1985 FORD GRANADA fuel pump
[x] Cancel search: fuel pumpPage 101 of 255
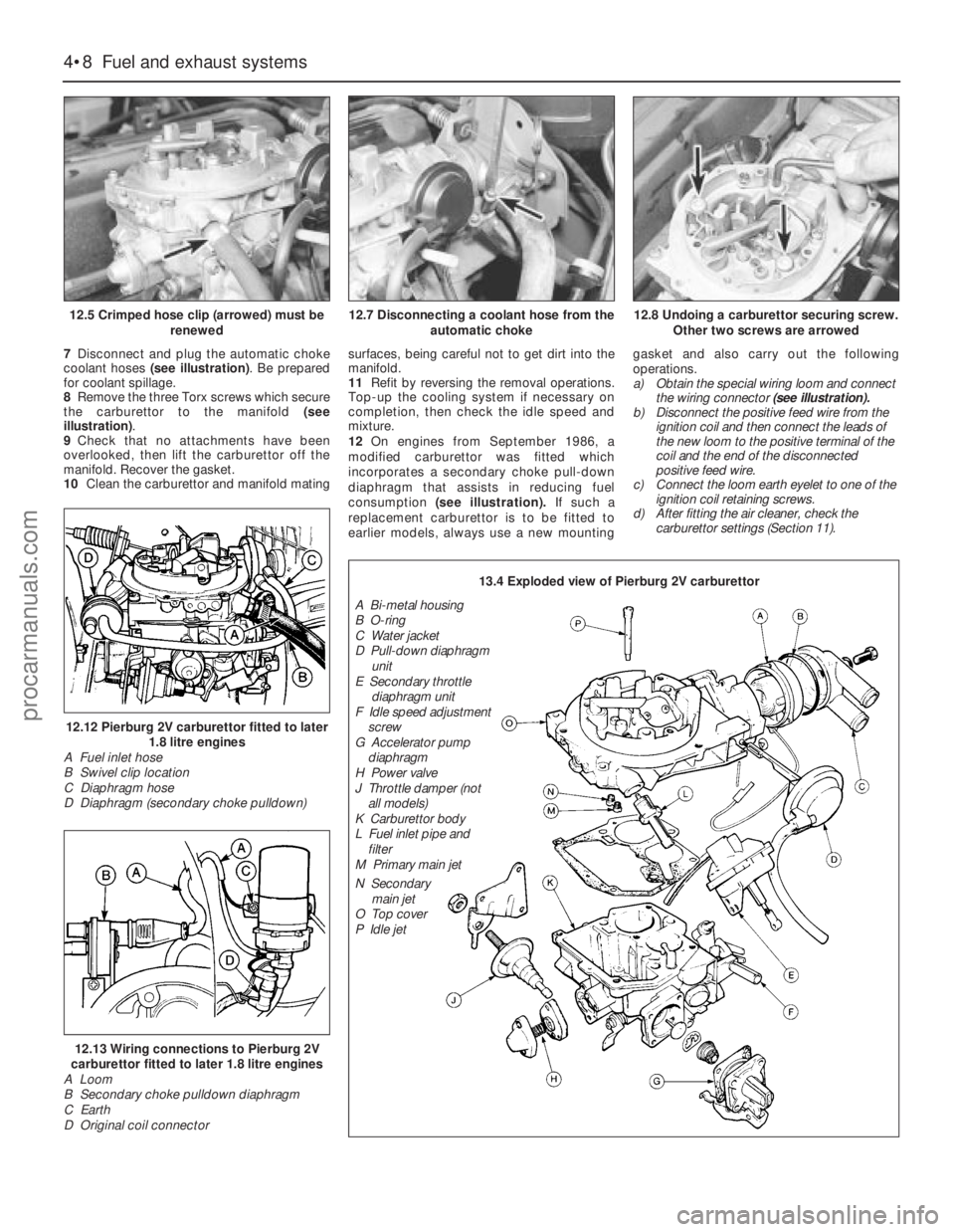
7Disconnect and plug the automatic choke
coolant hoses (see illustration). Be prepared
for coolant spillage.
8Remove the three Torx screws which secure
the carburettor to the manifold (see
illustration).
9Check that no attachments have been
overlooked, then lift the carburettor off the
manifold. Recover the gasket.
10Clean the carburettor and manifold matingsurfaces, being careful not to get dirt into the
manifold.
11Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Top-up the cooling system if necessary on
completion, then check the idle speed and
mixture.
12On engines from September 1986, a
modified carburettor was fitted which
incorporates a secondary choke pull-down
diaphragm that assists in reducing fuel
consumption (see illustration).If such a
replacement carburettor is to be fitted to
earlier models, always use a new mountinggasket and also carry out the following
operations.
a)Obtain the special wiring loom and connect
the wiring connector(see illustration).
b)Disconnect the positive feed wire from the
ignition coil and then connect the leads of
the new loom to the positive terminal of the
coil and the end of the disconnected
positive feed wire.
c)Connect the loom earth eyelet to one of the
ignition coil retaining screws.
d)After fitting the air cleaner, check the
carburettor settings (Section 11).
4•8Fuel and exhaust systems
12.5 Crimped hose clip (arrowed) must be
renewed
12.12 Pierburg 2V carburettor fitted to later
1.8 litre engines
A Fuel inlet hose
B Swivel clip location
C Diaphragm hose
D Diaphragm (secondary choke pulldown)
12.13 Wiring connections to Pierburg 2V
carburettor fitted to later 1.8 litre engines
A Loom
B Secondary choke pulldown diaphragm
C Earth
D Original coil connector
12.7 Disconnecting a coolant hose from the
automatic choke12.8 Undoing a carburettor securing screw.
