1988 FIAT TEMPRA wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 14 of 171

October 1991 2.0 i.e. 16v introduced, with 1995cc, 16 valve
high-performance DOHC engine, catalytic converter, sports
suspension, front and rear disc brakes. ABS available as
option.
January 1992 Existing Tipo models lightly facelifted and
redesignated 1.4 Formula, 1.45, 1.6S, 1.6SX, 1.9TD SX,
1.8 i.e. SX. 1.7D discontinued. SX versions with digital
instruments.
Tempra 1.9 TDS (turbo diesel) Station Wagon introduced. 1.4
and 1.9D saloons discontinued.
May 1992 Tempra 1.8 i.e. SX Saloon and Station Wagon
discontinued.
June 1992 Tempra 2.0 i.e. SX saloon and station wagon
models introduced, with high performance 1995cc DOHC fuel
injected engine, catalytic converter and disc brakes front and
rear.
Tipo 1.4 and all Tipo and Tempra 1.6 models (except Selecta)
now with a catalytic converter and fuel injection in place of
Weber twin-choke carburettor. Designated i.e. in badging.
December 1992 Tipo 1.8 i.e. and 1.6 Selecta discontinued.
February 1993 Tipo 2.0 i.e. GT introduced. Slightly lower
performance and spec, version of the 16v model.
July 1993 Tipo 1.4 now available as a 3-door or 5-door
hatchback. 2.0 i.e. 16v now only available as 3-door. Tipo 2.0
i.e. GT replaced by similar spec. 2.0 i.e. SLX.
Tempra 2.0 i.e. SX saloons and estates now only available
with auto, gearbox. Otherwise, SX models become known as
SLX, with colour-coded mirrors and ABS brakes. Most Tempras
now with body-coloured bumpers. 1.9D (non turbo Diesel re-
introduced).
All Tipo and Tempra models now with revised front-end
styling
-
narrower headlights and revised grille. Improved crash
protection, including side impact beams, safety steering wheel
and uprated brakes. Power steering, central locking, electric
windows all standard.
February 1994 Tipo 1.7 non-turbo diesel re-introduced as
1.7 DS.
May 1994 Tempra 1.9DS Station Wagon introduced.
September 1994 Most models available with driver's airbag,
fire prevention system and seat belt pre-tensioners.
December 1994 Tempra 1.6 i.e. versions get M.P.I, engine.
February/March 1995 All models with VIN number window
etching and immobiliser standard on all Tempra petrol models.
October 1995 Immobiliser fitted to Tempra D and TD models.
