1967 CHEVROLET CAMARO electrical
[x] Cancel search: electricalPage 99 of 659

HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING 1A-76
Fig.
112—-Heater Core Removal—Four-Season System (Corvette)
3.
Replace the core case into the car as described
under Heater and Air Distributor Assembly.
COMPRESSOR
The same basic six.cylinder reciprocating compressor
is used in all systems.
Two variations of the basic compressor are used. One,
with a displacement of 12.6 cu. in. is used with the Four-
Season System. The second model, having displacement
of 10.8 cu. in. is used with the Universal and All-Weather
Systems.
AH Systems
Removal
1.
Purge the refrigerant from the system.
2.
Remove connector attaching bolt and connector. Seal
connector outlets.
3.
Disconnect electrical lead to clutch actuating coil.
4.
Loosen brace and pivot bolts and detach belt.
5. Remove the nuts and bolts attaching the compressor
brackets to the mounting bracket.
6. Before beginning any compressor disassembly, drain
and measure oil in the compressor. Check for
evidence of contamination to ..determine if remainder
of system requires servicing. Compressor Servicing
information is located in the Chassis Overhaul
Manual.
Installation
1.
li oil previously drained from the compressor upon
removal shows no evidence of contamination, replace
a like amount of fresh refrigeration oil into the com-
pressor before reinstallatLon. If it was necessary to
service the entire system because of excessive con-
tamination in the oil removed, install a full charge of
"fresh refrigeration oil in the compressor. (See
Checking Compressor Oil Charge under Checking
Oil)
2.
Position compressor on the mounting bracket and
install all nuts, bolts and lock washers.
3.
Install the connector assembly to the compressor
rear head, using new "O" rings.
4.
Connect the electrical lead to the coil and install
and adjust compressor belt.
5. Evacuate and charge the system.
6. Leak test the system and check for proper operation.
Fig.
113—Heater Hoses^-Four-Season System (Corvette)
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 112 of 659

CORVETTE BODY 1B-5
Fig.
4—Scribing
Line
Around
Hood
Hingje
2.
Remove cowl "kick" pad grille. |
3.
Disengage control cable fastened to cowl vent by nut
retainer. !
4.
Remove vent control knob retained by
|
set screw.
5. Remove center console trim and pass control cable
under instrument panel with care, avoiding damage
to electrical connections. j
Installation
Install vent assembly following removal procedure in
reverse order. Check operation of vent. Connect positive
battery cable.
Fig.
6—Instrument
Panel Tray
2.
Remove four screws retaining side reveal moldings.
3.
Remove upper reveal molding after marking molding
and header rail to ease reinstallation as shown in
Figure 14.
4.
Mark position of lower reveal molding as shown in
Figure 15 and pry molding out of weatherstrip.
5. From inside vehicle carefully pry weatherstrip from
pinchweld flange of windshield frame (fig. 16) and
work windshield-weatherstrip assembly out of body
opening toward front of vehicle.
Checking Windshield Body Opening
When the vehicle has been involved in a collision or in
cases where windshield has been subject to "strain
WINDSHIELD
Consult Figure 12 for parts identification.
Removal
1.
Remove side, upper and lower garnish moldings
(fig. 13).
Fig.
5—Emblem dnd
Vent Grille
1.
Screen
Assembly
2.
Pad
Assembly
L H.
Fig.
7-Cowl
Area Trim
3.
Pad
Assembly
R. H. 5.
Cover
4.
Trim Panel
Assembly
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 122 of 659

CORVETTE BODY 1B-15
Fig.
32—Removing Regulator
GLASS RUN CHANNEL-REAR
Removal
For parts identification refer to Figure 41.
1.
Remove door trim assembly as outlined in this
section.
2.
Remove window glass assembly as outlined in this
section.
3.
Remove 2 channel retaining screws and pass chan-
nels out through large opening in door inner panel
(fig. 42).
Fig.
33—Removing Ventilator Assembly 19437
Installation
1.
Position run channel in door and install bolts loosely.
2.
Install window glass as outlined in this section.
3.
Make necessary adjustments to channel as outlined
under Doors - Adjustments - Door Windows.
