1989 FORD FIESTA cooling
[x] Cancel search: coolingPage 3 of 296

Lubricants and fluids
Refer to end of “Weekly Checks”
Capacities
Engine oil
At oil and filter change:HCS engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 3.25 litres
CVH and PTE engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
3.50 litresZetec engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 4.25 litres
Difference between dipstick minimum and maximum level notches . . . 0.5 to 1.0 litre
Cooling system
HCS engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . 7.1 litresCVH and PTE engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 7.6 litresZetec engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . 7.0 litres
Fuel tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 42.0 litres
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 3.1 litres
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
3.5 litres
Engine
Direction of crankshaft rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Clockwise (seen from right-hand side of vehicle)
Oil filter: HCS, CVH and PTE engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion C104
Zetec engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . Champion C148
Cooling system
Coolant protection at standard 40% antifreeze/water mixture ratio:Slush point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . -25ºC (-13ºF)Solidifying point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . -30ºC (-22ºF)
Coolant specific gravity at standard 40% antifreeze/water
mixture ratio and 15ºC/59ºF - with no other additives in coolant . . . . . 1.061
Fuel system
Idle speed*: 1.0, 1.1 and 1.3 litre HCS (carburettor) engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 750 ± 50 rpm (cooling fan running)
1.4 and 1.6 litre CVH (carburettor) engines:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
800 ± 50 rpm (cooling fan running)CTX automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 50 rpm (cooling fan running)
1.6 litre CVH (EFi fuel injection) engines: Idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 900 ± 50 rpmBase idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . 750 ± 50 rpm
Idle mixture CO content*: 1.0, 1.1 and 1.3 litre HCS (carburettor) engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 ± 0.5%
1.4 litre CVH (carburettor) engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 ± 0.25%
1.6 litre CVH (carburettor) engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 ± 0.5%
1.6 litre CVH (fuel injection) engines:Non turbo models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 0.8 ± 0.25%
Turbo models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . 1.5 ± 0.25%
*Note: The idle speed and mixture CO content is only adjustable on the engines \
