1989 FORD FIESTA compression ratio
[x] Cancel search: compression ratioPage 10 of 296

3 Engine oil and filter renewal
1
1Make sure that you have all the necessary
tools before you begin this procedure (see
illustration) . You should also have plenty of
rags or newspapers handy, for mopping up
any spills.
2 To avoid any possibility of scalding, and to
protect yourself from possible skin irritants
and other harmful contaminants in used
engine oils, it is advisable to wear gloves
when carrying out this work. 3
Access to the underside of the vehicle is
greatly improved if the vehicle can be lifted on a
hoist, driven onto ramps, or supported by axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ).
Warning: Do not work under a
vehicle which is supported only
by an hydraulic or scissors-type
jack, or by bricks, blocks of
wood, etc. 4
If this is your first oil change, get under the
vehicle and familiarise yourself with the
position of the engine oil drain plug location in
the sump. The engine and exhaust
components will be warm during the actual
work, so try to anticipate any potential
problems while the engine and accessories
are cool.
5 The oil should preferably be changed when
the engine is still fully warmed-up to normal
operating temperature, just after a run (the
needle on the temperature gauge should be in
the “Normal” sector of the gauge); warm oil
and sludge will flow out more easily. Park the
vehicle on firm, level ground, apply the
handbrake firmly, then select 1st or reverse
gear (manual transmission) or the “P” position
(automatic transmission). Open the bonnet
and remove the engine oil filler cap from the
cylinder head cover, then remove the oil level
dipstick from its tube (see “Weekly Checks”).
6 Raise the front of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands (see “Jacking and
Vehicle Support” ). Remove the front right-
hand roadwheel to provide access to the oil
1 Introduction
This Chapter is designed to help the home
mechanic maintain his/her vehicle for safety,
economy, long life and peak performance.
This Chapter contains a master
maintenance schedule, followed by Sections
dealing specifically with each task in the
schedule. Visual checks, adjustments,
component renewal and other helpful items
are included. Refer to the accompanying
illustrations of the engine compartment and
the underside of the vehicle for the locations
of the various components.
Servicing your vehicle in accordance with
the mileage/time maintenance schedule and
the following Sections will provide a planned
maintenance programme, which should result
in a long and reliable service life. This is a
comprehensive plan, so maintaining some
items but not others at the specified service
intervals will not produce the same results. As you service your vehicle, you will
discover that many of the procedures can -
and should - be grouped together, because of
the particular procedure being performed, or
because of the close proximity of two
otherwise-unrelated components to one
another. For example, if the vehicle is raised
for any reason, the exhaust should be
inspected at the same time as the suspension
and steering components.
The first step of this maintenance
programme is to prepare yourself before the
actual work begins. Read through all the Sections relevant to the work to be carried
out, then make a list and gather together all
the parts and tools required. If a problem is
encountered, seek advice from a parts
specialist or a dealer service department.
2 Intensive maintenance
1
If, from the time the vehicle is new, the
routine maintenance schedule is followed
closely, and frequent checks are made of fluid
levels and high-wear items, as suggested
throughout this manual, the engine will be
kept in relatively good running condition, and
the need for additional work will be minimised.
2 It is possible that there will be some times
when the engine is running poorly due to the
lack of regular maintenance. This is even more
likely if a used vehicle, which has not received
regular and frequent maintenance checks, is
purchased. In such cases, additional work
may need to be carried out, outside of the
regular maintenance intervals.
3 If engine wear is suspected, a compression
test (refer to Part A, B or C of Chapter 2) will
provide valuable information regarding the
overall performance of the main internal
components. Such a test can be used as a
basis to decide on the extent of the work to
be carried out. If, for example, a compression
test indicates serious internal engine wear,
conventional maintenance as described in this
Chapter will not greatly improve the
performance of the engine, and may prove a waste of time and money, unless extensive
overhaul work (Chapter 2D) is carried out first.
4
The following series of operations are those
often required to improve the performance of
a generally poor-running engine:
Primary operations
a) Clean, inspect and test the battery (See
“Weekly Checks”).
b) Check all the engine-related fluids (See
“Weekly Checks”).
c) Check the condition of the auxiliary drivebelt (Section 4).
d) Check and if necessary adjust the valve
clearances on HCS engines (Section 7).
e) Renew the spark plugs and clean and inspect the HT leads (Section 21).
f) Check the condition of the air cleaner filter element and renew if necessary
(Section 24).
g) Check and if necessary adjust the idle speed and mixture settings - where
applicable (Section 9).
h) Renew the fuel filter - fuel injection models (Section 30).
i) Check the condition of all hoses, and check for fluid leaks (Section 5).