4.
Replace door window and door trim panel.
WINDOW REGULATOR-MANUAL
For parts identification see Figure 41.
Removal
1.
Remove trim panel as outlined in this section.
2.
Remove door window glass as outlined in this
section.
3.
Remove screws retaining regulator assembly to
door panel.
4.
Remove screws holding lower guide rail to door
panel.
5. Remove regulator assembly from large access open-
ing as shown in Figure 43.
Installation
Regulator may be installed by following removal pro-
cedure in reverse order. Always lubricate all guide rails
and rollers when regulator is disassembled. Test regula-
tor thoroughly before installing door trim panel. Adjust
window as outlined in this section.
WINDOW REGULATOR-POWER
In cases where window will not operate, check electri-
cal connections first. Figure 44 illustrates lpcation of
junctions, switches and circuit breaker.
Removal
Perform operations 1 thru 5 under Window Regulator-
Manual Removal. Note, however, that electrical connec-
tors must be removed from motor before performing
any operation on regulator. Figure 44 illustrates in-
stallation of regulator on door and regulator wiring.
Disassembly
NOTE:
Do not attempt to remove motor from
regulator until the following operations are per-
formed. THIS IS A SAFETY ITEM; arm is
spring-loaded and may cause injury if not locked
in position when motor is removed.
Refer to Figure 45.
1.
Place regulator assembly in vise.
2.
Using jumper leads to 12 volt power supply, operate
motor until semi-circular hole in sector gear cen-
ters over one of two weld nuts on mounting plate.
3.
Screw a l/4"-20 x 1" bolt into weld nut so that end
passes through hole in sector gear. It may be neces-
sary to enlarge hole in gear slightly with file or
drill. Install nut on bolt to lock arm in position.
Installation
1.
Be sure lock bolt has been removed if regulator
has been disassembled.
2.
Install lubricated regulator assembly and guide rails
in door in reverse order of removal.
3.
Install window as outlined in this section.
4.
Making sure connectors are securely installed on
motor, test operation of window thoroughly.
5. Install door trim panel and handles as outlined in
this section.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 234 of 659

BRAKES
SECTION 5
CONTENTS OF THIS SECTION
Duo Servo Brakes
Disc Brakes
Page
5-1 Power Brakes
5-24 Special Tools
Page
5-31
5-32
DUO-SERVO BRAKES
INDEX
Page
General Description 5-1
Maintenance and Adjustments 5-3
Hydraulic Brake Fluid .. . 5-3
Bleeding Hydraulic System 5-3
Pressure Bleeding 5-3
Manual Bleeding 5_4
Push Rod to Main Cylinder Clearance 5-5
Hydraulic Brake Lines 5-5
Hydraulic Brake Hose 5-5
Hydraulic Brake Tubing 5-6
Brake Adjustment. .................... 5-7
Service Brake 5-7
Parking Brake 5-8
Component Replacement and Repairs 5-9
Parking Brake - Chevrolet, Chevelle and
Camaro 5^9
Pedal Assembly 5-9
Front Cable ,. . . 5-9
Center Cable 5-9
Rear Cables. . 5-9
Parking Brake - Chevy n 5-9
Lever Assembly 5-9
Idler Lever 5-11
Front Cable 5-11
Rear Cable . . ; 5-12
Parking Brake - Corvette 5-13
Lever Assembly . . . . 5-13
Front Cable 5-14
Rear Cable . . 5-14
Brake Pedal 5-15
Shoes and Linings 5-16
Organic 5-16
Metallic 5-17
Main Cylinder 5-18
Wheel Cylinders 5-21
Anchor Pin 5-22
Front Wheel 5-22
Rear Wheel 5-22
Brake Drums • 5-22
Brake Pipe Distribution and Switch Assembly . . . . . 5-23
Camaro Pressure Regulator Valve 5-23
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
All 1967 models are equipped with a new split brake
system as a safety feature. If a wheel cylinder or brake
line should fail at either the front end or rear end of
the vehicle, the operator can still bring the vehicle to
a controlled stop. The system is designed with separate
hydraulic systems for the front and rear brake using
a dual master cylinder (fig. 1). The design of the master
cylinder is similar to that used on the 1966 Corvette
in that it has two entirely separate reservoirs and outlets
in a common body casting. The front reservoir and outlet
is connected to the front wheel brakes, and the rear
reservoir and outlet is connected to the rear wheel
brakes. Two pistons within the master cylinder receive
mechanical pressure from the brake pedal push rod and
transmit it through the brake lines as hydraulic pressure
to the wheel cylinders. The filler cap is accessible from
inside the engine compartment.