shown above. On all other engines, it is controlled by the engine
management system, and cannot be checked or adjusted without specialised\
test equipment.
Air filter element: 1.0, 1.1 and 1.3 litre HCS engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion W153
1.4 litre CVH and PTE engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion W226
1.6 litre CVH (carburettor) engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion W226
1.6 litre CVH (fuel injection) engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion U557
1.6 and 1.8 litre Zetec engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion U612
Fuel filter:
HCS, CVH (fuel injection) and PTE engines:Without quick-release fuel line fittings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion L204
With quick-release fuel line fittings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion type not available
Zetec engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . Champion L218
1•2Servicing Specifications
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 6 of 296
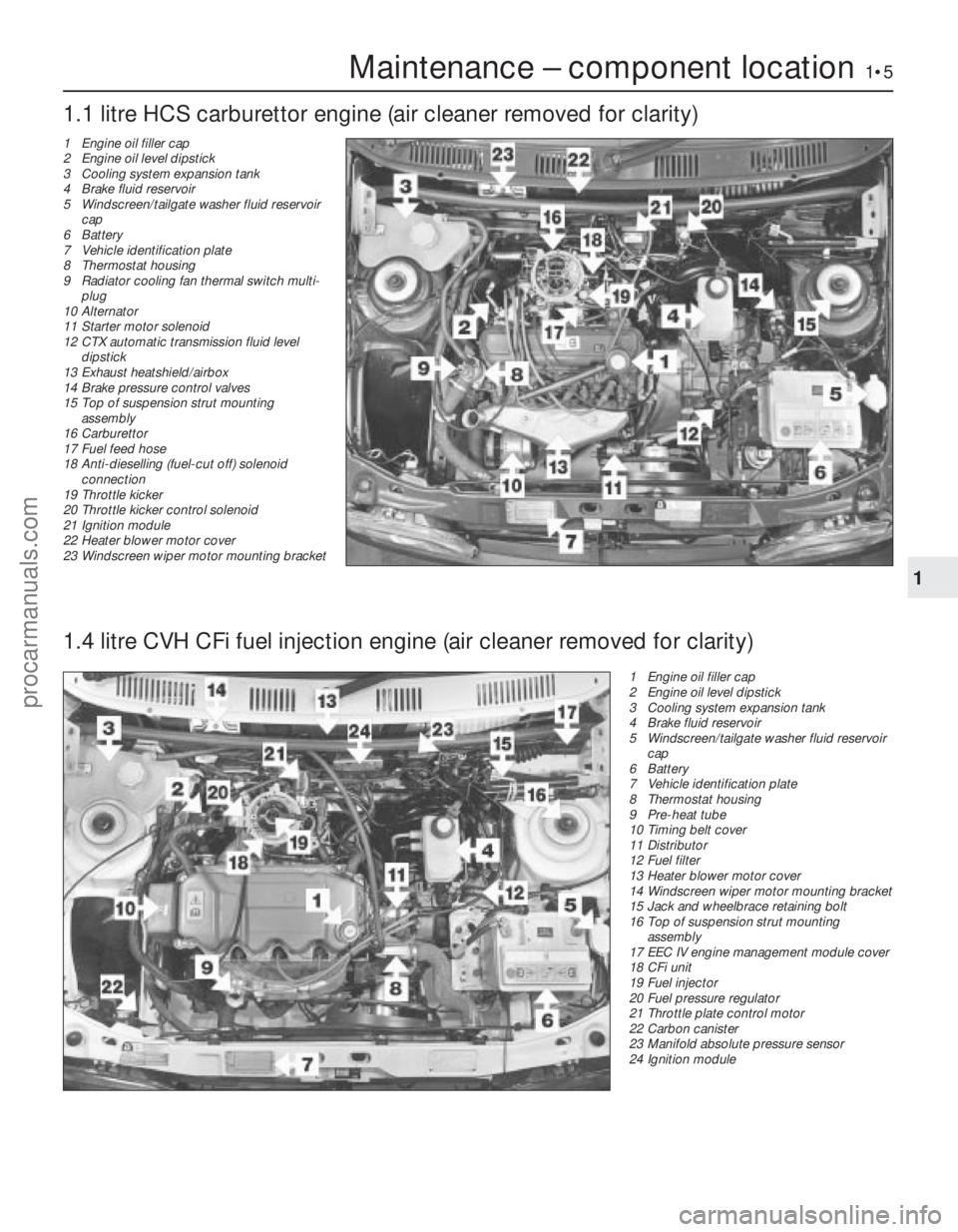
Maintenance – component location1•5
1 Engine oil filler cap
2 Engine oil level dipstick
3 Cooling system expansion tank
4 Brake fluid reservoir
5 Windscreen/tailgate washer fluid reservoircap
6 Battery
7 Vehicle identification plate
8 Thermostat housing
9 Pre-heat tube
10 Timing belt cover
11 Distributor
12 Fuel filter
13 Heater blower motor cover
14 Windscreen wiper motor mounting bracket
15 Jack and wheelbrace retaining bolt
16 Top of suspension strut mounting
assembly
17 EEC IV engine management module cover
18 CFi unit
19 Fuel injector
20 Fuel pressure regulator
21 Throttle plate control motor
22 Carbon canister
23 Manifold absolute pressure sensor
24 Ignition module
1.1 litre HCS carburettor engine (air cleaner removed for clarity)
1
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
1.4 litre CVH CFi fuel injection engine (air cleaner removed for clarity)
1 Engine oil filler cap
2 Engine oil level dipstick
3 Cooling system expansion tank
4 Brake fluid reservoir
5 Windscreen/tailgate washer fluid reservoir
cap
6 Battery
7 Vehicle identification plate
8 Thermostat housing
9 Radiator cooling fan thermal switch multi- plug
10 Alternator
11 Starter motor solenoid
12 CTX automatic transmission fluid level
dipstick
13 Exhaust heatshield/airbox
14 Brake pressure control valves
15 Top of suspension strut mounting
assembly
16 Carburettor
17 Fuel feed hose
18 Anti-dieselling (fuel-cut off) solenoid
connection
19 Throttle kicker
20 Throttle kicker control solenoid
21 Ignition module
22 Heater blower motor cover
23 Windscreen wiper motor mounting bracket
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 7 of 296
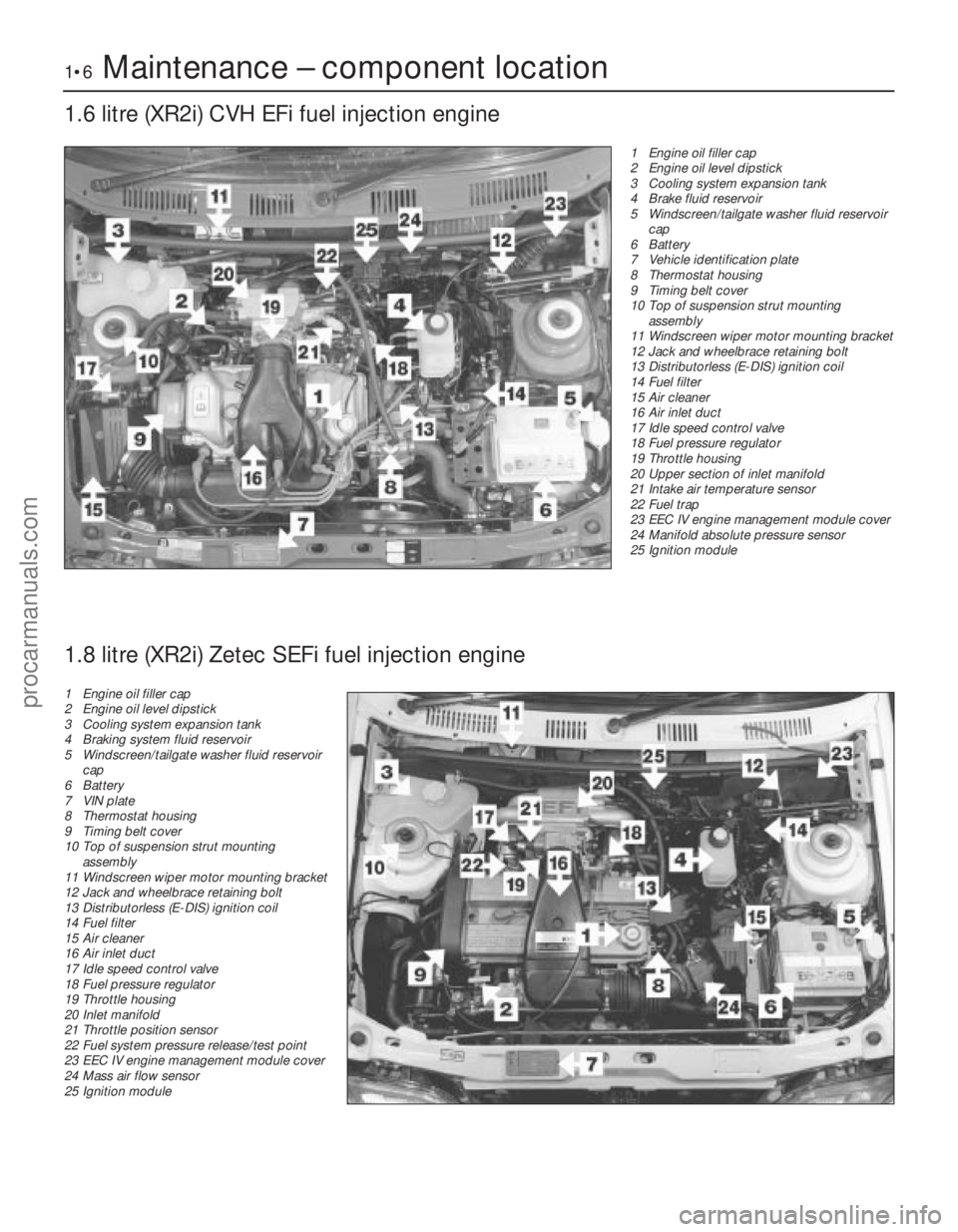
1•6Maintenance – component location