End of 1995 Tipo discontinued.
Mid-1996 Tempra discontinued.
PART B: VITAL STATISTICS
All Tipo models
-
55 litres, except petrol with catalytic converter
- 51
litres.
All Tempra models
-
65 litres, except petrol with catalytic converter
-
62 litres.
Wheels and Tyres
ENGINE PRESSED STEEL RADIAL TYRE PRESSURES (cold)
WHEEL RIM TYPE TUBELESS FRONT REAR
TYRE TYPE average load heavy load average load heavy load
TIPO MODELS
1.4 and 1.6 Petrol 5.00B x 13H 165/70R13S 2.0 bar/29 psi 2.0 bar/29 psi 1.9 bar/28 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi
1697 Diesel 5.00B x 13H 165/70R 13S 2.1 bar/30 psi 2.1 bar/30 psi 1.9 bar/28 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi
Turbo D 5.5J x 14H
175/65 R
14T 2.2 bar/32 psi 2.4 bar/35 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi 2.4 bar/35 psi
1.4 i.e./1.6 i.e. (1993-on) 5.5J x 14H
165/65 R
14T 2.0 bar/29 psi 2.0 bar/29 psi 1.9 bar/28 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi
1.7D (1993-on) 5.5J x 14H 165/65R 14T 2.1 bar/30 psi 2.1 bar/30 psi 1.9 bar/28 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi
Option
-
certain models 5.5J x 14AH2 185/60R 14H 2.2 bar/32 psi 2.4 bar/35 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi 2.4 bar/35 psi
TEMPRA MODELS
Early 1.4 and 1.6
Saloons 5.00B x 13H 165/70R 13S/T 2.0 bar/29 psi 2.0 bar/29 psi 2.0 bar/29 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi
1.6 SX Saloon 5.5J x 14H 165/65R 14T 2.0 bar/29 psi 2.0 bar/29 psi 2.0 bar/29 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi
1.9D/1.9 TD Saloon
and Late 1.6 i.e. 5.5J x 14H 175/65R 14T/H 2.2 bar/32 psi 2.4 bar/35 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi 2.4 bar/35 psi
1.6/1.9D/1.9TD
Station Wagons 5.5J x 14H 175/65R 14H 2.2 bar/32 psi 2.4 bar/35 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi 3.0 bar/44 psi
Option for Station 5.5J x 14H or AH2 185/60 R 14H 2.2 bar/32 psi 2.4 bar/35 psi 2.2 bar/32 psi 3.0 bar/44 psi
Wagons (alloy)
SPARE WHEEL
-
ALL TIPO AND TEMPRA MODELS (speed limit 50 mph)
Tempra TD Saloon and
ALL Station Wagons 4.00B x 14H 105/70 B14 4.2
bar/61
psi
All other models 4.00Bx14H 135/80 B14 2.8
bar/41
psi
Page 15 of 171
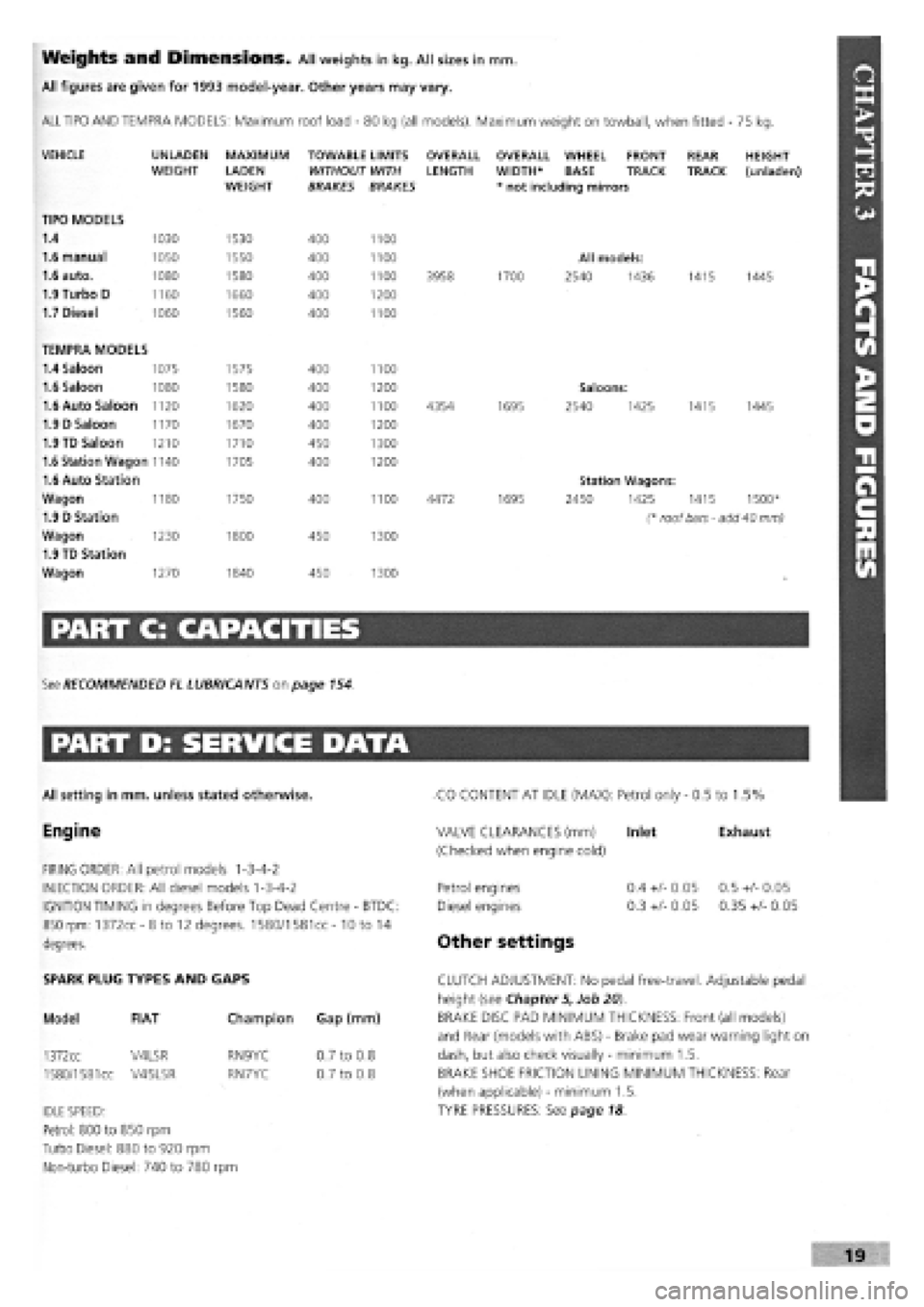
Weights and Dimensions. All weights in kg. All sizes in mm.
