1989 FORD FIESTA fuel pressure
[x] Cancel search: fuel pressurePage 76 of 296

3Referring to Chapter 1 for details, drain the
coolant and engine oil. Refit the drain plug to
the sump on completion.
4 Remove the bonnet as described in
Chapter 11.
5 Remove the air cleaner assembly as
described in the relevant Part of Chapter 4.
6 Release the retaining clips and detach the following coolant hoses. Allow for coolant
spillage as the hoses are detached
(see
illustrations) :
a) All hoses at the thermostat housing.
b) Bottom hose from the radiator to the
water pump.
c) Heater hoses at the bulkhead and water
pump.
d) Inlet manifold coolant supply hose (where
applicable).
7 Disconnect the fuel trap vacuum hose from
the inlet manifold.
8 Disconnect the brake servo unit vacuum
hose from the inlet manifold, by pushing the
hose retainer in towards the manifold and
simultaneously pulling free the hose (see
illustration) .
9 Refer to the relevant Part of Chapter 4 for
details, and detach the accelerator cable.
Where applicable, detach the choke cable
from the carburettor.
10 Compress the quick-release couplings at
the sides, and detach the fuel supply hose
and return hose from the fuel pump, CFi unit
or fuel rail (see illustration) . Allow for fuel
spillage as the hoses are disconnected, and
plug the exposed ends to prevent further spillage and the ingress of dirt. Position the
hoses out of the way.
11
Note their locations and disconnect the
wiring connectors from the following (see
illustrations) :
a) Coolant temperature gauge sender unit.
b) The oil pressure switch.
c) The radio earth lead.
d) The cooling fan thermostatic switch.
e) The DIS/E-DIS ignition coil.
f) The crankshaft speed/position sensor.
g) The engine coolant temperature sensor.
h) The idle cut-off valve.
12 Disconnect the remaining wiring multi-
plugs from the engine sensors at the inlet
manifold and from the oxygen sensor
(where fitted) in the exhaust manifold or
downpipe.
13 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ).
14 Unscrew the retaining nuts, and detach
the exhaust downpipe from the exhaust
manifold. Remove the seal from the joint
flange.
15 Refer to Chapter 5A for details, and
remove the starter motor.
16 Undo the two retaining bolts, and remove
the clutch lower cover plate.
17 Unscrew the retaining bolt, and
detach the gearshift stabiliser from the
transmission.
18 Unscrew and remove the engine/
Engine removal and overhaul procedures 2D•7
3.8 Detach the servo vacuum hose from
the manifold3.6b Disconnect the bottom hose (A) andthe heater hose (B) from the water pump3.6a Disconnect the overflow hose (A) and the top hose (B) from the thermostat housing
3.11b Engine crankshaft position sensorand multi-plug
3.11a Wiring connections to the HCS engine
A Idle cut-off valve
B DIS ignition coil
C Engine coolant temperature sensor
D Oil pressure switch
3.10 Fuel supply (A) and return (B) hose connections at the fuel pump
2D
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
Whenever you disconnect any vacuum
lines, coolant or emissions hoses,
wiring connectors and fuel lines,
always label them clearly, so that they
can be correctly reassembled. Masking
tape and/or a touch-up paint applicator
work well for marking items. Take
instant photos, or sketch the locations
of components and brackets.
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 78 of 296

7Refer to the relevant Part of Chapter 4 for
details, and disconnect the accelerator cable
from the throttle linkage and support/adjuster
bracket. Where applicable, also disconnect
the choke cable. Position the cable(s) out of
the way.
8 On carburettor models, disconnect the fuel
supply hose from the fuel pump, and the
return hose from the carburettor.
9 On CFi models, detach the fuel hose at the
injector/pressure regulator unit, and the return
line, by compressing the couplings whilst
pulling the hoses free from their connections.
On EFi and SEFi models, unscrew the union
nut to detach the fuel line from the fuel rail;
release the retaining clip to detach the return
pipe from the pressure regulator. Plug the
exposed ends of the hoses and connections,
to prevent fuel spillage and the ingress of dirt.
Position the hoses out of the way.
10 Press the clamp ring inwards, and
simultaneously pull free the brake servo hose from the inlet manifold. Position it out of the
way.
11
On CFi and EFi models, detach the
vacuum hose from the MAP sensor, and the
hose between the carbon canister and the fuel
injection unit (see illustration) .
12 Note their connections and routings, and
detach the following wiring connections,
according to model (see illustrations):
a) Coolant temperature sender unit.
b) Oil pressure switch.
c) E-DIS ignition coil unit. or distributor.
d) Coolant temperature sensor.
e) Cooling fan thermostatic switch.
f) Carburettor.
g) Earth lead (radio).
h) Reversing light switch (from transmission).
i) Crankshaft position sensor.
j) Earth leads from the transmission and engine.
