1991 FORD FESTIVA alternator
[x] Cancel search: alternatorPage 43 of 454
Back To Article
ALTERNATOR & REGULATOR
1991 ELECT RICAL Alternators & Regulators
DESCRIPTION
Mitsubishi alternator is a 50-amp, conventional 3-phase, self-rectifying type unit, containing 6 diodes (3 main diodes and a smaller diode trio)
and a case-mounted Integrated Circuit (IC) regulator. A charge indicator light in the instrument panel indicates charging system mal fu n ct io n s.
See Fig. 1
.
Fig. 1: Charging System Wiring Schematic
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
ADJUSTMENTS
BELT TENSION
BELT ADJUSTMENTS
(1)
ON-VEHICLE TESTING
ALTERNATOR OUTPUT
ApplicationNew BeltUsed Belt
A/C & P/S Belts110-125 (50-57)92-110 (42-50)
Alt. Belt110-130 (50-60)95-110 (43-50)
(1)Tension in Lbs. (Kg) Using Strand Tension Gauge
NOTE:Before testing, check alternator wiring harness connections, drive belt tension and battery voltage.
Ensure battery cables and engine ground cable are clean and tight. Wait at least 30 seconds after
starting engine before m easuring voltage.
CAUT ION: DO NOT start engine with "L" and "S" term inal connectors disconnected from alternator. DO NOT allow
"L" term inal to contact ground while engine is running. See Fig. 2
.
Page 1 of 3 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - ALTERNATOR & REGULATOR 1991 ELECTRICAL Alternators & Regulators
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 44 of 454
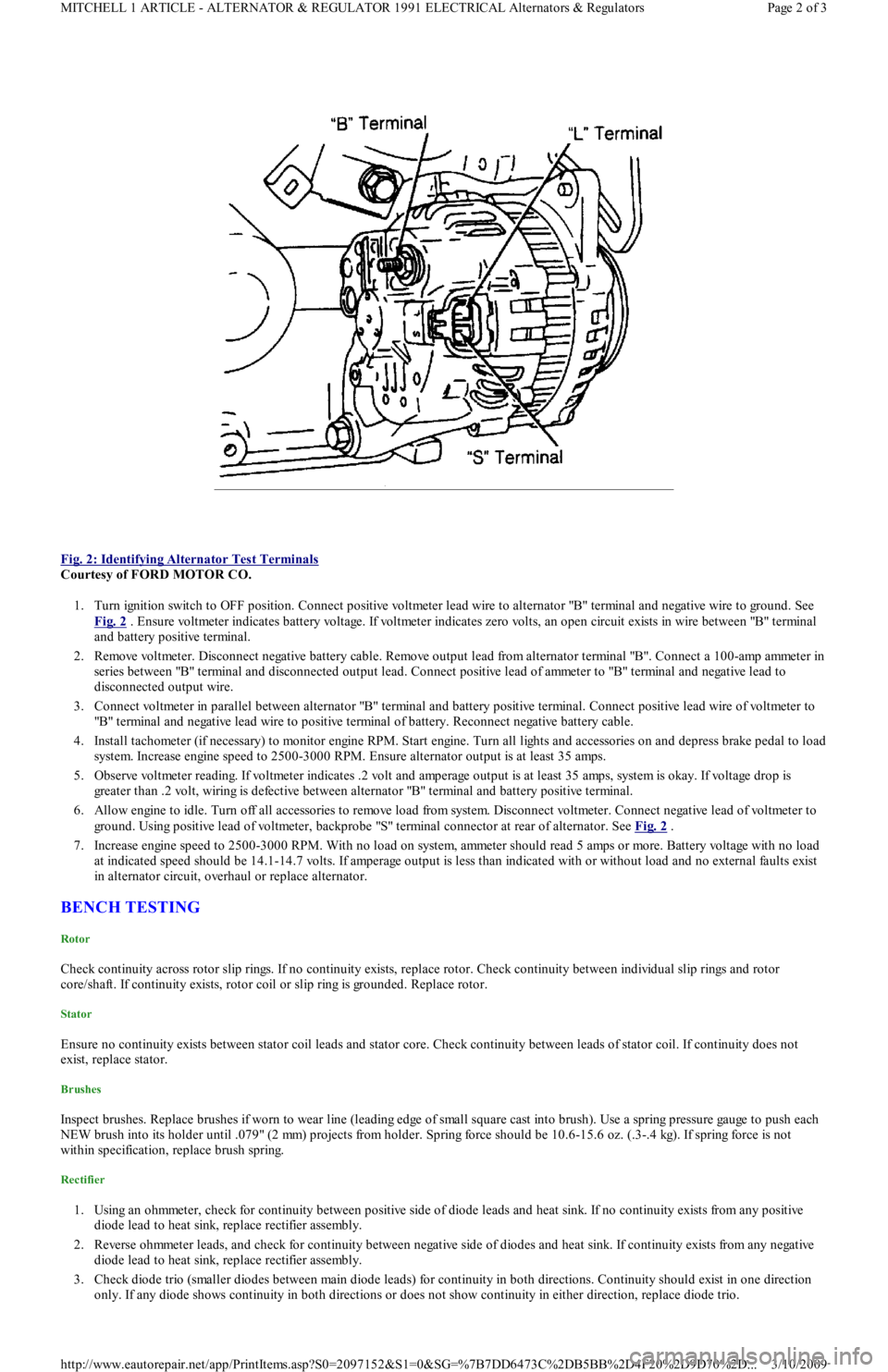
Fig. 2: Identifying Alternator Test Terminals
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
1. Turn ignition switch to OFF position. Connect positive voltmeter lead wire to alternator "B" terminal and negative wire to ground. See
Fig. 2
. Ensure voltmeter indicates battery voltage. If voltmeter indicates zero volts, an open circuit exists in wire between "B" terminal
and battery positive terminal.
2. Remove voltmeter. Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove output lead from alternator terminal "B". Connect a 100-amp ammeter in
series between "B" terminal and disconnected output lead. Connect positive lead of ammeter to "B" terminal and negative lead to
disconnected output wire.
3. Connect voltmeter in parallel between alternator "B" terminal and battery positive terminal. Connect positive lead wire of voltmeter to
"B" terminal and negative lead wire to positive terminal of battery. Reconnect negative battery cable.