1.6 litre (XR2i) CVH EFi fuel injection engine
1595Ford Fiesta Remake1 Engine oil filler cap
2 Engine oil level dipstick
3 Cooling system expansion tank
4 Brake fluid reservoir
5 Windscreen/tailgate washer fluid reservoir
cap
6 Battery
7 Vehicle identification plate
8 Thermostat housing
9 Timing belt cover
10 Top of suspension strut mounting
assembly
11 Windscreen wiper motor mounting bracket
12 Jack and wheelbrace retaining bolt
13 Distributorless (E-DIS) ignition coil
14 Fuel filter
15 Air cleaner
16 Air inlet duct
17 Idle speed control valve
18 Fuel pressure regulator
19 Throttle housing
20 Upper section of inlet manifold
21 Intake air temperature sensor
22 Fuel trap
23 EEC IV engine management module cover
24 Manifold absolute pressure sensor
25 Ignition module
1.8 litre (XR2i) Zetec SEFi fuel injection engine
1 Engine oil filler cap
2 Engine oil level dipstick
3 Cooling system expansion tank
4 Braking system fluid reservoir
5 Windscreen/tailgate washer fluid reservoir
cap
6 Battery
7 VIN plate
8 Thermostat housing
9 Timing belt cover
10 Top of suspension strut mounting
assembly
11 Windscreen wiper motor mounting bracket
12 Jack and wheelbrace retaining bolt
13 Distributorless (E-DIS) ignition coil
14 Fuel filter
15 Air cleaner
16 Air inlet duct
17 Idle speed control valve
18 Fuel pressure regulator
19 Throttle housing
20 Inlet manifold
21 Throttle position sensor
22 Fuel system pressure release/test point
23 EEC IV engine management module cover
24 Mass air flow sensor
25 Ignition module
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 13 of 296

V-belt and flat “polyvee” type
drivebelt with rack-and-pinion type
adjuster
12Loosen off the alternator mounting bolts
and the adjusting arm mounting bolt. Slacken
the pinion central locking bolt, and turn the
pinion nut as required to take up the tension
of the drivebelt. Hold it at the required setting,
and tighten the central bolt securely to lock
the adjuster arm and set the tension (see
illustrations) .
13 Tighten the alternator mounting and
adjusting arm bolts securely.
14 Refit the auxiliary drivebelt cover (where
applicable) and roadwheel, then lower the
vehicle to the ground.
15 Run the engine for about five minutes,
then recheck the tension.
Flat “polyvee” type drivebelt with
tensioner pulley adjuster (HCS engine
power steering pump drivebelt)
16 Slacken the tensioner pulley centre bolt
then turn the adjuster bolt at the base of the
tensioner pulley bracket, as required, to take
up the tension of the drivebelt. When the belt
deflection is correct, tighten the adjuster
pulley centre retaining bolt.
17 Refit the auxiliary drivebelt cover (where
applicable) and roadwheel, then lower the
vehicle to the ground.
18 Run the engine for about five minutes,
then recheck the tension.