13 Disconnect the wiring at the following
additional items specific to fuel injection
models only.
a) Inlet air temperature sensor.
b) Vehicle speed sensor.
c) Throttle plate control motor (CFi models).
d) Throttle position sensor.
e) Injector harness connector.
f) Idle speed control valve (EFi and SEFi models).
14 Unscrew the retaining bolt and detach the
bracket locating the wiring and coolant hoses
above the transmission. 15
Disconnect the speedometer drive cable
from the transmission.
16 On manual transmission models,
disconnect the clutch cable from the release
lever at the transmission (see Chapter 6 for
details). Position the cable out of the way.
17 On vehicles fitted with the anti-lock
braking system, refer to Chapter 9 and release
the left-hand modulator from its mounting
bracket, without disconnecting the rigid brake
pipes or return hose. Tie the modulator
securely to the bulkhead.
18 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ). Allow
sufficient clearance under the vehicle to
withdraw the engine and transmission units
from under the front end.
19 On XR2i models, refer to Chapter 10 and
remove the front suspension crossmember.
20 Where applicable on catalytic converter-
equipped vehicles, release the multi-plug from
the bracket and disconnect the wiring
connector from the oxygen sensor in the
exhaust downpipe.
21 Undo the three retaining bolts, detach the
exhaust downpipe from the manifold, and
collect the gasket from the flange joint. Now
disconnect the exhaust downpipe from the
rest of the system, and remove it from the
vehicle.
22 Where fitted, undo the four retaining nuts
and two bolts securing the front part of the
exhaust heat shield to the floor, then remove
the heat shield.
23 Refer to Chapter 5A and remove the
alternator and starter motor. On models with
power steering, refer to Chapter 10 and
remove the power steering pump.
Manual transmission models
24 On 4-speed models, select 2nd gear; on
5-speed models, select 4th gear, to assist in
correct adjustment of the gearchange during
reassembly. If it is likely that the gear lever will
be moved from this position before refitting,
mark the relative position of the transmission
shift rod and the selector shaft before
separating them. Undo the clamp bolt, and
then pull free and detach the shift rod from the
selector shaft (see illustration) .
Engine removal and overhaul procedures 2D•9
4.12b . . . the oil pressure switch . . .4.12a Disconnect the wiring at the
temperature gauge sender unit . . .4.11 Vacuum hose to MAP sensor (A) and brake servo (B)
4.24 Manual transmission shift rod clamp
bolt (A), stabiliser-to-transmission bolt (B)
and washer (C)4.12c . . . and the crankshaft position sensor
2D
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
Whenever you disconnect
any vacuum lines, coolant or
emissions hoses, wiring
connectors and fuel lines,
always label them clearly, so that they
can be correctly reassembled. Masking
tape and/or a touch-up paint applicator
work well for marking items. Take
instant photos, or sketch the locations
of components and brackets.
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 79 of 296

25Unscrew the retaining bolt, and detach
the shift rod stabiliser from the transmission.
As it is detached, note the washer located
between the stabiliser and the transmission.
Tie the stabiliser and the shift rod up out of
the way.
Automatic transmission models
26 Unclip and detach the wiring connector
from the starter inhibitor switch (on the
transmission housing).
27 Referring to the relevant Part of Chapter 4
for details, unhook the accelerator (cam plate)
cable from the carburettor or fuel injection unit
(as applicable) at the transmission end of
the cable. Undo the retaining bolt and
detach the cable sheath bracket from the
transmission. Detach the cam plate cable
from the link.
28 Undo the two nuts from the selector cable
bracket which connects it to the lever on the
selector shaft. Disconnect the yoke from the
lever on the selector shaft and the cable from
the lever.
29 Unscrew the union nuts, and disconnect
the oil cooler feed and return pipes from the
transmission. Allow for a certain amount of
spillage, and plug the connections to prevent
the ingress of dirt.
All models
30 Unscrew the retaining nut and withdraw
the Torx-type clamp bolt securing the lower
suspension arm to the spindle carrier on each
side.
31 Refer to Chapter 10 for details, and
detach the right-hand and left-hand track rod
end balljoints from the spindle carriers.
32 On vehicles fitted with the anti-lock
braking system, refer to Chapter 9 and release
the right-hand modulator from its mounting
bracket without disconnecting the rigid brake
pipes or return hose. Tie the modulator
securely to the bulkhead. Additionally, undo
the three bolts securing the modulator
bracket.