5 If the above operations do not prove fully
effective, carry out the following operations:
Secondary operations
All the items listed under “Primary
operations”, plus the following: a) Check the charging system (Chapter 5A).
b) Check the ignition system (Chapter 5B).
c) Check the fuel system (Chapter 4A, 4B,
4C and 4D).
e) Renew the ignition HT leads (Section 21).
Maintenance procedures1•9
3.2 These tools are required when changing the engine oil and filter
1
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
Every 5000 miles (8000 km) or 6 months, whichever occurs first
Frequent oil changes are the
best preventive
maintenance the home
mechanic can give the
engine, because ageing oil becomes
diluted and contaminated, which leads
to premature engine wear.
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 28 of 296

2A
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
General
Engine type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . Four-cylinder, in-line overhead valve
Engine code:1.0 litre carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . TLB
1.1 litre carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . GUE or GUD
1.1 litre CFi fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . G6A
1.3 litre carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . JBC
1.3 litre CFi fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . J6B
Capacity: 1.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 999 cc
1.1 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 1118 cc
1.3 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 1297 cc
Bore:
1.0 and 1.1 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68.68 mm
1.3 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 73.96 mm
Stroke:
1.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 67.40 mm
1.1 and 1.3 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75.48 mm
Compression ratio:
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . 9.5:1
CFi fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.8:1
Firing order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . 1-2-4-3 (No 1 cylinder at timing chain end)
Direction of crankshaft rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Clockwise (seen from right-hand side of vehicle)
Valves
Valve clearance (cold): Inlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.20 mm
Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 0.30 mm
Chapter 2 Part A:
HCS engine in-car repair procedures
Auxiliary drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1
Compression test - description and interpretation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Crankshaft oil seals - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Crankshaft pulley - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Cylinder head - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Cylinder head rocker cover - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Cylinder head rocker gear - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . 6
Engine oil and filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1
Engine oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See
“Weekly Checks”
Engine/transmission mountings - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . 15 Flywheel - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 1
Oil pump - dismantling, inspection and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Oil pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Sump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Timing chain cover - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Timing chain, sprockets and tensioner - removal, inspection
and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 10
Top Dead Centre (TDC) for No 1 piston - locating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Valve clearances - checking and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2A•1
Specifications Contents
Easy, suitable for
novice with little
experience Fairly easy,
suitable
for beginner with
some experience Fairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,
suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanic Very difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 29 of 296

Lubrication
Engine oil type/specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See “Lubricants, fluids and tyre pressures”
Engine oil capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . See “Lubricants, fluids and tyre pressures”
Oil pressure: At idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 0.60 barsAt 2000 rpm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 1.50 bars
Oil pump clearances: Outer rotor-to-body . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 0.14 to 0.26 mm
Inner rotor-to-outer rotor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.051 to 0.127 mm
Rotor endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 0.025 to 0.06 mm
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Camshaft thrust plate bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 4
Camshaft sprocket bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. 1813
Crankshaft pulley bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . 115 85
Rocker shaft pedestal bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4332
Flywheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . 6749
Sump: Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 7 5
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7
Stage 3 (with engine warm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7
Oil pressure switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . 1410
Cylinder head bolts (may be re-used once only): Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 3022
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten a further 90º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten a further 90º
Timing chain tensioner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 8 6
Timing chain cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . 9 7
Crankshaft rear oil seal housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1813
Rocker cover bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . 5 4
Oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 1813
Oil pump cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 9 7
Engine mountings: Engine mounting (right-hand):Bolt to body (in wheel arch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 to 58 30 to 43
Nut to body (by suspension strut) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 to 58 30 to 43
Bracket to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54 to 72 40 to 53
Rubber insulator to bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71 to 95 52 to 70
Transmission mounting fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Refer to Chapter 7A or 7B
Note: Refer to Part D of this Chapter for remaining torque wrench settings.
2A•2 HCS engine in-car repair procedures
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
1 General information
How to use this Chapter
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to repair
procedures possible while the engine is still
installed in the vehicle, and includes only the
Specifications relevant to those procedures.
Similar information concerning the 1.4 and
1.6 litre CVH and PTE engines, and the 1.6
and 1.8 litre Zetec engines, will be found in
Parts B and C of this Chapter respectively.
Since these procedures are based on the
assumption that the engine is installed in the
vehicle, if the engine has been removed from
the vehicle and mounted on a stand, some
of the preliminary dismantling steps outlined
will not apply. Information concerning engine/transmission
removal and refitting, and engine overhaul, can
be found in Part D of this Chapter, which also
includes the Specifications relevant to those
procedures.
