1985 FORD GRANADA warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 47 of 255

manifold. Piston blow-by gases are drawn
through the oil separator and the vent valve to
the inlet manifold. The blow-by gases are then
drawn into the engine together with the fuel/air
mixture. Refer to Chapter 1 for maintenance of
the system.
The following operations can be carried out
without removing the engine from the vehicle.
a)Removal of the camshafts.
b)Removal and servicing of the cylinder
head.
c)Removal of the timing chain and
sprockets.
d)Removal of the oil pump.
e)Removal of the sump.
f)Removal of the pistons and connecting
rods.
g)Removal of the big-end bearings.
h)Removal of the engine mountings.
i)Removal of the clutch and flywheel.
j)Removal of the crankshaft front and rear
oil seals.
The following operations can only be carried
out after removing the engine from the vehicle.
a)Removal of the crankshaft main bearings.
b)Removal of the crankshaft.
Note: A hoist and lifting tackle will be required
to lift the engine out of the vehicle.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the bonnet.
3On carburettor models, remove the air cleaner.
4On fuel-injection models, remove the air
inlet hose, plenum chamber and air cleaner lid
as an assembly.
5Disconnect the breather hose from the
camshaft cover, and unscrew the bolt
securing the hose support bracket to the left-
hand side of the cylinder head (see
illustration).
6Drain the cooling system.
7To provide additional working space,
remove the radiator.8Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
water pump housing on the left-hand side of
the engine and the cylinder head (see
illustration).
9Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing.
10Disconnect the heater coolant hose from
the inlet manifold.
11Where applicable, release the coolant
hose from the bracket under the carburettor
automatic choke housing.
12Disconnect the throttle cable and (where
necessary) speed control cable from the
throttle linkage.
13On carburettor models, disconnect the
vacuum pipe from the engine management
module.
14Disconnect the brake servo vacuum hose
(where necessary) from the inlet manifold.
15On fuel-injection models, disconnect the
vacuum pipes from the MAP sensor (located
on the suspension turret on the right-hand
side of the engine compartment) and, where
applicable, the air conditioning system.
16On carburettor models, disconnect the
fuel supply and return hoses at the
carburettor, and plug the ends of the hoses to
minimise petrol spillage. Take adequate fire
precautions.
17On fuel-injection models, slowly loosen
the fuel feed union at the fuel rail to relieve the
pressure in the fuel system before
disconnecting the union. Be prepared for
petrol spillage and take adequate fire
precautions. Disconnect the fuel feed hose,and disconnect the fuel return hose from the
fuel pressure regulator. Plug the ends of the
hoses to minimise petrol spillage.
18Disconnect the HT lead from the ignition
coil, and unclip it from the timing chain cover.
19Disconnect the wiring from the following
components as applicable, depending on
model. Then free the wiring loom from any
necessary retaining clips or ties and position it
clear of the engine.
a)Alternator.
b)Starter motor.
c)Oil pressure warning lamp switch.
d)Temperature gauge sender.
e)Cooling fan switch.
f)Anti-dieselling valve (carburettor models).
g)Automatic choke heater (carburettor
models).
h)Engine coolant temperature sensor.
i)Crankshaft speed/position sensor.
j)Air charge temperature sensor.
k)Throttle position sensor.
l)Fuel temperature sensor.
m)Fuel injectors.
20Remove the water pump/alternator
drivebelt, then unbolt the power steering
pump from the mounting bracket and move it
clear of the engine. Note that there is no need
to disconnect the fluid hoses, but make sure
that the pump is adequately supported to
avoid straining them.
21On models fitted with air conditioning,
unbolt the air conditioning compressor from the
mounting bracket, and move it clear of the
engine (see illustration). Do notdisconnect the
hoses, but make sure that the compressor is
adequately supported to avoid straining them.
22Unscrew and remove the top engine-to-
gearbox bolts which are accessible from the
engine compartment. Note the location of the
bolts, and the positions of the earth strap and
any wiring clips attached to the bolts.
23Unscrew the securing bolt, and
disconnect the earth lead from the rear left-
hand side of the cylinder head.
24Unscrew the nuts securing the engine
mountings to the engine mounting brackets.
25Apply the handbrake, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking”).
26Drain the engine oil into a container.
5Engine - removal leaving manual
gearbox in vehicle
4Major operations requiring
engine removal
3Major operations possible with
the engine in the vehicle
2B•4DOHCengine
5.5 Removing the hose support bracket
bolt from the cylinder head5.8 Water pump coolant hoses (viewed
from above)
5.21 Air conditioning compressor mounting
bolts (arrowed) (viewed from underneath)
Warning: Vehicles equipped with
air conditioning: Components of
the air conditioning system may
obstruct work being undertaken
on the engine, and it is not always possible
to unbolt and move them aside sufficiently,
within the limits of their flexible pipes. In
such a case, the system should be
discharged by a Ford dealer or air
conditioning specialist. Refer also to the
precautions given in Chapter 3.
procarmanuals.com
Page 48 of 255

27Remove the starter motor.
28Remove the exhaust downpipe.
29Ensure that the steering wheel is
positioned in the straight-ahead position then,
using a dab of paint or a suitable marker pen,
make alignment marks between the
intermediate shaft lower clamp and steering
gear pinion. Slacken and remove the lower
clamp bolt then disconnect the intermediate
shaft from the steering gear (see illustration).