33 Insert a suitable lever between the right-
hand driveshaft inner joint and the
transmission housing, and prise free the
driveshaft from the transmission; be prepared
for oil spillage from the transmission case
through the vacated driveshaft aperture. As it
is being prised free, simultaneously pull the
roadwheel outwards on that side, to enable
the driveshaft inboard end to separate
from the transmission. Once it is free,
suspend and support the driveshaft from the
steering gear, to prevent unnecessary strain
being placed on the driveshaft joints.
34 Insert a suitable plastic plug (or if
available, an old driveshaft joint), into the
transmission driveshaft aperture, to
immobilise the gears of the differential unit.
35 Proceed as described above in
paragraphs 33 and 34, and disconnect the
left-hand driveshaft from the transmission.
36 Connect a suitable lift hoist and sling to
the engine, connecting to the lifting eyes. When securely connected, take the weight of
the engine/transmission unit so that the
tension is relieved from the mountings.
37
Undo the retaining bolts and nuts and
detach the right-hand engine mounting from
the vehicle body.
38 Undo the four bolts securing the
transmission bearer to the underside of the
vehicle body. The transmission bearer is
removed with the engine/transmission
assembly.
39 Unscrew the three retaining bolts, and
remove the auxiliary drivebelt cover from
under the crankshaft pulley.
40 The engine/transmission unit should now
be ready for removal from the vehicle. Check
that all of the associated connections and
fittings are disconnected from the engine and
transmission, and positioned out of the way.
41 Enlist the aid of an assistant to help
steady and guide the power unit down
through the engine compartment as it is
removed. If available, position a suitable
engine trolley or crawler board under the
engine/transmission so that when lowered,
the power unit can be withdrawn from the
front end of the vehicle, and then moved to
the area where it is to be cleaned and
dismantled. On automatic transmission
models, particular care must be taken not to
damage the transmission fluid pan (sump)
during the removal and subsequent refitting
processes.
42 Carefully lower the engine and
transmission unit, ensuring that no fittings
become snagged. Detach the hoist and
remove the power unit from under the vehicle.
43 Referring to the relevant Part of Chapter 7,
separate the transmission from the engine.
44 While the engine/transmission is removed,
check the mountings; renew them if they are
worn or damaged. Similarly, check the
condition of all coolant and vacuum hoses
and pipes (see Chapter 1). Components that
are normally hidden can now be checked
properly, and should be renewed if there is
any doubt at all about their condition. Where
the vehicle is fitted with manual transmission,
take the opportunity to inspect the clutch
components (see Chapter 6). It is regarded by
many as good working practice to renew the
clutch assembly as a matter of course,
whenever major engine overhaul work is
carried out. Check also the condition of all
components (such as the transmission oil
seals) disturbed on removal, and renew any
that are damaged or worn.
Refitting
45 Refitting is a reversal of removal, however
note the following additional points:
a) Refer to the applicable Chapters and Sections as for removal.
b) Fit new spring clips to the grooves in the
inboard end of the right- and left-hand
driveshaft joints. Lubricate the splines
with transmission oil prior to fitting. c) Renew the exhaust flange gasket when
reconnecting the exhaust. Ensure that all
wires are routed clear of the exhaust
system and, on catalytic converter
models, ensure that the heat shields are
securely and correctly fitted.
d) Ensure that all earth lead connections are
clean and securely made.
e) Tighten all nuts and bolts to the specified torque.
f) Fit a new oil filter, and refill the engine and transmission with oil, with reference to
Chapter 1.
g) Refill the cooling system with reference to Chapter 1.
h) Refit the alternator and starter motor with reference to Chapter 5A.
i) Where applicable, refit the power steering pump with reference to Chapter 10.
46 When engine and transmission refitting is
complete, refer to the procedures described
in Section 19 before restarting the engine.
5 Engine/transmission -
removal and refitting
(Zetec engines)
3
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when disconnecting
any part of the fuel system.
Don’t smoke, or allow naked flames or
bare light bulbs, in or near the work area,
and don’t work in a garage where a
natural-gas appliance (such as a clothes
dryer or water heater) is installed. If you
spill petrol on your skin, rinse it off
immediately. Have a fire extinguisher rated
for petrol fires handy, and know how to
use it.
Note: Read through the entire Section, as well
as reading the advice in Section 2, before
beginning this procedure. The engine and
transmission are removed as a unit, lowered to
the ground and removed from underneath,
then separated outside the vehicle.
Removal
1 Park the vehicle on firm, level ground, apply
the handbrake firmly, and slacken the nuts
securing both front roadwheels.
2 Depressurise the fuel system as described
in Chapter 4D.
3 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
4 Place protective covers on the wings, then
remove the bonnet (see Chapter 11).