Other two screws are arrowed
13.4 Exploded view of Pierburg 2V carburettor
A Bi-metal housing
B O-ring
C Water jacket
D Pull-down diaphragm
unit
E Secondary throttle
diaphragm unit
F Idle speed adjustment
screw
G Accelerator pump
diaphragm
H Power valve
J Throttle damper (not
all models)
K Carburettor body
L Fuel inlet pipe and
filter
M Primary main jet
N Secondary
main jet
O Top cover
P Idle jet
procarmanuals.com
Page 103 of 255
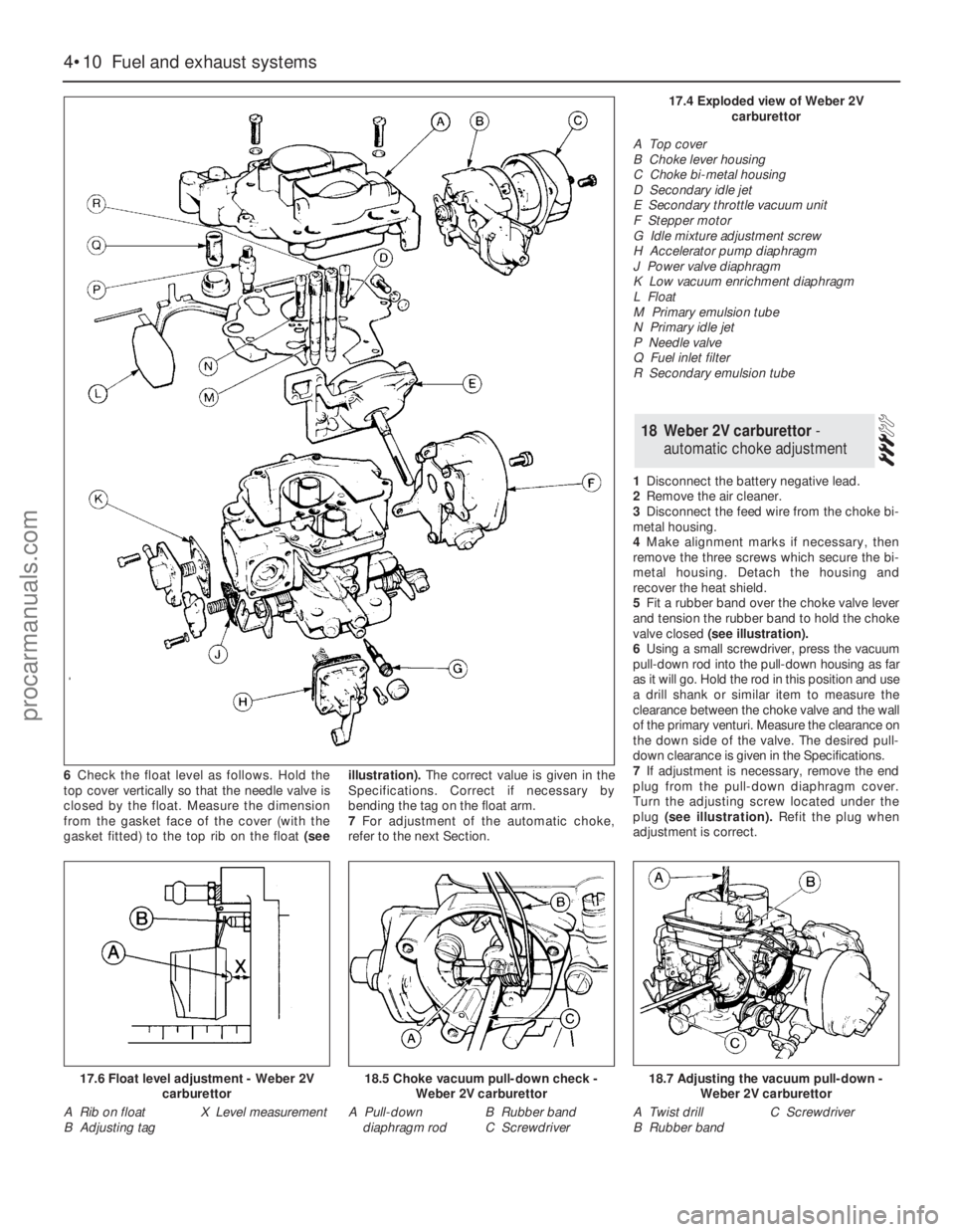
6Check the float level as follows. Hold the
top cover vertically so that the needle valve is
closed by the float. Measure the dimension
from the gasket face of the cover (with the
gasket fitted) to the top rib on the float(seeillustration).The correct value is given in the
Specifications. Correct if necessary by
bending the tag on the float arm.
7For adjustment of the automatic choke,
refer to the next Section.1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the air cleaner.
3Disconnect the feed wire from the choke bi-
metal housing.
4Make alignment marks if necessary, then
remove the three screws which secure the bi-
metal housing. Detach thehousing and
recover the heat shield.
5Fit a rubber band over the choke valve lever
and tension the rubber band to hold the choke
valve closed(see illustration).
6Using a small screwdriver, press the vacuum
pull-down rod into the pull-down housing as far
as it will go. Hold the rod in this position and use
a drill shank or similar item to measure the
clearance between the choke valve and the wall
of the primary venturi. Measure the clearance on
the down side of the valve. The desired pull-
down clearance is given in the Specifications.
7If adjustment is necessary, remove the end
plug from the pull-down diaphragm cover.
Turn the adjusting screw located under the
plug (see illustration).Refit the plug when
adjustment is correct.