30Working inside the vehicle, place a
wooden block under the clutch pedal to raise
it fully against the stop, so holding the
automatic adjuster pawl clear of the toothed
quadrant.
31Disconnect the clutch cable from the
clutch release arm, and pass the cable
through the bellhousing.
32Support the gearbox with a trolley jack,
using a block of wood between the jack and
the gearbox to spread the load.
33Unscrew and remove the remaining
engine-to-gearbox bolts, and remove the bolt
from the engine adapter plate (see
illustration). Recover any shims fitted
between the sump and the gearbox when
removing the lower engine-to-gearbox bolts.
34Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant wires, pipes and hoses have been
disconnected and positioned clear of the
engine to facilitate engine removal.
35Attach a suitable hoist to the engine lifting
brackets located at the front and rear of the
cylinder head, and carefully take the weight of
the engine.
36To improve clearance in the engine
compartment when lifting the engine, unbolt
the engine mounting brackets from the
cylinder block, and remove them (see
illustration).
37Detach the brake lines from the front
suspension crossmember (see illustration).
38Support the crossmember with a jack (do
not remove the jack from under the gearbox),
then loosen the bolts securing the
crossmember to the underbody. Remove the
bolts from one side, and carefully lower the
crossmember to allow sufficient room for the
sump to clear the steering rack and
crossmember when pulling the engine
forwards from the gearbox (see illustration).39Gently raise the engine, then pull it
forwards to disconnect it from the gearbox.
Ensure that the gearbox is adequately
supported, and take care not to strain the
gearbox input shaft.
40Once clear of the gearbox, lift the engine
from the vehicle, taking care not to damage
the components in the engine compartment.
Note:Refer to Part A, Section 4 of this
Chapter and to the warning that appears at the
start of Section 5 before proceeding. A
suitable hoist and lifting tackle will be required
for this operation.
1Proceed as described in paragraphs 1 to 21
of Section 5.
2Unscrew and remove the top engine-to-
transmission bolts which are accessible from
the engine compartment. Note the location of
the earth strap, vacuum pipe bracket, and
transmission dipstick tube bracket, as
applicable.
3Proceed as described in paragraphs 23 to 29
of Section 5.4Where applicable, remove the bolt securing
the transmission fluid dipstick tube to the left-
hand side of the cylinder block.
5Working through the starter motor aperture,
unscrew the four torque converter-to-
driveplate nuts. It will be necessary to turn the
crankshaft, using a suitable spanner on the
crankshaft pulley bolt, in order to gain access
to each bolt in turn through the aperture.
6Support the transmission with a trolley jack,
using a block of wood between the jack and
the transmission to spread the load.
7Unscrew and remove the remaining engine-
to-transmission bolts, and remove the bolt
from the engine adapter plate. Recover any
shims fitted between the sump and the
transmission when removing the lower engine-
to-transmission bolts. Where applicable, pull
the blanking plug from the adapter plate.
8Proceed as described in paragraphs 34 to 38
of Section 5.
9Gently raise the engine, then pull the engine
forwards to disconnect it from the
transmission. Ensure that the torque converter
is held firmly in place in the transmission
housing, otherwise it could fall out resulting in
fluid spillage and possible damage. It may be
necessary to rock the engine a little to release
it from the transmission.
10Once clear of the transmission, lift the
engine from the vehicle, taking care not to
damage the components in the engine
compartment.
6Engine - removal leaving
automatic transmission in vehicle
DOHCengine 2B•5
2B
5.29 Intermediate shaft lower clamp bolt
(arrowed)5.33 Engine adaptor plate bolt (arrowed)5.36 Remove the engine mounting brackets
to improve clearance
5.37 Removing a brake line securing clip
from the suspension crossmember5.38 Removing a suspension crossmember
securing bolt
It may be necessary to rock
the engine a little to release it
from the gearbox.
procarmanuals.com
Page 49 of 255

Note: Refer to Part A, Section 4 of this Chapter
and to the warning that appears at the start of
Section 5 before proceeding. A hoist and lifting
tackle will be required for this operation.
1Proceed as described in paragraphs 1 to 21
of Section 5.
2Unscrew the securing bolt, and disconnect
the earth lead from the rear left-hand side of
the cylinder head.
3Unscrew the nuts securing the engine
mountings to the engine mounting brackets.
4Jack up the vehicle and support it securely
on axle stands (see “Jacking”). Ensure that
there is enough working room beneath the
vehicle.
5To improve access, disconnect the exhaust
downpipe from the manifold and remove the
exhaust system.
6Drain the engine oil into a suitable container.
7On models fitted with a catalytic converter,
release the securing clips and withdraw the
exhaust heat shield from under the vehicle for
access to the propeller shaft.
8Remove the propeller shaft.
9Where applicable, bend back the locktabs,
then unscrew the two bolts in each case
securing the two anti-roll bar mounting clamps
to the vehicle underbody. Lower the anti-roll
bar as far as possible.
10Proceed as described in paragraphs 30
and 31 of Section 5.
11Support the gearbox with a trolley jack,
using a block of wood between the jack and
the gearbox to spread the load.
12Unscrew the four nuts securing the
gearbox crossmember to the vehicle
underbody. Unscrew the central bolt securing
the crossmember to the gearbox, and remove
the crossmember. Note the position of the
earth strap, where applicable. Recover the
mounting cup, and the exhaust mounting
bracket and heat shield (as applicable).