Engine description
The engine is an overhead valve, water-
cooled, four cylinder in-line design,
designated HCS (High Compression Swirl).
The engine is mounted transversely at the
front of the vehicle together with the
transmission to form a combined power unit. The crankshaft is supported in three or five
shell-type main bearings. The connecting rod
big-end bearings are also split shell-type, and
are attached to the pistons by interference-fit
gudgeon pins. Each piston is fitted with two
compression rings and one oil control ring. The camshaft, which runs on bearings
within the cylinder block, is chain-driven from
the crankshaft, and operates the valves via
pushrods and rocker arms. The valves are
each closed by a single valve spring, and
operate in guides integral in the cylinder head. The oil pump is mounted externally on the
crankcase, incorporates a full-flow oil filter,
and is driven by a skew gear on the camshaft.
On carburettor versions, the fuel pump is also
driven from the camshaft, via an eccentric
lobe.
Repair operations possible with
the engine in the car
The following work can be carried out with
the engine in the car:
a) Compression pressure - testing.
b) Cylinder head rocker cover - removal
and refitting.
c) Valve clearances - adjustment.
d) Rocker shaft assembly - removal,
inspection and refitting.
e) Cylinder head - removal and refitting
f) Cylinder head and pistons - decarbonising.
g) Crankshaft pulley - removal and refitting.
h) Crankshaft oil seals - renewal.
i) Timing chain, sprockets and tensioner -
removal, inspection and refitting.
j) Oil filter renewal.
k) Oil pump - removal and refitting.
l) Sump - removal and refitting.
m) Flywheel - removal, inspection and
refitting.
n) Engine/transmission mountings -
inspection and renewal.
Note: It is possible to remove the pistons and
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 30 of 296

connecting rods (after removing the cylinder
head and sump) without removing the engine.
However, this is not recommended. Work of
this nature is more easily and thoroughly
completed with the engine on the bench, as
described in Chapter 2D.
2 Compression test-
description and interpretation
2
1 When engine performance is down, or if
misfiring occurs which cannot be attributed to
the ignition or fuel systems, a compression
test can provide diagnostic clues as to the
engine’s condition. If the test is performed
regularly, it can give warning of trouble before
any other symptoms become apparent.
2 The engine must be fully warmed-up to
normal operating temperature, the oil level
must be correct and the battery must be fully
charged. The aid of an assistant will also be
required.
3 On fuel injection engines, refer to Chap-
ter 12 and remove the fuel pump fuse from the
fusebox. Now start the engine and allow it to
run until it stalls.
4 Disable the ignition system by
disconnecting the multi-plug from the DIS or
E-DIS ignition coil. Remove all the spark plugs
with reference to Chapter 1 if necessary.
5 Fit a compression tester to the No 1
cylinder spark plug hole - the type of tester
which screws into the plug thread is to be
preferred.
6 Arrange for an assistant to hold the
accelerator pedal fully depressed to the floor,
while at the same time cranking the engine
over for several seconds on the starter motor.
Observe the compression gauge reading. The
compression will build up fairly quickly in a
healthy engine. Low compression on the first
stroke, followed by gradually-increasing
pressure on successive strokes, indicates
worn piston rings. A low compression on the
first stroke which does not rise on successive
strokes, indicates leaking valves or a blown
head gasket (a cracked cylinder head could
also be the cause). Deposits on the underside
of the valve heads can also cause low
compression. Record the highest gauge
reading obtained, then repeat the procedure
for the remaining cylinders.
7 Due to the variety of testers available, and
the fluctuation in starter motor speed when
cranking the engine, different readings
are often obtained when carrying out
the compression test. For this reason, actual
compression pressure figures are not quoted
by Ford. However, the most important factor
is that the compression pressures are uniform
in all cylinders, and that is what this test is
mainly concerned with.
8 Add some engine oil (about three squirts
from a plunger type oil can) to each cylinder
through the spark plug holes, and then repeat
the test. 9
If the compression increases after the oil is
added, it is indicative that the piston rings are
definitely worn. If the compression does not
increase significantly, the leakage is occurring
at the valves or the head gasket. Leakage
past the valves may be caused by burned
valve seats and/or faces, or warped, cracked
or bent valves.
10 If two adjacent cylinders have equally low
compressions, it is most likely that the head
gasket has blown between them. The
appearance of coolant in the combustion
chambers or on the engine oil dipstick would
verify this condition.
11 If one cylinder is about 20 percent lower
than the other, and the engine has a slightly
rough idle, a worn lobe on the camshaft could
be the cause.