18Weber 2V carburettor -
automatic choke adjustment
4•10Fuel and exhaust systems
17.6 Float level adjustment - Weber 2V
carburettor
A Rib on float
B Adjusting tagX Level measurement
18.5 Choke vacuum pull-down check -
Weber 2V carburettor
A Pull-down
diaphragm rodB Rubber band
C Screwdriver
18.7 Adjusting the vacuum pull-down -
Weber 2V carburettor
A Twist drill
B Rubber bandC Screwdriver
17.4 Exploded view of Weber 2V
carburettor
A Top cover
B Choke lever housing
C Choke bi-metal housing
D Secondary idle jet
E Secondary throttle vacuum unit
F Stepper motor
G Idle mixture adjustment screw
H Accelerator pump diaphragm
J Power valve diaphragm
K Low vacuum enrichment diaphragm
L Float
M Primary emulsion tube
N Primary idle jet
P Needle valve
Q Fuel inlet filter
R Secondary emulsion tube
procarmanuals.com
Page 105 of 255
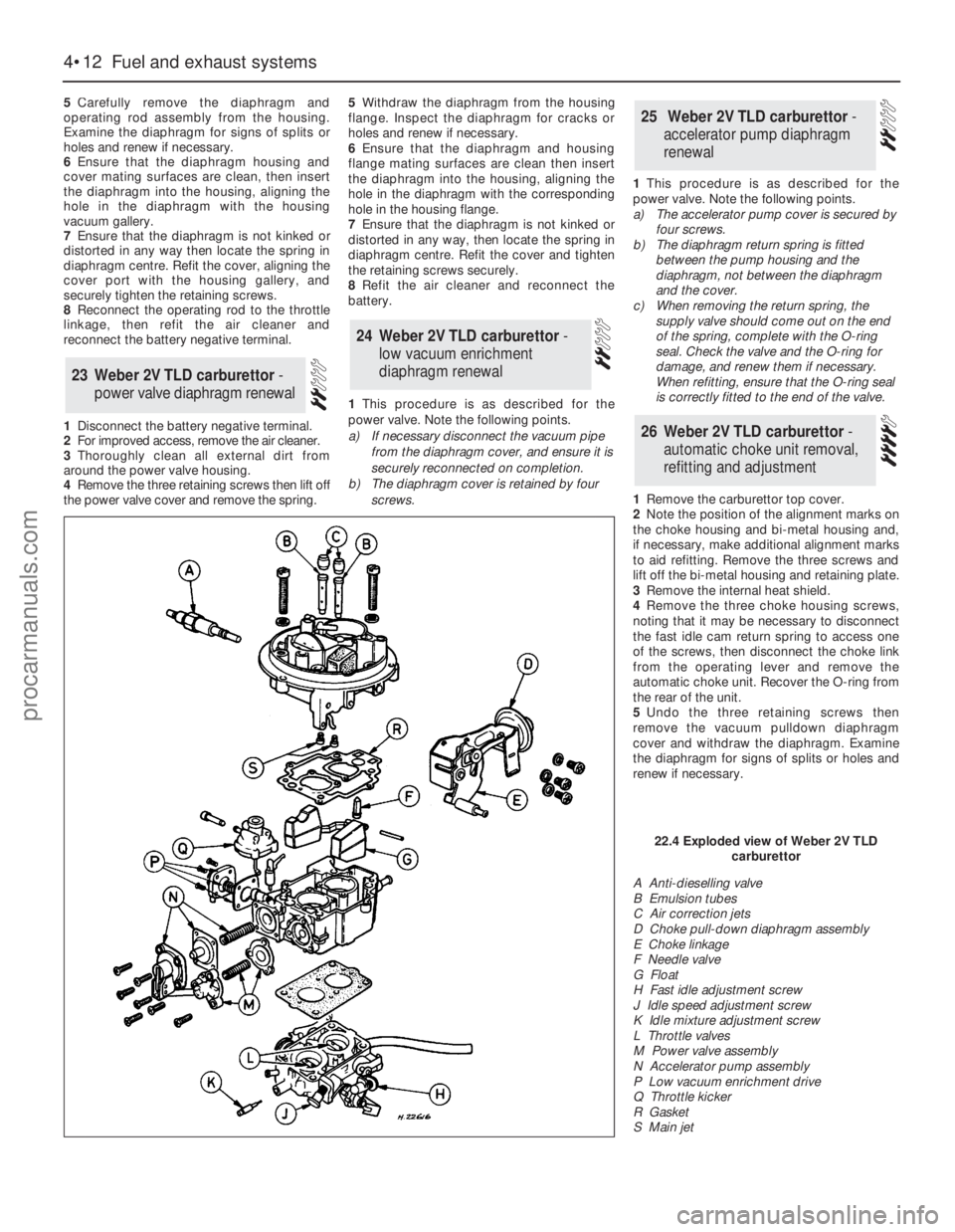
5Carefully remove the diaphragm and
operating rod assembly from the housing.
Examine the diaphragm for signs of splits or
holes and renew if necessary.
6Ensure that the diaphragm housing and
cover mating surfaces are clean, then insert
the diaphragm into the housing, aligning the
hole in the diaphragm with the housing
vacuum gallery.
7Ensure that the diaphragm is not kinked or
distorted in any way then locate the spring in
diaphragm centre. Refit the cover, aligning the
cover port with the housing gallery, and
securely tighten the retaining screws.
8Reconnect the operating rod to the throttle
linkage, then refit the air cleaner and
reconnect the battery negative terminal.
1Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2For improved access, remove the air cleaner.
3Thoroughly clean all external dirt from
around the power valve housing.
4Remove the three retaining screws then lift off
the power valve cover and remove the spring.5Withdraw the diaphragm from the housing
flange. Inspect the diaphragm for cracks or
holes and renew if necessary.
6Ensure that the diaphragm and housing
flange mating surfaces are clean then insert
the diaphragm into the housing, aligning the
hole in the diaphragm with the corresponding
hole in the housing flange.
7Ensure that the diaphragm is not kinked or
distorted in any way, then locate the spring in
diaphragm centre. Refit the cover and tighten
the retaining screws securely.
8Refit the air cleaner and reconnect the
battery.
