1900 MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE bulb
[x] Cancel search: bulbPage 224 of 408

CHASSIS ELECTRICAL 6-21
Fig. 82 low-beam headlight pattern alignment
93156pE.3 Fig. 85 Remove the washer fluid reservoir
retaining screws . . .
Fig. 83 High-beam headlight pattern alignment
headlight beams on the wall. If done in a garage,
darken the area around the wall as much as possible
by closing shades or hanging cloth over the win-
dows.
3. Turn the headlights ON and markthe wall at
the center of each light’s low br ram, then switch on
the brights and mark the center of each lights high
beam. A short length of maskin g tape which is visible
from the front of the
whir+ ma . ._..._._ . .._ y be used. Although
marking all four po:
sitions is advisable, marking one
position from each
light should be sufficient.
4. If neithar he; ~. __
Irn on one side is working, and if
another like-sized vehicle is available, park the sec-
nnri nm in the wart cnnt whrw the whirlo um md
headli! jhts ON and adjust the beams to marcn me
I. Disconnect the negative battery cable. marks on the wall.
2. Remove any necessary components to access 6.
the bulbs. Have the headlight adjustment checked as
soon as possible by a reputable repair shop.
3. Rotate the bulb sockets and rotate them coun-
terclockwise to remove them.
4. Grasp the bulb and remove it from the socket REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
Parking And Side Marker Lights
p See Figures 84, 85, 88, 87, 88, and 89 !ss the parking and side
1~ nn loo4-98 Galant mod-
I
1 I-
5315@61
lens. 1 Fio. 8
then move the reservoir out of
3. Remove the lens from the front fascia.
4. Grasp the bulb socket and rotate it counter- marker lamp bult, _.. ._“~-
clockwise to remove it from the lamp.
5. Pull the bulb out to remove it from the socket. 5. The installation is the reverse of removal.
6. Installation is the reverse of removal. Front turn Signal
p See Figures 91
1. Disconnect tl
2. Remove the t 0, 91, 92, and 93