A new brake pipe distribution and switch assembly
is mounted below the main cylinder. The front and rear
hydraulic brake lines are routed from the main cylinder,
through the brake pipe distribution and switch assembly,
to the front and rear brakes as shown in Figure 2. The
switch is wired electrically to the brake alarm indicator
light on the instrument panel. In the event of fluid loss
in either the front or rear brake system the indicator
on the instrument panel will illuminate red. (The indi-
cator will also' be illuminated when the parking brake is
applied.)
On Camaro models equipped with air conditioning, the
rear brake hydraulic line is routed through a pressure
regulator valve mounted on the left frame side rail
(fig. 3). The valve controls the hydraulic pressure to
the rear brakes resulting in the correct pressure balance
between the front and rear hydraulic systems.
The self-adjusting brakes (fig. 4), used on both front
and rear of all models, are the Duo-Servo single anchor
type which utilize the momentum of the vehicle to assist
in the brake application. The self-energizing or
self-
actuating force is applied to both brake shoes at each
wheel in both forward and reverse motion. The brake
shoe linings are bonded to the shoes.
Wheel cylinders are the double piston type permitting
even distribution of pressure to each brake shoe. To
keep out dust and moisture, both ejads of each wheel
cylinder are sealed with a rubber booC The wheel
cylinders have no adjustments.
The Chevrolet, Chevelle, and Camaro parking brakes
have a foot operated ratchet type pedal mounted to the
left of the steering column. A cable assembly connects
the pedal to an intermediate cable by means of an equal-
izer, where the adjustment for the parking brake is
incorporated. The intermediate cable attaches to the
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 256 of 659
BRAKES 5-23
Fig.
34—Brake Drum Access Hole
2.
Install brake drum, aligning tang with wheel hub
(fig. 18).
3.
Install wheel and tire assembly.
. 4. Make final brake adjustment as outlined in this
section and check brake operation.
BRAKE PIPE DISTRIBUTION AND SWITCH
ASSEMBLY (Fig. 2)
Removal
1.
Disconnect battery cable.
2.
Disconnect electrical lead from switch assembly.
3.
Place dry rags below the switch to absorb any fluid
spilled during removal of switch.
4.
Disconnect four hydraulic lines from connections
at switch. If necessary, loosen line connections at
main cylinder to loosen lines. Cover open line ends
with clean, lint-free material to prevent foreign
matter from entering the system.
5.
Remove mounting screw and remove switch from
vehicle.
Installation
1.
Make sure new switch is clean and free of dust and
lint. If any doubt exists, wash switch in Declene,
or equivalent, and dry with air.
2.
Place switch in position and secure to bracket with
mounting screw.
3.
Remove protective material from open hydraulic
brake lines and connect lines to switch. If necessary,
tighten brake line connections at main cylinder.
4.
Connect switch electrical lead.
5.
Connect battery cable.
6. Bleed the brake systems as outlined in this section.
CAMARO PRESSURE REGULATOR VALVE
(AIR CONDITIONED MODELS ONLY)
Removal (Fig. 3)
1.
Place dry rags below valve to absorb any fluid
spilled during removal of valve.
2.
Disconnect hydraulic brake lines from both sides
of switch. Cover open line ends with clean, lint-free
material to prevent foreign matter from entering
the system.
3.
Remove mounting screw and remove switch from
vehicle.
Installation
1.
Make sure new valve is clean and free of dust and
lint. If any doubt exists, wash valve in Declene, or
equivalent, and dry with air.
2.
Place valve in position and secure to frame side
rail with mounting screw.
3.
Remove protective material from open hydraulic
brake lines and connect lines to each side of valve.