4. Install tachometer (if necessary) to monitor engine RPM. Start engine. Turn all lights and accessories on and depress brake pedal to load
system. Increase engine speed to 2500-3000 RPM. Ensure alternator output is at least 35 amps.
5. Observe voltmeter reading. If voltmeter indicates .2 volt and amperage output is at least 35 amps, system is okay. If voltage drop is
greater than .2 volt, wiring is defective between alternator "B" terminal and battery positive terminal.
6. Allow engine to idle. Turn off all accessories to remove load from system. Disconnect voltmeter. Connect negative lead of voltmeter to
ground. Using positive lead of voltmeter, backprobe "S" terminal connector at rear of alternator. See Fig. 2
.
7. Increase engine speed to 2500-3000 RPM. With no load on system, ammeter should read 5 amps or more. Battery voltage with no load
at indicated speed should be 14.1-14.7 volts. If amperage output is less than indicated with or without load and no external faults exist
in alternator circuit, overhaul or replace alternator.
BENCH TESTING
Rotor
Check continuity across rotor slip rings. If no continuity exists, replace rotor. Check continuity between individual slip rings and rotor
core/shaft. If continuity exists, rotor coil or slip ring is grounded. Replace rotor.
Stator
Ensure no continuity exists between stator coil leads and stator core. Check continuity between leads of stator coil. If continuity does not
exist, replace stator.
Brushes
Inspect brushes. Replace brushes if worn to wear line (leading edge of small square cast into brush). Use a spring pressure gauge to push each
NEW brush into its holder until .079" (2 mm) projects from holder. Spring force should be 10.6-15.6 oz. (.3-.4 kg). If spring force is not
within specification, replace brush spring.
Rectifier
1. Using an ohmmeter, check for continuity between positive side of diode leads and heat sink. If no continuity exists from any positive
diode lead to heat sink, replace rectifier assembly.
2. Reverse ohmmeter leads, and check for continuity between negative side of diodes and heat sink. If continuity exists from any n e ga t ive
diode lead to heat sink, replace rectifier assembly.
3. Check diode trio (smaller diodes between main diode leads) for continuity in both directions. Continuity should exist in one direction
only. If any diode shows continuity in both directions or does not show continuity in either direction, replace diode trio.
