Page 1197 of 2389

IDLE AND OR 2,500 RPM HC CO
CONCENTRATION CHECK
METHOD
HINT: This check is used only to determine whether or not
the idle HC/CO complies with regulations.
1. INITIAL CONDITIONS
(b) Engine at normal operating temperature
(b) Air cleaner installed
(e) All pipes and hoses of air induction system connected
(d) All operating accessories switched OFF
(e) All vacuum lines properly connected
HINT: All vacuum hoses for EGR systems, etc. should be
properly connected.
(f) EFI system wiring connectors fully plugged
(g) Ignition timing set correctly
(h) Transmission in N range
(i) Tachometer and HC/CO meter calibrated and at hand
2. START ENGINE
3. RACE ENGINE AT 2,500 RPM FOR APPROX. 2
MINUTES
4. INSERT HC/CO METER TESTING PROBE INTO
TAILPIPE AT LEAST 40 cm (1.3 ft)
5. CHECK HC/CO CONCENTRATION AT IDLE
Complete the measuring within three times.
HINT: When performing the 2 mode (2,500 rpm and idle)
test, follow the measurement order prescribed by the regula-
tions.
If the HC/CO concentration at 2,500 rpm does not comply
with regulations, try the following procedure.
Race the engine again at 2,500 rpm for approx. 1 minute
and quickly repeat steps 4 and 5 above.
This may correct the problem.
± ENGINE MECHANICALIdle and or 2 500 rpm HC CO Concentration Check MethodEM±20
Page 1289 of 2389
(f) Lift the engine out of the vehicle slowly and carefully.
NOTICE: Be careful not to hit the PS gear housing or neutral
start switch.
(g) Make sure the engine is clear of all wiring, hoses and
cables.
(h) Place the engine and transaxle assembly onto the stand.
36. SEPARATE ENGINE AND TRANSAXLE (d) Remove the through bolt, three bolts (2WD, M/T), four
bolts (Others) and LH mounting insulator.
(e) Remove the three bolts and LH mounting bracket. (b) (2WD)
Remove the bolt, four nuts and RH mounting insula-
tor.
(c) (4WD)
Remove the through bolt, two nuts and RH mounting
insulator.
± ENGINE MECHANICALCylinder Block (3S±FE)EM±112
Page 1322 of 2389
(f) Lift the engine out of the vehicle slowly and carefully.
NOTICE: Be careful not to hit the PS gear housing or
neutral start switch.
(g) Make sure the engine is clear of all wiring, hoses and
cables.
(h) Place the engine. and transaxle assembly onto the
stand. (d) Remove the through bolt, nut, four bolts and LH
mounting insulator.
(e) Remove the three bolts and LH mounting bracket. (b) (w/ A.B.S.)
Remove the clamp bolts of the PS oil cooler pipes.
(c) Remove the bolt, four nuts and RH mounting insulator.
39. (A/T)
REMOVE STARTER
40. SEPARATE ENGINE AND TRANSAXLE
± ENGINE MECHANICALCylinder Block (2VZ±FE)EM±145
Page 1420 of 2389
�2002
All rights reserved. This book may not be
reproduced or copied, in whole or in part, without the
written permission of Toyota Motor Corporation.
FOREWORD
This manual has been prepared for use when
performing terminal repairs, wire repairs, or connector
repairs on vehicles.
A step±by±step section on connector repair and
terminal repair is included.
There is a section of charts with terminal and connector
illustrations, part numbers, and notes on terminal
removal.
By using this guide, a satisfactory repair of the wiring
harness and connectors in Toyota vehicles will be easy
to achieve.
All information in this manual is based on the latest
product information at the time of publication. However,
specifications and procedures are subject to change
without notice.