13Lower the gearbox slightly on the jack,
then remove the circlip, and disconnect the
speedometer drive cable from the gearbox.
14Disconnect the wiring from the reversing
lamp switch, and on models with fuel-injection,
disconnect the wiring from the vehicle speed
sensor mounted in the side of the gearbox.
15Slacken and remove the two bolts and
washers (one either side) securing the gear
linkage support bracket to the gearbox.
16Using a pin punch, drive out the roll pin
securing the gearchange rod to the gear linkage.
17Attach a hoist to the engine lifting brackets
located at the front and rear of the cylinder head,
and slowly take the weight of the engine. Arrange
the lifting tackle so that the engine/gearbox
assembly will assume a steep angle of
approximately 40°to 45°as it is being removed.
18To improve clearance in the engine
compartment when lifting the engine, unboltthe engine mounting brackets from the
cylinder block, and remove them.
19Ensure that the steering wheel is positioned
in the straight-ahead position then, using a dab
of paint or a marker pen, make alignment marks
between the intermediate shaft lower clamp
and steering gear pinion. Slacken and remove
the lower clamp bolt then disconnect the
intermediate shaft from the steering gear.
20Detach the brake lines from the front
suspension crossmember.
21Support the crossmember with a jack (do not
remove the jack from under the gearbox), then
loosen the bolts securing the crossmember to the
underbody. Remove the crossmember securing
bolts, and carefully lower the crossmember to
allow sufficient room for the engine sump to clear
the steering rack and crossmember as the
engine/gearbox assembly is removed.
22Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant wires, pipes and hoses have been
disconnected to facilitate removal of the
engine/gearbox assembly.
23Raise the engine/gearbox, at the same
time lowering the trolley jack which is
supporting the gearbox.
24Place a suitable rod across the vehicle
underbody to support the gear linkage support
bracket whilst the gearbox is removed.
25Tilt the engine/gearbox assembly using
the hoist and the trolley jack, until the
assembly can be lifted from the vehicle. Take
care not to damage surrounding components.
26If the vehicle is to be moved, with the
engine/gearbox assembly removed, temporarily
refit the suspension crossmember and the anti-
roll bar to the underbody, and reconnect the
steering column to the intermediate shaft.
27To separate the engine from the gearbox,
proceed as follows.
28Remove the starter motor.
29Support the engine and gearbox
horizontally on blocks of wood.
30Unscrew the engine-to-gearbox bolts,
noting the locations of the bolts, and the
positions of the earth strap and any wiring clips
attached to the bolts. Recover any shims fitted
between the sump and the gearbox when
removing the lower engine-to-gearbox bolts.
31Unscrew the bolt from the engine adapter
plate.
32Pull the engine and gearbox apart, taking
care not to strain the gearbox input shaft. It
may be necessary to rock the units slightly to
separate them.
Note: Refer to Part A, Section 4 of this
Chapter and to the warning that appears at the
start of Section 5 before proceeding. A
suitable hoist and lifting tackle will be required
for this operation. Any suspected faults in the
automatic transmission should be referred to a
Ford dealer or automatic transmissionspecialist before removal of unit, as the
specialist fault diagnosis equipment is
designed to operate with the transmission in
the vehicle.
1Proceed as described in paragraphs 1 to 21
of Section 5.
2Unscrew the securing bolt, and disconnect
the earth lead from the rear left-hand side of
the cylinder head.
3Unscrew the nuts securing the engine
mountings to the engine mounting brackets.
4Jack up the vehicle and support it securely
on axle stands (see “Jacking”). Ensure that
there is enough working room beneath the
vehicle.
5To improve access, disconnect the exhaust
downpipe from the manifold and remove the
exhaust system .
6Drain the engine oil into a suitable container.
7On models fitted with a catalytic converter,
release the securing clips and withdraw the
exhaust heat shield from under the vehicle for
access to the propeller shaft.
8Remove the propeller shaft.
9Where applicable, bend back the locktabs,
then unscrew the two bolts in each case
securing the two anti-roll bar mounting clamps
to the vehicle underbody. Lower the anti-roll
bar as far as possible.
10Support the transmission with a trolley
jack, using a block of wood between the jack
and the transmission to spread the load.
11Unscrew the four bolts securing the
transmission crossmember to the vehicle
underbody. Unscrew the central bolt securing
the crossmember to the transmission, and
remove the crossmember. Note the position of
the earth strap, where applicable. Recover the
mounting cup, and the exhaust mounting
bracket and heat shield (as applicable).
12Lower the transmission slightly on the jack.
13Unscrew the unions and disconnect the
fluid cooler pipes from the transmission. Plug
the open ends of the pipes and the
transmission to prevent dirt ingress and fluid
leakage. Where applicable, detach the fluid
cooler pipe bracket from the engine mounting
bracket, and move it to one side.
14Remove the two clips securing the
selector rod, and detach the selector rod from
the manual selector lever, and the selector
lever on the transmission.
15Disconnect the wiring from the starter
inhibitor switch, downshift solenoid, lock-up
clutch, reversing lamp switch, and where
applicable, the 3rd/4th gearchange solenoid.
16Remove the securing screw, and
disconnect the speedometer cable (where
fitted) from the transmission extension
housing. Plug the opening in the transmission
to prevent dirt ingress.
17Proceed as described in paragraphs 17 to 26
of Section 7, substituting transmission for
gearbox and ignoring paragraph 24.