1This procedure is as describedfor the
power valve. Note the following points.
a)If necessary disconnect the vacuum pipe
from the diaphragm cover, and ensure it is
securely reconnected on completion.
b)The diaphragm cover is retained by four
screws.1This procedure is as described for the
power valve. Note the following points.
a)The accelerator pump cover is secured by
four screws.
b)The diaphragm return spring is fitted
between the pump housing and the
diaphragm, not between the diaphragm
and the cover.
c)When removing the return spring, the
supply valve should come out on the end
of the spring, complete with the O-ring
seal. Check the valve and the O-ring for
damage, and renew them if necessary.
When refitting, ensure that the O-ring seal
is correctly fitted to the end of the valve.
1Remove the carburettor top cover.
2Note the position of the alignment marks on
the choke housing and bi-metal housing and,
if necessary, make additional alignment marks
to aid refitting. Remove the three screws and
lift off the bi-metal housing and retaining plate.
3Remove the internal heat shield.
4Remove the three choke housing screws,
noting that it may be necessary to disconnect
the fast idle cam return spring to access one
of the screws, then disconnect the choke link
from the operating lever and remove the
automatic choke unit. Recover the O-ring from
the rear of the unit.
5 Undo the three retaining screws then
remove the vacuum pulldown diaphragm
cover and withdraw the diaphragm. Examine
the diaphragm for signs of splits or holes and
renew if necessary.
26Weber 2V TLD carburettor -
automatic choke unit removal,
refitting and adjustment
25Weber 2V TLD carburettor -
accelerator pump diaphragm
renewal
24Weber 2V TLD carburettor -
low vacuum enrichment
diaphragm renewal
23Weber 2V TLD carburettor -
power valve diaphragm renewal
4•12Fuel and exhaust systems
A Anti-dieselling valve
B Emulsion tubes
C Air correction jets
D Choke pull-down diaphragm assembly
E Choke linkage
F Needle valve
G Float
H Fast idle adjustment screw
J Idle speed adjustment screw
K Idle mixture adjustment screw
L Throttle valves
M Power valve assembly
N Accelerator pump assembly
P Low vacuum enrichment drive
Q Throttle kicker
R Gasket
S Main jet
22.4 Exploded view of Weber 2V TLD
carburettor
procarmanuals.com
Page 106 of 255
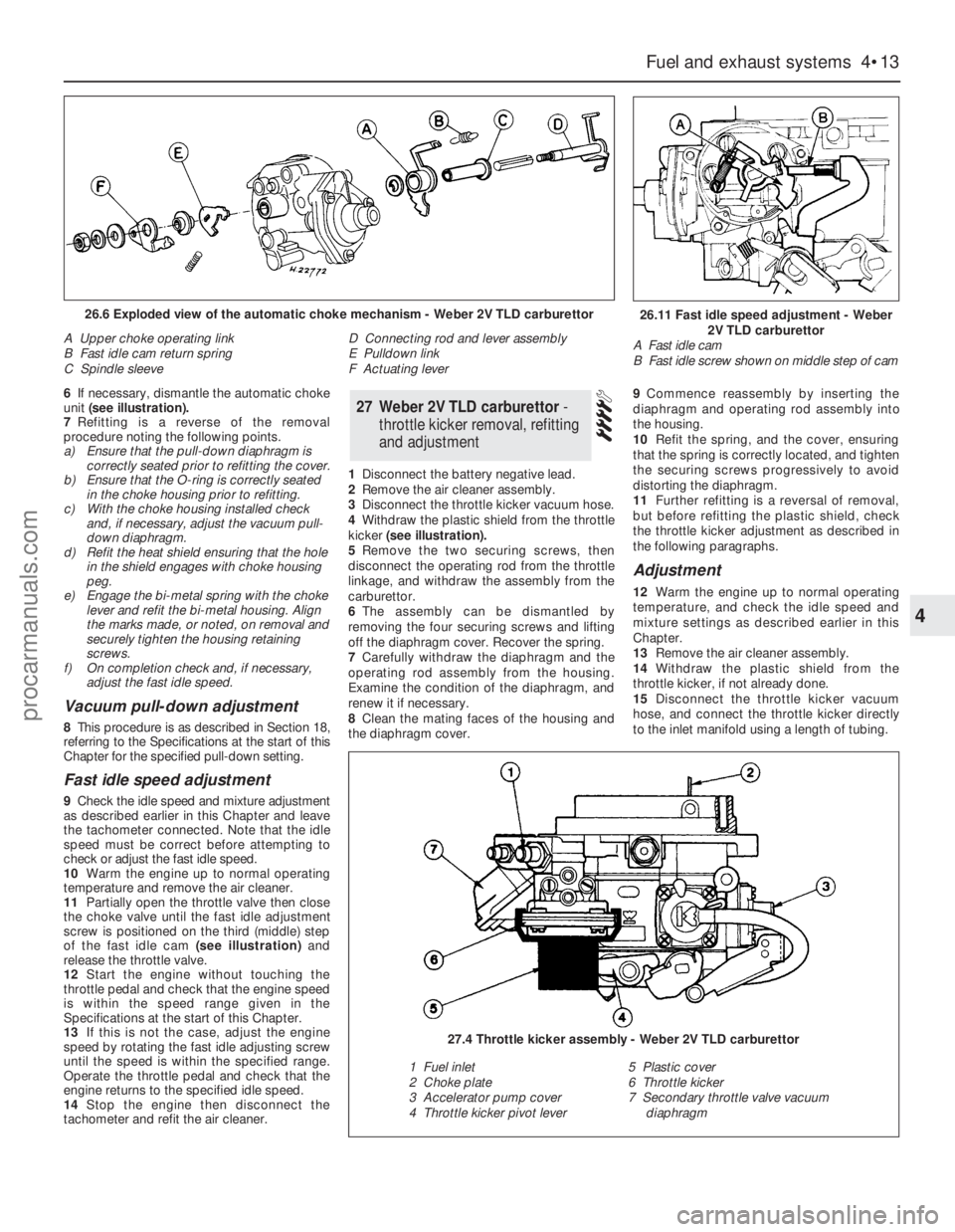
6If necessary, dismantle the automatic choke
unit (see illustration).
7Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure noting the following points.
a)Ensure that the pull-down diaphragm is
correctly seated prior to refitting the cover.
b)Ensure that the O-ring is correctly seated
in the choke housing prior to refitting.
c)With the choke housing installed check
and, if necessary, adjust the vacuum pull-
down diaphragm.
d)Refit the heat shield ensuring that the hole
in the shield engages with choke housing
peg.
e)Engage the bi-metal spring with the choke
lever and refit the bi-metal housing. Align
the marks made, or noted, on removal and
securely tighten the housing retaining
screws.
f)On completion check and, if necessary,
adjust the fast idle speed.
Vacuum pull-down adjustment
8This procedure is as described in Section 18,
referring to the Specifications at the start of this
Chapter for the specified pull-down setting.
Fast idle speed adjustment
9Check the idle speed and mixture adjustment
as described earlier in this Chapter and leave
the tachometer connected. Note that the idle
speed must be correct before attempting to
check or adjust the fast idle speed.
10Warm the engine up to normal operating
temperature and remove the air cleaner.
11Partially open the throttle valve then close
the choke valve until the fast idle adjustment
screw is positioned on the third (middle) step
of the fast idle cam(see illustration)and
release the throttle valve.
12Start the engine without touching the
throttle pedal and check that the engine speed
is within the speed range given in the
Specifications at the start of this Chapter.
13If this is not the case, adjust the engine
speed by rotating the fast idle adjusting screw
until the speed is within the specified range.
Operate the throttle pedal and check that the
engine returns to the specified idle speed.
14Stop the engine then disconnect the
tachometer and refit the air cleaner.1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the air cleaner assembly.
3Disconnect the throttle kicker vacuum hose.
4Withdraw the plastic shield from the throttle
kicker(see illustration).
5Remove the two securing screws, then
disconnect the operating rod from the throttle
linkage, and withdraw the assembly from the
carburettor.
6The assembly can be dismantled by
removing the four securing screws and lifting
off the diaphragm cover. Recover the spring.
7Carefully withdraw the diaphragm and the
operating rod assembly from the housing.
Examine the condition of the diaphragm, and
renew it if necessary.
8Clean the mating faces of the housing and
the diaphragm cover.9Commence reassembly by inserting the
diaphragm and operating rod assembly into
the housing.
10Refit the spring, and the cover, ensuring
that the spring is correctly located, and tighten
the securing screws progressively to avoid
distorting the diaphragm.
11Further refitting is a reversal of removal,
but before refitting the plastic shield, check
the throttle kicker adjustment as described in
the following paragraphs.
Adjustment
12Warm the engine up to normal operating
temperature, and check the idle speed and
mixture settings as described earlier in this
Chapter.
13Remove the air cleaner assembly.
14Withdraw the plastic shield from the
throttle kicker, if not already done.
15Disconnect the throttle kicker vacuum
hose, and connect the throttle kicker directly
to the inlet manifold using a length of tubing.
27Weber 2V TLD carburettor -
throttle kicker removal, refitting
and adjustment
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•13
4
26.11 Fast idle speed adjustment - Weber
2V TLD carburettor
A Fast idle cam
B Fast idle screw shown on middle step of cam26.6 Exploded view of the automatic choke mechanism - Weber 2V TLD carburettor
A Upper choke operating link
B Fast idle cam return spring
C Spindle sleeveD Connecting rod and lever assembly
E Pulldown link
F Actuating lever
27.4 Throttle kicker assembly - Weber 2V TLD carburettor
1 Fuel inlet
2 Choke plate
3 Accelerator pump cover
4 Throttle kicker pivot lever5 Plastic cover
6 Throttle kicker
7 Secondary throttle valve vacuum
diaphragm
procarmanuals.com
Page 107 of 255

16Start the engine and note the engine
speed (rpm). The engine speed should
increase above the normal idle speed, and
should be as given in the Specifications.
17If the engine speed is not as specified,
remove the tamperproof plug from the top of
the throttle kicker housing, and turn the
adjustment screw to give the specified speed.
18On completion of adjustment, fit a new
tamperproof cap.
19Disconnect the tubing from the inlet
manifold, and reconnect the throttle kicker
vacuum hose.
20Refit the plastic shield and the air cleaner.
On 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 models especially,
residual pressure will remain in the fuel lines
long after the vehicle was last used therefore
the fuel system must be depressurised before
any hose is disconnected; the system is
depressurised via the vent valve on the fuel
rail, noting that it may be necessary to depress
the valve several times before the pressure is
fully released. As an added precaution place a
rag over the valve as it is depressed to catch
any fuel which is forcibly expelled. Before
carrying out any operation on the fuel system
refer to the precautions given in Safety first! at
the beginning of this Manual and follow them
implicitly. Petrol is a highly dangerous and
volatile liquid and the precautions necessary
when handling it cannot be overstressed.
Access to the relays is obtained by
removing the facia top cover (crash pad).
The relays are located on the passenger
side(see illustration). Also see Chapter 13,
Section 16.
See Chapter 1, Section 41.
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
1Idle speed is controlled by the EEC IV
module and no direct adjustment is possible.
2Idle mixture adjustment should not be
necessary on a routine basis. After component
renewal or a similar circumstance it may be
checked and adjusted as follows.
3The engine must be at operating temperature.
The valve clearances must be correct, the air
cleaner element must be clean and the ignition
system must be in good condition.
4Connect an exhaust gas analyser (CO
meter) and a tachometer (rev. counter) to the
engine as instructed by their makers.
5Run the engine at 3000 rpm for 15 seconds,
then allow it to idle. Repeat the procedure
every 60 seconds until adjustment is
complete.
6With the engine idling after the 3000 rpm
burst, record the CO level when the reading
has stabilised. The desired value is given in the
Specifications.