5 Drain the cooling system and the engine oil
(see Chapter 1).
6 Remove the air inlet components and the
complete air cleaner assembly as described in
Chapter 4D.
7 Equalise the pressure in the fuel tank by
removing the filler cap, then release the fuel
feed and return quick-release couplings, and
pull the hoses off the fuel pipes. Plug or cap
all open fittings.
2D•10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 80 of 296

8Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage as described in Chapter 4D.
Secure the cable clear of the
engine/transmission.
9 Releasing its wire clip, unplug the wiring
connector from the power steering pressure
switch (where fitted), then disconnect the
earth cable from the engine lifting eye. Refit
the bolt after disconnecting the cable.
10 Marking or labelling all components as
they are disconnected, disconnect the
vacuum hoses as follows:
a) From the rear of the inlet manifold.
b) The braking system vacuum servo unit
hose - from the inlet manifold (see
Chapter 9 for details).
c) While you are there, trace the vacuum line
from the pulse-air filter housing, and
disconnect it from the pulse-air solenoid
valve.
d) Secure all these hoses so that they won’t
get damaged as the engine/transmission
is removed.
11 Unbolt the engine/transmission-to-body earth lead from the transmission
(see
illustration) . Disconnect the speedometer
drive cable (see Chapter 12) and secure it
clear of the engine/transmission.
12 Disconnect the earth strap at the top of
the engine/transmission flange, and the
adjacent bolt securing the wiring harness clip.
13 Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, disconnect the clutch cable (see
Chapter 6).
14 Marking or labelling all components as
they are disconnected, disconnect the engine
wiring connectors as follows (see
illustrations) :
a) The multi-plug from the E-DIS ignition
coil.
b) The radio interference suppressor from
the DIS ignition coil.
c) The reversing light switch multi-plug.
d) The engine main wiring loom multi-plug
behind the E-DIS ignition coil.
e) The crankshaft speed/position sensor and vehicle speed sensor multi-plugs.
f) The oxygen sensor multi-plug.
15 Unbolt the exhaust manifold heat shield,
and lift it clear.
16 Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see
Chapter 1).
17 Marking or labelling all components as
they are disconnected and catching as much
as possible of the escaping coolant in the
drain tray, disconnect the cooling system
hoses and pipes as follows:
a) The coolant hoses at the thermostat housing. b)
The coolant hose at the metal cross pipe
lower connection.
c) The radiator top and bottom hoses.
18 Where applicable, detach the power
steering pump pressure pipe clips, release the
unions and disconnect the pump pressure
and return lines. Collect the fluid in a
suitable container, and plug the disconnected
unions.
19 On vehicles fitted with the anti-lock
braking system, refer to Chapter 9 and release
the left-hand modulator from its mounting
bracket, without disconnecting the rigid brake
pipes or return hose. Tie the modulator
securely to the bulkhead.
20 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ). Remove
the front roadwheels.
21 Refer to Chapter 5 if necessary, and
disconnect the wiring from the starter motor
and alternator.
22 Disconnect the oil pressure switch wiring
connector.
23 On automatic transmission models,
disconnect the starter inhibitor switch wiring
and disconnect the selector cable (see
Chapter 7B). Secure the cable clear of the
engine/transmission.
24 Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, disconnect the gearchange
linkage and transmission support rod from the
rear of the transmission - make alignment
marks as they are disconnected (see
illustrations) .
Engine removal and overhaul procedures 2D•11
5.14b . . . the radio interference
suppressor . . .5.14a Disconnect the wiring multi-plugfrom the ignition coil . . .5.11 Unbolt the engine/transmission-to-body earth lead from the transmission
5.24b . . . and transmission support rod5.24a Disconnect the gearchange linkage . . .5.14c . . . and the reversing light switch
2D
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
Whenever you disconnect
any vacuum lines, coolant or
emissions hoses, wiring
connectors and fuel lines,
always label them clearly, so that they
can be correctly reassembled. Masking
tape and/or a touch-up paint applicator
work well for marking items. Take
instant photos, or sketch the locations
of components and brackets.
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 94 of 296
Plastigauge to the scale printed on the
Plastigauge envelope, to obtain the running
clearance (see illustration 17.15) . Compare it
to the Specifications, to make sure the
clearance is correct.
14 If the clearance is not as specified, seek
the advice of a Ford dealer or similar engine
reconditioning specialist - if the crankshaft
journals are in good condition it may be
possible simply to renew the shells to achieve
the correct clearance. If this is not possible,
the crankshaft must be reground by a
specialist, who can also supply the necessary
undersized shells. First though, make sure
that no dirt or oil was trapped between the
bearing shells and the connecting rod or cap
when the clearance was measured. Also,
recheck the crankpin diameter. If the
Plastigauge was wider at one end than the
other, the crankpin journal may be tapered.