Flat “polyvee” type drivebelt with
automatic adjuster
19 As mentioned above, this type of drivebelt
is tensioned by an automatic tensioner;
regular checks are not required, and manual
“adjustment” is not possible.
20 If you suspect that the drivebelt is slipping
and/or running slack, or that the tensioner is
otherwise faulty, it must be renewed. To do
this, remove the drivebelt as described below,
then unbolt and remove the tensioner. On
fitting the new tensioner, ensure that it is
aligned correctly on its mountings, and
tightened to the specified torque wrench
setting.
Renewal
21 Open the bonnet. Jack up the front right-
hand side of the vehicle, and support it
securely on an axle stand. Remove the
roadwheel, then remove the auxiliary drivebelt
lower cover (where fitted) from inside the
wheel arch.
22 The routing of the drivebelt around the
pulleys is dependent on the drivebelt type,
and on whether power steering is fitted.
Before removing the drivebelt, it’s a good idea
to sketch the belt run around the pulleys; this
will save a lot of frustration when it comes to
refitting. Note that on HCS engines with
power steering, to renew the alternator/
water pump drivebelt it will be necessary to
remove the power steering pump drivebelt
first.
23 If the existing drivebelt is to be refitted,
mark it, or note the maker’s markings on its
flat surface, so that it can be installed the
same way round.
24 To renew a drivebelt with manual
adjustment, slacken the belt tension fully as
described above, according to type. Slip the
belt off the pulleys, then fit the new belt,
ensuring that it is routed correctly. If fitting a
flat “polyvee” type drivebelt, arrange it on the
grooved pulleys so that it is centred in
their grooves, and not overlapping their raised
sides. With the belt in position, adjust the
tension as previously described.
25 To renew the flat, “polyvee” type drivebelt
with automatic adjuster, reach up between
the body and the engine (above the
crankshaft pulley), and apply a spanner to the
hexagon in the centre of the automatic
tensioner’s pulley. Rotate the tensioner pulley
clockwise to release its pressure on the
drivebelt, then slip the drivebelt off the
crankshaft pulley, and release the tensioner
again (see illustration) . Note that on certain
models, a self-cocking tensioner is fitted, and
that this will remain in the released position.
Working from the wheel arch or engine
compartment as necessary, and noting its
routing, slip the drivebelt off the remaining
pulleys and withdraw it.
26 Check all the pulleys, ensuring that their
grooves are clean, and removing all traces of oil and grease. Check that the tensioner
works properly, with strong spring pressure
being felt when its pulley is rotated clockwise,
and a smooth return to the limit of its travel
when released.
27
If the original drivebelt is being refitted,
use the marks or notes made on removal, to
ensure that it is installed to run in the same
direction as it was previously. To fit the
drivebelt, arrange it on the grooved pulleys so
that it is centred in their grooves, and not
overlapping their raised sides, and is routed
correctly. Start at the top, and work down to
finish at the crankshaft pulley; rotate the
tensioner pulley clockwise, slip the drivebelt
onto the crankshaft pulley, then release the
tensioner again.
28 Using a spanner applied to the crankshaft
pulley bolt, rotate the crankshaft through at
least two full turns clockwise to settle the
drivebelt on the pulleys, then check that
the drivebelt is properly installed.
29 Refit the auxiliary drivebelt cover (where
applicable) and roadwheel, then lower the
vehicle to the ground.
5 Underbonnet check for fluid leaks and hose condition
1
General
1High temperatures in the engine
compartment can cause the deterioration of
the rubber and plastic hoses used for engine,
accessory and emissions systems operation.
Periodic inspection should be made for
cracks, loose clamps, material hardening and
leaks.
2 Carefully check the large top and bottom
radiator hoses, along with the other smaller-
diameter cooling system hoses and metal
pipes; do not forget the heater hoses/pipes
which run from the engine to the bulkhead.
Inspect each hose along its entire length,
replacing any that is cracked, swollen or
shows signs of deterioration. Cracks may
become more apparent if the hose is
1•12Every 10 000 miles or 12 months
4.25 Automatic drivebelt tensioner - “polyvee” type drivebelt
Turn tensioner clockwise to release tension4.12b When the tension is correct, hold
the adjuster nut, and tighten the central bolt securely to lock the adjuster arm4.12a Rack-and-pinion type auxiliary drivebelt adjuster
A Adjuster arm
B Pinion (adjuster) nut
C Central (locking) bolt
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 14 of 296

squeezed (see illustration) . If you are using
non-Ford specification antifreeze, and so
have to renew the coolant every two years or
so, it’s a good idea to renew the hoses at that
time, regardless of their apparent condition.
3 Make sure that all hose connections are
tight. A leak in the cooling system will usually
show up as white- or rust-coloured deposits
on the areas adjoining the leak; if the spring
clamps that are used to secure the hoses in
this system appear to be slackening, they
should be renewed to prevent the possibility
of leaks.
4 Some other hoses are secured to their
fittings with clamps. Where clamps are used,
check to be sure they haven’t lost their
tension, allowing the hose to leak. If clamps
aren’t used, make sure the hose has not
expanded and/or hardened where it slips over
the fitting, allowing it to leak.