Page 2 of 3 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - ALTERNATOR & REGULATOR 1991 ELECTRICAL Alternators & Regulators
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 45 of 454
TROUBLE SHOOTING
OVERHAUL
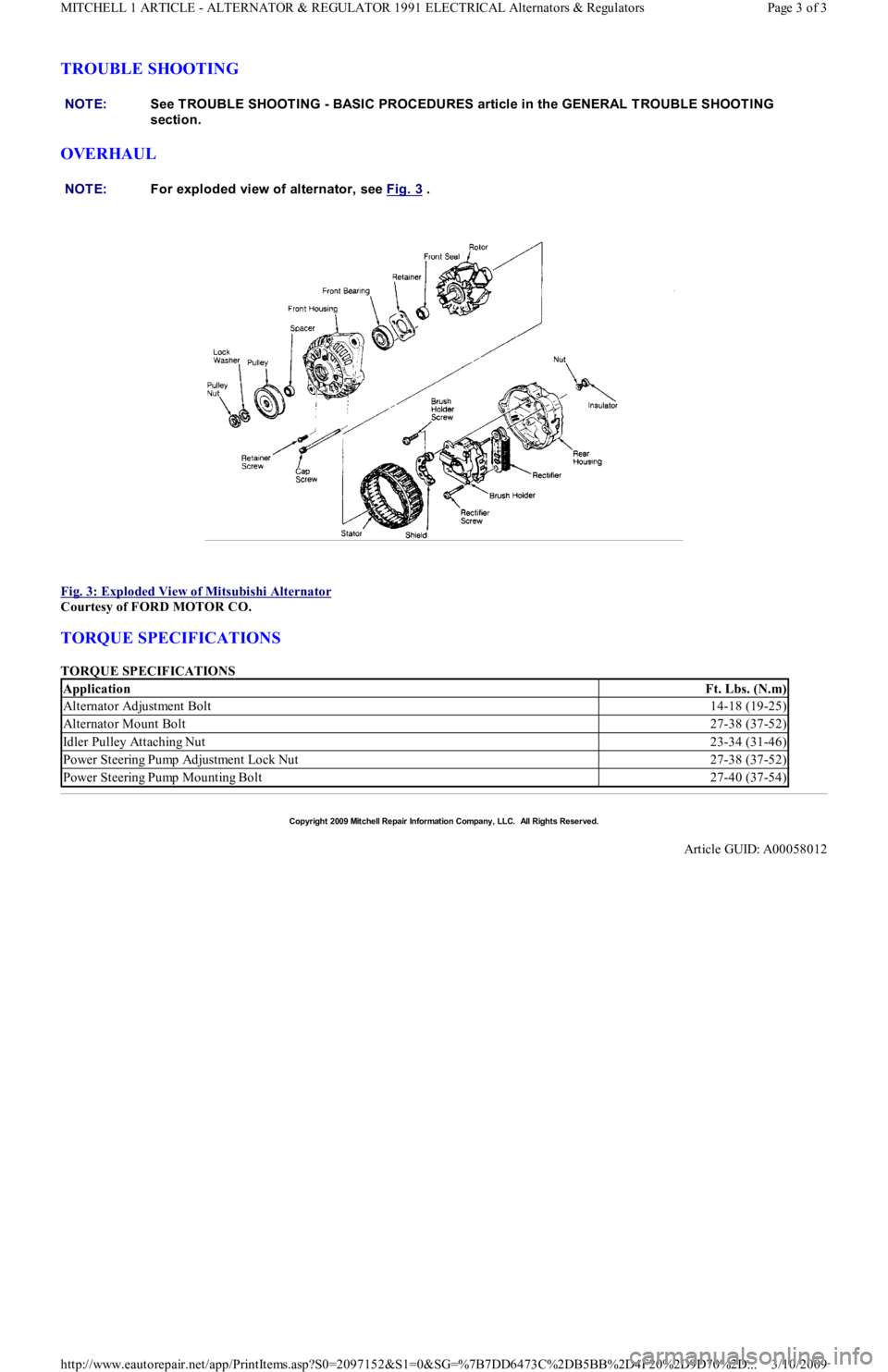
Fig. 3: Exploded View of Mitsubishi Alternator
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS NOTE:See T ROUBLE SHOOT ING - BASIC PROCEDURES article in the GENERAL T ROUBLE SHOOT ING
section.
NOTE:For exploded view of alternator, see Fig. 3
.