Page 1422 of 2389
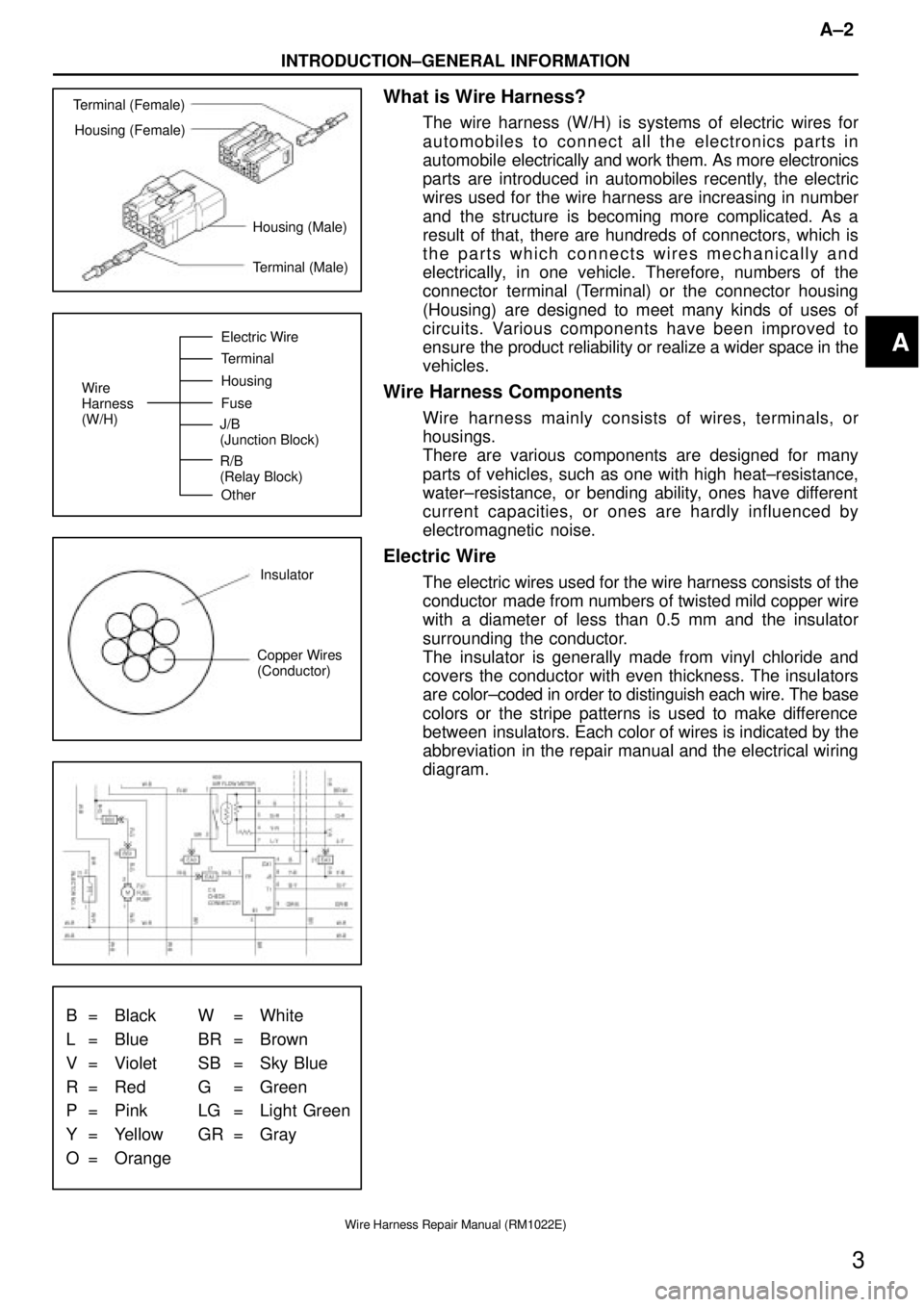
Terminal (Female)
Housing (Female)
Housing (Male)
Terminal (Male)
Wire
Harness
(W/H)Electric Wire
Terminal
Housing
Fuse
Other J/B
(Junction Block)
R/B
(Relay Block)
Insulator
Copper Wires
(Conductor)
B = Black W = White
L = Blue BR = Brown
V = Violet SB = Sky Blue
R = Red G = Green
P = Pink LG = Light Green
Y = Yellow GR = Gray
O = Orange
A±2
INTRODUCTION±GENERAL INFORMATION
3
Wire Harness Repair Manual (RM1022E)
What is Wire Harness?
The wire harness (W/H) is systems of electric wires for
automobiles to connect all the electronics parts in
automobile electrically and work them. As more electronics
parts are introduced in automobiles recently, the electric
wires used for the wire harness are increasing in number
and the structure is becoming more complicated. As a
result of that, there are hundreds of connectors, which is
the parts which connects wires mechanically and
electrically, in one vehicle. Therefore, numbers of the
connector terminal (Terminal) or the connector housing
(Housing) are designed to meet many kinds of uses of
circuits. Various components have been improved to
ensure the product reliability or realize a wider space in the
vehicles.
