1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO brake
[x] Cancel search: brakePage 287 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 287
DRIVE TRAIN
MANUAL TRANSMISSION
UNDERSTANDING THE MANUAL TRANSMISSION
Because of the way an internal combus tion engine breathes, it can produce
torque (or twisting force) only withi n a narrow speed range. Most overhead
valve pushrod engines must turn at about 2500 rpm to produce their peak
torque. Often by 4500 rpm, they are prod ucing so little torque that continued
increases in engine speed produce no power increases.
The torque peak on overhead camshaft engines is, generally, much higher, but
much narrower.
The manual transmission and clutch are employed to vary the relationship
between engine RPM and the speed of the w heels so that adequate power can
be produced under all circumst ances. The clutch allows engine torque to be
applied to the transmission input shaft gradually, due to mechanical slippage.
The vehicle can, consequently, be star ted smoothly from a full stop.
The transmission changes the ratio between the rotating speeds of the engine
and the wheels by the use of gears. 4-speed or 5-speed transmissions are most
common. The lower gears al low full engine power to be applied to the rear
wheels during acceleration at low speeds.
The clutch driveplate is a thin disc, the center of which is splined to the
transmission input shaft. Both sides of the disc are covered with a layer of
material which is similar to brake li ning and which is capable of allowing
slippage without roughness or excessive noise.
The clutch cover is bolted to the engine flywheel and incorporates a diaphragm
spring which provides the pressure to engage the clutch. The cover also houses
the pressure plate. When the clutch pe dal is released, the driven disc is
sandwiched between the pressu re plate and the smooth surface of the flywheel,
thus forcing the disc to turn at th e same speed as the engine crankshaft.
The transmission contains a mainshaft which passes all the way through the
transmission, from the clutch to the dr iveshaft. This shaft is separated at one
point, so that front and rear portions can turn at different speeds.
Power is transmitted by a countershaft in the lower gears and reverse. The
gears of the countershaft mesh with gear s on the mainshaft, allowing power to
be carried from one to the other. Countershaft gears are often integral with that
shaft, while several of the mainshaft gea rs can either rotate independently of
the shaft or be locked to it. Shifting from one gear to the next causes one of the
gears to be freed from rotating with the shaft and locks another to it. Gears are
locked and unlocked by internal dog clutc hes which slide between the center of
the gear and the shaft. The forward gears us ually employ synchronizers; friction
Page 295 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 295
of the spring bow outward, pushing the pre
ssure plate into closer contact with
the clutch disc. As the disc and plate mo ve closer together, friction between the
two increases and slippage is reduced until, when full spring pressure is applied
(by fully releasing the pedal) the speed of the disc and plate are the same. This
stops all slipping, creating a direct connection between the plate and disc which
results in the transfer of power from t he engine to the transmission. The clutch
disc is now rotating with the pressure plate at engine speed and, because it is
splined to the transmission shaft, the shaft now turns at the same engine speed.
The clutch is operating properly if: 1. It will stall the engine when released with the vehicle held stationary.
2. The shift lever can be moved freel y between 1st and reverse gears when
the vehicle is stationary and the clutch disengaged.
APPLICATION
All 1982-83 vehicles use a mechanical (non-hydraulic) clutch; 1984-92 models
use a hydraulic clutch. With the hydraulic clutch, no adjustment of the clutch
pedal or the linkage is required. On t he mechanical type, the only required
adjustment is to maintain the proper clutch pedal freeplay. The freeplay\
adjustment is very important, for it determines the engaging and disengaging
characteristics of the clutch assembly.
The clutch assembly consists of: a flywheel, a pressure plate, a throwout
bearing and fork, a clutch pedal, and an actuating lever (non-hydraulic) or a
master cylinder/slave cylinder (hydraulic).
The hydraulic system utilizes a remote re servoir which is mounted to the power
brake booster, a master cy linder mounted to the cowl p anel and a slave cylinder
that is mounted to the bell housing. Th e system is operated directly by the
clutch pedal. When adding fl uid to the reservoir, always use a type which meets
DOT 3 specifications.
CAUTION - The clutch driven disc contains asbestos, which has been
determined to be a cancer causing agen t. Never clean clutch surfaces with
compressed air! Avoid inhaling any dus t from any clutch surface! When
cleaning clutch surfaces, use a commercia lly available brake cleaning fluid.
FREE-PLAY ADJUSTMENT
MECHANICAL LINKAGE 1. Disconnect the return sp ring at the clutch fork.