ApplicationFt. Lbs. (N.m)
Alternator Adjustment Bolt14-18 (19-25)
Alternator Mount Bolt27-38 (37-52)
Idler Pulley Attaching Nut23-34 (31-46)
Power Steering Pump Adjustment Lock Nut27-38 (37-52)
Power Steering Pump Mounting Bolt27-40 (37-54)
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00058012
Page 3 of 3 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - ALTERNATOR & REGULATOR 1991 ELECTRICAL Alternators & Regulators
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 65 of 454

Fig. 2: Ground Numbers & Locations (2001 & Prior Model Years)
WIRING DIAGRAM COMPONENT LOCATIONS
When trying to locate a component in a wiring diagram and you don't know the specific system where it is located, use this handy component
locator to find the system wiring diagram in which the component is located. Then, go to that system and locate the component within the
wiring diagram.
For example, if you don't know the specific system in which the ignition switch is located, look up ignition switch in the wiring diagram
component location tables and go to the appropriate wiring diagram(s) which contain either full or partial views of the ignition switch. The full
view of the ignition switch is located in Power Distribution.
The first listing for the component will be the full or most complete view of the component. Additional listings will be partial views of the
component. Not all components are used on all models.
All components will have a partial view in Ground Distribution and Power Distribution. Data Link Connectors show connecting circuits
between modules. Alternate names for components may be listed in wiring diagram component locations tables.
WIRING DIAGRAM COMPONENT LOCATIONS
ComponentWiring Diagram
ABS Electronic Control UnitAnti-Lock Brakes; Data Link Connectors
ABS Hydraulic UnitAnti-Lock Brakes
Acceleration SensorAnti-Lock Brakes
Accessory Delay RelayPower Windows
A/C Compressor Clutch RelayEngine Performance
A/C SensorEngine Performance
A/C Pressure SwitchEngine Performance
Adaptive Lamp Control ModuleExterior Lights
Air Bag(s)Air Bag Restraint System
Air Bag ModuleAir Bag Restraint System
Air Bag Sensor(s)Air Bag Restraint System
Air Injection Pump RelayEngine Performance
Air Temperature SensorOverhead Console
Alternator (Generator)Generators & Regulators
Anti-Theft Control ModuleAnti-Theft System; Starters
Page 3 of 6 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Using Mitchell1's Wiring Diagrams
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B959286D2%2D3A85%2D4BFC%2D9C5C%2D
...
Page 69 of 454
Back To Article
WIRING DIAGRAMS
1991 WIRING DIAGRAMS Ford Motor Co.
IDENTIFICATION
COMPONENT LOCATION MENU
COMPONENT LOCATIONS
WIRING DIAGRAMS
ComponentFigure No. (Location)
A/C RELAY3 (B 8)
A/T SELECT LIGHT3 (E 8)
ALTERNATOR1 (C 3)
BACK-UP LIGHT SWITCH5 (D 19)
BATTERY1 (A 2)
BLOWER SWITCH3 (C 9)
BRAKE WARNING SWITCH1 (C 2)
CIG LTR4 (E 14)
CLUTCH INTERLOCK SWITCH (M/T)1 (B 2)
CONDENSER FAN (A/T)3 (C 8)
COOLANT FAN MOTOR1 (D 3)
COOLANT FAN RELAY1 (D 3)
DEFOG SWITCH5 (C 16)
DIR/HAZARD SWITCH4 (B-C 12)
ELECT CONTROL ASSY (ECA)2 (A 4-7)
FRONT WASHER MOTOR1 (E 3)
FRONT WIPER MOTOR1 (E 3)
FRONT WIPER/WASHER SWITCH5 (A 16)
FUEL PUMP INERTIA SWITCH2 (D 4)
FUEL PUMP RELAY2 (C 4)
FUSE BLOCK3 (D-E 9-10)
HEADLIGHT RELAY4 (D 14)
HORN RELAY3 (E 11)
HORN SWITCH4 (E 15)
IGNITION COIL2 (E 5)
IGNITION KEY REMINDER SWITCH4 (E 13)
IGNITION SWITCH3 (C-D 11)
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER4 (A-E 15)
INSTRUMENT PANEL LIGHT CONTROL4 (D-E 12)
INTERIOR LIGHT SWITCH4 (E 14)
LIGHT SWITCH4 (C-D 12)
MAIN FUSE PANEL1 (A 3)
MAIN RELAY2 (D 5)
NEUTRAL SAFETY SWITCH (A/T)1 (B 2)
PARKING LIGHT RELAY4 (C 14)
PASSIVE RESTRAINT CONTROL MODULE3 (A 11)
REAR WASHER MOTOR5 (D 17)
REAR WIPER/WASHER SWITCH5 (E 16)
SHIFT LOCK SERVO ASSY4 (A 12)
STARTER1 (B 3)
STOP LIGHT SWITCH5 (D 19)
TIMER/BUZZER UNIT4 (E 12)
TRUNK LIGHT5 (B 16)
WAC RELAY3 (B 8)
Page 1 of 6 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - WIRING DIAGRAMS 1991 WIRING DIAGRAMS Ford Motor Co.