All figures are given for 1993 model-year. Other years may vary.
ALL TIPO AND TEMPRA MODELS: Maximum roof load
-
80 kg (all models). Maximum weight on towball, when fitted - 75 kg.
VEHICLE
TIPO MODELS
1.4
1.6 manual
1.6 auto.
1.9 Turbo D
1.7 Diesel
UNLADEN WEIGHT
1030
1050
1080
1160
1060
MAXIMUM
LADEN WEIGHT
1530
1550
1580
1660
1560
TOWABLE LIMITS WITHOUT WITH BRAKES BRAKES
400
400
400
400
400
1100
1100
1100
1200
1100
OVERALL LENGTH
3958
OVERALL WHEEL FRONT WIDTH* BASE TRACK * not including mirrors
1700
All models:
2540 1436
REAR TRACK
1415
HEIGHT (unladen)
1445
TEMPRA MODELS
1.4 Saloon 1075 1575 400 1100
1.6 Saloon 1080 1580 400 1200 Saloons:
1.6 Auto Saloon 1120 1620 400 1100 4354 1695 2540 1425 1415 1445
1.9 D Saloon 1170 1670 400 1200
1.9 TD Saloon 1210 1710 450 1300
1.6 Station Wagon 1140 1705 400 1200
1.6 Auto Station Station Wagons:
Wagon 1180 1750 400 1100 4472 1695 2450 1425 1415 1500*
1.9 D Station (* roof bars - add 40 mm)
Wagon 1230 1800 450 1300
1.9 TD Station
Wagon 1270 1840 450 1300
PART C: CAPACITIES
See RECOMMENDED EL LUBRICANTS on page 154.
PART D: SERVICE DATA
All setting in mm. unless stated otherwise.
Engine
FIRING ORDER: All petrol models 1-3-4-2
INJECTION ORDER: All diesel models 1-3-4-2
IGNITION TIMING in degrees Before Top Dead Centre
-
BTDC:
850 rpm: 1372cc-8to 12 degrees. 1580/1581cc- 10 to 14
degrees.
CO CONTENT AT IDLE (MAX): Petrol only
-
0.5 to 1.5%
Exhaust VALVE CLEARANCES (mm) Inlet
(Checked when engine cold)
Petrol engines
Diesel engines
Other settings
0.4
+/-
0.05
0.3
+/-
0.05
0.5
+/-
0.05
0.35
+/-
0.05
SPARK PLUG TYPES AND GAPS
Model FIAT
1372cc V4LSR
1580/1581
cc V45LSR
Champion Gap (mm)
RN9YC
RN7YC
IDLE SPEED:
Petrol: 800 to 850 rpm
Turbo Diesel: 880 to 920 rpm
Non-turbo Diesel: 740 to 780 rpm
0.7 to 0.8
0.7 to 0.8
CLUTCH ADJUSTMENT: No pedal free-travel. Adjustable pedal
height (see Chapter 5, Job 20).
BRAKE DISC PAD MINIMUM THICKNESS: Front (all models)
and Rear (models with ABS)
-
Brake pad wear warning light on
dash, but also check visually
-
minimum 1.5.
BRAKE SHOE FRICTION LINING MINIMUM THICKNESS: Rear
(when applicable)
-
minimum 1.5.
