1988 PONTIAC FIERO oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 480 of 1825
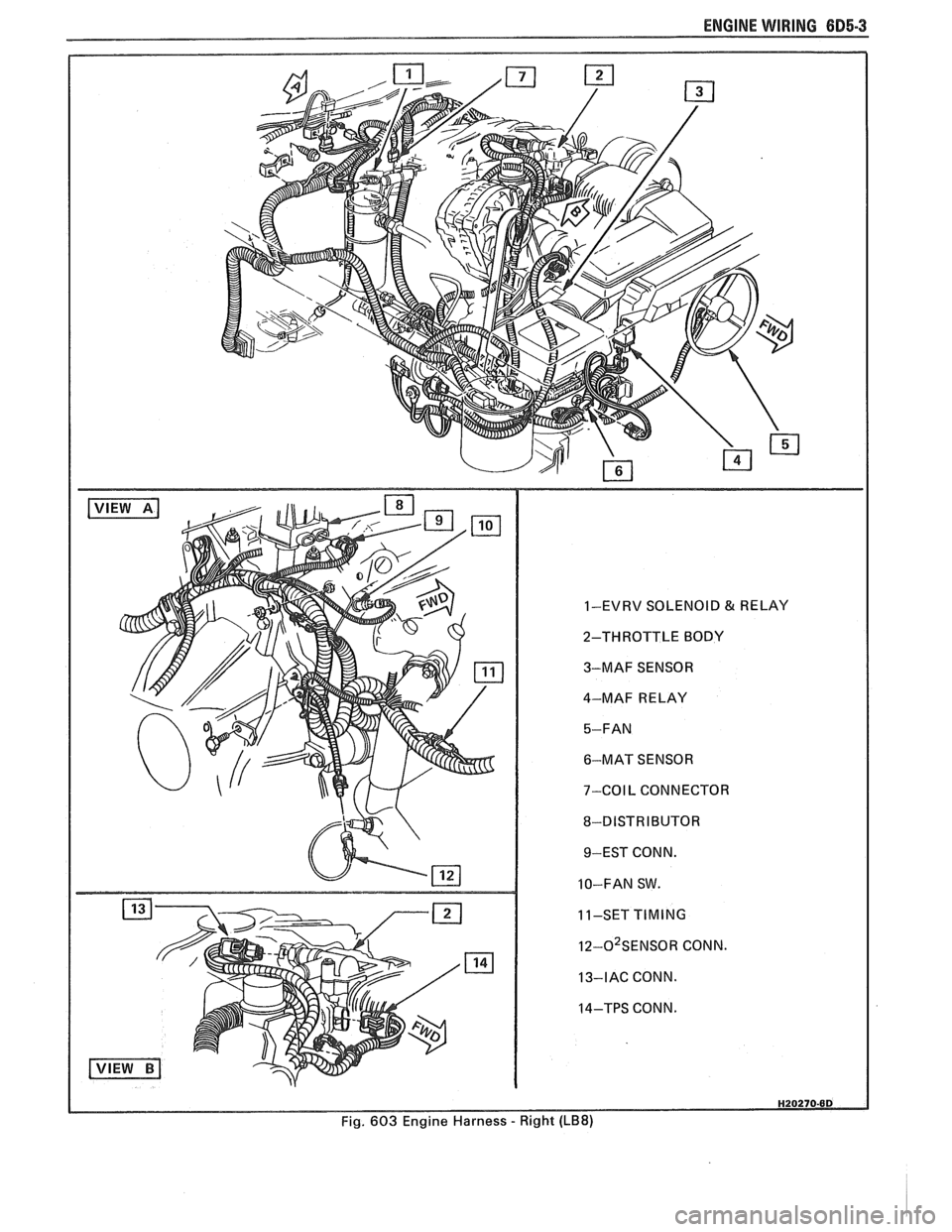
ENGINE WIRING 605.3
1-EVRV SOLENOID & RELAY
2-THROTTLE BODY
3-MAF SENSOR
4-MAF RELAY
6-MAT SENSOR
7-COIL CONNECTOR
8-DISTRIBUTOR 9-EST CONN.