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B959286D2%2D3A85%2D4BFC%2D9C5C%2D
...
Page 75 of 454
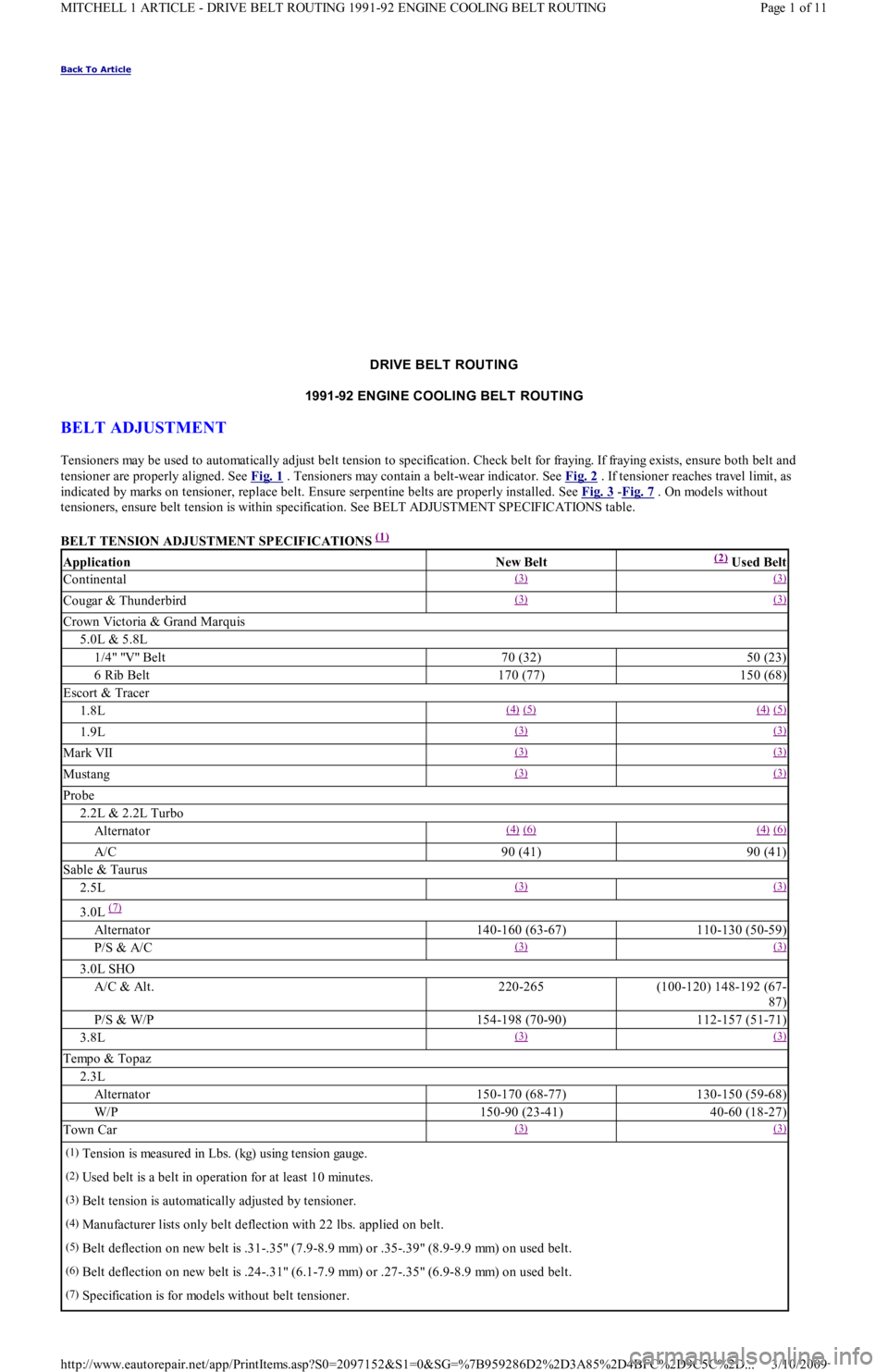
Back To Article
DRIVE BELT ROUTING
1991-92 ENGINE COOLING BELT ROUT ING
BELT ADJUSTMENT
Tensioners may be used to automatically adjust belt tension to specification. Check belt for fraying. If fraying exists, ensure both belt and
tensioner are properly aligned. See Fig. 1
. Tensioners may contain a belt-wear indicator. See Fig. 2 . If tensioner reaches travel limit, as
indicated by marks on tensioner, replace belt. Ensure serpentine belts are properly installed. See Fig. 3
-Fig. 7 . On models without
tensioners, ensure belt tension is within specification. See BELT ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS table.