5 Check all fluid reservoirs, filler caps, drain
plugs and fittings etc, looking for any signs
of leakage of oil, transmission and/or brake
hydraulic fluid, coolant and power steering
fluid. If the vehicle is regularly parked in the
same place, close inspection of the ground
underneath it will soon show any leaks. As
soon as a leak is detected, its source must
be traced and rectified. Where oil has been
leaking for some time, it is usually necessary
to use a steam cleaner, pressure washer or
similar, to clean away the accumulated
dirt, so that (when the engine is run again)
the exact source of the leak can be
identified.
Vacuum hoses
6 It’s quite common for vacuum hoses,
especially those in the emissions system, to be
colour-coded, or to be identified by coloured stripes moulded into them. Various systems
require hoses with different wall thicknesses,
collapse resistance and temperature
resistance. When renewing hoses, be sure the
new ones are made of the same material.
7
Often the only effective way to check a
hose is to remove it completely from the
vehicle. If more than one hose is removed, be
sure to label the hoses and fittings to ensure
correct installation.
8 When checking vacuum hoses, be sure to
include any plastic T-fittings in the check.
Inspect the fittings for cracks, and check the
hose where it fits over the fitting for distortion,
which could cause leakage.
9 A small piece of vacuum hose (quarter-inch
inside diameter) can be used as a
stethoscope to detect vacuum leaks. Hold
one end of the hose to your ear, and probe
around vacuum hoses and fittings, listening
for the “hissing” sound characteristic of a
vacuum leak. Warning: When probing with the
vacuum-hose stethoscope, be
very careful not to come into
contact with moving engine
components such as the auxiliary
drivebelt, radiator electric cooling fan, etc.
Fuel hoses
Warning: There are certain
precautions which must be
taken when inspecting or
servicing fuel system
components. Work in a well-ventilated
area, and do not allow open flames
(cigarettes, appliance pilot lights, etc.) or
bare light bulbs near the work area. Mop
up any spills immediately, and do not store
fuel-soaked rags where they could ignite.
10 Check all fuel hoses for deterioration and
chafing. Check especially for cracks in areas
where the hose bends, and also just before
fittings, such as where a hose attaches to the
fuel filter.
11 High-quality fuel line, usually identified by
the word “Fluoroelastomer” printed on the
hose, should be used for fuel line renewal.
Never, under any circumstances, use
unreinforced vacuum line, clear plastic tubing
or water hose for fuel lines.
12 Spring- type clamps are commonly used
on fuel lines. These clamps often lose their
tension over a period of time, and can be
“sprung” during removal. Replace all
spring- type clamps with screw clamps
whenever a hose is replaced.
Metal lines
13 Sections of metal piping are often used
for fuel line between the fuel filter and the
engine. Check carefully to be sure the piping
has not been bent or crimped, and that cracks
have not started in the line.
14 If a section of metal fuel line must be
renewed, only seamless steel piping should
be used, since copper and aluminium piping
don’t have the strength necessary to
withstand normal engine vibration. 15
Check the metal brake lines where they
enter the master cylinder and ABS hydraulic
unit (if used) for cracks in the lines or loose
fittings. Any sign of brake fluid leakage calls
for an immediate and thorough inspection of
the brake system.
6 Engine compartment wiring check
1
1With the vehicle parked on level ground,
apply the handbrake firmly and open the
bonnet. Using an inspection light or a small
electric torch, check all visible wiring within
and beneath the engine compartment.
2 What you are looking for is wiring that is
obviously damaged by chafing against sharp
edges, or against moving suspension/
transmission components and/or the auxiliary
drivebelt, by being trapped or crushed
between carelessly-refitted components, or
melted by being forced into contact with the
hot engine castings, coolant pipes, etc. In
almost all cases, damage of this sort is
caused in the first instance by incorrect
routing on reassembly, after previous work
has been carried out.
3 Depending on the extent of the problem,
damaged wiring may be repaired by rejoining
the break or splicing-in a new length of wire,
using solder to ensure a good connection,
and remaking the insulation with adhesive
insulating tape or heat-shrink tubing, as
appropriate. If the damage is extensive, given
the implications for the vehicle’s future
reliability, the best long-term answer may well
be to renew that entire section of the loom,
however expensive this may appear.
4 When the actual damage has been
repaired, ensure that the wiring loom is re-
routed correctly, so that it is clear of other
components, and not stretched or kinked, and
is secured out of harm’s way using the plastic
clips, guides and ties provided.
5 Check all electrical connectors, ensuring
that they are clean, securely fastened, and
that each is locked by its plastic tabs or wire
clip, as appropriate. If any connector shows
external signs of corrosion (accumulations of
white or green deposits, or streaks of “rust”),
or if any is thought to be dirty, it must be
unplugged and cleaned using electrical
contact cleaner. If the connector pins are
severely corroded, the connector must be
renewed; note that this may mean the renewal
of that entire section of the loom - see your
local Ford dealer for details.
6 If the cleaner completely removes the
corrosion to leave the connector in a
satisfactory condition, it would be wise to
pack the connector with a suitable material
which will exclude dirt and moisture,
preventing the corrosion from occurring
again; a Ford dealer may be able to
recommend a suitable product.