Wire Harness Components
Wire harness mainly consists of wires, terminals, or
housings.
There are various components are designed for many
parts of vehicles, such as one with high heat±resistance,
water±resistance, or bending ability, ones have different
current capacities, or ones are hardly influenced by
electromagnetic noise.
Electric Wire
The electric wires used for the wire harness consists of the
conductor made from numbers of twisted mild copper wire
with a diameter of less than 0.5 mm and the insulator
surrounding the conductor.
The insulator is generally made from vinyl chloride and
covers the conductor with even thickness. The insulators
are color±coded in order to distinguish each wire. The base
colors or the stripe patterns is used to make difference
between insulators. Each color of wires is indicated by the
abbreviation in the repair manual and the electrical wiring
diagram.
A
Page 1428 of 2389
Push
Equal Amperage Rating
A±8
INTRODUCTION±CIRCUIT PROTECTION
9
Wire Harness Repair Manual (RM1022E)
CIRCUIT PROTECTION
All electrical circuits are protected against excessive loads which might occur because of shorts or
overloads in the wiring system. Such protection is provided by a fuse, circuit breaker, or fusible link, A
short circuit may cause a fuse to blow or a circuit breaker to open.
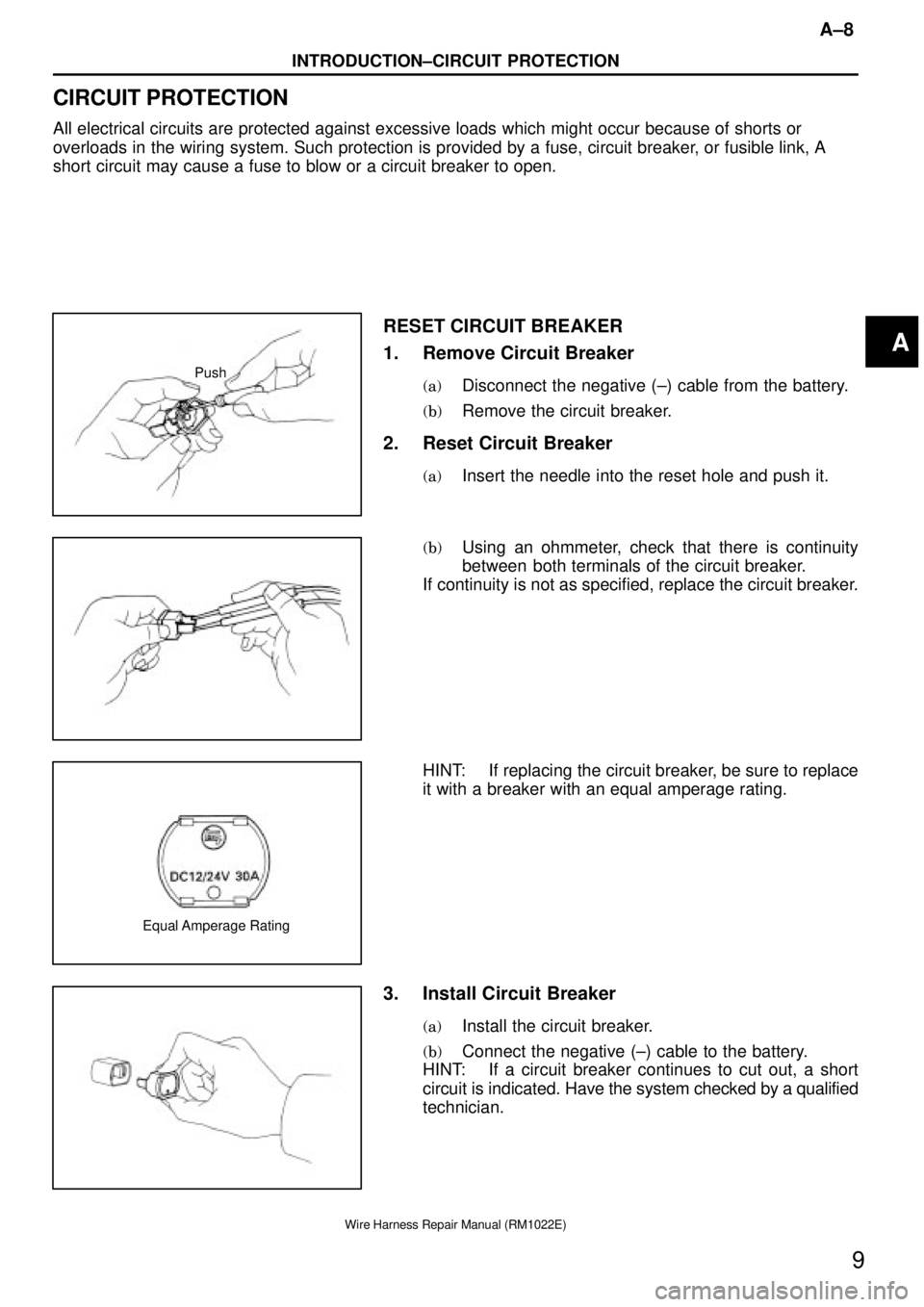
RESET CIRCUIT BREAKER
1. Remove Circuit Breaker
(a)Disconnect the negative (±) cable from the battery.