TYRE PRESSURES: See page 18
Page 19 of 171

PART F: TORQUE WRENCH SETTINGS
Key for engine types and sizes: A
-
1372cc; B
-
1581cc;
C
-
1697cc Diesel; D
-
1929cc Diesel; E
-
1929cc Turbo Diesel.
Engine
Screw retaining caps to crankcase (M10 x 1.25)
Screw retaining intermediate and central caps to crankcase (M12 x 1.25)...
Self-locking screw retaining front and rear caps to crankcase (M12 x 1.25)
Bolt, cylinder head to engine block (M10 x 1.25)
IMPORTANT NOTE: All torque settings shown in
Newton-meters (Nm). Bolt, nut or screw sizes in
brackets in left-hand column.
Bolt, cylinder head to engine block (M12 x 1.25)
Bolts, top to bottom cylinder head (M8)
Nut for connecting rod cap retaining bolt (M9 x 1)
Screw, connecting rod cap (M10 x 1)
Screw retaining engine vent to crankcase
(M8)
(M8)
Screw retaining front cover to crankcase
(MlOx 1.25)
(M8)
Bolt retaining rear cover (flywheel side) to crankcase (M6)
Nut retaining inlet and exhaust ducts to cylinder head
(M8)
(M8)
Screw, flywheel to crankshaft
(M10x 1.25)
(M12
x
1.25)
Lower belt cover retaining screw (M8)
Screw, damping flywheel to drive gear (M8)
Nut retaining auxiliary drive pulley to crankshaft (M20 x 1.25)
Screw retaining drive shaft to crankshaft (*) (M14 x 1.5 left)
Screw, timing gears
(M10x 1.25)
(M12x 1.25)
Belt tensioner retaining bolt
(M8)
(M10x 1.25)
Fixed belt tensioner retaining screw (M10 x 1.25)
Screw retaining auxiliary component driven gear (oil pump) (M10 x 1.25)
Nut for camshaft cap retaining stud (M8)
Nut retaining camshaft and air vacuum pump end mounts (M8)
Combustion prechamber retaining ring (M32 x 1.5)
Nut, injection pump stud (M8)
Screw, injection pump (M8)
Nut fastening flexible block to coolant pump case (M12 x 1.25)
Nut, injection pump gear (M12 x 1.75)
Screw retaining reaction bracket to oil filter support and injection pump (M8).
Top retaining screw or nut, oil filter support and injection pump (M12 x 1.25)
Lower retaining screw, oil filter support and injection pump (M10 x 1.25)
Complete injector (M24 x 2)
Glow plugs (M12 x 1.25)
Nuts retaining fuel delivery line to injection pump and injector (M12 x 1.25)...
Bolt, coolant pump to engine block (M8 x 1)
Bolt retaining cover and bracket to coolant pump case (M8)
Oil pressure switch (M14 x 1.5)
Coolant temperature sender unit
(M16 x 1.5 tapered)
(M18x 1.5 tapered)
Coolant temperature thermal switch (M16 x 1.5 tapered)
(*) The bolt need not be greased.
A B C D E Torque (Nm)
• • 80
• • • 113
• • • 113
• • 40
+
90 degrees
+ 90 deqrees
• • • 100
+
90 degrees
+ 90 deqrees
• • 28
• • 51
• • • 25 + 50 deqrees
• •
• • •
25
20
• • 50
25
• 10
• •
• • •
28
25
• •
• • •
83
142
• • 25
• • • 28
• • 155
• • • 190
• •
• • •
83
118
• •
• • •
25
44
• • • 44
• • 83
• • • 19
• • • 19
• • • 118
• • • 25
• • • 25
• • 80
• • • 49
• • • 29
• • • 98
• • • 71
• • • 55
• • • 15
• • • 29
• • • 25
• • • 23
32
• •
• • • 34
30
• • 30
expert22 fl/i* http://rutracker.org 23
Page 22 of 171

Handbrake Control
Screw with broad flange retaining handbrake and gear lever to body (M8)
Bolt retaining handbrake and gearlever to body (M8)
Screw with normal flange retaining handbrake lever bracket to plate (M8)
Screw with normal flange retaining handbrake cable slide plate to
floorpan (M6)
Screw with long flange for fastening handbrake cable reaction bracket to
floor (M8)
Screw with broad flange retaining pedal unit to dashboard (M8)
Self-locking nut for bolt retaining brake servo to pedal unit (M8)
Nut for through screw joining brake and clutch pedals to pedal unit (M8).