7 Check the condition of the battery
Every 10 000 miles or 12 months1•13
5.2 Hoses, like drivebelts, have a habit of
failing at the worst possible time - to
prevent the inconvenience of a blown radiator or heater hose, inspect them
carefully as shown here
1
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 15 of 296

connections - remake the connections or
renew the leads if a fault is found. Use the
same techniques to ensure that all earth
points in the engine compartment provide
good electrical contact through clean, metal-
to-metal joints, and that all are securely
fastened. (In addition to the earth connection
at the engine lifting eye, and that from the
transmission to the body/battery, there are
others in various places, so check carefully).
8Refer to Section 21 for details of spark plug
(HT) lead checks.
7 Valve clearance adjustment
2
Refer to Chapter 2, Part A.
8 Manual transmission oil level check
1
1The manual transmission does not have a
dipstick. To check the oil level, raise the
vehicle and support it securely on axle stands,
making sure that the vehicle is level. On the
lower front side of the transmission housing,
you will see the filler/level plug. Unscrew and
remove it - an Allen key or bit will probably be
required (see illustration) .
2 With the plug removed, check the oil level.
To do this accurately, make up an oil level
check dipstick from a short length of welding
rod or similar material. Make a 90º bend in the
rod, then mark the downward leg in 5 mm
increments. The dipstick is then inserted
through the filler plug orifice so that the
unmarked leg rests flat on the plug orifice
threads, with the marked leg dipped in the oil.
Withdraw the dipstick and read off the level of
oil.
3 The oil level must be maintained between 0
and 5 mm below the lower edge of the
filler/level plug hole. Top up (if necessary),
using fresh transmission oil of the specified
type and using a syringe, or a plastic bottle
and tube. Refit and tighten the filler/level plug
to the specified torque on completion. 4
The need for regular topping-up can only
be due to a leak, which should be found and
rectified without delay.
5 Regular oil changing is not specified by the
manufacturer’s, but the oil can be drained, if
required, by removing the selector shaft cap
nut and locking assembly.
9 Idle speed and mixture check and adjustment
4
General
1Many of the engines fitted to Fiesta models
are equipped with fuel injection systems of
one sort or another which are entirely
controlled by the engine management system.
On most of these vehicles, it isn’t possible to
make any adjustments to the idle speed or the
mixture settings without specialist test
equipment of a type usually only found at a
Ford dealer or fuel injection specialist.
However, the very nature of these highly-
sophisticated systems means they don’t go
out of tune very often (if ever), so that it’s one
less maintenance operation to worry about.
2 On carburettor engines and 1.6 litre EFi fuel
injection engines, certain checks and
adjustments are necessary as part of the
service requirements, and these are described
below.
Idle speed and mixture check
and adjustment - carburettor
engines
Note: Later carburettors are fitted with
tamperproof mixture adjusting screws,
consisting of a hexagon-shaped socket with a
pin in the centre. Such screws require the use
of Ford service tool 23-032 to alter their
settings; if this tool (or a suitable equivalent) is
not available, the CO level will have to be
checked, and any necessary adjustment will
have to be made, by a Ford dealer.
3 Before carrying out the following checks
and adjustments, ensure that the spark plugs
are in good condition and correctly gapped
(Section 21). To carry out the checks/adjustments, an accurate tachometer
and an exhaust gas analyser (CO meter) will
be required.
4
Make sure that all electrical components
are switched off during the following
procedures.
5 Connect a tachometer to the engine in
accordance with its manufacturer’s
instructions, and insert the probe of an
exhaust gas analyser (CO meter) into the
exhaust tailpipe. As previously mentioned,
these items are essential in obtaining an
accurate setting. If they are not available, an
approximate check/adjustment can be made
as a temporary measure, providing they are
further checked out as soon as is possible
using a tachometer and a CO meter (or by a
Ford dealer).
6 Run the engine at a fast idle speed until it
reaches its normal operating temperature and
the radiator cooling fan cuts in. Turn the
engine off, then disconnect the radiator
cooling fan lead at the thermostatic switch
connector. Now connect a temporary wire to
the fan switch multi-plug, as shown (see
illustration) to enable the fan to operate
continuously during the following checks and
adjustments (if this is specified). Take care to
keep clear of the fan during the following
operations when working in the engine
compartment.
7 Where fitted, disconnect the throttle kicker
vacuum pipe, and plug the end. To identify
the throttle kicker unit, refer to Chapter 4A.
8 Check that the vehicle lighting and other
electrical loadings (apart from the radiator
cooling fan) are switched off, then restart the
engine. Increase the engine speed to 3000 rpm
for 30 seconds, and repeat this at three-minute
intervals during the check/adjustment
procedures. This will ensure that any excess
fuel is cleared from the inlet manifold.
9 Ensure that the throttle is fully released, allow
the meters to stabilise for a period of 5 to
30 seconds is normally sufficient, then check
the idle speed against that specified. If adjust-
ment is necessary, turn the idle speed
adjusting screw until the engine is idling at the
specified speed (see illustrations) . Any checks
and adjustments must be completed within
30 seconds of the meters stabilising.