2. Hold the pedal against the rubber bumper on the dash brace.
3. Push the clutch fork so that th e throwout bearing lightly contacts the
pressure plate fingers.
Page 302 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 302
7. To install, reverse the removal
procedures. Torque the master cylinder-
to-cowl brace nuts to 10-15 ft. lbs. (14-20 Nm). Fill master cylinder with
new hydraulic fluid conforming to DO T 3 specifications. Bleed and check
the hydraulic clutch system for leaks.
OVERHAUL 1. Remove the filler cap and drain fl uid from the master cylinder.
2. Remove the reservoir and seal from the master cylinder. Pull back the
dust cover and remove the snapring.
3. Remove the push rod assembly. Usi ng a block of wood, tap the master
cylinder on it to eject the plunger a ssembly from the cylinder bore.
4. Remove the seal (carefully) from the front of the plunger assembly,
ensuring no damage occurs to the plunger surfaces.
5. From the rear of t he plunger assembly, remove the spring, the support,
the seal and the shim.
6. Using clean brake fluid, clean all of the parts.
7. Inspect the cylinder bore and t he plunger for ridges, pitting and/or
scratches, the dust cover for wear and cracking; replace the parts if any
of the conditions exist.
To assemble: 8. Use new seals, lubric ate all of the parts in clean brake fluid, fit the
plunger seal to the plunger and reve rse the disassembly procedures.
9. Insert the plunger assembly, va lve end leading into the cylinder bore
(easing the entrance of the plunger seal).
10. Position the push rod assembly into the cylinder bore, then install a new
snapring to retain the push rod. Install dust cover onto the master
cylinder. Lubricate the inside of t he dust cover with Girling® Rubber
Grease or equivalent.
Be careful not to use any lubricant that will deteriorate rubber dust covers or
seals.
SLAVE CYLINDER
On vehicles equipped with a hydraulic clutch release mechanism, the slave
cylinder is located on the left side of the bellhousing and controls the clutch
release fork operation.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Raise and safely support the front of the vehicle on jackstands.
3. Disconnect the hydraulic line from clutch master cylinder. Remove the
line-to-chassis screw and the c lip from the chassis.
Be sure to plug the line opening to k eep dirt and moisture out of the system.
Page 303 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 303
4. Remove the slave cyli
nder-to-bellhousing nuts.
5. Remove the push rod and the slav e cylinder from the vehicle, then
overhaul it (if necessary).
6. To install, reverse the removal pr ocedures. Lubricate leading end of the
slave cylinder with Girli ng® Rubber Lube or equiva lent. Torque the slave
cylinder-to-bellhousing nuts to 10-15 ft. lbs. (14-20 Nm). Fill the master
cylinder with new brake fluid conformi ng to DOT 3 specifications. Bleed
the hydraulic system.
OVERHAUL 1. Remove the shield, the pushrod and the dust cover from the slave cylinder, then inspect the cover for damage or deterioration.
2. Remove the snapring form t he end of the cylinder bore.
3. Using a block of wood, tap the slave cylinder on it to eject the plunger,
then remove the seal and the spring.
4. Using clean brake fluid, clean all of the parts.
5. Inspect the cylinder bore and the plunger for ridges, pitting and/or
scratches, the dust cover for wear and cracking; replace the parts if any
of the conditions exist.
To assemble: 6. Use new seals and lubricat e all of the parts in clean brake fluid. Install
the spring, the plunger seal and the plunger into the cylinder bore, then
install anew snapring.
7. Lubricate the inside of the dust co ver with Girling® Rubber Grease or
equivalent, then install it into the slave cylinder.
Be careful not to use any lubricant that will deteriorate rubber dust covers or
seals.
BLEEDING THE HYDRAULIC CLUTCH
Bleeding air from the hydrau lic clutch system is necessary whenever any part of
the system has been disconnect ed or the fluid level (in the reservoir) has been
allowed to fall so low that air has been drawn into the master cylinder.
1. Fill master cylinder reservoir wit h new brake fluid conforming to DOT 3
specifications.
2. Raise and safely support the front of the vehicle on jackstands.
3. Remove the slave cylinder attaching bolts.
4. Hold slave cylinder at approximatel y 45 degrees with the bleeder at
highest point. Fully depress clutch pedal and open the bleeder screw.
5. Close the bleeder screw and release clutch pedal.
6. Repeat the procedure until all of t he air is evacuated from the system.
Check and refill master cylinder reserv oir as required to prevent air from
being drawn through the master cylinder.