Self-locking nut retaining accelerator pedal to pedal unit (M6)
Nut retaining brake pump to brake servo (M8)
Steering
Self-locking nut retaining steering link ball pin to cast iron pillar (M10 x 1.25)..
Bolt retaining steering and/or power steering box to front beam (M10 x 1.25).
Nut for side steering link (M12 x 1.25)
Self-locking nut retaining steering shaft universal joint forks (M8)
Self-locking nut retaining steering wheel to column (M16 x 1.5)
Bolt retaining steering column mount to body (M6)
Self-locking nut for steering wheel position adjustment device (tighten nut
to specified torque with lever in locked position) (M12 x 1.25)
Nut for screw retaining steering column to support (M8)
Self-locking nut with polyamide ring retaining damper to steering box (M8)
Union for oil delivery fitting from pump to power steering, on power
steering (M14 x 1.5)
Union for adjustable oil delivery fitting from pump to p.s., on power
steering (M16 x 1.5)
Union for oil delivery fitting from power steering to reservoir (M12 x 1.5)
Union oil return fitting from reservoir to pump (M18 x 1.5)
Front Suspension
Screw with broad flange retaining front of front beam to body
(M12 x 1.25)
Screw with normal flange for nut retaining rear of front beam to body
(M10
x
1.25)
Screw with flat and tapered washer for nut retaining front and rear ext.
of wishbone connection plates to beam (M10 x 1.25)
Screws with flat and tapered washer for nut retaining front and rear inner
swinging arm connection plates to beam (M10 x 1.25)
Flanged nut fastening top of damper to block (M12 x 1.25)
Screw with broad flange retaining top damper block to body (M8)
Self-locking nut retaining damper to pillar (M10 x 1.25)
Self-locking nut for screw retaining wishbone head and joint to pillar
(M10
x
1.25)
Screw with tapered and flat safety washer retaining stabilizer bar
support plate to beam (M8)
Self-locking nut retaining end of anti-roll bar to rod (M10 x 1.25)
Self-locking nut retaining bar to front suspension arm (M10 x 1.25)
Nut retaining front wheel hub to coupling
(M22 x 1.5)i
(M24
x
1.5)
Wheel stud (M12 x 1.25).....
Rear Suspension
Screw with broad flange retaining front flexible block to rear subframe
(M12 x 1.25)
A B C D E Torque (Nm)
• • • • • 28
• • • • • 15
• • • • • 28
8.5
35
32
15
32
4.4
20 .
A B C D E Torque (Nm)
• • • • • 34
70
34
• • • • • 20
50
7.4
24
24
15
30
35
20
34
A B c D E Torque (Nm)
108
80
69
69
100
40
70
70
40
70
31
• • • • • •
24
28
86
A B c D E Torque (Nm)
108
Page 23 of 171

Screw with broad flange retaining rear flexible block to body (M12 x 1.25)..
Nut for stud retaining rear swinging arm to subframe (M16 x 1.5)
Nut for screw retaining lower damper to suspension (M12 x 1.25)
Screw retaining top of damper to mount (M10 x 1.25)
Nut for pivot pin retaining rear hub (M22 x 1.5)
Bolt retaining stabilizer bar to rear suspension arm (M10 x 1.25)
Bolt retaining stabilizer bar support plate to rear suspension arm (M8)
Wheel stud (M12 x 1.25)
Nut with self-locking flange retaining headlight alignment corrector
receiver to rear suspension (M8)
Nut with self-locking flange retaining lower receiver rod pin (M6)
Bolt with normal notched flange retaining automatic headlight
alignment device mount (M8)
Bolt with normal notched flange retaining receiver connection bracket with
rear suspension wishbone (M6)
Nut for bolt retaining square lever to wishbone (M8)
A B c D E Torque (Nm)
• • • • • 108
• • • • • 150
• • • • • 88
• • • • • 60
• • • • • 280
• • • • • 56
• • • • • 28
• • • • • 86
• • • • • 6.4
• • • • • 3.9
• • • • • 12
• • • • • 3.9
• • • • • 15
PART G: IDENTIFICATION NUMBERS
Finding the Numbers
G1: There are four sets of identification numbers in all. First,
there is the Vehicle Identification (V.I.N.) Number, or chassis
number (a). Second, is the engine number. Position (b) is the
engine number position on all engines; the engine illustrated
is
the 1.4 and 1.6 petrol engine. Also, see G4 and G5.