15 Carefully scrape all traces of the
Plastigauge material off the journal and the
bearing surface. Be very careful not to scratch
the bearing - use your fingernail or the edge of a credit card.
Final piston/connecting rod
refitting
16 Make sure the bearing surfaces are
perfectly clean, then apply a uniform layer of
clean molybdenum disulphide-based grease,
engine assembly lubricant, or clean engine oil,
to both of them. You’ll have to push the piston
into the cylinder to expose the bearing surface
of the shell in the connecting rod.
17 Slide the connecting rod back into place
on the crankpin (big-end) journal, refit the big-
end bearing cap, and then tighten the bolts as
described above.
18 Repeat the entire procedure for the
remaining piston/connecting rod assemblies.
19 The important points to remember are:
a) Keep the backs of the bearing shells and the recesses of the connecting rods and
caps perfectly clean when assembling
them.
b) Make sure you have the correct
piston/rod assembly for each cylinder -
use the etched cylinder numbers to
identify the front-facing side of both the
rod and its cap.
c) The arrow on the piston crown must face the timing belt/chain end of the engine.
d) Lubricate the cylinder bores with clean
engine oil.
e) Lubricate the bearing surfaces when refitting the big-end bearing caps after the
running clearance has been checked. 20
After all the piston/connecting rod
assemblies have been properly installed,
rotate the crankshaft a number of times by
hand, to check for any obvious binding.
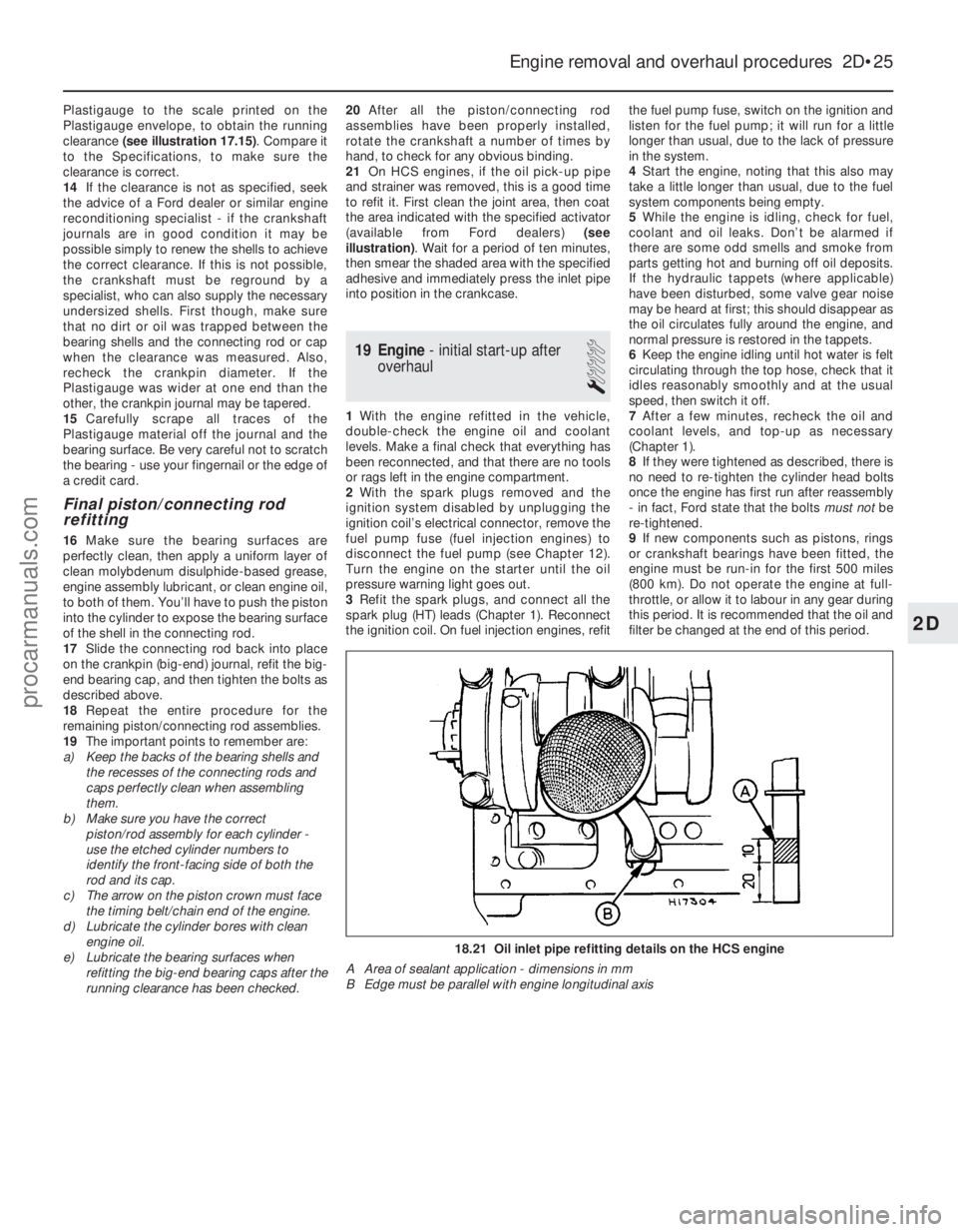
21 On HCS engines, if the oil pick-up pipe
and strainer was removed, this is a good time
to refit it. First clean the joint area, then coat
the area indicated with the specified activator
(available from Ford dealers) (see
illustration) . Wait for a period of ten minutes,
then smear the shaded area with the specified
adhesive and immediately press the inlet pipe
into position in the crankcase.