12 On completion of the checks, refit the
spark plugs and reconnect the HT leads and
the ignition coil plug. Refit the fuel pump fuse
to the fusebox.
3 Top Dead Centre (TDC) for No 1 piston - locating
2
1Top dead centre (TDC) is the highest point
of the cylinder that each piston reaches as the
crankshaft turns. Each piston reaches its TDC
position at the end of its compression stroke,
and then again at the end of its exhaust
stroke. For the purpose of engine timing, TDC
at the end of the compression stroke for No 1
piston is used. On the HCS engine, No 1
cylinder is at the crankshaft pulley/timing
chain end of the engine. Proceed as follows.
2 Ensure that the ignition is switched off.
Disconnect the HT leads from the spark plugs,
then unscrew and remove the plugs as
described in Chapter 1.
3 Turn the engine over by hand (using a
spanner on the crankshaft pulley) to the point
where the timing mark on the crankshaft
pulley aligns with the TDC (0) mark or TDC
reference pointer on the timing cover (see
illustration) . As the pulley mark nears the
timing mark, the No 1 piston is simultaneously
approaching the top of its cylinder. To ensure
that it is on its compression stroke, place a
finger over the No 1 cylinder plug hole, and feel to ensure that air pressure exits from the
cylinder as the piston reaches the top of its
stroke.
4
A further check to ensure that the piston is
on its compression stroke can be made by
first removing the air cleaner (refer to the
relevant Part of Chapter 4), then unbolting and
removing the rocker cover, so that the
movement of the valves and rockers can be
observed.
5 With the TDC timing marks on the
crankshaft pulley and timing cover in
alignment, rock the crankshaft back and forth
a few degrees each side of this position, and
observe the action of the valves and rockers
for No 1 cylinder. When No 1 piston is at the
TDC firing position, the inlet and exhaust valve
of No 1 cylinder will be fully closed, but the
corresponding valves of No 4 cylinder will be
seen to rock open and closed.
6 If the inlet and exhaust valves of No 1
cylinder are seen to rock whilst those of
No 4 cylinder are shut, the crankshaft will
need to be turned one full rotation to bring
No 1 piston up to the top of its cylinder on the
compression stroke.
7 Once No 1 cylinder has been positioned at
TDC on the compression stroke, TDC for any
of the other cylinders can then be located by
rotating the crankshaft clockwise (in its
normal direction of rotation), 180º at a time,
and following the firing order (see
Specifications).
4 Cylinder head rocker cover -
removal and refitting
1
Removal
1 Where necessary for access, remove the air
cleaner as described in the relevant Part of
Chapter 4.
2 Detach the HT leads from the spark plugs.
Pull on the connector of each lead (not the
lead itself), and note the order of fitting.
3 Remove the engine oil filler cap and
breather hose (where fitted).
4 Unscrew the four retaining bolts, and lift the
rocker cover clear of the cylinder head.
Remove the gasket.
HCS engine in-car repair procedures 2A•3
3.3 Timing mark on the crankshaft pulley aligned with the TDC (0) mar\
k on the timing cover
2A
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 40 of 296

2B
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
General
Engine type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . Four-cylinder, in-line overhead camshaft
Engine code:1.4 litre CVH engine: Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. FUF or FUG
CFi fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . F6E
1.4 litre PTE engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . F4A
1.6 litre CVH engine: Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. LUH
EFi fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . LJC or LJD
Turbo models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . LHA
Capacity:
1.4 litre CVH and PTE engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1392 cc
1.6 litre CVH engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 1596 cc
Bore:
1.4 litre CVH and PTE engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77.24 mm
1.6 litre CVH engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 79.96 mm
Stroke:
1.4 litre CVH and PTE engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74.30 mm
1.6 litre CVH engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 79.52 mm
Compression ratio:
1.4 litre CVH carburettor engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.5:1
1.4 litre CVH CFi fuel injection engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.5:1
1.4 litre PTE engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . 9.5:1
1.6 litre CVH engine: Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. 9.5:1
EFi fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.75:1
Turbo models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . 8.0:1
Firing order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . 1-3-4-2 (No 1 cylinder at timing belt end)
Direction of crankshaft rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Clockwise (seen from right-hand side of vehicle)
Chapter 2 Part B:
CVH and PTE engine in-car repair procedures
Auxiliary drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1
Camshaft oil seal - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Camshaft, rocker arms and tappets - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 11
Compression test - description and interpretation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Crankshaft oil seals - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Crankshaft pulley - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Cylinder head - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Cylinder head rocker cover - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Engine oil and filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1
Engine oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See
“Weekly Checks”
Engine/transmission mountings - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 Flywheel/driveplate - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . 18
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 1
Oil pump - dismantling, inspection and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Oil pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Sump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Timing belt - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Timing belt covers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Timing belt tensioner and sprockets - removal, inspection
and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . 9
Top Dead Centre (TDC) for No 1 piston - locating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Valve clearances - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2B•1
Specifications Contents
Easy, suitable for
novice with little
experience Fairly easy,
suitable
for beginner with
some experience Fairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,
suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanic Very difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 42 of 296

1 General information
How to use this Chapter
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to repair
procedures possible while the engine is still
installed in the vehicle, and includes only the
Specifications relevant to those procedures.