7If adjustment is necessary, remove the
tamperproof plug from the mixture adjusting
screw on the underside of the vane airflow
meter (see illustration).
8On V6 models, note that adjustment should
first be carried out on the front airflow meter.The rear meter should only be adjusted if the
range of adjustment on the front meter is
insufficient.
9Turn the mixture adjusting screw with a
hexagon key until the CO level is correct (see
illustration).
10Stop the engine and disconnect the test
gear.
11Fit a new tamperproof plug if required.
DOHC engine
Note: Before carrying out any adjustments
ensure that the ignition timing and spark plug
gaps are as specified. To carry out the
adjustments, an accurate tachometer and an
exhaust gas analyser (CO meter) will be
required.
12Idle speed is controlled by the EEC IV
module, and manual adjustment is not possible,
although the “base” idle speed can be adjusted
by a Ford dealer using special equipment.
13On models with a catalytic converter, the
mixture is controlled by the EEC IV module,
and no manual adjustment is possible.
14On models without a catalytic converter,
the idle mixture can be adjusted as follows.
15Run the engine until it is at normal
operating temperature.
16Stop the engine and connect a tachometer
and an exhaust gas analyser in accordance
with the manufacturer’s instructions.
17Start the engine and run it at 3000 rpm
for 15 seconds, ensuring that all electrical
loads (headlamps, heater blower, etc) are
switched off, then allow the engine to idle, and
check the CO content. Note that the reading
will initially rise, then fall and finally stabilise.
18If adjustment is necessary, remove the
cover from the mixture adjustment
potentiometer (located on the right-hand side
of the engine compartment, behind the MAP
sensor), and turn the screw to give the
specified CO content (see illustration).
19If adjustment does not produce a change
in reading, the potentiometer may be at the
extreme of the adjustment range. To centralise
the potentiometer, turn the adjustment screw
20 turns clockwise followed by 10 turns anti-
clockwise, then repeat the adjustment
procedure.
31Fuel-injection system - idle
speed and mixture adjustment
30Fuel filter - renewal
29Fuel-injection system relays -
location
28Fuel-injection system -
depressurisation
4•14Fuel and exhaust systems
31.18 Remove the cover from the mixture
adjustment potentiometer31.9 Idle mixture adjustment - fuel-injection
models
29.2 Fuel injection system relays - 2.4 and
2.9 litre V6 engines
A Power relayB Fuel pump relay
31.7 Tamperproof plug (arrowed) covering
mixture adjusting screw
Airflow meter is inverted for photo
procarmanuals.com
Page 114 of 255

55Release the throttle position sensor wiring
connector from the clip under the throttle
body, and separate the two halves of the
connector.
56Remove the fuel-injectors.
57Check that all relevant wiring, hoses and
pipes have been disconnected to facilitate
removal of the manifold.
58Unscrew the ten bolts and two nuts
securing the inlet manifold to the cylinder
head, and carefully withdraw the manifold.
Recover the gasket.
59Recover the two plastic spark plug
spacers from the recesses in the cylinder head
(see illustration).
60If desired, the manifold can be dismantled
with reference to the relevant paragraphs of
this Chapter.
61Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.
a)Ensure that the spark plug spacers are in
position in the cylinder head recesses
before refitting the manifold.
b)Ensure manifold and cylinder head mating
surfaces are clean and dry and fit a new
gasket.
c)Tighten the manifold retaining nuts and
bolts evenly and progressively to the
specified torque.
d)Refit the fuel-injectors.
e)Make sure that all hoses, pipes and wires
are securely reconnected in their original
positions.
f)On completion, refill the cooling system.
g)Check the adjustment of the throttle cable
and where necessary, adjust the speed
control cable so that only a small amount
of slack is present in the cable.
h)Where applicable, check and if necessary
adjust the idle speed and mixture.
V6 engines
62Disconnect the battery negative lead.
63Drain the cooling system.
64Remove the throttle linkage cover.
65Release the hose clips and move the
airflow meter-to-manifold trunking aside.
Unclip or remove the crankcase ventilation
hose.
66Disconnect the radiator top hose and the
heater hose from the outlet at the front of the
manifold. Be prepared for some coolant spillage.67Disconnect the multi-plugs from the idle
speed control valve, the temperature gauge
sender unit; the coolant temperature sensor
and the throttle position sensor. Also
disconnect the injector wiring harness.
68Disconnect the throttle cable from the
linkage, unclip it and move it aside. On
automatic transmission models, also
disconnect the downshift cable or multi-plug,
as applicable.
69Disconnect the fuel feed and return pipes.
Be prepared for fuel spillage.
70Remove the HT leads and the distributor.
71Remove the plenum chamber, which is
secured by eight bolts.
72Remove the rocker covers, which are each
secured by seven bolts.
73Disconnect the water pump bypass hose
from the inlet manifold.
74Remove the eight bolts which secure the
inlet manifold to the cylinder heads.
75Lift off the manifold complete with fuel
pressure regulator, fuel rail, throttle body
housing etc. If it is stuck, carefully lever it free.
Do not apply leverage at the mating faces.
Recover the gasket.
76Clean all mating faces, being careful to
keep dirt out of ports and other orifices.
Obtain new gaskets for both the cylinder head
and plenum chamber sides of the manifold,
and for the rocker covers.
77Commence refitting by applying sealant
(Ford part No A70X-19554-BA, or equivalent)
around the ports and coolant passages on the
cylinder head.
78Apply sealant around the apertures on
both sides of the gasket. then fit the gasket to
the cylinder heads.
79Refit the manifold and insert the securing
bolts. Tighten the bolts, in the order shown
(see illustration),through the first four stages
given in the Specifications.
80Refit the water pump bypass hose.
81Refit the rocker covers, using new
gaskets. The adhesive sides of the gaskets
must face the covers.
82Reverse the remaining removal
operations, but do not refit the throttle linkage
cover yet.