19 Engine - initial start-up after
overhaul
1
1 With the engine refitted in the vehicle,
double-check the engine oil and coolant
levels. Make a final check that everything has
been reconnected, and that there are no tools
or rags left in the engine compartment.
2 With the spark plugs removed and the
ignition system disabled by unplugging the
ignition coil’s electrical connector, remove the
fuel pump fuse (fuel injection engines) to
disconnect the fuel pump (see Chapter 12).
Turn the engine on the starter until the oil
pressure warning light goes out.
3 Refit the spark plugs, and connect all the
spark plug (HT) leads (Chapter 1). Reconnect
the ignition coil. On fuel injection engines, refit the fuel pump fuse, switch on the ignition and
listen for the fuel pump; it will run for a little
longer than usual, due to the lack of pressure
in the system.
4
Start the engine, noting that this also may
take a little longer than usual, due to the fuel
system components being empty.
5 While the engine is idling, check for fuel,
coolant and oil leaks. Don’t be alarmed if
there are some odd smells and smoke from
parts getting hot and burning off oil deposits.
If the hydraulic tappets (where applicable)
have been disturbed, some valve gear noise
may be heard at first; this should disappear as
the oil circulates fully around the engine, and
normal pressure is restored in the tappets.
6 Keep the engine idling until hot water is felt
circulating through the top hose, check that it
idles reasonably smoothly and at the usual
speed, then switch it off.
7 After a few minutes, recheck the oil and
coolant levels, and top-up as necessary
(Chapter 1).
8 If they were tightened as described, there is
no need to re-tighten the cylinder head bolts
once the engine has first run after reassembly
- in fact, Ford state that the bolts must notbe
re-tightened.
9 If new components such as pistons, rings
or crankshaft bearings have been fitted, the
engine must be run-in for the first 500 miles
(800 km). Do not operate the engine at full-
throttle, or allow it to labour in any gear during
this period. It is recommended that the oil and
filter be changed at the end of this period.
Engine removal and overhaul procedures 2D•25
18.21 Oil inlet pipe refitting details on the HCS engine
A Area of sealant application - dimensions in mm
B Edge must be parallel with engine longitudinal axis
2D
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 99 of 296

the radiator top hose from the thermostat
housing’s water outlet (see illustration).
9 Unscrew the retaining bolts, and remove
the water outlet from the thermostat housing.
10 Withdraw the thermostat from the housing
noting the position of the air bleed valve, and
how the thermostat is installed (which end is
facing outwards) (see illustration).
Testing
General check
11Before assuming the thermostat is to
blame for a cooling system problem, check
the coolant level, auxiliary drivebelt tension
and condition (see Chapter 1) and
temperature gauge operation.
12 If the engine seems to be taking a long
time to warm up (based on heater output or
temperature gauge operation), the thermostat
is probably stuck open. Renew the thermostat.
13 If the engine runs hot, use your hand to
check the temperature of the radiator top
hose. If the hose isn’t hot, but the engine is,
the thermostat is probably stuck closed,
preventing the coolant inside the engine from
escaping to the radiator - renew the
thermostat.
Caution: Don’t drive the vehicle without a
thermostat. The lack of a thermostat will
slow warm-up time. The engine
management system’s ECU will then stay
in warm-up mode for longer than
necessary, causing emissions and fuel
economy to suffer. 14
If the radiator top hose is hot, it means
that the coolant is flowing and the thermostat
is open. Consult the “Fault finding” section at
the end of this manual to assist in tracing
possible cooling system faults.
Thermostat test
15 If the thermostat remains in the open
position at room temperature, it is faulty, and
must be renewed as a matter of course.