Similar information concerning the 1.3 litre
HCS engine, and the 1.6 and 1.8 litre Zetec
engines, will be found in Parts A and C of this
Chapter respectively. Since these procedures
are based on the assumption that the engine
is installed in the vehicle, if the engine has
been removed from the vehicle and mounted
on a stand, some of the preliminary
dismantling steps outlined will not apply.
Information concerning engine/transmission
removal and refitting, and engine overhaul, can
be found in Part D of this Chapter, which also
includes the Specifications relevant to those
procedures.
Engine description
The engine is a four-cylinder, in-line
overhead camshaft type, designated CVH
(Compound Valve angle, Hemispherical
combustion chamber) or PTE (Pent roof, high
Torque, low Emission). The PTE engine was
introduced for 1994 and, apart from
modifications to the cylinder head, camshaft
and intake system, is virtually identical to the
CVH engine it replaces. The engine is
mounted transversely at the front of the
vehicle together with the transmission to form
a combined power unit. The crankshaft is supported in five split-
shell type main bearings within the cast-iron
crankcase. The connecting rod big-end
bearings are split-shell type, and the pistons
are attached by interference-fit gudgeon pins.
Each piston has two compression rings and
one oil control ring.
The cylinder head is of light alloy
construction, and supports the camshaft in five
bearings. Camshaft drive is by a toothed
composite rubber timing belt, which is driven by
a sprocket on the front end of the crankshaft.
The timing belt also drives the water pump,
which is mounted below the cylinder head. Hydraulic cam followers (tappets) operate the
rocker arms and valves. The tappets are
operated by pressurised engine oil. When a
valve closes, the oil passes through a port in the
body of the cam follower, through four grooves
in the plunger and into the cylinder feed
chamber. From the chamber, the oil flows to a
ball-type non-return valve and into the pressure
chamber. The tension of the coil spring causes
the plunger to press against the valve, and so
eliminates any free play. As the cam lifts the
follower, the oil pressure in the pressure
chamber is increased, and the non-return valve
closes off the port feed chamber. This in turn
provides a rigid link between the cam follower,
the cylinder and the plunger. These then rise as a unit to open the valve. The cam follower-to-
cylinder clearance allows the specified quantity
of oil to pass from the pressure chamber, oil only
being allowed past the cylinder bore when the
pressure is high during the moment of the valve
opening. When the valve closes, the escape of
oil will produce a small clearance, and no
pressure will exist in the pressure chamber. The
feed chamber oil then flows through the non-
return valve and into the pressure chamber, so
that the cam follower cylinder can be raised by
the pressure of the coil spring, eliminating free
play until the valve is operated again.
As wear occurs between the rocker arm
and the valve stem, the quantity of oil that
flows into the pressure chamber will be
slightly more than the quantity lost during the
expansion cycle of the cam follower.
Conversely, when the cam follower is
compressed by the expansion of the valve, a
slightly smaller quantity of oil will flow into the
pressure chamber than was lost. A rotor-type oil pump is mounted on the
timing cover end of the engine, and is driven
by a gear on the front end of the crankshaft. A
full-flow type oil filter is fitted, and is mounted
on the side of the crankcase.
Repair operations possible with
the engine in the car
The following work can be carried out with
the engine in the car:
a) Compression pressure - testing.
b) Rocker cover - removal and refitting.
c) Timing belt - removal, refitting and
adjustment.
d) Camshaft oil seal - renewal.
e) Camshaft - removal and refitting.
f) Cylinder head - removal and refitting.
g) Cylinder head and pistons - decarbonising.
h) Crankshaft pulley - removal and refitting.
i) Crankshaft oil seals - renewal.
j) Oil filter renewal.
k) Sump - removal and refitting.
l) Flywheel - removal, inspection and refitting.
m) Mountings - removal and refitting.
Note: It is possible to remove the pistons and
connecting rods (after removing the cylinder
head and sump) without removing the engine.
However, this is not recommended. Work of
this nature is more easily and thoroughly
completed with the engine on the bench, as
described in Chapter 2D.