BELT TENSION ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS
(1)
ApplicationNew Belt(2) Used Belt
Continental(3) (3)
Cougar & Thunderbird(3) (3)
Crown Victoria & Grand Marquis
5.0L & 5.8L
1/4" "V" Belt70 (32)50 (23)
6 Rib Belt170 (77)150 (68)
Escort & Tracer
1.8L(4) (5) (4) (5)
1.9L(3) (3)
Mark VII(3) (3)
Mustang(3) (3)
Probe
2.2L & 2.2L Turbo
Alternator(4) (6) (4) (6)
A/C90 (41)90 (41)
Sable & Taurus
2.5L(3) (3)
3.0L (7)
Alternator140-160 (63-67)110-130 (50-59)
P/S & A/C(3) (3)
3.0L SHO
A/C & Alt.220-265(100-120) 148-192 (67-
87)
P/S & W/P154-198 (70-90)112-157 (51-71)
3.8L(3) (3)
Tempo & Topaz
2.3L
Alternator150-170 (68-77)130-150 (59-68)
W/P150-90 (23-41)40-60 (18-27)
Town Car(3) (3)
(1)Tension is measured in Lbs. (kg) using tension gauge.
(2)Used belt is a belt in operation for at least 10 minutes.
(3)Belt tension is automatically adjusted by tensioner.
(4)Manufacturer lists only belt deflection with 22 lbs. applied on belt.
(5)Belt deflection on new belt is .31-.35" (7.9-8.9 mm) or .35-.39" (8.9-9.9 mm) on used belt.
(6)Belt deflection on new belt is .24-.31" (6.1-7.9 mm) or .27-.35" (6.9-8.9 mm) on used belt.
(7)Specification is for models without belt tensioner.
Page 1 of 11 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - DRIVE BELT ROUTING 1991-92 ENGINE COOLING BELT ROUTING
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B959286D2%2D3A85%2D4BFC%2D9C5C%2D
...
Page 90 of 454
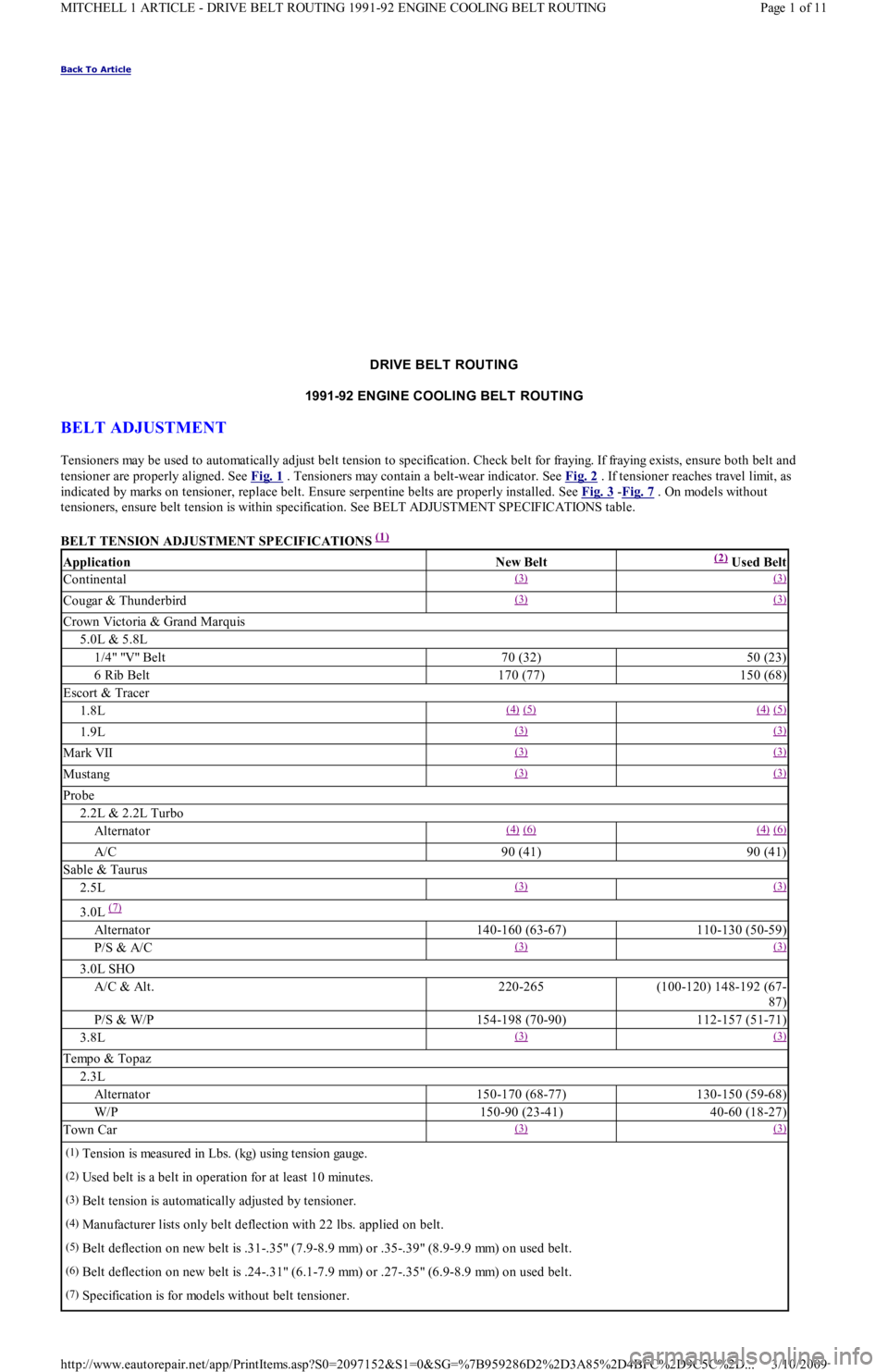
Back To Article
DRIVE BELT ROUTING
1991-92 ENGINE COOLING BELT ROUT ING
BELT ADJUSTMENT