83When the cooling system has beenrefilled, reconnect the battery and start the
engine. Check for fuel and other leaks.
84Bring the engine to operating temperature,
then stop it and carry out the final tightening of
the inlet manifold bolts as follows.
85Release the air inlet trunking. Unplug the
idle speed control valve and the throttle
position sensor. Unbolt the plenum chamber
and move it aside, disconnecting vacuum and
breather hoses as necessary.
86Slacken, but do not remove, the two bolts
which secure the fuel rail to the manifold.
87Tighten the inlet manifold bolts to the
Stage 5 specified torque, again following the
sequence shown. A special cranked spanner
(Ford tool No 21-079, or equivalent)(see
illustration)will be needed to tighten No 4
bolt when the distributor is fitted. In the
absence of such a spanner, remove the
distributor again.
88Tighten the fuel rail securing bolts.
89Refit the disturbed components. Run the
engine again and check the ignition timing and
the exhaust CO level .
90Refit the throttle linkage cover.
SOHC and all V6 engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Apply copious quantities of penetrating oil
to the manifold and exhaust pipe flange nuts
and bolts.
3On carburettor models, remove the air
cleaner and the hot air pick-up pipe.
4Unbolt any heat shields or shrouds from the
manifold.
5Unbolt the exhaust pipe(s) from the manifold
flange. Support the exhaust system if
necessary.
6Unbolt the manifold from the cylinder head
and remove it. Recover the gasket.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Use a new gasket, and apply anti-seize
compound to the various nuts and bolts.
Tighten the manifold fastenings to the
specified torque.
41Exhaust manifold(s) - removal
and refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•21
4
40.59 Removing a spark plug spacer from
the cylinder head recess40.79 Inlet manifold bolt tightening
sequence
Arrow points to front of engine40.87 Cranked spanner needed for
tightening V6 inlet manifold bolt with
distributor fitted
procarmanuals.com
Page 119 of 255

The ignition system is responsible for
igniting the fuel/air charge in each cylinder at
the correct moment. The components of the
system are the spark plugs, ignition coil,
distributor and connecting leads. Overall
control of the system is one of the functions of
the engine management module. Fuel-
injection models have a subsidiary ignition
module mounted on the distributor.
There are no contact breaker points in the
distributor. A square wave signal is generated
by the distributor electro-magnetically; this
signal is used by the engine management
module as a basis for switching the coil LT
current. Speed-related (centrifugal) advance is
also handled by the module. On carburettor
models, ignition timing is also advanced under
conditions of high inlet manifold vacuum.The engine management models are “black
boxes” which regulate both the fuel and the
ignition systems to obtain the best power,
economy and emission levels. The module
fitted to carburettor models is known as the
ESC II (Electronic Spark Control Mk II) module.
On fuel-injection models the more powerful
EEC IV (Electronic Engine Control Mk IV)
module is used.
Both types of module receive inputs from
sensors monitoring coolant temperature,
distributor rotor position and (on some
models) manifold vacuum. Outputs from the
module control ignition timing, inlet manifold
heating and (except on 1.8 litre models) idle
speed. The EEC IV module also has overall
control of the fuel-injection system, from
which it receives information.
Provision is made for the ignition timing to
be retarded to allow the use of low octane fuel
if necessary. On all except 1.8 litre models
there is also a facility for raising the idle speed.The EEC IV module contains self-test
circuitry which enables a technician with the
appropriate test equipment to diagnose faults
in a very short time. A Limited Operation
Strategy (LOS) means that the car is still
driveable, albeit at reduced power and
efficiency, in the event of a failure in the
module or its sensors.
Due to the complexity and expense of the
test equipment dedicated to the engine
management system, suspected faults should
be investigated by a Ford dealer, or other
competent specialist. This Chapter deals with
component removal and refitting, and with
some simple checks and adjustments.
On DOHC carburettor engines, the basic
operating principles of the ignition system are
as described above. A development of the
ESC II (Electronic Spark Control ll) system is
used to control the operation of the engine.
The ESC II module receives information from a
crankshaft speed/position sensor and an
1General information and
precautions
5•2Engine electrical systems
Ignition coil
Make . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Bosch, Femsa or Polmot
Primary resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.72 to 0.86 ohm
Secondary resistance:
All except DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5 to 7.0 k ohms
DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5 to 8.6 k ohms
Output voltage (open-circuit):
All except DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25 kV minimum
DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 kV minimum
HT leads
Maximum resistance per lead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 k ohms
Distributor
Make . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Bosch or Motorcraft
Rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Clockwise (viewed from above)
Automatic advance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Controlled by module
Dwell angle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Controlled by module
Ignition timing (see text)
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines:
Leaded fuel (97 octane):
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10°BTDC
Fuel-injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC
Unleaded fuel (95 octane):
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6°BTDC
Fuel-injection models:
2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8°BTDC
2.8 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC (no change)
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines:
Models with catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15°BTDC
Models without catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC*
* Standard setting for 97 octane leaded fuel.
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Alternator adjusting strap:
To steering pump bracket (OHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2616 to 19
To front cover (V6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Spark plugs:
All models except 2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2815 to 21
2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 to 4022 to 30
Air charge temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Engine coolant temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Fuel rail temperature sensor (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Crankshaft speed/position sensor screw (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 to 52 to 4
procarmanuals.com
Page 120 of 255

engine coolant temperature sensor. The
crankshaft speed/position sensor is activated
by a toothed disc on the rear of the crankshaft,
inside the cylinder block. The disc has 35
equally spaced teeth (one every 10°), with a
gap in the 36th position. The gap is used by
the sensor to determine the crankshaft
position relative to Top Dead Centre (TDC) of
No 1 piston.
The ignition advance is a function of the
ESC II module, and is controlled by vacuum.