Page 334 of 875
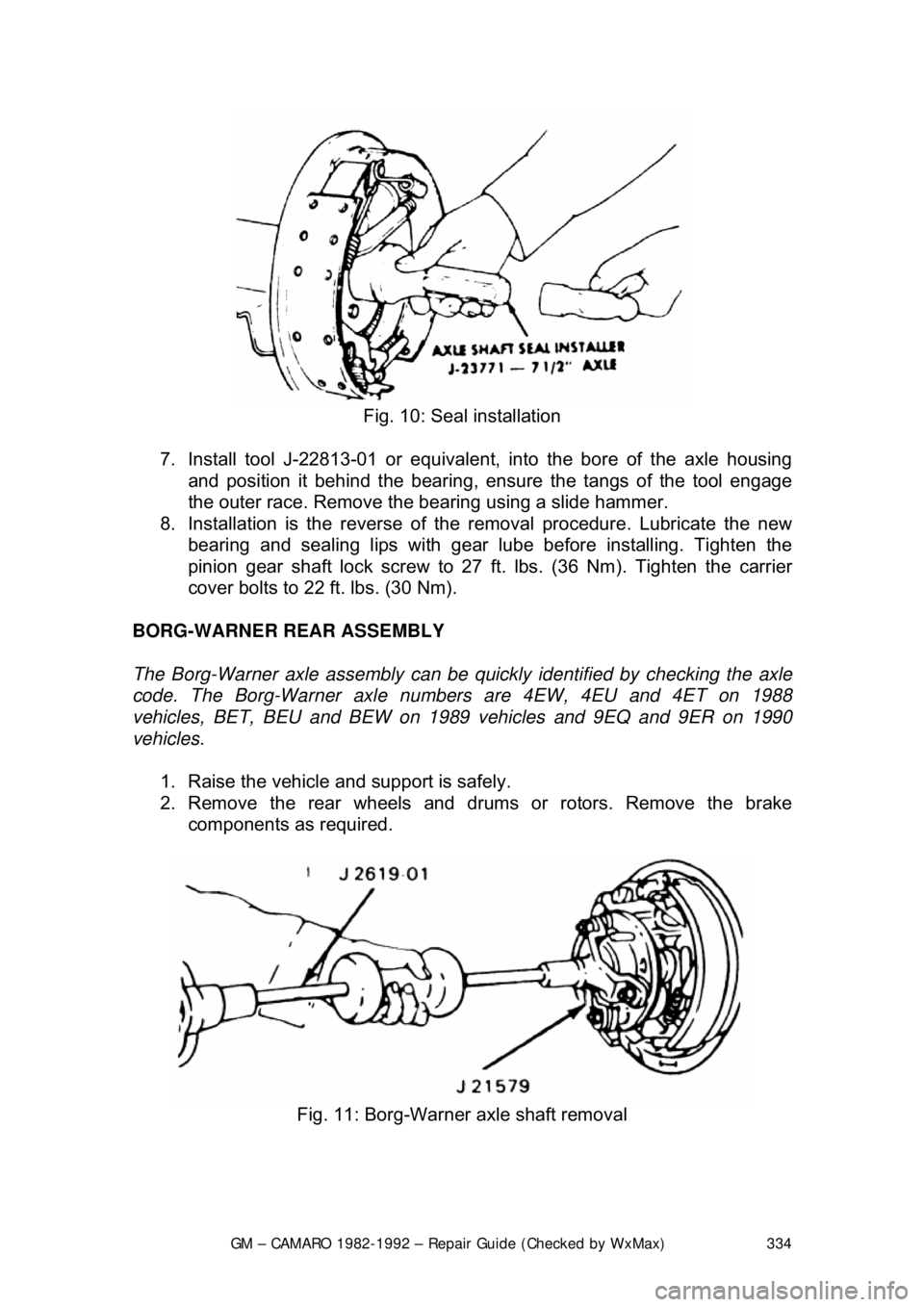
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 334
Fig. 10: Seal installation
7. Install tool J-22813-01 or equivalent, into the bore of the axle housing
and position it behind t he bearing, ensure the tangs of the tool engage
the outer race. Remove the bearing using a slide hammer.
8. Installation is the reverse of the removal procedure. Lubricate the new
bearing and sealing lips wi th gear lube before installing. Tighten the
pinion gear shaft lock screw to 27 ft. lbs. (36 Nm). Tighten the carrier
cover bolts to 22 ft. lbs. (30 Nm).