18To separate the engine from the
transmission, proceed as follows.
19Remove the starter motor.
20Support the engine and transmission
horizontally on blocks of wood.
8Engine/automatic
transmission assembly -
removal and separation
7Engine/manual gearbox
assembly - removal and
separation
2B•6DOHCengine
procarmanuals.com
Page 51 of 255
together, guide the torque converter studs
through the holes in the driveplate. When the
engine is positioned flush with the engine
adapter plate and the transmission housing,
check that the torque converter is free to move
axially a small amount before refitting and
tightening the engine-to-transmission bolts.
6Do not tighten the torque converter-to-
driveplate nuts until the lower engine-to-
transmission bolts have been fitted and
tightened.
7Ensure that the roadwheels and the steering
wheel are in the straight-ahead position then
align the marks made on removal and
reconnect the intermediate shaft to the
steering gearing. Tighten the clamp bolt to the
specified torque.
8Reconnect the selector rod and adjust as
described in Chapter 7, PartB.
9Refit the propeller shaft.
10Refit the exhaust system.
11Fill the engine with the correct grade and
quantity of oil.
12Check the throttle cable adjustment. Where
necessary, also adjust the speed control cable
in the same way so that there is only a small
amount of slack present in the cable.
13Reconnect the coolant hoses to the water
pump housing.
14Fill the cooling system.
15Check and if necessary top-up the
transmission fluid level.
16Tighten all fixings to the specified torque,
where applicable.
Proceed as described in Part A, Section 23
of this Chapter but note that on certain
models, it may be necessary to unbolt the
engine mounting brackets from the cylinder
block to allow sufficient clearance to remove
the mountings.
1Refer to Part A, Section 8 of this Chapter,
paragraphs 1 to 8 inclusive.
2A selection of splined and Torx sockets will
be required to remove many of the bolts when
dismantling the engine.
3Before dismantling the main engine
components, the following externally mounted
ancillary components can be removed.
a)Inlet manifold (and carburettor, where
applicable).
b)Exhaust manifold.
c)Alternator.
d)Water pump, and thermostat.
e)Water pump/alternator drivebelt tensioner.
f)Distributor cap, HT leads and spark plugs.
g)Oil pressure warning lamp switch.
h)Crankshaft speed/position sensor.
i)Oil filter.
j)Dipstick.
k)Engine mounting brackets (if not already
done).
l)Crankcase ventilation pipe and hoses.m)Clutch.
n)Alternator mounting bracket.
o)Air conditioning compressor mounting
bracket (where applicable).
p)Engine lifting brackets.
Note: A puller will be required to remove the
crankshaft pulley. A new crankshaft pulley bolt,
a new timing chain tensioner plunger
assembly, new upper and lower timing chain
cover gaskets and a new camshaft cover
gasket and reinforcing sleeve sealing rings
must be used on refitting.
1If the engine is in the car, carry out thefollowing operations.
a)Disconnect the battery negative lead.
b)To improve access, remove the radiator. It
will be difficult to remove the crankshaft
pulley with the radiator in place.
c)On carburettor models, remove the air
cleaner.
d)On fuel-injection models, remove the air
inlet hose, plenum chamber and air
cleaner lid as an assembly.
e)Disconnect the breather hose from the
camshaft cover.
f)Remove the distributor cap and HT leads,
and the rotor arm and housing.
2Proceed as described in paragraphs 2 to 11
inclusive of Section 18 (see illustration).
3Remove the water pump/alternator
drivebelt.
15Timing chain and sprockets -
removal and refitting
14Engine dismantling - general