Tensioners may be used to automatically adjust belt tension to specification. Check belt for fraying. If fraying exists, ensure both belt and
tensioner are properly aligned. See Fig. 1
. Tensioners may contain a belt-wear indicator. See Fig. 2 . If tensioner reaches travel limit, as
indicated by marks on tensioner, replace belt. Ensure serpentine belts are properly installed. See Fig. 3
-Fig. 7 . On models without
tensioners, ensure belt tension is within specification. See BELT ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS table.
BELT TENSION ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS
(1)
ApplicationNew Belt(2) Used Belt
Continental(3) (3)
Cougar & Thunderbird(3) (3)
Crown Victoria & Grand Marquis
5.0L & 5.8L
1/4" "V" Belt70 (32)50 (23)
6 Rib Belt170 (77)150 (68)
Escort & Tracer
1.8L(4) (5) (4) (5)
1.9L(3) (3)
Mark VII(3) (3)
Mustang(3) (3)
Probe
2.2L & 2.2L Turbo
Alternator(4) (6) (4) (6)
A/C90 (41)90 (41)
Sable & Taurus
2.5L(3) (3)
3.0L (7)
Alternator140-160 (63-67)110-130 (50-59)
P/S & A/C(3) (3)
3.0L SHO
A/C & Alt.220-265(100-120) 148-192 (67-
87)
P/S & W/P154-198 (70-90)112-157 (51-71)
3.8L(3) (3)
Tempo & Topaz
2.3L
Alternator150-170 (68-77)130-150 (59-68)
W/P150-90 (23-41)40-60 (18-27)
Town Car(3) (3)
(1)Tension is measured in Lbs. (kg) using tension gauge.
(2)Used belt is a belt in operation for at least 10 minutes.
(3)Belt tension is automatically adjusted by tensioner.
(4)Manufacturer lists only belt deflection with 22 lbs. applied on belt.
(5)Belt deflection on new belt is .31-.35" (7.9-8.9 mm) or .35-.39" (8.9-9.9 mm) on used belt.