BORG-WARNER REAR ASSEMBLY
The Borg-Warner axle assembly can be quickly identified by checking the axle
code. The Borg-Warner axle num bers are 4EW, 4EU and 4ET on 1988
vehicles, BET, BEU and BEW on 1989 vehicles and 9EQ and 9ER on 1990
vehicles.
1. Raise the vehicle and support is safely.
2. Remove the rear wheels and drums or rotors. Remove the brake components as required.
Fig. 11: Borg-Warner axle shaft removal
Page 335 of 875
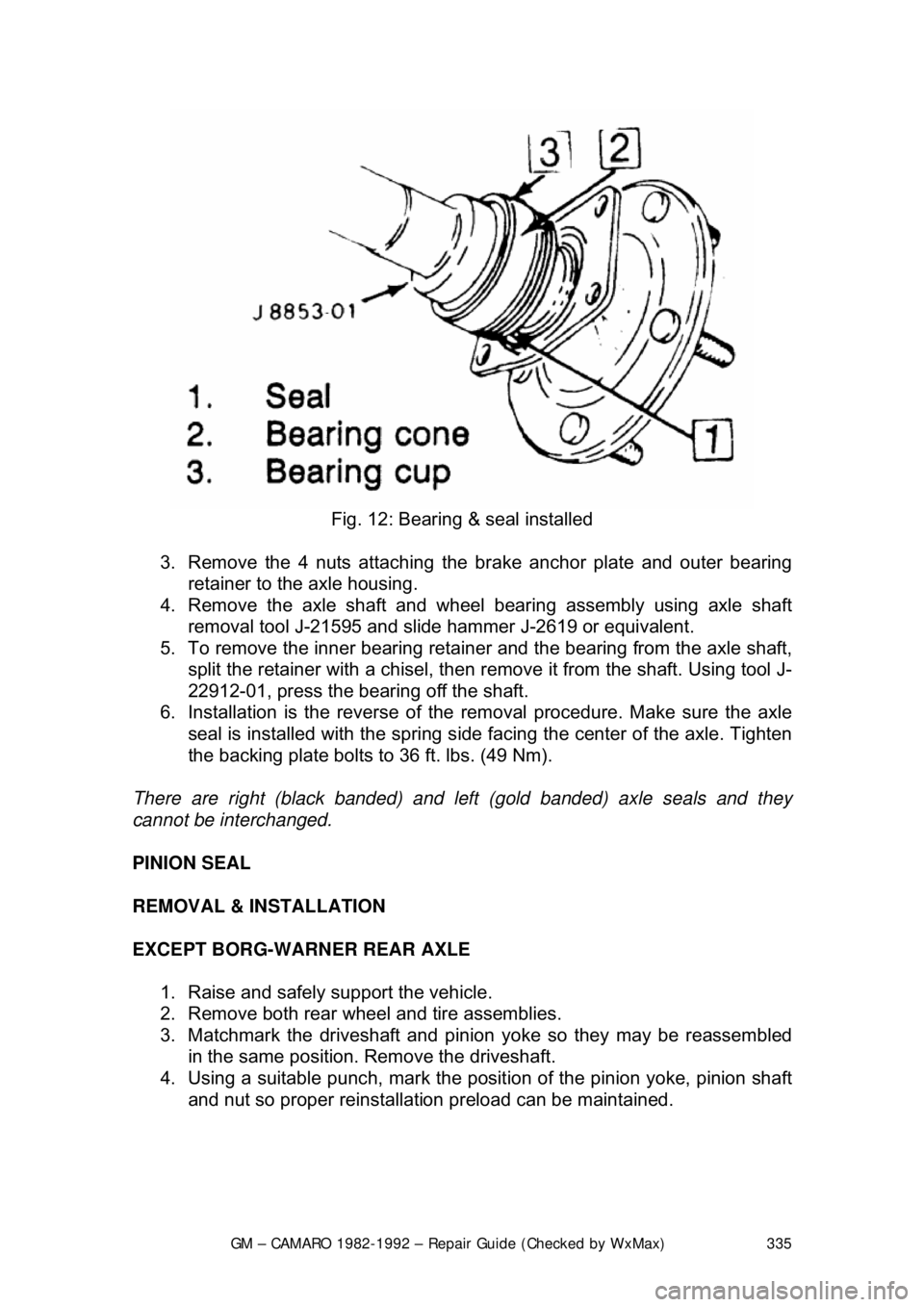
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 335
Fig. 12: Bearing & seal installed
3. Remove the 4 nuts attaching the brake anchor plate and outer bearing
retainer to the axle housing.