information
13Engine mountings - renewal
2B•8DOHCengine
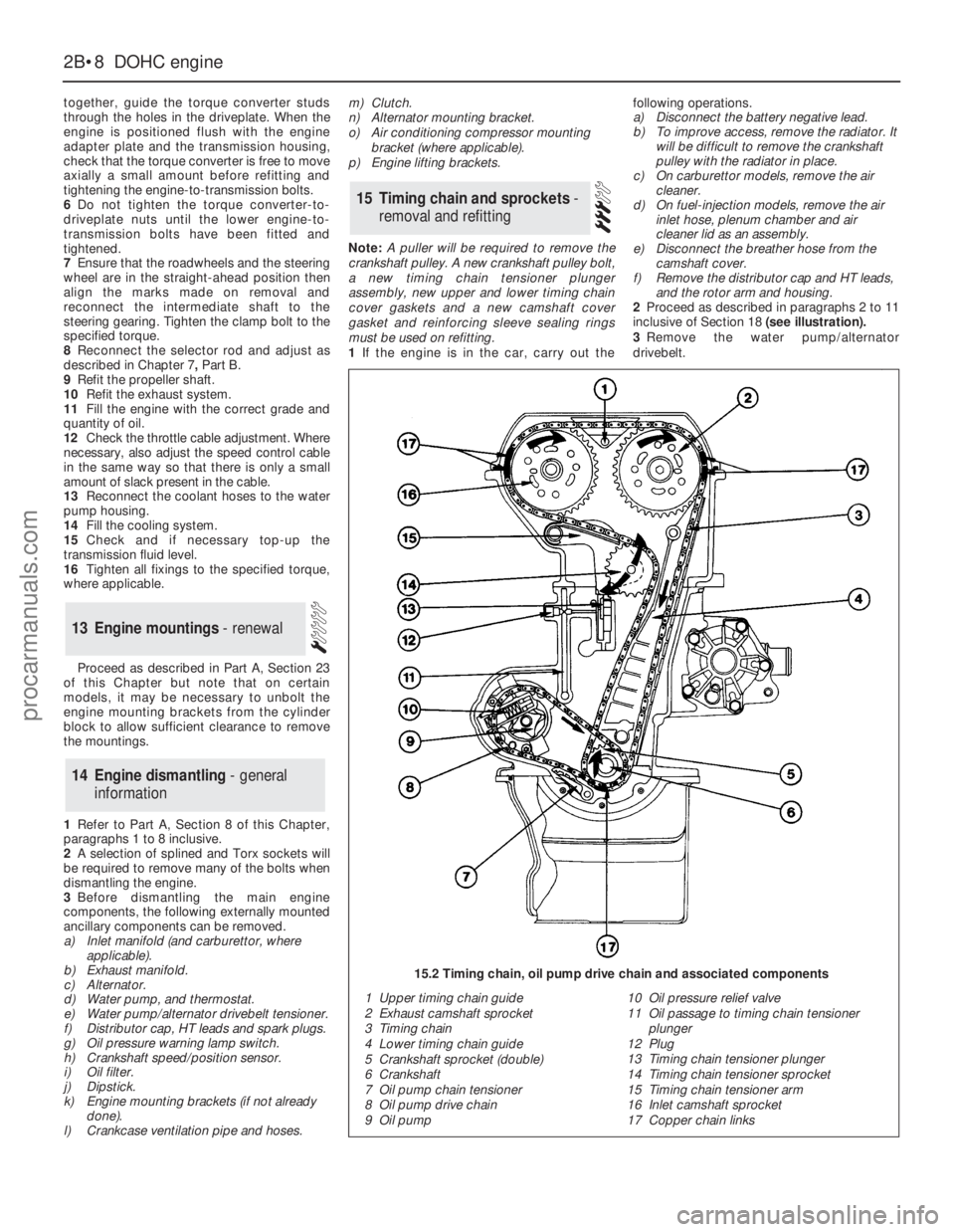
1 Upper timing chain guide
2 Exhaust camshaft sprocket
3 Timing chain
4 Lower timing chain guide
5 Crankshaft sprocket (double)
6 Crankshaft
7 Oil pump chain tensioner
8 Oil pump drive chain
9 Oil pump10 Oil pressure relief valve
11 Oil passage to timing chain tensioner
plunger
12 Plug
13 Timing chain tensioner plunger
14 Timing chain tensioner sprocket
15 Timing chain tensioner arm
16 Inlet camshaft sprocket
17 Copper chain links
15.2 Timing chain, oil pump drive chain and associated components
procarmanuals.com
Page 55 of 255

the chain. Secure the chain using a cable-tie
through two of the chain links to prevent it
from dropping off the crankshaft sprocket.
9Using a suitable pair of pliers, extract the
circlip from the chain tensioner arm pivot pin,
taking care not to drop it into the timing case,
then withdraw the pivot pin from the tensioner
arm. If the pivot pin proves difficult to
withdraw, an M6 bolt can be screwed into the
end to facilitate removal (see illustration).
10Lift the tensioner arm from the timing case.
11Lift the tensioner plunger assembly from the
cylinder head, and discard it (see illustration).12Take note of the markings on the camshaft
bearing caps, then progressively unscrew the
bearing cap securing nuts.
13Remove the bearing cap securing nuts,
then lift off the camshaft oil spray bars, and
the timing chain guide plate(see illustration).
14Lift off the bearing caps, and then lift out
the two camshafts (see illustrations).
15Withdraw the cam followers from their
locations in the cylinder head, keeping them in
order so that they can be refitted in theiroriginal locations (see illustration). It is
advisable to store the cam followers upright in
an oil bath until they are to be refitted. Ensure
that the depth of oil is sufficient to fully cover
the cam followers.
16Working at the front of the cylinder head,
unscrew the three small M8 cylinder head
bolts which are accessible through the timing
case(see illustration).
17Working in the reverse order to that shown
for tightening the cylinder head bolts(see
illustration), progressively loosen the
remaining cylinder head bolts, and withdraw
them from the cylinder head.
18Lift the cylinder head from the block. If the
cylinder head is stuck, tap it free with a soft-
faced mallet. Do not insert a lever into the joint
between the cylinder head and block, as this
may result in damage to the mating faces.
Place the cylinder head on blocks of wood to
prevent damage to the valves.
19Recover the gasket, and the locating
dowels if they are loose, noting the positions
of the locating dowels.
20Commence refitting as follows.
21Turn the crankshaft so that No 1 piston is
approximately 20.0 mm (0.8 in) before TDC.
This precaution will prevent possible contact
between the valves and pistons.
22Make sure that the mating faces of the
cylinder block and cylinder head are perfectly
clean, then refit the locating dowels (where
applicable) and locate a new gasket over the
2B•12DOHCengine
18.9 Removing the chain tensioner arm
pivot pin circlip
18.15 Withdrawing a cam follower
18.14a Lifting off a camshaft bearing cap
18.16 M8 cylinder head bolts (arrowed)
located at front of cylinder head
18.14b Lifting out the exhaust camshaft
18.17 Cylinder head bolt tightening
sequence
A Long M8 boltsB Short M8 bolt
18.11 Lifting the chain tensioner plunger
assembly from the cylinder head18.13 Lifting off a camshaft oil spray bar
The inlet camshaft is normally
identified by a green paint
mark. If necessary, identify
the camshafts so that they
can be refitted in their correct positions.