10-FAN SW.
11-SET
TIMING
I~-O~SENSOR CONN.
13-IAC CONN.
14-TPS CONN.
Fig. 603 Engine Harness
- Right (LB8)
Page 482 of 1825

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 6B.l
SECTION 6D
NE ELECTR
General Description ................................... 6D- 1 Cranking System ..................................... 6D- 1
Battery .................... ... .............................. 6D- 1 ....................................................... Diagnosis ,6D-2
.................................. Charging System - CS 6D- 1 Battery ................... .. ..................................... 6D1
......................................... Ignition System ............................................ 6D- 1 Cranking System 6D2
Charging System .......................... .. ............... 6D3 .................................. Distributor Ignition 6D- 1 Ignition Svstem .......................................... 6D4 - Engine Wiring ................................................ 6D5
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The engine electrical system includes the battery,
ignition (primary and secondary), starter (and related
wiring) and the generator (and related wiring). The
accompanying diagnosis charts will aid in
trouble-shooting system faults. When a fault is traced
to a particular component, refer to that components'
section of the service manual.
BATTERY
The sealed battery is standard on all cars.
The battery has three major functions in the
electrical system: First, it provides a source of energy
for
cranking the engine; Second, it acts as a voltage
stabilizer for the electrical system; And third, it can, for
a limited time, provide energy when the electrical load
used exceeds the output of the generator.
CHARGING SYSTEM-CS
The CS Charging System has several sizes
available, including the CS-130 and CS-144. The
number (130 or 144) denotes the
OD in mm of the
stator laminations.
CS generators use a new type regulator and a
diode trio is not used. A delta stator, rectifier bridge,
and rotor with slip rings and brushes are electrically
similar to earlier generators. A conventional pulley and
fan is used and, on the CS-130, an internal fan cools the
slip ring end frame, rectifier bridge and regulator.
IGNITION SYSTEM
Distributor Ignition
The ignition circuit consists of the battery,
distributor, ignition switch, spark plugs and primary
and secondary wiring. Refer to the Battery Section
(6D 1) for battery information.
Distri but~r
The High Energy Ignition (HEI) distributor with
Electronic Spark Timing (EST), used on most engines,
combines all ignition components in one unit. The
ignition coil is in the distributor cap and connects
through a resistance brush to the rotor. Another type of
HEVEST ignition system,
used on some engines,
has a separately mounted coil.
Ignition Timing
Timing specifications for each engine are listed in
Section 6E. When using a timing light, connect an
adapter between the No. 1 spark plug and the No. 1
spark plug wire, or use an inductive type
Secondary Wiring
The spark plug wiring used with ignition systems
is a carbon impregnated cord conductor, encased in an
8MM (5/16") diameter silicone rubber jacket. The
silicone jacket withstands very high temperatures and
also provides an excellent insulator for the higher
voltage of the system.
Spark Plugs
Resistor type, tapered seat spark plugs are used
on all engines, except those with aluminum heads.
lgnition Switch
The mechanical switch is located in the steering
column on the right hand side just below the steering
wheel.
CRANKING SYSTEM
The cranking circuit consists of the battery,
starting motor, ignition switch, and related electrical
wiring.
Starter Motor
Wound field starter motors have pole pieces,
arranged around the armature, that are energized by
wound field coils.
Solenoid
Enclosed shift lever cranking motors have the
shift lever mechanism and the solenoid plunger
enclosed in the drive housing, protecting them from
exposure to dirt, icing conditions and splash.