4. Remove the axle shaft and wheel bearing assembly using axle shaft removal tool J-21595 and slide hammer J-2619 or equivalent.
5. To remove the inner bearing retai ner and the bearing from the axle shaft,
split the retainer with a chisel, then re move it from the shaft. Using tool J-
22912-01, press the bearing off the shaft.
6. Installation is the reverse of the removal procedure. Make sure the axle
seal is installed with the spring side facing the center of the axle. Tighten
the backing plate bolts to 36 ft. lbs. (49 Nm).
There are right (black banded) and left (gold banded) axle seals and they
cannot be interchanged.
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
EXCEPT BORG-WARNER REAR AXLE 1. Raise and safely support the vehicle.
2. Remove both rear wheel and tire assemblies.
3. Matchmark the driveshaft and pinion yoke so they may be reassembled
in the same position. Remove the driveshaft.
4. Using a suitable punch, mark the posit ion of the pinion yoke, pinion shaft
and nut so proper reinstallati on preload can be maintained.
Page 338 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 338
seal preload. Turn the torque wrenc
h smoothly for several rotations and
record the amount of preload as the a ssembly is turning, not the initial
force required to start the assembly moving.
Preload is measured as the amount of torque required to turn the assembly.
5. Using a suitable tool to hold the pi nion yoke in place, remove the pinion
yoke nut and washer.
6. Place a suitable contai ner under the differential to catch any fluid that
may drain from the rear axle. Using a suitable tool, remove the pinion
flange.
7. Use a suitable tool to remove the pinion seal.
To install: 8. Inspect the seal surface of the pinion flange for tool marks, nicks or
damage and replace, as necessary. Examine the carrier bore and
remove any burrs that might cause leaks around the outside of the seal.
9. Install the seal 0.010 in. (0.2 5mm) below the flange surface using a
suitable seal installer.
10. Apply suitable seal lubricant to t he outer diameter of the pinion flange
and the sealing lip of the new seal.
11. Install the pinion flan ge on the drive pinion by taping with a soft hammer
until a few pinion threads projec t through the pinion flange.
12. Install the washer and pinion fla nge nut. While holding the pinion flange,
tighten the nut a little at a time and turn the drive pinion several
revolutions after each tightening, to set the bearing rollers. Check the
preload each time with a suitable inch pound to rque wrench until the
preload is 5 inch lbs. (0.6 Nm) more then the reading obtained during
disassembly.
13. Install the driveshaft.
14. Install the rear wheels and tires. Check and add the correct lubricant, as
necessary.
AXLE HOUSING
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Raise the vehicle and support it sa fely. Be sure that the rear axle
assembly is supported safely.
2. Disconnect shock absorbers from ax le. Remove the wheel assemblies.
3. Mark driveshaft and pinion flange, then disconnect driveshaft and support out of the way.
4. Remove brake line junction block bolt at axle housing. If necessary,
disconnect the brake lines at the junction block.
Page 340 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 340
10. Install the brake line j
unction block bolt at the ax le housing. Connect any
brake lines that were disconnected.
11. Install and secure the driveshaft a ligning the match marks made earlier.
12. Connect the shock absorbers to the axle and install the wheel
assemblies.
13. Lower the vehicle and replace any lost rear axle fluid.
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Raise and safely support the vehicle.
2. Place a suitable contai ner under the differential. Remove the carrier
cover and drain the gear oil.
3. Remove the drive axles.
4. Mark the differential bearing caps L and R to make sure they will be
reassembled in their original location.
5. Using a suitable tool, remove the di fferential carrier. Be careful not to
damage the gasket sealing surface wh en removing the unit. Place the
right and left bearing outer races of the side bearing assemblies and
shims in sets with the marked different ial bearings caps so they can be
reinstalled in their original positions.
To install: 6. Inspect the differential carrier housi ng for foreign material. Check the ring
and pinion for chipped teeth, exce ssive wear and scoring. Check the
carrier bearings visually and by feel . Clean the differential housing and
replace components, as necessary.
7. Install the differential carrier. C heck the carrier bearing preload along
with the ring and pinion backlash, then adjust, as necessary. Tighten the
differential bearing cap bolts to 55 ft. lbs. (75 Nm) except on Borg-
Warner rear axles which are ti ghtened to 40 ft. lbs. (54 Nm).
8. Install the axles.
9. Install the carrier cover using a new gasket. Tighten the carrier cover
bolts to 20 ft. lbs. (27 Nm). Add the proper type and quantity of gear oil to
axle assembly.