16 To test it fully, suspend the (closed)
thermostat on a length of string in a container
of cold water, with a thermometer beside it;
ensure that neither touches the side of the
container (see illustration) .
17 Heat the water, and check the temperature
at which the thermostat begins to open;
compare this value with that specified. It’s not
possible to check the fully-open temperature,
because this occurs above the boiling point of
water at normal atmospheric pressure. If the
temperature at which the thermostat began to
open was as specified, then it is most likely
that the thermostat is working properly at all
temperatures. Remove the thermostat, and
allow it to cool down; check that it closes fully.
18 If the thermostat does not open and close
as described, if it sticks in either position, or if
it does not open at the specified temperature,
it must be renewed.
Refitting
All models
19 Refitting is a reversal of removal. Clean
the mating surfaces carefully, and renew the thermostat’s O-ring seal or housing gasket, as
applicable.
20
On Zetec engines, ensure that the
thermostat is fitted with its air bleed valve
uppermost.
21 Tighten the thermostat housing/water
outlet bolts to the specified torque.
22 Refill the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
23 Refit the air cleaner or air inlet components,
as applicable, if removed for access.
24 Start the engine and allow it to reach
normal operating temperature, then check for
leaks and proper thermostat operation.
5 Radiator electric cooling fan assembly - testing, removal
and refitting
2
Note: Refer to the warnings given in Section 1
of this Chapter before starting work.
Testing
1 If it is suspected that the cooling fan is not
operating when high engine temperature
would normally require it to do so, first check
the relevant fuses and relays (see Chapter 12).
2 Detach the wiring multi-plug from the
thermostatic switch, which is located either in
the thermostat housing or at the right-hand end
of the radiator, next to the bottom hose (see
illustration) . Using a suitable piece of wire,
bridge the two connections within the plug.
Switch the ignition on and check if the cooling
fan operates. If the fan now operates, the
thermostatic switch is at fault, and should be
renewed as described in Section 6. Remove the
bridging wire from the plug, and reconnect the
wiring connector to complete the test.
3 If the fan failed to operate in the previous
test, either the fan motor is at fault, or there is
a fault in the wiring loom (see Chapter 12 for
testing details).
Removal
All models except Turbo
4 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
5 Detach the wiring multi-plug from the fan
motor and unclip the wiring from the retaining
clips on the shroud (see illustration).
3•4 Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
5.5 Disconnecting the multi-plug from the
radiator cooling fan motor5.2 Radiator cooling fan thermostatic
switch location on CVH engine thermostat
housing
4.16 Testing the thermostat4.10 Zetec engine thermostat removal4.8 Disconnect the coolant hoses from thewater outlet on a Zetec engine
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 107 of 296

Fuel pump
Delivery pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 0.24 to 0.38 bars
Carburettor data
Weber (1V) TLM carburettor - 1.0 litre HCS engines
Idle speed and mixture settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1Fast-idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 3400 ± 100 rpm
Float height . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . 26.0 ± 1.0 mm
Venturi diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 23 mm
Main jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Air correction jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 220
Weber (2V) TLDM carburettor - 1.1 litre HCS engines
Idle speed and mixture settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1Fast-idle speed:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 2800 rpm
CTX automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2600 rpm
Float height . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . 29.0 ± 1.0 mm
Throttle kicker speed: Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 1250 to 1350 rpm
CTX automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1050 to 1150 rpm
PrimarySecondary
Venturi diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 26 mm 28 mm
Main jet: Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 92122
CTX automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92112
Emulsion tube . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . F113 F75
Air correction jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 195 155
Weber (2V) TLDM carburettor - 1.3 litre HCS engines
Idle speed and mixture settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1 Fast-idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 2500 rpmFloat height . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . 29.0 ± 1.0 mm
Throttle kicker speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . 1900 ± 100 rpm
PrimarySecondary
Venturi diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 19 mm 20 mm
Main jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90122
Emulsion tube . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . F113 F75
Air correction jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 185 130
Weber (2V) DFTM carburettor - 1.4 litre CVH engines
Idle speed and mixture settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1 Fast-idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 2800 ± 100 rpm
Choke pull-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 2.7 to 3.2 mm
Float height . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . 8.0 ± 0.5 mm
Throttle kicker speed:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 1300 ± 50 rpm
CTX automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1100 ± 50 rpm (in Neutral)
PrimarySecondary
Venturi diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 21 mm 23 mm
Main jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100 125
Air correction jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 210 155
Emulsion tube . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . F22 F60
Idle jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4260
Weber (2V) TLD carburettor - 1.6 litre CVH engines
Idle speed and mixture settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1 Fast-idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 1800 ± 50 rpm (on third step of fast-idle cam)
Choke pull-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 4.7 ± 0.5 mm
Float height . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . 29.0 ± 0.5 mm
PrimarySecondary
Venturi diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 2123
Main jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117 127
Emulsion tube . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . F105 F71
Air correction jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 185 125
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Fuel pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 16 to 20 12 to 15
Inlet manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . 16 to 20 12 to 15
4A•2 Fuel system – carburettor engines
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 111 of 296

container which can be sealed (see
illustration) . Where quick-release couplings
are used on the fuel hoses, release the
protruding locking lugs on each union, by
squeezing them together and carefully pulling
the coupling apart. Note that the fuel supply
hose couplings are identified by a white
colour band and the return hose couplings by
a yellow colour band.