Third, there is the Model and Data Plate (c). See G3.
G2: Fourth, you will
need the Paint
Identification Plate
if you need to buy
paint. You'll find it
on the inside of the
hatchback door.
The numbers
shown on the plate
give the following
information: 1 -
Paint manufacturer; 2
-
Colour name; 3
-
Colour code;
4
-
Respray and touch-up code.
Vehicle Identification Numbers
See illustration G1, part a. There are two groups of codes
which are unique to your car. You should never buy a car
without checking first that the V.I.N, shown on the car matches
that on the vehicle registration document. The vehicle code is
also shown at position c on the Model and Data Plate and the
chassis serial number is also shown at position a.
Model and Data Plate
G3: The numbers
stamped on the
plate stand for the
following:
A
-
Manufacturer;
B
-
Homologation
number; C
-
Vehicle
identity code;
D
-
Chassis serial
number;
E
-
Maximum
authorised weight of vehicle, fully laden; F
-
Maximum autho-
rised weight of vehicle, fully laden plus trailer; G
-
Maximum
authorised weight on front axle; H
-
Maximum authorised
weight on rear axle; I
-
Engine type; L
-
Body code (see below);
M - Number for buying spares; N
-
Smoke opacity index
(diesel engines only).
Engine
Numbers
G4: On all petrol engines,
the number is on the top
of the crankcase at the
gearbox end.
G5: On diesel engines, look
on the crankcase, above the
water pump housing.
1
2
3
4
G2
r
B
r
B I B I
r
B
C I D I
r
B
I E I Kn
o o I F I Kq o o 1- I <3 I Kq o o
2- | H I Kq
o
MOTORE ENGINE
I I
N VERSIONE-VERSION •f
PER RICAM8:
N*
FOR SPARED
L I
1 G3
Page 24 of 171

Please read the whole of the CHAPTER 1, SAFETY FIRST! before carrying out any work on your car.
fUADTCSA I En Hr
GETTIIMG THROUGH THE MOT
This chapter is for owners in Britain whose
vehicles need to pass the 'MoT' test.
Obviously, you won't be able to examine
your car to the same degree of
thoroughness as the MoT testing station.
But you can reduce the risk of being one of
the 4 out of 10 who fail the test first time by
following this check-list.
iMFTri
The checks shown below are correct at the
time of writing but do note that they are
becoming stricter all the time. Your local
MoT testing station will have the latest
information, should you need it.
1 p Chapter Contents -
Page No. Page No.
PART A: INSIDE THE CAR 28 PART C: VEHICLE RAISED OFF THE GROUND 30
PART B: VEHICLE ON THE GROUND 29 PART D: EXHAUST EMISSIONS 31
PART A: INSIDE THE CAR
Steering Wheel and Column
O 1. Try to move the steering wheel towards and away from you and then from side to side. There should be no appreciable movement or play. Check that the steering wheel is not loose on the column.
02 . Lightly grip the steering wheel between thumb and finger and turn from side to side. Cars with a steering rack: free play should not exceed approximately 13 mm (0.5 in.), assuming a 380 mm (15 in.) diameter steering wheel. Cars fitted with a steering box: free play should not exceed approximately 75 mm (3.0 in.), assuming a 380 mm (15 in.) diameter steering wheel.
Ob . If there is a universal joint at the bottom of the steering column inside the car, check for movement. Place your hand over the joint while turning the steering wheel to-and-fro a little way with your other hand. If ANY free play can be felt, the joint must be replaced.
04. Ensure that there are no breaks or loose components
on the steering wheel itself.
Electrical Equipment
OS . With the ignition turned on, ensure that the horn works okay.
OE . Check that the front wipers work.
07 . Check that the windscreen washers work.
o 8. Check that the internal warnings for the indicator and hazard warning lights work okay.