2 Compression test -
description and interpretation
2
Refer to Section 2 in Part A of this Chap-
ter.
3 Top Dead Centre (TDC) for
No 1 piston - locating
2
1Top dead centre (TDC) is the highest point
of the cylinder that each piston reaches as the
crankshaft turns. Each piston reaches its TDC
position at the end of its compression stroke,
and then again at the end of its exhaust
stroke. For the purpose of engine timing, TDC
on the compression stroke for No 1 piston is
used. No 1 cylinder is at the timing belt end of
the engine. Proceed as follows.
2 Remove the upper timing belt cover as
described in Section 7.
3 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ).
4 Undo the retaining bolts, and remove the
cover from the underside of the crankshaft
pulley.
5 Fit a spanner onto the crankshaft pulley bolt,
and turn the crankshaft in its normal direction
of rotation (clockwise, viewed from the pulley
end) to the point where the crankshaft pulley
timing notch is aligned with the TDC (0) timing
mark on the timing belt cover.
6 Although the crankshaft is now in top dead
centre alignment, with piston Nos 1 and 4 at
the top of their stroke, the No 1 piston may
not be on its compression stroke. To confirm
that it is, check that the timing pointer on the
camshaft sprocket is exactly aligned with the
TDC mark on the front face of the cylinder
head (see illustrations) . If the pointer is not
aligned, turn the crankshaft pulley one further
CVH and PTE engine in-car repair procedures 2B•3
3.6b Camshaft sprocket timing mark
aligned with the TDC mark on the front
face of the cylinder head3.6a Crankshaft pulley notch (arrowed)aligned with the TDC (0) mark on the
timing belt cover
2B
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
Turning the engine will be
easier if the spark plugs are
removed first - see Chapter 1.
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 43 of 296

complete turn, and all the markings should
now align.
7With the engine set at No 1 piston on TDC
compression, refit the crankshaft pulley cover,
lower the vehicle and refit the upper timing
belt cover.
4 Cylinder head rocker cover -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
2 Remove the air cleaner assembly and air
inlet components as necessary for access as
described in the relevant Part of Chapter 4.
Disconnect the crankcase ventilation hose
from the rocker cover.
3 Remove the timing belt upper cover as
described in Section 7.
4 Referring to the relevant Part of Chapter 4
for details, disconnect the accelerator cable
from the throttle linkage and from the adjuster
bracket above the rocker cover. Position the
cable out of the way.
5 Where applicable, disconnect the choke
cable from the carburettor, referring to
Chapter 4A for details.
6 Unscrew and remove the rocker cover
retaining bolts and washers, then lift the cover
from the cylinder head. Note that a new
rocker cover gasket will be needed on
refitting.
Refitting
7 Before refitting the rocker cover, clean the
mating surfaces of both the cylinder head and
the cover.
8 Locate the new gasket in position, then fit
the cover retaining bolts and washers. Ensure
that the grooves in the plate washers are
facing upwards as they are fitted (see
illustrations) . Tighten the cover retaining
bolts to the specified torque wrench setting.
Refer to Chapter 4 for details on reconnecting
the accelerator cable, choke cable, air inlet
components and air cleaner (as applicable).
9 Refit the timing belt cover and reconnect
the battery earth lead.
5 Valve clearances -
general information
It is necessary for a clearance to exist
between the tip of each valve stem and the
valve operating mechanism, to allow for the
expansion of the various components as the
engine reaches normal operating
temperature. On most older engine designs, this meant
that the valve clearances (also known as
“tappet” clearances) had to be checked and
adjusted regularly. If the clearances were
allowed to be too slack, the engine would be
very noisy, its power output would suffer, and
its fuel consumption would increase. If the
clearances were allowed to be too tight, the
engine’s power output would be reduced, and
the valves and their seats could be severely
damaged. These engines employ hydraulic tappets
which use the lubricating system’s oil
pressure to automatically take up the
clearance between each camshaft lobe and
its respective valve stem. Therefore, there is
no need for regular checking and adjustment
of the valve clearances. However, it is
essential that only good-quality oil of the
recommended viscosity and specification is
used in the engine, and that this oil is always
changed at the recommended intervals. If this
advice is not followed, the oilways and
tappets may become clogged with particles of
dirt, or deposits of burnt (inferior) engine oil,
so that the system cannot work properly;
ultimately, one or more of the tappets may fail,
and expensive repairs may be required. On starting the engine from cold, there will
be a slight delay while full oil pressure builds
up in all parts of the engine, especially in the
tappets; the valve components, therefore,
may well “rattle” for about 10 seconds or so,
and then quieten. This is a normal state of
affairs, and is nothing to worry about,
provided that all tappets quieten quickly and
stay quiet. After the vehicle has been standing for
several days, the valve components may
“rattle” for longer than usual, as nearly all the oil will have drained away from the engine’s
top-end components and bearing surfaces.