4.
Bleed brake system as outlined in this section.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE
Page 326 of 659

SECTION 6Y
ENGINE ELECTRICAL
CONTENTS
OF
THIS SECTION
Page
System
6Y-19
6Y-32
6Y-34
BATTERY
INDEX
Page
General Description 6Y_i
Types of Batteries 6Y-1
Dry Charged Batteries 6Y-2
Activating Dry Charged Batteries 6Y-2
Wet Charged Batteries 6Y 2
Periodic Service 6Y-3
Common Causes of Failure 6Y-3
Delco Eye 6Y_3
Electrolyte Level
AY
3
Water Usage ] \ 6Y_3
Cleaning 6Y_4
Cables 6Y_4
Carrier and Holddown 6Y-4
Page
Safety Precautions 6Y-4
Charging Procedures . . gY_4
Slow Charging gY-4
Fast Charging . * 6Y-4
Emergency Boost Charging 6Y-4
Test Procedures QY-S
Visual Inspection 6Y-5
Instrument 6Y-5
Full Charge Hydrometer Test. 6Y-5
Specific Gravity Readings 6Y-5
Cell Comparison Test . 6Y-5
Installing Battery 6Y-5
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The battery (fig. lb) is made up of a number of separ-
ate elements, each located in an individual cell in a hard
rubber case. Each element consists of an assembly of
positive plates and negative plates containing dissimilar
active materials and kept apart by separators. Hie ele-
ments are immersed in an electrolyte composed of dilute
sulfuric acid. Plate straps located on the top of each ele-
ment connect all the positive plates and all the negative
plates into groups. The elements are connected in series
electrically by connectors that pass directly through the
case partitions between cells. The battery top is a one-
piece cover of hard rubber construction. Tfte cell con-
nectors, by-passing through the cell partitions, connect
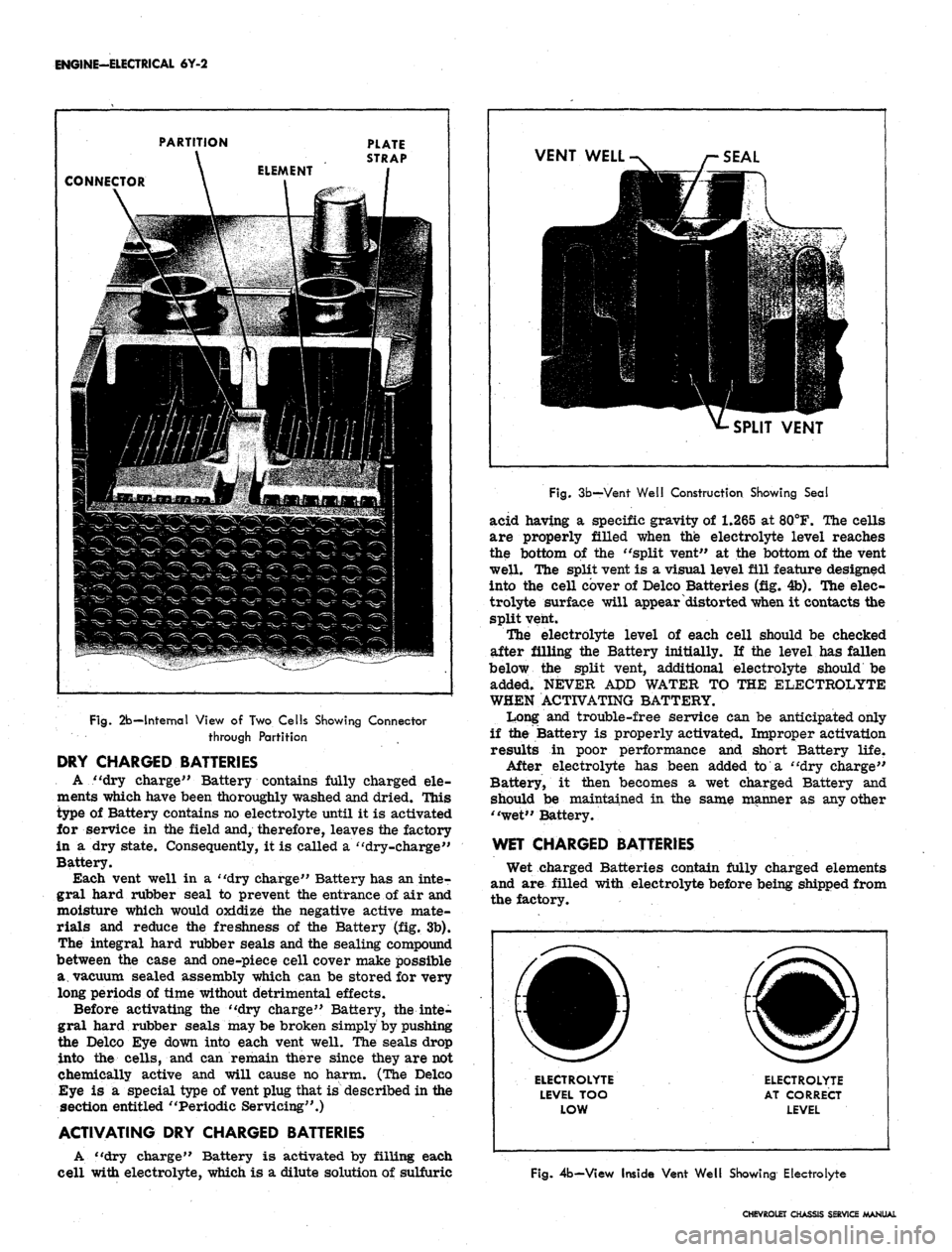
the elements along the shortest practical path (fig. 2b).
With the length of the electrical circuit inside the
Battery reduced to a minimum, the internal voltage drop
is decreased resulting in improved performance, par-
ticularly during engine cranking at low temperatures.
The hard, smooth one-piece cover greatly reduces the
tendency for corrosion to form on the top of the Battery.
The cover is bonded to the case with sealing compound
that forms an air tight seal between the cover and case.
Protection for the Battery charging circuit (10 gage
wire) is provided by a pigtail lead which is a fusible Hnk
off the battery positive cable (14 gage wire). This lead is
