
CANISTER PURGE VALVE
This valve opens to purge vapors from the carbon canister into the engine intake system. The valve is part of the canister purge solenoid.
ROLLOVER VENT VALVE
This valve, located in front of the fuel tank, blocks the vapor line in case of vehicle rollover.
This valve, located in front of the fuel tank, blocks the vapor line in case of vehicle rollover.
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
The catalytic converter is in the exhaust system, between the exhaust manifold and the muffler. It converts certain pollutants in the exhaust
Page 5 of 6 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - E - THEORY/OPERATION 1991 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford/Mercury Theory & Operation
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 199 of 454

Back To Article
GENERAL INFORMATION
Com m only Used Abbreviations
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
"A"
A
Amperes
ABS
Anti-Lock Brakes
ABRS
Air Bag Restraint System
AC
Alternating Current
A/C
Air Conditioning
ACCS
A/C Cycling Switch
ACCUM
Accumulator
ACCY
Accessory
ACT
Air Charge Temperature Sensor
ADJ
Adjust or Adjustable
ADV
Advance
AFS
Airflow Sensor
AI
Air Injection
AIR or A.I.R.
Air Injection Reactor
AIS
Air Injection System
Alt.
Alternator or Altitude
Amp./amp/amps
Ampere NOTE:T his article is intended for general inform ation purposes only. T his inform ation m ay not apply to all
m akes and m odels. Not all abbreviations are covered as m anufacturers add new ones every day.
Page 1 of 15 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Commonly Used Abbreviations
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 200 of 454

ASCS
Air Suction Control Solenoid
ASD
Auto Shutdown
ASDM
Air Bag System Diagnostic Module
ASV
Air Suction Valve
A/T
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
ATC
Automatic Temperature Control
ATDC
After Top Dead Center
ATF
Automatic Transmission Fluid
ATS
Air Temperature Sensor
Aux.
Auxiliary
Avg.
Average
AXOD
Automatic Transaxle Overdrive (Ford Models Only)
"B"
BAC
By-Pass Air Control
BAP
Barometric Absolute Pressure Sensor
BARO
Barometric
Batt.
Battery
Bbl.
Barrel (Example: 4-Bbl.)
BCM
Body Control Module
BHP
Brake Horsepower
BMAP
Page 2 of 15 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Commonly Used Abbreviations
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 201 of 454

Barometric and Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
BOO
Brake On-Off Switch
B/P
Backpressure
BPS
Barometric Pressure Sensor
BPT
Backpressure Transducer
BTDC
Before Top Dead Center
BTU
British Thermal Unit
BVSV
Bimetallic Vacuum Switching Valve
"C"
° C
Celsius (Degrees)
Calif.
California
CANP
Canister Purge
CARB
California Air Resources Board
CAT
Catalytic Converter
CB
Circuit Breaker
CBD
Closed Bowl Distributor
cc
cubic centimeter
CCC
Computer Command Control
CCD
Computer Controlled Dwell
CCOT
Cycling Clutch Orifice Tube
CCW
Counterclockwise
Page 3 of 15 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Commonly Used Abbreviations
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...