While this is only to be expected, care must
be taken not to damage the engine under
these circumstances - avoid high-speed
running until all the tappets are refilled with oil
and operating normally. With the vehicle
stationary, hold the engine at no more than a
fast idle speed (maximum 2000 to 2500 rpm)
for 10 to 15 minutes, or until the noise ceases.
Do not run the engine at more than 3000 rpm
until the tappets are fully charged with oil and
the noise has ceased.
If the valve components are thought to be
noisy, or if a light rattle persists from the top
end after the engine has warmed up to normal
operating temperature, take the vehicle to a
Ford dealer for expert advice. Depending on
the mileage covered and the usage to which
each vehicle has been put, some vehicles may
be noisier than others; only a good mechanic
experienced in these engines can tell if the
noise level is typical for the vehicle’s mileage,
or if a genuine fault exists. If any tappet’s
operation is faulty, it must be renewed
(Section 11).
6 Crankshaft pulley -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
2 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ).
3 Unbolt and remove the cover from the
underside of the crankshaft pulley.
4 Remove the auxiliary drivebelt as described
in Chapter 1.
5 If timing belt renewal is also intended, set
the engine at TDC as described in Section 3
before removing the crankshaft pulley and
retaining bolt.
6 To prevent the crankshaft from turning as
the pulley bolt is loosened off, remove the
starter motor as described in Chapter 5A, and
then lock the starter ring gear using a suitable
lever (see illustration) .
2B•4 CVH and PTE engine in-car repair procedures
6.6 Using a suitable bar to lock the
flywheel ring gear4.8b Rocker cover retaining bolts and plate washers4.8a Fitting a new gasket to the rocker cover
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 44 of 296
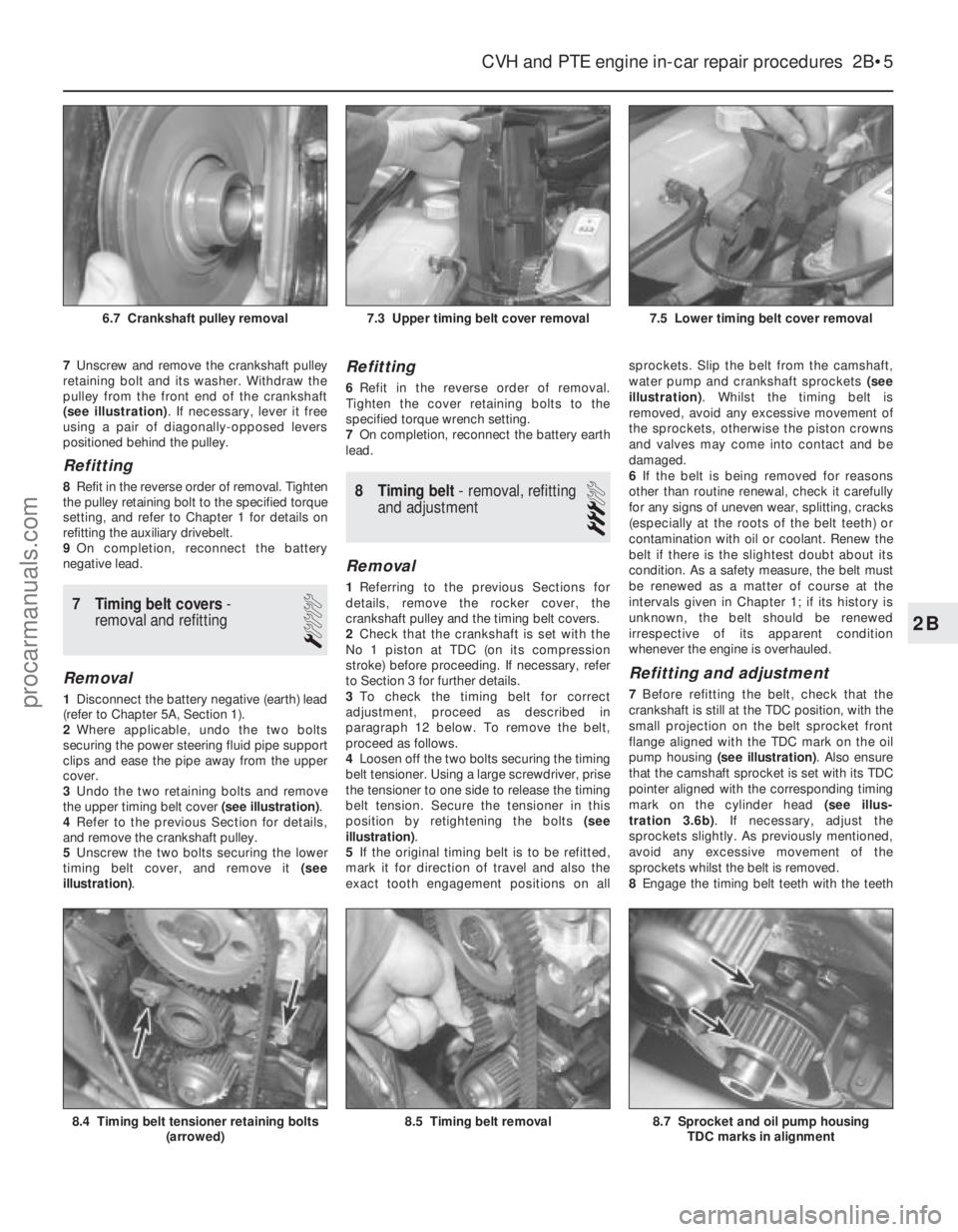
7Unscrew and remove the crankshaft pulley
retaining bolt and its washer. Withdraw the
pulley from the front end of the crankshaft
(see illustration) . If necessary, lever it free
using a pair of diagonally-opposed levers
positioned behind the pulley.
Refitting
8 Refit in the reverse order of removal. Tighten
the pulley retaining bolt to the specified torque
setting, and refer to Chapter 1 for details on
refitting the auxiliary drivebelt.
9 On completion, reconnect the battery
negative lead.
7 Timing belt covers -
removal and refitting
1
Removal
1 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
2 Where applicable, undo the two bolts
securing the power steering fluid pipe support
clips and ease the pipe away from the upper
cover.
3 Undo the two retaining bolts and remove
the upper timing belt cover (see illustration).
4 Refer to the previous Section for details,
and remove the crankshaft pulley.