an integral part of the Battery cable assembly and serv-
icing requires replacing the complete cable assembly.
TYPES
OF
BATTERIES
There are two types of Batteries—the "dry charge"
type and the "wet charge" type. The difference in types
depends on the method of manufacture.
ONE PIECE
CELL COVER
VENT PLUG
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
INDICATOR
HOLD-DOWN SLOT
Fig.
lb—Battery
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 327 of 659
ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-2
PARTITION
PLATE
STRAP
CONNECTOR
Fig.
2b—Internal View of Two Cells Showing Connector
through Partition
DRY CHARGED BATTERIES
A "dry charge" Battery contains fully charged ele-
ments which have been thoroughly washed and dried. Hiis
type of Battery contains no electrolyte until it is activated
for service in the field and, therefore, leaves the factory
in a dry state. Consequently, it is called a "dry-charge"
Battery.
Each vent well in a "dry charge" Battery has an inte-
gral hard rubber seal to prevent the entrance of air and
moisture which would oxidize the negative active mate-
rials and reduce the freshness of the Battery (fig. 3b).
The integral hard rubber seals and the sealing compound
between the case and one-piece cell cover make possible
a. vacuum sealed assembly which can be stored for very
long periods of time without detrimental effects.
Before activating the "dry charge" Battery, the inte-
gral hard rubber seals may be broken simply by pushing
the Delco Eye down into each vent well. The seals drop
into the cells, and can remain there since they are not
chemically active and will cause no harm. (The Delco
Eye is a special type of vent plug that is described in the
section entitled "Periodic Servicing".)
ACTIVATING DRY CHARGED BATTERIES
A "dry charge" Battery is activated by filling each
cell with electrolyte, which is a dilute solution of sulfuric
VENT WELL
SEAL
SPLIT VENT
Fig. 3b—Vent Well Construction Showing Seal
acid having a specific gravity of 1.265 at 80°F. The cells
are properly filled when the electrolyte level reaches
the bottom of the "split vent" at the bottom of the vent
well. The split vent is a visual level fill feature designed
into the cell cover of Delco Batteries (fig. 4b). The elec-
trolyte surface will appear distorted when it contacts the
split vent.