Page 488 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN E) 6E2-3
........ FUEL METER COVER ASSEMBLY C2-7
FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLIES .......... C2-8
FUEL METER BODY ASSEMBLY ......... C2-9
..... THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS) C2-10
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE ........ 62-1 1
THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
.......... C2-11
MINIMUM IDLE SPEED CHECK .......... C2-12
... THROTTLE BODY INJECTION (TBI) UNIT C2-13
FUEL
HOSEIPIPE ASSEMBLIES .......... C2-13
Materials ...................... C2-13
Fuel Line Repair .................. C2-13
FUEL PUMP RELAY .................. C2-13
............... OILPRESSURESWITCH C2-13
PARTS INFORMATION ................. C2-14
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve Check
Chart C-2C
..................... C2-16
SECTION C3
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C3-1
........................ PURPOSE C3-1
VAPOR CANISTER
................... C3-1
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM
....... C3-1
IN-TANK PRESSURE CONTROL VALVE
. . C3-2
.... RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION C3-2
........................ DIAGNOSIS C3-2
VISUAL CHECK OF CANISTER
.......... C3-2
CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID
.......... C3-2
ON-CAR SERVICE ................. C3-2
FUEL VAPOR CANISTER
R/R ............ C3-2
CANISTER HOSES
.................... C3-2
PARTS INFORMATION ................ C3-2
Canister Purge Valve Check
Chart C-3
...................... C3-4
SECTION
C4
IGNITION SYSTEM I EST
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C4-1
PURPOSE ........................ C4-1
OPERATION ...................... C4-1
.. DIAGNOSIS ................... ... C4-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT EST OPER ...... C4-1
HOW CODE 42 IS DETERMINED ....... C4-2
CODE12 ........................ C4-2
CHECKING EST PERFORMANCE ........ C4-2
ON-CAR SERVICE .................... C4-2
SETTINGTIMING .................. C4-2
PARTS INFORMATION ................ C4-2
Ignition System Check
Chart C-4
................... .. . C4-4
SECTION C5
ELECTRONIC SPARK CONTROL (ESC) SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
................ C5-1
PURPOSE ..*...................... C5-1
OPERATION
....................... C5-1
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C5-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT ESC OPERATION
. C5-1
ON-CAR SERVICE
..................... C5-1 ESC
KNOCK SENSOR
................ C5-1
ESCMODULE
...................... C5-1
PARTS INFORMATION ................. C5-2
Electronic Spark Control (ESC) System Check
Chart C-5
...................... C5-4
SECTION C6
AIR INJECTION REACTION (A.I.R.) SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C6-1
PURPOSE
.*....................... C6-1
OPERATION
...................... C6-1