1•14Every 10 000 miles or 12 months
9.9a Idle speed adjusting screw (A) and
mixture adjusting screw (B) (Weber TLM
carburettor)9.6 Cooling fan thermostatic switch multi-plug with temporary bridging wire
connected8.1 Manual transmission oil level/filler
plug (A), and selector shaft cap nut (B)
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 16 of 296

10If adjustment to the mixture is required,
the tamperproof cap will need to be removed
from the carburettor to gain access to the
mixture screw. To do this, first unclip the fuel
trap from the side of the air cleaner unit, then
remove the air cleaner unit, ensuring that the
crankcase ventilation trap remains connected.
Prise free the tamperproof cap (with the aid of
a thin-bladed screwdriver), then with the
vacuum and emissions control pipes
connected to it, relocate the air cleaner unit
temporarily into position.
11 Turn the mixture adjustment screw
clockwise to weaken the mixture, or
anti-clockwise to richen it, until the CO
reading is as given in the Specifications. If a
CO meter is not being used, weaken the
mixture as described, then enrich the mixture until the maximum engine speed is obtained,
consistent with even running.
12
If necessary, re-adjust the idle speed then
check the CO reading again. Repeat as
necessary until both the idle speed and CO
reading are correct.
13 Where required by law (as in some
European countries), fit a new tamperproof
cap to the mixture adjustment screw.
14 Disconnect the tachometer and the CO
meter, refit the air cleaner unit, and reconnect
the fan switch lead to complete.
Base idle speed and mixture
check and adjustment - 1.6 litre
EFi engines
15 Proceed as described above in
paragraphs 3 to 6 inclusive, then continue as
follows.
16 Run the engine at a fast idle speed until it
reaches its normal operating temperature and
the cooling fan cuts in. Check the CO content
of the exhaust, and compare it against the
specified reading. If the CO content reading is
incorrect, it can be adjusted by prising free
the tamperproof cap for access to the mixture
CO adjustment screw (see illustration), and
turning the screw in the required direction to
suit.
17 The operational idle speed is controlled by
the EEC IV engine management module and is
not adjustable. However, if the base idle
speed is incorrect, the module will not have an
accurate datum point from which to establish the normal operational idle speed. If idle
problems have been experienced, the base
idle speed should be checked as follows.
18
Disconnect the multi-plug from the idle
speed control valve and increase the engine
speed to 2000 rpm, hold it at that speed for
30 seconds, then fully release the throttle and
check if the base idle speed registered is as
specified.
19 If adjustment is necessary, prise free the
tamperproof plug using a suitable small
screwdriver to gain access to the base idle
speed adjustment screw in the throttle body.
Turn the screw in the required direction to
adjust the base idle speed to the specified
amount. Turning the screw anti-clockwise
increases the idle speed (see illustration).
20 Increase the engine speed to 2000 rpm
again, hold it at that speed for 30 seconds,
then fully release the throttle once more.
Check and further adjust the base idle speed
if required, then fit a new tamperproof plug
into position.
21 Reconnect the idle speed control valve
multi-plug and check that the engine speed
briefly rises to about 900 rpm, then drops
down to the specified normal idle speed.
22 On completion, disconnect the
tachometer and the CO meter, but continue
running the engine at idle speed for a period
of about five minutes, to enable the engine
management module to relearn its values
before switching it off.
10 Steering, suspension and roadwheel check
2
Front suspension and steering
check
1Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ).
2 Visually inspect the balljoint dust covers
and the steering gear gaiters for splits, chafing
or deterioration (see illustrations) . Any wear
of these components will cause loss of
Every 10 000 miles or 12 months1•15
9.9d Idle speed mixture adjusting
screw (A) and idle speed adjusting screw (B) (Weber TLD carburettor)9.9c Idle speed mixture adjusting
screw (A) and idle speed adjusting screw (B) (Weber DFTM carburettor)9.9b Idle speed adjusting screw (A) and
mixture adjusting screw (B) (Weber TLDM carburettor)
10.2a Check the condition of the track rodend balljoint dust cover (arrowed)9.19 Base idle speed adjustment screw(arrowed) on the 1.6 litre EFi engine
9.16 Adjusting the idle mixture CO content on the 1.6 litre EFi engine
1
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 22 of 296

23 Coolant renewal
1
Note: If the antifreeze used is Ford’s own, the
coolant need not be renewed for the life of the
vehicle. If the vehicle’s history is unknown, if
antifreeze of lesser quality is known to be in
the system, or simply if you prefer to follow
conventional servicing intervals, the coolant
should be changed periodically (typically,
every 3 years) as described here. Refer also to
“Antifreeze - notes on renewal” in this
Section.
Warning: Do not allow
antifreeze to come in contact
with your skin or painted
surfaces of the vehicle. Flush
contaminated areas immediately with
plenty of water. Don’t store new coolant,
or leave old coolant lying around, where
it’s accessible to children or pets - they’re
attracted by its sweet smell. Ingestion of
even a small amount of coolant can be
fatal! Wipe up garage-floor and drip-pan
spills immediately. Keep antifreeze
containers covered, and repair cooling
system leaks as soon as they’re noticed.