The electrolyte level of each cell should be checked
after filling the Battery initially. If the level has fallen
below the split vent, additional electrolyte should be
added. NEVER APD WATER TO THE ELECTROLYTE
WHEN ACTIVATING BATTERY.
Ir?ong and trouble-free service can be anticipated only
if the Battery is properly activated. Improper activation
results in poor performance and short Battery life.
After electrolyte has been added to a "dry charge"
Battery, it then becomes a wet charged Battery and
should be maintained in the same manner as any other
"wet" Battery.
WET CHARGED BATTERIES
Wet charged Batteries contain fully charged elements
and are filled with electrolyte before being shipped from
the factory.
ELECTROLYTE
LEVEL TOO
LOW
ELECTROLYTE
AT CORRECT
LEVEL
Fig. 4b-View Inside Vent Well Showing Electrolyte
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 328 of 659

ENGINE-EIECTRICAI 6Y-3
PERIODIC SERVICING
Since the Battery is a perishable item which requires
periodic servicing, a good maintenance program will
insure the longest possible Battery life.
COMMON CAUSES OF FAILURE
If the Battery tests good but fails to perform satis-
factorily in service for no apparent reason, the following
are some of the more important factors that may point to
the cause of the trouble.
1.
Vehicle accessories inadvertently left on overnight to
cause a discharged condition.
2.
Slow speed driving of short duration, to cause an
3.
undercharged condition.
A vehicle
capacity.
electrical load exceeding the generator
4.
Defect in the charging system such as high resist-
ance, slipping fan belt, faulty generator or voltage
regulator.
5. Battery abuse, including failure to keep the Battery
top clean, cable clamps and posts clean and tight,
and improper addition of water to the cells.
LEVEL INDICATOR
The Battery features an electrolyte level indicator,
which is a specially designed vent plug with a transparent
rod extending through the center (fig. 5b). When the elec-
trolyte is at the proper level, the lower tip of the rod is
immersed, and the exposed top of the rod will appear
very dark; when the level falls below the tip of the rod,
the top will glow. ,
The Indicator reveals at a glance if water is needed,
without the necessity of removing the vent plugs (fig. 6b).
The Level Indicator is used in only one cell (second
cell cap from positive Battery post) because when the
electrolyte level is low in one cell, it is normally low in
all cells. Thus when the Indicator shows water is needed,
check the level in all six cells.
An alternate method of checking the electrolyte level is
to remove the vent plug and visually observe the electro-
lyte level in the vent well. The bottom of the vent well
features a split vent which will cause the surface of the
electrolyte to appear distorted when it makes contact.
The electrolyte level is. correct when the distortion first
appears at the bottom of the split vent (fig. 4b).
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
The electrolyte level in the Battery should be checked
regularly. In hot weather, particularly during trip driv-
ing, checking should be more frequent because of more
rapid loss of water. If the electrolyte level is found to be
low, then colorless, odorless, drinking water should be
added to each cell until the liquid level rises to the split
vent located in the bottom of the vent well. DO NOT
OVERFILL because this will cause loss of electrolyte
resulting in poor performance, short life, and excessive
corrosion.
CAUTION: During service only water should be
added to the Battery, not electrolyte.
The liquid level in the cells should never be allowed to
drop below the top of the plates, as the portion of the
INDICATOR
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
CORRECT
Fig.
5b—Cut-Away View Showing Electrolyte at Proper Level
with Indicator Having Dark Appearance
plates exposed to air may be permanently damaged with a
resulting loss in performance.
WATER USAGE
Excessive usage of water indicates the Battery is being
overcharged. The most common causes of overcharge
are high Battery operating temperatures, too high a volt-
age regulator setting, poor regulator ground wire con-
nection. Normal Battery water usage is approximately
one to two ounces per month per battery.
INDICATOR
Fig.
6b—Cut-Away View Showing Electrolyte at Low Level
with Indicator Having Light Appearance
CHASSIS SBtVKZ MANUAL