6 Disconnect the filler neck sensing pipe
connection from the rear of the tank (see
illustration) .
7 Support beneath the tank to hold it in
position and remove its four securing bolts
(see illustration) .
8 Partially lower the fuel tank and disconnect
the ventilation tube from the tank top surface
and also disconnect the sender unit multi-
plug. The filler pipe should release from its
fuel tank seal location as the tank is
withdrawn.
Inspection
9 Whilst removed, the fuel tank can be
inspected for damage or deterioration.
Removal of the sender unit (see Section 9) will
allow a partial inspection of the interior. If the
tank is contaminated with sediment or water,
swill it out with clean petrol. Do not under any
circumstances undertake any repairs on a
leaking or damaged fuel tank; this work must
be carried out by a professional who has
experience in this critical and potentially-
dangerous work.
10 Whilst the fuel tank is removed from the
vehicle, it should not be placed in an area
where sparks or open flames could ignite the
fumes coming out of the tank. Be especially
careful inside garages where a natural-gas
type appliance is located, because the pilot
light could cause an explosion.
11 Check the condition of the filler pipe seal
in the fuel tank, and renew it if necessary.
Refitting
All models
12 Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure. Apply a light smear of grease to the
filler pipe seal, to ease fitting. Ensure that all
connections are securely fitted. Where quick-
release fuel couplings are fitted, press them together until the locking lugs snap into their
groove. If evidence of contamination was
found, do not return any previously-drained
fuel to the tank unless it is carefully filtered first.
9
Fuel gauge sender unit -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Ford specify the use of their service tool
23-014 (a large box spanner with projecting
teeth to engage the fuel gauge sender unit
retaining ring’s slots) for this task. While
alternatives are possible, in view of the difficulty
experienced in removing and refitting the
sender unit, owners are strongly advised to
obtain the correct tool before starting work. The
help of an assistant will be required. Refer to the
warning note in Section 1 before proceeding.
Removal
1 Remove the fuel tank as described in
Section 8.
2 Engage the special tool into the sender unit
then carefully turn the sender unit and release
it from the top of the tank.
Refitting
3 Refit the sender unit in the reverse order of
removal. Be sure to fit a new seal, and
lubricate it with a smear of grease to prevent it
from distorting when fitting the sender unit.
10 Fuel tank ventilation tube -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding.
Removal
1 The fuel tank ventilation tube runs from the
top surface of the fuel tank to the combined roll-
over/anti-trickle-fill valve assembly mounted in
the left-hand rear wheelarch (see illustration).
Its purpose is to eliminate any possibility of
vacuum or pressure build-up in the fuel tank.
2 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
3 Chock the front wheels then jack up the
rear of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and vehicle support” ). Remove
the left-hand rear roadwheel.
4 Support the fuel tank from underneath on a
suitable jack, using a large thick sheet of
board to spread the weight, then undo and
remove the four fuel tank securing bolts.
5 Lower the fuel tank slightly in such a manner
so as to allow access to disconnect the
ventilation tube from the tank top surface.
Ensure that the fuel tank does not foul or strain
any adjacent components as it is lowered;
take appropriate action, as necessary.
6 Disconnect the ventilation tube from the
combined roll-over/anti-trickle-fill valve, release
the tube from its retaining clips and remove.
Refitting
7 Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, ensuring that the fuel tank filler
pipe is located correctly with the tank.
11 Fuel tank filler pipe -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding.
Removal
1 Remove the fuel tank as described in
Section 8.
4A•6 Fuel system – carburettor engines
10.1 Combined roll-over anti-trickle-fill valve assembly
A Tube ventilating to atmosphere
B Ventilation tube from fuel tank
8.7 Fuel tank securing bolts (arrowed)8.6 Filler neck sensing pipe connection at the rear of the fuel tank
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
8.5 Fuel feed and return pipe connections
(arrowed)procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su