AIR CONTROL PEDES VALVE .......... C6-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
.... C6-2
DIAGNOSIS
........................ C6-2
OPERATIONAL CHECKS
.....*........ C6-2
AirPump ...................... C6-2
Hoses and Pipes
................. C6-3
Check Valve
.................... C6-3
ON-CAR SERVICE
.................... C6-3
DRIVEBELT ...................... C6-3
AIR INJECTION PUMP
............... C6-3
AIR INJECTION CONTROL
(PEDES) VALVE
.................. C6-3
AIR INJECTION CHECK VALVE ......... C6-4
PARTS INFORMATION
................ C6-4
AIR Management Check
. Pedes Valve
Chart C-6
..................... C6-6
SECTION C7
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C7-1
PURPOSE
........................ C7-1
OPERATION
...................... C7-1
EGRCONTROL
..................... C7-1
NEGATIVE BACKPRESSURE VALVE
...... C7-1
EGR VALVE IDENTIFICATION
.......... C7-2
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
.... C7-2
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C7-2
ON-CAR SERVICE
..................... C7-2
EGRVALVE
....................... C7-2
EGR Manifold Passage
............. C7-2
EGR CONTROL SOLENOID
............. C7-3
PARTS INFORMATION
................. C7-3
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Check
Chart C-7
...................... C7-4
SECTION
C8
TRANSMISSION CONVERTER CLUTCH
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C8-1
PURPOSE
........................ C8-1
OPERATION
...................... C8-1
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
............... C8-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT TCC
OPERATION
..................... C8-2
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C8-2
ON-CAR SERVICE .................... C8-2
PARTS INFORMATION ................. C8-2
Page 493 of 1825
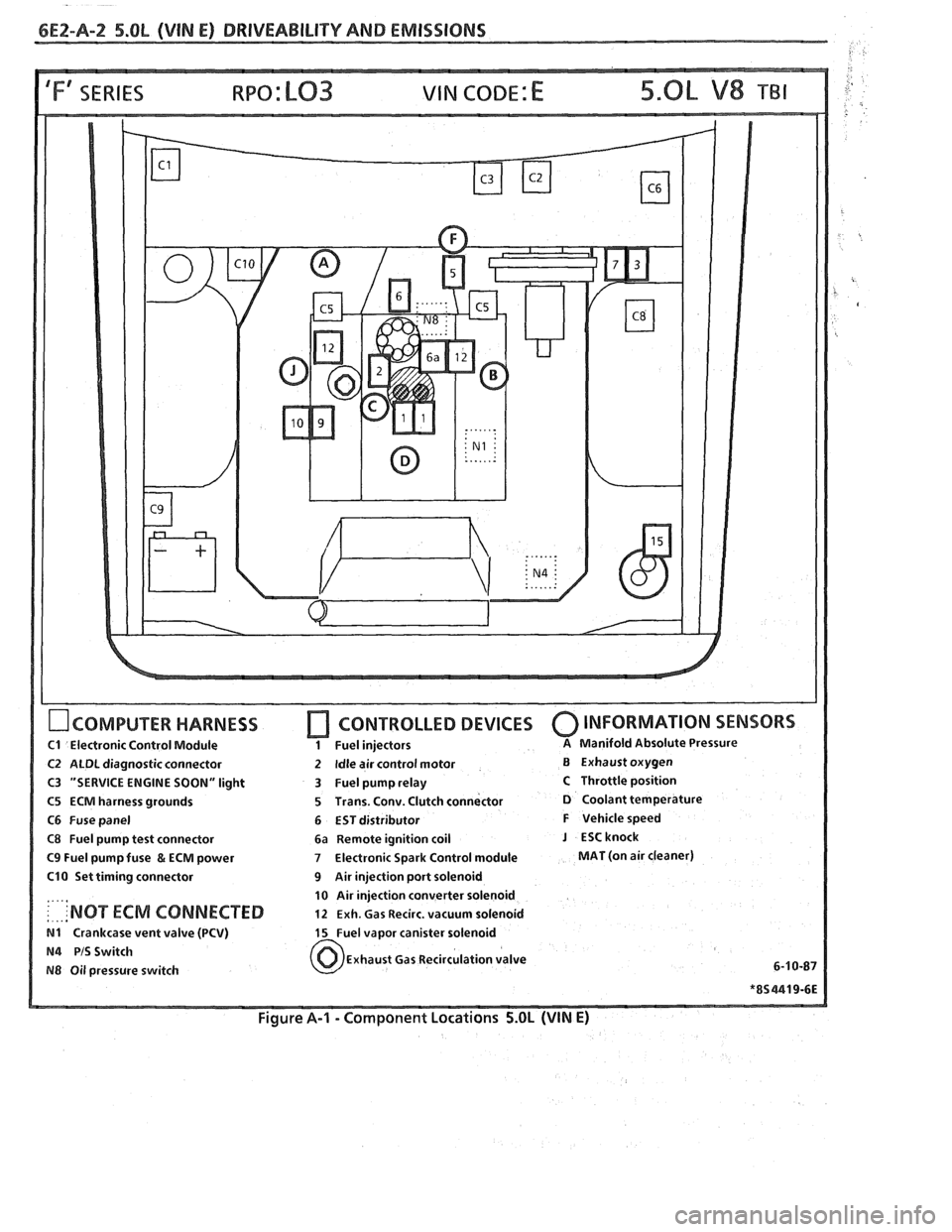
6E2-A-2 5.OL (VIN E) DRIVEABILIW AND EMISSIONS
IFf SERIES VIN CODE: E
OCOMPUTER HARNESS
C1 Electronic Control Module
C2 ALDL diagnostic connector
C3 "SERVICE ENGINE SOON" light
C5 ECM harness grounds
C6 Fuse panel
C8 Fuel pump test connector
C9 Fuel pump fuse & ECM power
C10 Set timing connector
....,
: . ... 'NOT ECM CONNECTED
N1 Crankcase vent valve (PCV)
N4 PIS Switch
N8 Oil pressure switch
[7 CONTROLLED DEVICES 0 INFORMATION SENSORS
1 Fuel injectors A Manifold Absolute Pressure
2 Idle air control motor B Exhaust oxygen
3 Fuel pump relay
C Throttle position
5 Trans. Conv. Clutch connector
D Coolant temperature
6 EST distributor
F Vehicle speed
6a Remote ignition coil
J ESCknock
7 Electronic Spark Control module MAT (on air cleaner)
9 Air injection port solenoid
10 Air injection converter solenoid
12 Exh. Gas Recirc. vacuum solenoid
15 Fuel vapor canister solenoid
Exhaust Gas Recirculation valve
6-1
0-87
Figure A-I - Component Locations 5.OL (VIN E)
Page 501 of 1825

6EZ-A-10 5.0L (VIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
TO OIL PRESS. SW.