Warning: Take care when removing
the plunger assembly; injury could
result if the piston flies out. A new
timing chain tensioner plunger
assembly should be installed on refitting.
procarmanuals.com
Page 56 of 255
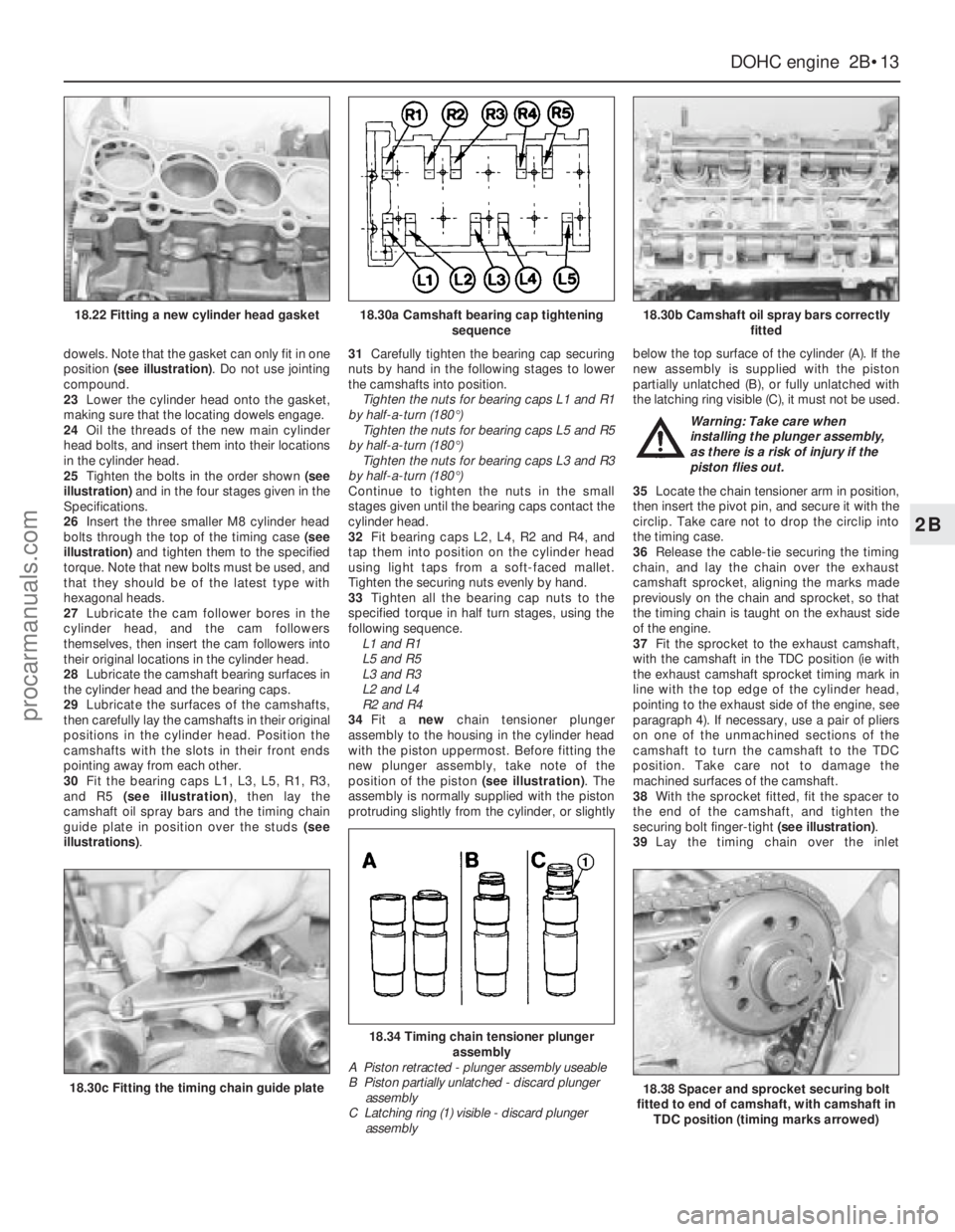
dowels. Note that the gasket can only fit in one
position (see illustration). Do not use jointing
compound.
23Lower the cylinder head onto the gasket,
making sure that the locating dowels engage.
24Oil the threads of the new main cylinder
head bolts, and insert them into their locations
in the cylinder head.
25Tighten the bolts in the order shown (see
illustration)and in the four stages given in the
Specifications.
26Insert the three smaller M8 cylinder head
bolts through the top of the timing case (see
illustration)and tighten them to the specified
torque. Note that new bolts must be used, and
that they should be of the latest type with
hexagonal heads.
27Lubricate the cam follower bores in the
cylinder head, and the cam followers
themselves, then insert the cam followers into
their original locations in the cylinder head.
28Lubricate the camshaft bearing surfaces in
the cylinder head and the bearing caps.
29Lubricate the surfaces of the camshafts,
then carefully lay the camshafts in their original
positions in the cylinder head. Position the
camshafts with the slots in their front ends
pointing away from each other.