(b)Remove the circuit breaker.
2. Reset Circuit Breaker
(a)Insert the needle into the reset hole and push it.
(b)Using an ohmmeter, check that there is continuity
between both terminals of the circuit breaker.
If continuity is not as specified, replace the circuit breaker.
HINT: If replacing the circuit breaker, be sure to replace
it with a breaker with an equal amperage rating.
3. Install Circuit Breaker
(a)Install the circuit breaker.
(b)Connect the negative (±) cable to the battery.
HINT: If a circuit breaker continues to cut out, a short
circuit is indicated. Have the system checked by a qualified
technician.
A
Page 1836 of 2389
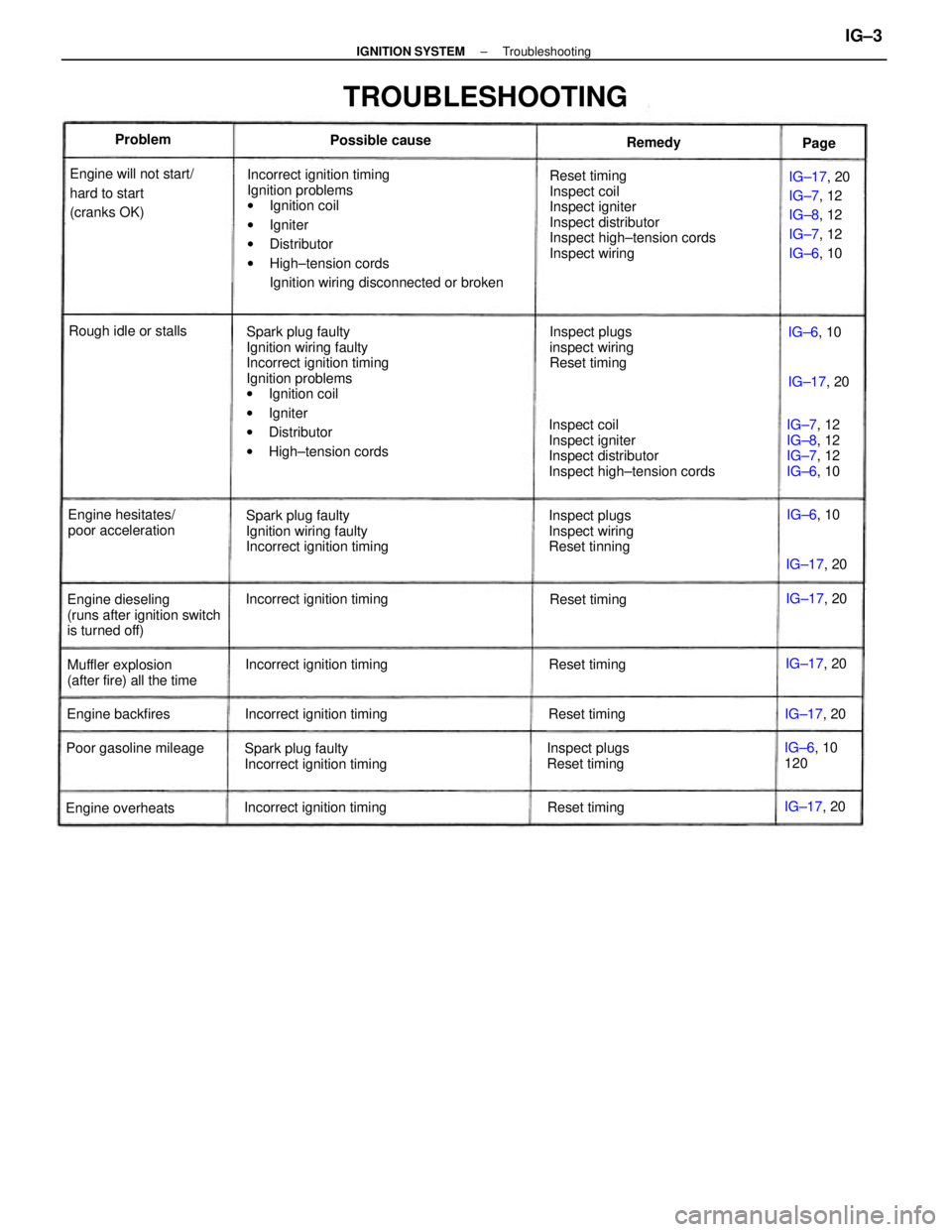
Incorrect ignition timing
Ignition problems
wIgnition coil
wIgniter
wDistributor
wHigh±tension cords
Ignition wiring disconnected or broken
Spark plug faulty
Ignition wiring faulty
Incorrect ignition timing
Ignition problems
wIgnition coil
wIgniter
wDistributor
wHigh±tension cordsReset timing
Inspect coil
Inspect igniter
Inspect distributor
Inspect high±tension cords
Inspect wiring
Inspect coil
Inspect igniter
Inspect distributor
Inspect high±tension cords
Spark plug faulty