&FUEL PUMP RELAY
BATTERY
12 V
. . . . . . . . FUSIBLE LINK 15 WAY
439 PNWBLK
419
BRNNVHT
SERIAL DATA
451
WHTIBLK
450 BLWHT
ALDL CONNECTOR
NO "SERVICE ENGINE SOON" "LIGHT
5.OL (VIN E) "F'" SERIES (TBI)
Circuit Description:
There should always be a steady "Service Engine Soon" light, when the ignition is "ON" and engine stopped.
Battery is supplied directly to the light bulb.
The electronic control module (ECM) will control the light and
turn it "ON" by providing a ground path through CKT 419 to the ECM.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Battery feed CKT 340 is protected by a
20amp in-
line fuse. If this fuse was blown, refer to wiring
diagram on the facing page of Code 54.
2. Using a test light connected to 12 volts, probe each
of the system ground circuits to be sure
a good
ground is present. See ECM terminal end view in
front of this section for ECM pin locations of
ground circuits.
Diagnostic Aids:
Engine runs ok, check:
@ Faulty light bulb
@ CKT419open
@ Gage fuse blown. This will result in no oil, or
generator lights, seat belt reminder, etc.
Engine cranks, but will not run.
@ Continuous battery - fuse or fusible link open.
@ ECM ignition fuse open.
@ Battery CKT 340 to ECM open.
o Ignition CKT 439 to ECM open.
@ Poor connection to ECM.
Page 503 of 1825

6E2-A-12 5.OL (VIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
TO OIL PRESS. SW. ECM
&FUEL PUMP RELAY
FUSE
& HOLDER BATTERY 12 V . . . . . . . .
FUSIBLE LINK
439
PNWBLK
419 BRNNVHT
- -
451 WHTIBLK
450
BLWHT
ALDL CONNECTOR
8-4-87
55 1235-6E
CHART A-2
NO ALDL DAM OR WON"T FLASH CODE 12
'SERVICE ENGINE SOON" LLlGHT "ON" "STEADY
5.OL (VIN E) "F" "SERIES (TBI)
Circuit Description:
There should always be a steady "Service Engine Soon" light, when the ignition is "ON" and engine stopped.
Battery is supplied directly to the light bulb. The electronic control module
(ECM) will turn the light "ON" by
grounding CKT 419 at the ECM.
With the diagnostic terminal grounded, the light should flash
a Code 12, followed by any trouble code(s)
stored in memory.
A steady light suggests a short to ground in the light control CKT 419, or an open in diagnostic CKT 451.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. If there is a problem with the ECM that causes
a
"Scan" tool to not read serial data, then the ECM
should not flash a Code
12. If Code 12 does flash,
be sure that the "Scan" tool is working properly on
another vehicle. If the "Scan" is functioning
properly and CKT 461 is OK, the PROM or ECM
may
be at fault for the NO ALDL symptom.