30Fit the bearing caps L1, L3, L5, R1, R3,
and R5 (see illustration), then lay the
camshaft oil spray bars and the timing chain
guide plate in position over the studs (see
illustrations).31Carefully tighten the bearing cap securing
nuts by hand in the following stages to lower
the camshafts into position.
Tighten the nuts for bearing caps L1 and R1
by half-a-turn (180°)
Tighten the nuts for bearing caps L5 and R5
by half-a-turn (180°)
Tighten the nuts for bearing caps L3 and R3
by half-a-turn (180°)
Continue to tighten the nuts in the small
stages given until the bearing caps contact the
cylinder head.
32Fit bearing caps L2, L4, R2 and R4, and
tap them into position on the cylinder head
using light taps from a soft-faced mallet.
Tighten the securing nuts evenly by hand.
33Tighten all the bearing cap nuts to the
specified torque in half turn stages, using the
following sequence.
L1 and R1
L5 and R5
L3 and R3
L2 and L4
R2 and R4
34Fit a newchain tensioner plunger
assembly to the housing in the cylinder head
with the piston uppermost. Before fitting the
new plunger assembly, take note of the
position of the piston (see illustration). The
assembly is normally supplied with the piston
protruding slightly from the cylinder, or slightlybelow the top surface of the cylinder (A). If the
new assembly is supplied with the piston
partially unlatched (B), or fully unlatched with
the latching ring visible (C), it must not be used.
35Locate the chain tensioner arm in position,
then insert the pivot pin, and secure it with the
circlip. Take care not to drop the circlip into
the timing case.
36Release the cable-tie securing the timing
chain, and lay the chain over the exhaust
camshaft sprocket, aligning the marks made
previously on the chain and sprocket, so that
the timing chain is taught on the exhaust side
of the engine.
37Fit the sprocket to the exhaust camshaft,
with the camshaft in the TDC position (ie with
the exhaust camshaft sprocket timing mark in
line with the top edge of the cylinder head,
pointing to the exhaust side of the engine, see
paragraph 4). If necessary, use a pair of pliers
on one of the unmachined sections of the
camshaft to turn the camshaft to the TDC
position. Take care not to damage the
machined surfaces of the camshaft.
38With the sprocket fitted, fit the spacer to
the end of the camshaft, and tighten the
securing bolt finger-tight (see illustration).
39Lay the timing chain over the inlet
DOHCengine 2B•13
2B
18.22 Fitting a new cylinder head gasket18.30a Camshaft bearing cap tightening
sequence18.30b Camshaft oil spray bars correctly
fitted
18.30c Fitting the timing chain guide plate
18.34 Timing chain tensioner plunger
assembly
A Piston retracted - plunger assembly useable
B Piston partially unlatched - discard plunger
assembly
C Latching ring (1) visible - discard plunger
assembly
18.38 Spacer and sprocket securing bolt
fitted to end of camshaft, with camshaft in
TDC position (timing marks arrowed)
Warning: Take care when
installing the plunger assembly,
as there is a risk of injury if the
piston flies out.
procarmanuals.com
Page 61 of 255

9Extract the bearing shells, and recover the
thrustwashers, keeping them identified for
location.
10The crankshaft and bearings can be
examined and if necessary renovated.
11Commence refitting as follows(see
illustration).
12Wipe the bearing shell locations in the
crankcase, and the crankshaft journals with a
soft non-fluffy rag.
13If the old main bearing shells are to be
renewed (not to do so is a false economy,
unless they are virtually new) fit the five upper
halves of the main bearing shells to their
locations in the crankcase.
14Fit the thrustwashers to the centre main
bearing location, using a little grease to retain
them if necessary. The oil grooves in the
thrustwashers must face outwards (ie facing
the crankshaft webs). Note that where
standard thrustwashers have been fitted in
production, the centre main bearing is
unmarked, but if oversize (0.38 mm)
thrustwashers have been fitted, the centre
main bearing will carry a yellow paint mark.
15Lubricate the crankshaft journals and the
upper and lower main bearing shells with
clean engine oil, then carefully lower the
crankshaft into the crankcase.
16Lubricate the crankshaft main bearing
journals again, and then fit the main bearing caps
in their correct locations, with the arrows on the
caps pointing towards the front of the engine.
17Fit the main bearing cap bolts, noting that
the studded bolts secure bearing caps Nos 3
and 5.
18Lightly tighten all the securing bolts, then
progressively tighten all bolts to the specified
torque.
19Check that the crankshaft rotates freely.
Some stiffness is to be expected with newcomponents, but there must be no tight spots
or binding.
20Check that the crankshaft endfloat is
within the specified limits by inserting a feeler
blade between the centre crankshaft web and
the thrustwashers.
21Refit the sump mounting plate to the front
of the cylinder block, and tighten the securing
bolts to the specified torque.
22Carefully wind a thin layer of tape around
the rear edge of the crankshaft to protect the
oil seal lips as the rear oil seal is installed.
23Refit the crankshaft rear oil seal housing,
using a new gasket, and tighten the securing
bolts to the specified torque.
24Install the new oil seal with reference to
Section 24.
25With the oil seal installed, carefully pull the
tape from the edge of the crankshaft.
26Refit the pistons and connecting rods as
described previously in this Chapter.
27Refit the flywheel/driveplate, and the
timing chain and crankshaft sprocket.
Proceed as described in Part A, Section 27
of this Chapter, noting that the production
bearing undersizes are indicated as follows.
Yellow or red paint marks on crankshaft —
standard diameter main bearing journals.