(6)Belt deflection on new belt is .24-.31" (6.1-7.9 mm) or .27-.35" (6.9-8.9 mm) on used belt.
(7)Specification is for models without belt tensioner.
Page 1 of 11 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - DRIVE BELT ROUTING 1991-92 ENGINE COOLING BELT ROUTING
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B959286D2%2D3A85%2D4BFC%2D9C5C%2D
...
Page 101 of 454

Back To Article
ENGINE OVERHAUL
1991-92 FORD MOT OR CO. ENGINES 1.3L & 1.6L 4-Cylinder
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
Engine can be identified by Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) on metal tab attached to instrument panel. Tab is close to windshield on
driver's side and is visible through windshield. VIN has 17 characters. The 8th character identifies engine.
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION CODES
ADJUSTMENTS
VALVE ARRANGEMENT
Firewall Side
In t ake val ves.
Radiator Side
Exhaust valves.
VALVE CLEARANCE ADJUSTMENT
Hydraulic lifters are used. Adjustment is NOT possible nor necessary.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE
Remove rear seat. Remove fuel pump access panel. Disconnect fuel pump electrical connector. Start engine and allow to idle until engine dies.
ENGINE
Removal (1.3L)
1. Remove battery and battery tray. Index hood-to-hinge and remove hood. Drain coolant. Drain engine oil and transaxle fluid. Disconnect
vane airflow meter connector, vane airflow meter and hose.
2. Remove oil dipstick, cooling fan and radiator assembly. Disconnect accelerator cable from mounting bracket and throttle lever.
Disconnect speedometer cable at transaxle. Mark and disconnect fuel lines at fuel pump. Plug fuel lines. Remove heater hoses. Remove
brake booster vacuum hose. Disconnect transaxle vacuum hose.
3. Remove charcoal canister hoses from engine. Disconnect engine wiring harness. Remove alternator and brackets. Remove engine ground
strap. Raise vehicle and remove catalytic converter.
4. Disconnect A/C compressor without removing hoses, and set compressor aside. Disconnect distributor wiring at coil. On automatic
transaxle models, remove shift lever-to-manual shaft assembly nut. Remove shift cable from transaxle. Loosen front wheel bolts. Raise
vehicle and remove wheel assemblies.
5. Remove stabilizer mounting nuts and brackets. Remove lower arm clamp bolts and nuts. Pull lower arms downward, separating lower
arms from knuckles. Separate halfshafts and install Differential Plugs (T87C-7025-C) between differential side gears. See FWD AXLE
SHAFTS article in DRIVE AXLES Section.
6. On manual transaxle vehicles, disconnect clutch control cable and shift control cable rod. Remove stabilizer bar from transaxle. Remove
catalytic converter inlet pipe. Support engine assembly with hoist. Remove rear crossmember mount bolts. Remove front and rear engine
mount nuts.
7. Remove crossmember. Lower vehicle and attach engine lift hooks. Remove right engine mount bolt. Remove engine/transaxle assembly.
Remove gusset plates. Remove starter and flywheel cover. Remove torque converter bolts on automatic transaxle. Remove engine-to-
transaxle bolts. Separate transaxle from engine.
Installation (1.3L)
1. Install transaxle to engine in reverse order of removal. Attach hoist to engine/transaxle assembly and position in vehicle. Support engine
in chassis and install engine mount bolts. Raise vehicle and install front engine mount nut. Tighten nuts to specification. See TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS table at end of article.
2. Position crossmember onto mounts and chassis. Tighten rear nut. Install mount-to-crossmember nuts and tighten. Remove differential
plugs and install halfshafts. To complete installation, reverse removal procedure. Tighten all bolts/nuts to specifications. Fill all fluid NOTE:For engine repair procedures not covered in this article, see ENGINE OVERHAUL PROCEDURES
-
GENERAL INFORMATION
article in the GENERAL INFORMAT ION section.
ApplicationVIN Code
Festiva
1.3L SOHC PFIH
Capri
1.6L DOHC PFIZ
1.6L DOHC PFI TURBO6
NOTE:When rem oving engine m ounts, m ark and note location and position to ensure proper installation.
Engine and transaxle are rem oved as an assem bly.
Page 1 of 19 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - ENGINE OVERHAUL 1991-92 FORD MOTOR CO. ENGINES 1.3L & 1.6L 4-Cylinder
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B959286D2%2D3A85%2D4BFC%2D9C5C%2D
...