5 Unscrew the two bolts securing the lower
timing belt cover, and remove it (see
illustration) .
Refitting
6Refit in the reverse order of removal.
Tighten the cover retaining bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
7 On completion, reconnect the battery earth
lead.
8 Timing belt - removal, refitting
and adjustment
3
Removal
1 Referring to the previous Sections for
details, remove the rocker cover, the
crankshaft pulley and the timing belt covers.
2 Check that the crankshaft is set with the
No 1 piston at TDC (on its compression
stroke) before proceeding. If necessary, refer
to Section 3 for further details.
3 To check the timing belt for correct
adjustment, proceed as described in
paragraph 12 below. To remove the belt,
proceed as follows.
4 Loosen off the two bolts securing the timing
belt tensioner. Using a large screwdriver, prise
the tensioner to one side to release the timing
belt tension. Secure the tensioner in this
position by retightening the bolts (see
illustration) .
5 If the original timing belt is to be refitted,
mark it for direction of travel and also the
exact tooth engagement positions on all sprockets. Slip the belt from the camshaft,
water pump and crankshaft sprockets
(see
illustration) . Whilst the timing belt is
removed, avoid any excessive movement of
the sprockets, otherwise the piston crowns
and valves may come into contact and be
damaged.
6 If the belt is being removed for reasons
other than routine renewal, check it carefully
for any signs of uneven wear, splitting, cracks
(especially at the roots of the belt teeth) or
contamination with oil or coolant. Renew the
belt if there is the slightest doubt about its
condition. As a safety measure, the belt must
be renewed as a matter of course at the
intervals given in Chapter 1; if its history is
unknown, the belt should be renewed
irrespective of its apparent condition
whenever the engine is overhauled.
Refitting and adjustment
7 Before refitting the belt, check that the
crankshaft is still at the TDC position, with the
small projection on the belt sprocket front
flange aligned with the TDC mark on the oil
pump housing (see illustration) . Also ensure
that the camshaft sprocket is set with its TDC
pointer aligned with the corresponding timing
mark on the cylinder head (see illus-
tration 3.6b) . If necessary, adjust the
sprockets slightly. As previously mentioned,
avoid any excessive movement of the
sprockets whilst the belt is removed.
8 Engage the timing belt teeth with the teeth
CVH and PTE engine in-car repair procedures 2B•5
7.5 Lower timing belt cover removal7.3 Upper timing belt cover removal6.7 Crankshaft pulley removal
8.7 Sprocket and oil pump housing
TDC marks in alignment8.5 Timing belt removal8.4 Timing belt tensioner retaining bolts (arrowed)
2B
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su