Green line on crankshaft front counterweight
— main bearing journals 0.25 mm
undersize.
Green spot on counterweight — big-end
bearing journals 0.25 mm undersize.
Refer to Part A, Section 25 of this Chapter,
but note that the connecting rod bolts should
be renewed on reassembly, and when
renewing the cylinder head bolts, the latest
type bolts with hexagonal heads should
always be used.
Proceed as described in Part A, Section 35
of this Chapter, noting the following points.
a)If the cylinder head has been removed,
pay particular attention to the note at the
beginning of Section 18.
b)If removed during any dismantling
operations, new flywheel driveplate bolts
and connecting rod bolts must be used.
c)After reassembling the main engine
components, refer to paragraph 3 of
Section 14 and refit the ancillary
components listed.Refer to Part A, Section 51 of this Chapter,
but note that when the engine is first started, a
metallic tapping noise may be heard. This is
due to the timing chain tensioner plunger
assembly taking time to pressurize with oil,
resulting in a temporarily slack chain. The
noise should stop after a short time, once oil
pressure has built up.
1When engine performance is down, or if
misfiring occurs which cannot be attributed to
the ignition or fuel system, a compression test
can provide diagnostic clues. If the test is
performed regularly it can give warning of
trouble before any other symptoms become
apparent.
2The engine must be at operating
temperature, the battery must be fully charged
and the spark plugs must be removed. The
services of an assistant will also be required.
3Disable the ignition system by dismantling
the coil LT feed. Fit the compression tester to
No 1 spark plug hole. (The type of tester which
screws into the spark plug hole is to be
preferred.)
4Have the assistant hold the throttle wide
open and crank the engine on the starter.
Record the highest reading obtained on the
compression tester.
5Repeat the test on the remaining cylinders,
recording the pressure developed in each.
6Desired pressures are given in the
Specifications. If the pressure in any cylinder
is low, introduce a teaspoonful of clean engine
oil into the spark plug hole and repeat the test.
7If the addition of oil temporarily improves
the compression pressure, this indicates that
bore or piston wear was responsible for the
pressure loss. No improvement suggests that
leaking or burnt valves, or a blown head
gasket, may be to blame.
8A low reading from two adjacent cylinders is
almost certainly due to the head gasket
between them having blown.
9On completion of the test, refit the spark
plugs and reconnect the coil LT feed.
35Compression test -
description and interpretation
34Initial start-up after overhaul
or major repair
33Engine reassembly - general
information
32Examination and renovation -
general information
31Crankshaft and bearings -
examination and renovation
2B•18DOHCengine
30.11 Crankshaft main bearings and
associated components
1 Bearing cap
2 Thrustwasher
3 Stud for oil baffle
4 Identification markings
5 Bearing shell without oil groove
6 Bearing shell with oil groove
7 Bearing seat in cylinder block
procarmanuals.com
Page 62 of 255

Chapter 2 Part C:
2.4, 2.8 and 2.9 litre V6 engines
Ancillary components - refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Ancillary components - removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Camshaft and bearings - examination and renovation . . . . . . . . . .22
Camshaft and intermediate plate - refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Camshaft and intermediate plate - removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Compression test - description and interpretation . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Crankcase ventilation system - general information . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Crankshaft and bearings - examination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Crankshaft and main bearings - refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Crankshaft and main bearings - removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Crankshaft front oil seal - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Crankshaft rear oil seal - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Cylinder bores - examination and renovation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Cylinder heads - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Cylinder heads - refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Cylinder heads - removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Engine - refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Engine - removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Engine dismantling - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Engine mountings - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Engine reassembly - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Examination and renovation - general infomation . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19Flywheel/driveplate and adapter plate - refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Flywheel/driveplate and adapter plate - removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Flywheel ring gear - examination and renovation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Initial start-up after overhaul or major repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Major operations possible with the engine in the vehicle . . . . . . . . .2
Major operations requiring engine removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Methods of engine removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Oil pump - dismantling, examination and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . .27
Oil pump - refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Oil pump - removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Pistons and connecting rods - examination and renovation . . . . . .25
Pistons and connecting rods - refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Pistons and connecting rods - removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Rocker shaft - dismantling, examination and reassembly . . . . . . . .20
Sump - refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Sump - removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Tappets and pushrods - examination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Timing cover and drive - refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Timing cover and drive - removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Valve clearances - checking and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
2.8 litre engine
General
Manufacturer’s code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . PRE
Bore - mm (in) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93.0 (3.66)
Stroke - mm (in) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68.5 (2.70)
Cubic capacity - cc (cu in) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2792 (170)
Compression ratio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.2:1
Compression pressure at cranking speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.5 to 12.5 bar (167 to 181 lbf/in
2)
Maximum power (DIN, kW @ rpm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110 @ 5800
Maximum torque (DIN, Nm @ rpm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216 @ 3000
Lubrication system
Oil type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See “Lubricants and fluids”
Oil capacity (drain and refill, including filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.25 litres (7.5 pints) approx
Oil pressure (SAE 10W/30 oil at 80°C/176°F):
At 750 rpm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 bar
At 2000 rpm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.5 bar
Oil pressure relief valve opening pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 to 4.7 bar
Oil pressure warning light switch setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.3 to 0.5 bar
2C•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
2C
procarmanuals.com