Ignition wiring faulty
Incorrect ignition timingIG±17, 20
IG±7, 12
IG±8, 12
IG±7, 12
IG±6, 10
Spark plug faulty
Incorrect ignition timing Engine will not start/
hard to start
(cranks OK)
TROUBLESHOOTING
Engine dieseling
(runs after ignition switch
is turned off)Inspect plugs
Inspect wiring
Reset tinningInspect plugs
inspect wiring
Reset timing
Muffler explosion
(after fire) all the timeEngine hesitates/
poor accelerationIG±7, 12
IG±8, 12
IG±7, 12
IG±6, 10
Inspect plugs
Reset timing Incorrect ignition timing
Incorrect ignition timing
Incorrect ignition timing
Incorrect ignition timing Poor gasoline mileageRough idle or stalls
IG±6, 10
120
Engine overheatsEngine backfiresPossible cause
Reset timing
Reset timingReset timingReset timingIG±17, 20 IG±17, 20
IG±17, 20
IG±17, 20 IG±17, 20
IG±17, 20 Problem
IG±6, 10
IG±6, 10 Remedy
Page
± IGNITION SYSTEMTroubleshootingIG±3
Page 1838 of 2389
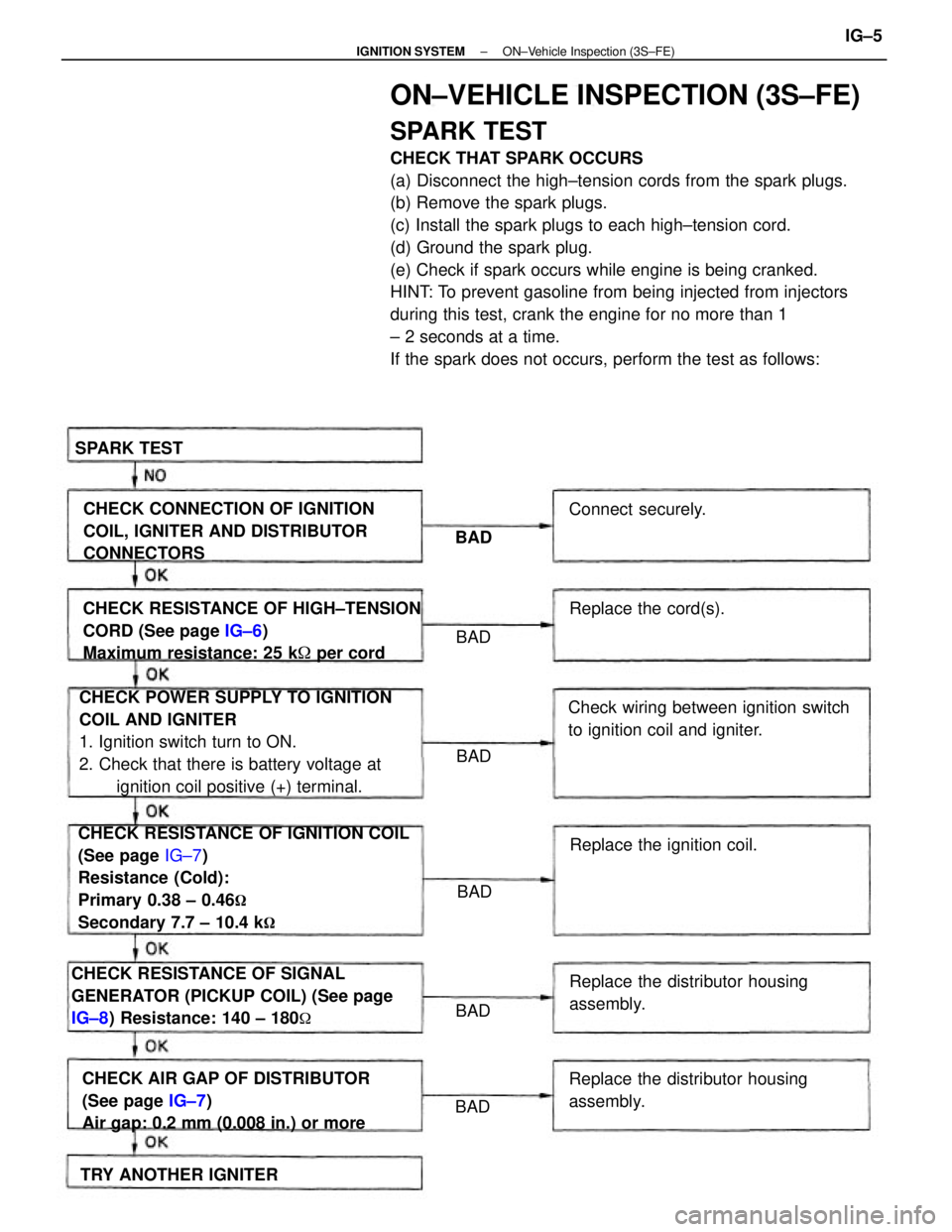
ON±VEHICLE INSPECTION (3S±FE)
SPARK TEST
CHECK THAT SPARK OCCURS
(a) Disconnect the high±tension cords from the spark plugs.
(b) Remove the spark plugs.
(c) Install the spark plugs to each high±tension cord.
(d) Ground the spark plug.