2. If the light goes "OFF" when the ECM connector is
disconnected, then CKT 419 is not shorted to
ground.
3. This step will check for an open diagnostic CKT
45 1.
4. At this point, the "Service Engine Soon" light
wiring is OK. The problem is a faulty ECM or
PROM. If Code 12 does not flash, the ECM should
be replaced using the original PROM. Replace the
PROM only after trying an ECM, as a defective
PROM is an unlikely cause of the problem.
Page 519 of 1825
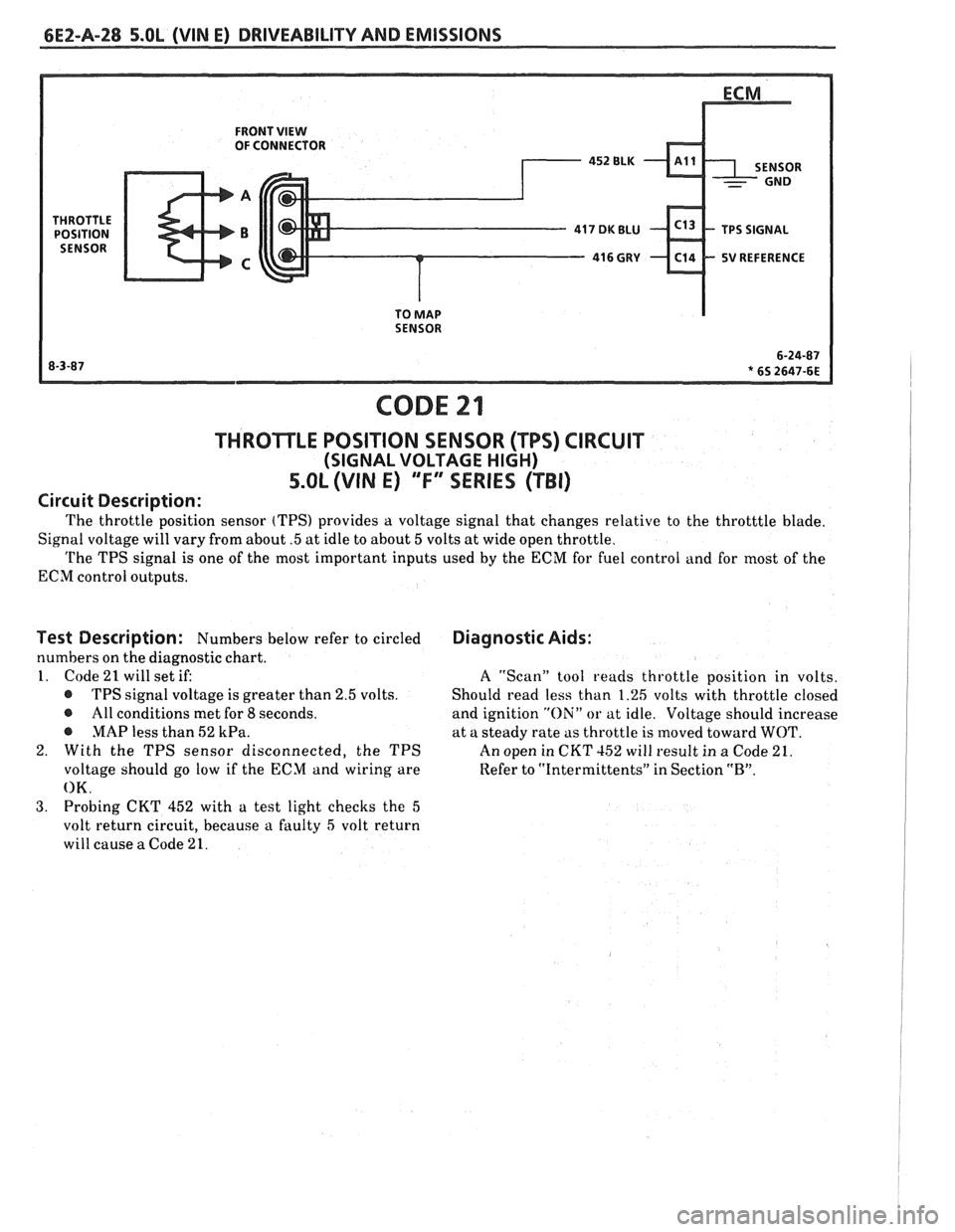
6EZ-A-28 5.OL (VIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FRONT VIEW OF CONNECTOR
5V REFERENCE
TO
MAP SENSOR
CODE 21
THROTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS) CIRCUIT
(SIGNAL VOLTAGE HIGH)
5.OL (VIN E) "F" "SERIES ("FBI)
Circuit Description:
The throttle position sensor (TPS) provides a voltage signal that changes relative to the throtttle blade.