The module is connected to the carburettor by
a vacuum pipe, and a transducer in the
module translates the vacuum signal into an
electrical voltage. From the vacuum signal, the
module determines engine load; engine speed
and temperature are determined from the
crankshaft speed/position sensor and the
engine coolant temperature sensor. The
module has a range of spark advance settings
stored in the memory, and a suitable setting is
selected for the relevant engine speed, load
and temperature. The degree of advance can
thus be constantly varied to suit the prevailing
engine speed and load conditions.
On DOHC fuel-injected engines, a
development of the EEC IV (Electronic Engine
Control IV) engine management system is
used to control both the ignition and fuel-
injection systems. The EEC IV module receives
information from a crankshaft speed/position
sensor (the same as that fitted to the
carburettor models), a throttle position sensor,
an engine coolant temperature sensor, a fuel
temperature sensor, an air charge temperature
sensor, a Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
sensor, and a vehicle speed sensor (mounted
on the gearbox). Additionally, on models with
a catalytic converter, an additional input is
supplied to the EEC IV module from an
exhaust gas oxygen (HEGO) sensor. On
models with automatic transmission,
additional sensors are fitted to the
transmission to inform the EEC IV module
when the transmission is in neutral, and when
the downshift is being operated.
The module provides outputs to control the
fuel pump, fuel-injectors, idle speed, ignition
system and automatic transmission .
Additionally, on models with air conditioning,
the EEC IV module disengages the air
conditioning compressor clutch when starting
the engine or when the engine is suddenly
accelerated. On models fitted with a catalytic
converter, the EEC IV module also controls the
carbon canister purge solenoid valve.
Using the inputs from the various sensors,
the EEC IV module computes the optimum
ignition advance, and fuel-injector pulse
duration to suit the prevailing engine
conditions.
On 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines, the system
operates in much the same way as that fitted
to the DOHC fuel-injected engine, noting the
following points.
a)There is no crankshaft speed/position
sensor.
b)The vehicle speed sensor is only fitted to
models equipped with a catalytic
converter.Precautions
ESC II module
Although it will tolerate all normal under-
bonnet conditions, the ESC II module may be
adversely affected by water entry during
steam cleaning or pressure washing of the
engine bay.
If cleaning the engine bay, therefore, take
care not to direct jets of water or steam at the
ESC II module. If this cannot be avoided,
remove the module completely, and protect its
multi-plug with a plastic bag.
Ignition system HT voltage
Take care to avoid receiving electric shocks
from the HT side of the ignition system. Do not
handle HT leads, or touch the distributor or
coil, when the engine is running. When tracing
faults in the HT system, use well insulated
tools to manipulate live leads. Electronic
ignition HT voltage could prove fatal.
Electronic ignition systems
General
Further details of the various systems are
given in the relevant Sections of this Chapter.
While some repair procedures are given, the
usual course of action is to renew the
component concerned. The owner whose
interest extends beyond mere component
renewal should obtain a copy of the
Automobile Electrical & Electronic Systems
Manual, available from the publishers of this
manual.
It is necessary to take extra care when
working on the electrical system, to avoid
damage to semi-conductor devices (diodes
and transistors), and to avoid the risk of
personal injury. In addition to the precautions
given in Safety first!at the beginning of this
manual, observe the following when working
on the system:
Always remove rings, watches, etc before
working on the electrical system.Even with the
battery disconnected, capacitive discharge
could occur if a component’s live terminal is
earthed through a metal object. This could
cause a shock or nasty burn.
Do not reverse the battery connections.
Components such as the alternator, electronic
control units, or any other components having
semi-conductor circuitry, could be irreparably
damaged.
If the engine is being started using jump
leads and a slave battery, connect thebatteries positive-to-positiveand negative-to-
negative(see “Jump starting”). This also
applies when connecting a battery charger.
Never disconnect the battery terminals, the
alternator, any electrical wiring, or any test
instruments, when the engine is running.
Do not allow the engine to turn the alternator
when the alternator is not connected.
Never test for alternator output by “flashing”
the output lead to earth.
Never use an ohmmeter of the type
incorporating a hand-cranked generator for
circuit or continuity testing.
Always ensure that the battery negative lead
is disconnected when working on the
electrical system.
Before using electric-arc welding equipment
on the car, disconnect the battery, alternator,
and components such as the fuel-
injection/ignition electronic control unit, to
protect them from the risk of damage.
Refer to Chapter 13
1In normal use the battery should not require
charging from an external source, unless the
vehicle is laid up for long periods, when it
should be recharged every six weeks or so. If
vehicle use consists entirely of short runs in
darkness it is also possible for the battery to
become discharged. Otherwise, a regular
need for recharging points to a fault in the
battery or elsewhere in the charging system.
2There is no need to disconnect the battery
from the vehicle wiring when using a battery
charger, but switch off the ignition and leave
the bonnet open.
3Domestic battery chargers (up to about 6
amps output) may safely be used overnight
without special precautions. Make sure that
the charger is set to deliver 12 volts before
connecting it. Connect the leads (red or
positive to the positive terminal, black or
negative to the negative terminal) before
switching the charger on at the mains.
4When charging is complete, switch off at
the mains beforedisconnecting the charger
from the battery. Remember that the battery
will be giving off hydrogen gas, which is
potentially explosive.
5Charging at a higher rate should only be
carried out under carefully controlled
conditions. Very rapid or “boost” charging
should be avoided if possible, as it is liable to
cause permanent damage to the battery
through overheating.
6During any sort of charging, battery
electrolyte temperature should never exceed
38°C (100°F). If the battery becomes hot, or
the electrolyte is effervescing vigorously,
charging should be stopped.
3Battery - charging
2Electrical fault-finding - general
information
Engine electrical systems 5•3
5
Warning. The voltages produced
by the electronic ignition system
are considerably higher than those
produced by conventional
systems. Extreme care must be taken when
working on the system with the ignition
switched on. Persons with surgically-
implanted cardiac pacemaker devices
should keep well clear of the ignition
circuits, components and test equipment.
procarmanuals.com