(e) Check if spark occurs while engine is being cranked.
HINT: To prevent gasoline from being injected from injectors
during this test, crank the engine for no more than 1
± 2 seconds at a time.
If the spark does not occurs, perform the test as follows:
CHECK RESISTANCE OF IGNITION COIL
(See page IG±7)
Resistance (Cold):
Primary 0.38 ± 0.46
�
Secondary 7.7 ± 10.4 k�
CHECK POWER SUPPLY TO IGNITION
COIL AND IGNITER
1. Ignition switch turn to ON.
2. Check that there is battery voltage at
ignition coil positive (+) terminal. CHECK RESISTANCE OF HIGH±TENSION
CORD (See page IG±6)
Maximum resistance: 25 k� per cord
CHECK RESISTANCE OF SIGNAL
GENERATOR (PICKUP COIL) (See page
IG±8) Resistance: 140 ± 180
�
CHECK AIR GAP OF DISTRIBUTOR
(See page IG±7)
Air gap: 0.2 mm (0.008 in.) or moreCHECK CONNECTION OF IGNITION
COIL, IGNITER AND DISTRIBUTOR
CONNECTORS
Check wiring between ignition switch
to ignition coil and igniter.
Replace the distributor housing
assembly.
Replace the distributor housing
assembly.Replace the ignition coil.
TRY ANOTHER IGNITERReplace the cord(s). Connect securely. SPARK TEST
BAD BAD
BAD
BAD BAD
BAD
± IGNITION SYSTEMON±Vehicle Inspection (3S±FE)IG±5