Signal voltage will vary from about
.5 at idle to about 5 volts at wide open throttle.
The TPS signal is one of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel control and for most of the
ECM control outputs.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Code
21 will set if:
@ TPS signal voltage is greater than 2.5 volts.
@ All conditions met for 8 seconds.
@ MAP less than 52 kPa.
2. With the TPS sensor disconnected, the TPS
voltage should go low if the ECM and wiring are
OK.
3. Probing CKT 452 with a test light checks the 5
volt return circuit, because a faulty 5 volt return
will cause
a Code 21.
Diagnostic Aids:
A ''Scan" tool reads throttle position in volts.
Should read less than 1.26 volts with throttle closed
and ignition
"Oili" or at idle. Voltage should increase
at a steady rate as throttle is moved toward
WOT.
An open in CKT 152 will result in a Code 21.
Refer to
"Intermittents" in Section "B".
Page 541 of 1825
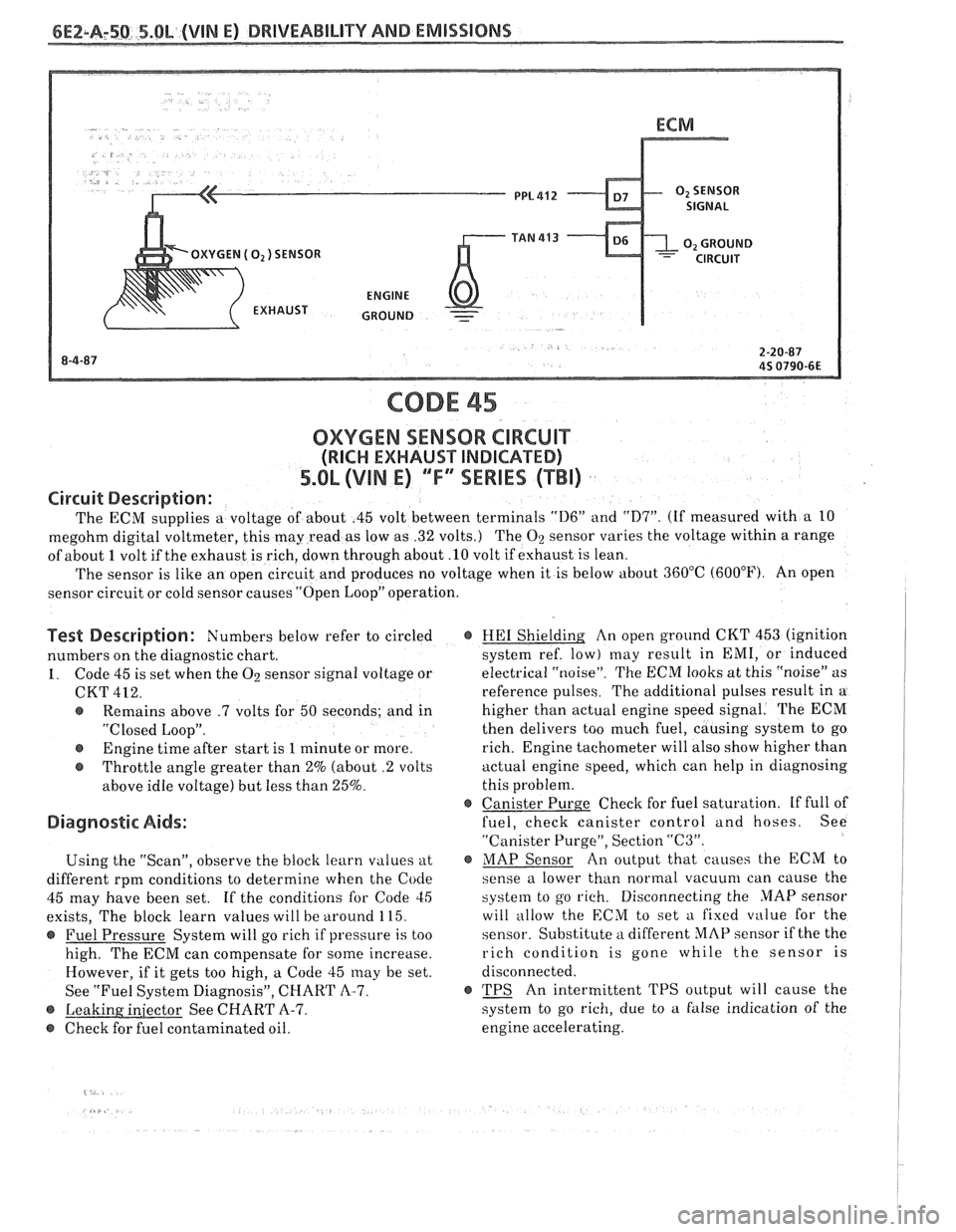
6EZ-A-50 5.0b (VIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
- GROUND -
CODE 45
OXYGEN SENSOR CIRCUIT
(RICH EXHAUST INDICAnEB)
5.OL (VlN E) ""FYESEBIES (TBI)
Circuit Description:
The ECM supplies a voltage of about .45 volt between terminals "D6" and "D7". (If measured with a 10
megohm digital voltmeter, this may read as low as .32 volts.) The
O2 sensor varies the voltage within a range
of about
1 volt if the exhaust is rich, down through about .10 volt if exhaust is lean.
The sensor is like an open circuit and produces no voltage when it is below about 360°C (600°F). An open
sensor circuit or cold sensor causes "Open Loop" operation.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Code 45 is set when the O2 sensor signal voltage or