Checks With An Assistant
O9 . Check that the front and rear side lights and number plate lights work and that the lenses and reflectors are secure, clean and undamaged.
o 10. Check the operation of the headlights (you won't be able to check the alignment yourself) and check that the lenses are undamaged. The reflectors inside the headlights must not be tarnished, nor must there be condensation inside the headlight.
o 11. Turn on the ignition and check the direction
indicators, front and rear and on the side markers.
o 12. Check that the hazard warning lights operate on the
outside of the vehicle, front and rear.
o 13. Check that the rear fog light/s, including the warning
light inside the car, all work correctly.
o 14. Check that the rear brake lights work correctly. These checks are carried out all around the vehicle with all four wheels on the ground.
o 15. Operate the brake lights, side lights and each indicator in turn, all at the same time. None should affect the operation of the others.
SAFETY FIRST!
• Follow the Safety information in CHAPTER 1, SAFETY FIRST! but bear in mind that the vehicle needs
to be even more stable than usual when raised off the ground.
• There must be no risk of it toppling off its stands or ramps while suspension and steering components
are being pushed and pulled in order to test them.
Page 25 of 171

Windscreen and Mirrors
O 16. In zone 'A' of your windscreen, no items of damage larger than 10 mm in diameter will be allowed. In the rest of the area swept by the windscreen wipers, no damage greater than 40 mm in diameter will be allowed, nor should windscreen stickers or other obstructions encroach on this area.
o 17. Check that the exterior mirror on the driver's side is in good condition.
o 18. There must be one other mirror in good condition, either inside the car or an external mirror on the passenger's side.
Brakes
O 19. You cannot check the brakes
properly without a rolling road brake
tester but you can carry out the
following checks:
O 20. Pull on the handbrake. It should be fully ON before the handbrake reaches the end of its travel.
O 21. Knock the handbrake from side to side and check that it does not then release itself.
O 22. Check the security of the handbrake mountings and check the floor around it for rust or splits.
o 23. Check that the brake pedal is in good condition and that, when you take hold of it and move it from side to side, there is not too much play.
o 24. Push the footbrake down hard, with your foot. If it creeps slowly down to the floor, there is probably a problem with the master cylinder. Release the pedal, and after a few seconds, press down again. If the pedal feels spongy or it travels nearly to the floor, there is air in the system or another MoT-failing fault with the brakes.
o 25. Check the servo unit (when
fitted) as follows: Pump the pedal
several times then hold it down hard.
Start the engine. As the engine starts,
the pedal should move down slightly.
If it doesn't the servo or the vacuum
hose leading to it may be faulty.
Seat Belts and Seats
O 26. Examine all of the webbing (pull out the belts from the inertia reel if necessary) for cuts, fraying or deterioration.
o 27. Check that each inertia reel belt retracts correctly.
o 28. Fasten and unfasten each belt to ensure that the buckles work correctly.
o 29. Tug hard on each belt and inspect the mountings, as far as possible, to ensure that all are okay.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Checks apply to
rear seat belts as much as front
ones.
O 30. Make sure that the seat runners and mountings are secure and that the back rest locks in the upright position.
Doors and Door Locks
O 31. Check that both front doors latch securely when closed and that both can be opened and closed from both outside and inside the car.
PART B: VEHICLE ON THE GROUND
Electrical Equipment
See Part A: INSIDE THE CAR for checks on the operation of the electrical equipment.
O 1. Examine the wiper blades and replace those that show any damage.
Vehicle Identification
Numbers (VIIU)
O 2. The VIN (or chassis number on older vehicles) must be clearly displayed and legible.
O 3. Number plates must be secure, legible and in good condition with correct spacing between letters and numbers. Any non-standard spacing will not be accepted.
Braking System
O 4. Inside the engine bay inspect the master cylinder, servo unit (if fitted), brake pipes and mountings. Look for corrosion, loose fitting or leaks.
Steering and Suspension
OS . While still in the engine bay, have your assistant turn the steering wheel lightly from side to side and look for play in steering universal joints or steering rack mountings and any other steering connections.
OE. If your vehicle is fitted with power steering, check the security and condition of the steering pump, hoses and drivebelt, in the engine bay.