Warning: Never remove the expansion
tank filler cap when the engine is running,
or has just been switched off, as the
cooling system will be hot, and the
consequent escaping steam and scalding
coolant could cause serious injury.
Coolant draining
Warning: Wait until the engine is
cold before starting this
procedure.
1 To drain the system, first remove the
expansion tank filler cap (see “Weekly
Checks” ).
2 If additional working clearance is required,
raise the front of the vehicle and support it securely on axle stands (see
“Jacking and
Vehicle Support” ).
3 Place a large drain tray beneath the
radiator, and unscrew the radiator drain plug -
you can use a small coin to do this, as the
plug’s slotted for this purpose (see
illustration) . Direct as much of the escaping
coolant as possible into the tray.
System flushing
4 With time, the cooling system may gradually
lose its efficiency, as the radiator core
becomes choked with rust, scale deposits
from the water, and other sediment (refer also
to “Antifreeze - notes on renewal” later in this
S ection). To minimise this, as well as using
only good-quality antifreeze and clean soft
water, the system should be flushed as follows
whenever any part of it is disturbed, and/or
when the coolant is renewed.
5 With the coolant drained, refit the drain
plug, and refill the system with fresh water.
Refit the expansion tank filler cap, start the
engine and warm it up to normal operating
temperature, then stop it and (after allowing it
to cool down completely) drain the system
again. Repeat as necessary until only clean
water can be seen to emerge, then refill finally
with the specified coolant mixture as
described below.
6 If only clean, soft water and good-quality
antifreeze (even if not to Ford’s specification)
has been used, and the coolant has been
renewed at the suggested intervals, the above
procedure will be sufficient to keep the
system clean for a considerable length of
time. If, however, the system has been
neglected, a more thorough operation will be
required, as follows.
7 First drain the coolant, then disconnect the
radiator top and bottom hoses. Insert a
garden hose into the top hose, and allow
water to circulate through the radiator until it
runs clean from the bottom outlet.
8 To flush the engine, insert the garden hose
into the thermostat water outlet, and allow
water to circulate until it runs clear from the
bottom hose. If, after a reasonable period, the
water still does not run clear, the radiator
should be flushed with a good proprietary
cleaning agent.
9 In severe cases of contamination, reverse-
flushing of the radiator may be necessary. To
do this, remove the radiator (Chapter 3), invert
it, and insert the garden hose into the bottom
outlet. Continue flushing until clear water runs
from the top hose outlet. A similar procedure
can be used to flush the heater matrix.
10 The use of chemical cleaners should be
necessary only as a last resort. Normally,
regular renewal of the coolant will prevent
excessive contamination of the system.
Coolant filling
11 With the cooling system drained and
flushed, ensure that all disturbed hose unions
are correctly secured, and that the radiator
drain plug is securely tightened. If it was
raised, lower the vehicle to the ground.
12 Prepare a sufficient quantity of the
specified coolant mixture (see below); allow
for a surplus, so as to have a reserve supply
for topping-up.
13 Slowly fill the system through the
expansion tank; since the tank is the highest
point in the system, all the air in the system
should be displaced into the tank by the rising
liquid. Slow pouring reduces the possibility of
air being trapped and forming airlocks.
14 Continue filling until the coolant level
reaches the expansion tank “MAX” level line,
then cover the filler opening to prevent
coolant splashing out.
15 Start the engine and run it at idle speed,
until it has warmed-up to normal operating
temperature and the radiator cooling fan has
cut in; watch the temperature gauge to check
for signs of overheating. If the level in the
expansion tank drops significantly, top-up to
the “MAX” level line, to minimise the amount
of air circulating in the system.
16 Stop the engine, allow it to cool down
completely (overnight, if possible), then
uncover the expansion tank filler opening and
top-up the tank to the “MAX” level line. Refit
the filler cap, tightening it securely, and wash
off any spilt coolant from the engine
compartment and bodywork.
17 After refilling, always check carefully all
components of the system (but especially any
unions disturbed during draining and flushing)
for signs of coolant leaks. Fresh antifreeze has
a searching action, which will rapidly expose
any weak points in the system.
18 If, after draining and refilling the system,
symptoms of overheating are found which did
not occur previously, then the fault is almost
certainly due to trapped air at some point in
the system, causing an airlock and restricting
the flow of coolant; usually, the air is trapped
because the system was refilled too quickly.
In some cases, airlocks can be released by
tapping or squeezing the various hoses. If the
problem persists, stop the engine and allow it
to cool down completely, before unscrewing
the expansion tank filler cap or disconnecting
hoses to bleed out the trapped air.
Antifreeze mixture
19 If the antifreeze used is not to Ford’s
specification, it should always be renewed at
the suggested intervals (typically, every 2 or
3 years). This is necessary not only to maintain
the antifreeze properties, but also to prevent
Every 30 000 miles (48 000 km) or three years, whichever
comes first
Every 30 000 miles or three years 1•21
23.3 Drain plug location at the base of the radiator - use a coin to unscrew the plug
1
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su