CKT
422.
@ Remains above .7 volts for 50 seconds; and in
"Closed Loop".
@ Engine time after start is 1 minute or more.
@ Throttle angle greater than 2% (about .2 volts
above idle voltage) but less than 25%.
Diagnostic Aids:
Using the "Scan", observe the block learn values at
different rpm conditions to determine when the
Code
45 may have been set. If the conditions for Code 45
exists, The block learn values will be around 115.
@ Fuel Pressure System will go rich if pressure is too
high. The ECM can compensate for some increase.
However, if it gets too high, a Code 45
may be set.
See "Fuel System Diagnosis", CHART
A-7.
Q See CHART A-7.
@ Check for fuel contaminated oil.
@ HE1 Shielding An open ground CKT 453 (ignition
system ref. low) may result in EMI, or induced
electrical "noise". The ECM looks
at this "noise" as
reference pulses. The additional pulses result in a
higher than actual engine speed signal. The ECM
then delivers too much fuel, causing system to go
rich. Engine tachometer will also show higher than
actual engine speed, which can help in diagnosing
this problem.
@ Canister Purge Check for fuel saturation. If full of
fuel, check canister control and hoses. See
"Canister Purge", Section
"(23".
@ MAP Sensor An output that causes the ECM to
sense a lower than normal
vacuum can cause the
system to go rich. Disconnecting the MAP sensor
will allow the ECM to set
a fixed value for the
sensor. Substitute a different MAP sensor if the the
rich condition is gone while the sensor is
disconnected.
r TPS An intermittent TPS output will cause the
system to go rich, due to
a false indication of the
engine accelerating.