O 7. Look and reach under the car while your assistant turns the steering wheel more vigorously from side to side. Place your hand over each track rod end in turn and inspect all of the steering linkages, joints and attachments for wear.
o 8. Go around the vehicle and
'bounce' each corner of the
vehicle in turn. Release at the lowest
point and the vehicle should rise and
settle in its normal position without
continuing to 'bounce' of its own
accord.
Page 26 of 171

PART C: VEHICLE RAISED OFF THE GROUND
Bodywork Structure
01
.
Any sharp edges on the external bodywork, caused by damage or corrosion will cause the vehicle to fail.
02 . Check all load bearing areas for corrosion. Open the doors and check the sills inside and out, above and below. Any corrosion in structural metalwork within 30 cm (12 in.) of seat belt mounting, steering and suspension attachment points will cause the vehicle to fail.
Wheels and Tyres
Under the Front of the
Car
You will need to support the front of the car on axle stands with the rear wheels firmly chocked in both directions.
OE . Have your helper turn the steering from lock to lock and check that the steering turns smoothly and that the brake hoses or pipes do not contact the wheel, tyre or any part of the steering or suspension.
TWI
Ob . To pass the test, the tread must be at least 1.6 mm deep throughout a continuous band comprising the central three-quarters of the width of the tread. The Tread Wear Indicators (TWI) will tell you when the limit has been reached, on most tyres.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Tyres are past their best, especially in wet conditions, well before this point is reached!
04 . Check that the front tyres match and that the rear tyres match each other
-
in terms of size and type but not necessarily make. They must be the correct size for the vehicle and the pressures must be correct.
05 . With each wheel off the ground in turn, check the inside and the outside of the tyre wall for cuts, lumps and bulges and check the wheel for damage. Note that tyres deteriorate progressively over a period of time and if they have degraded to this extent, replace them.
07 . Have your assistant hold down the brake pedal firmly. Check each brake flexible hose for bulges or leaks.
o 8. Inspect all the rigid brake pipes underneath the front of the vehicle for corrosion or leaks and also look for signs of fluid leaks at the brake calipers. Rigid fuel pipes need to be checked in the same way.
09 . At each full lock position, check the steering rack rubber gaiters for splits, leaks or loose retaining clips.
o 10. Check the track rod end dust covers to make sure they are in place.
o 11. Inspect each constant velocity joint gaiter
-
both inners and outers
-
for splits or damage. You will have to rotate each wheel to see the gaiters all the way round.
O 12. Check all of the suspension rubber mountings, including the anti-rollbar mountings (when fitted). Take a firm grip on each shock absorber in turn with both hands and try to twist the damper to check for deterioration in the top and bottom mounting bushes.
o 13. Underneath the front wheel arches, check that the shock absorbers are not corroded, that the springs have not cracked and that there are no fluid leaks down the body of the shock absorber.
o 14. While under the front end of the car, check the front of the exhaust system for security of fixing at the manifold, for corrosion and secure fixing to the mounting points.
o 15. Preferably working with a helper, grasp each front road wheel at the 12 o'clock and 6 o'clock positions and try rocking the wheel. Look for movement or wear at the suspension ball joints, suspension mountings, steering mountings and at the wheel bearing
-
look for movement between the wheel and hub. Repeat the test by grasping the road wheel at 3 o'clock and 9 o'clock and rocking once more.
o 16. Spin each wheel and check for noise or roughness in the wheel bearing and binding in either the wheel bearing or the brake.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Don't forget that on front wheel drive cars, the gearbox must be in neutral. There will be a certain amount of noise and drag from the drivetrain components.
O 17. If you suspect wear at any of the suspension points, try levering with a screwdriver to see whether or not you can confirm any movement in that area.
o 18. Vehicles fitted with other suspension types such as hydraulic suspension, torsion bar suspension etc. need to be checked in a similar way with the additional point that there must be no fluid leaks or damaged pipes on vehicles with hydraulic suspension.
Underneath the Rear
of the Car
O 19. Inspect the rear springs for security at their mounting points and for cracks, severe corrosion or damage.
o 20. Check the rear shock absorbers in the same way as the checks carried out for the fronts.
o 21. Check all rear suspension mounting points, including the rubbers to any locating rods or anti-rollbar that may be fitted.
O 22. Check all of the flexible and rigid brake pipes and the fuel pipes just as for the front of the vehicle.
30