I(? n,-.nn+:.m b.Hnn, nnL.L
z Ill7yau”e “allcly ul”IC. 10 retainino screws from the
spot from which the lights were marked. Turn the . ..I_ WIIY I.8 %,I” V”UVL”fdYI T.II”IU Lll” “VlllUlY ,.UU U,,” mark the beams using the same-side light. Then
switch the vehicles so the one to be aimed is back in
the original spot. It must be parked no closer to or
farther away from the wall than the second vehicle.
5. Perform any necessary repairs, but make sure
the vehicle is not moved, or is returned to the exact
by pulling it straight out.
Page 225 of 408
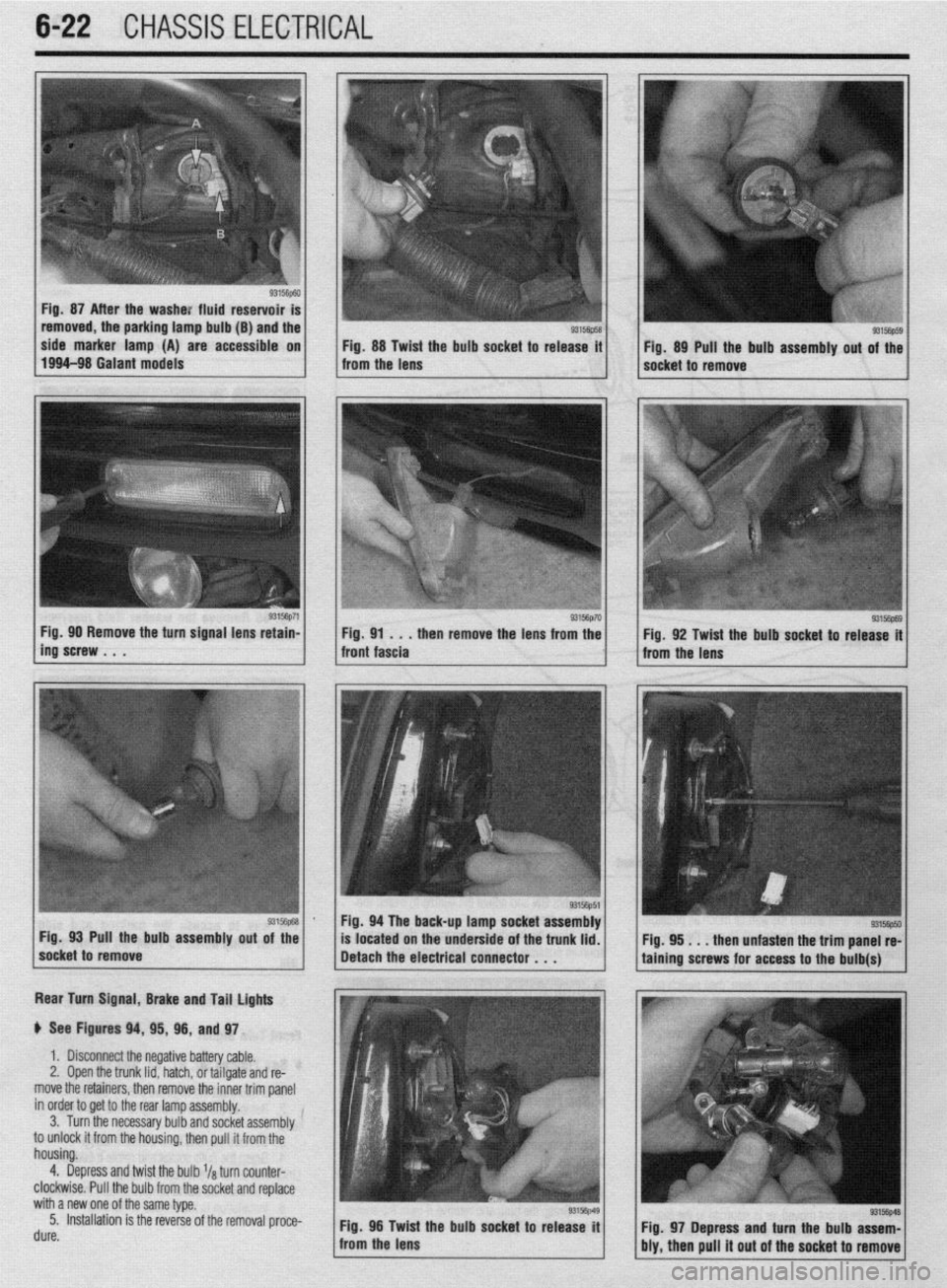
6-22 CHASSIS ELECTRICAL
b
Fig. 87 After the washe: fluid reservoir
removed, the parking lamp bulb (B) and the
side marker lamp (A) are accessible on
Fig. 88 Twist the bulb socket to release it
1994-98 Galant models
from the lens Fig. 89 Pull the bulb assembly out of the
socket to remove
g3156p71 / Fig 90 Remove the turn signal lens retain-
ing’screw . . . . then remove the lens from the
Rear Turn Signal, Brake and Tail lights
p See Figures 94, 95, 96, and 97.
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2, Open the trunk lid, hatch, or tailgate and re-
move the retainers, then remove the inner trim panel
in order to get to the rear lamp assembly.
3. Turn the necessary bulb and socket assembly
to unlock it from the housing, then pull it from the
housing.
4. Depress and twist the bulb l/a turn counter-
clockwise. Pull the bulb from the socket and replace
with a new one of the same type.
5. Installation is the reverse of the removal proce-
rl. ._^
UUIt?. Fig. 96 Twid
: the bulb socket to release it
from the lens
93156p69 Fig. 92 Twist the bulb socket to release it
from the lens
I
Fig. 94 The back-up lamp socket assembly
Pull the bulb assembly
out of the
located on the underside of the trunk lid.
. . . then unfasten the trim panel re-
Fig. 97 Depress and turn the bulb assem-
bly, then pull it out of the socket to remove
Page 226 of 408
![MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900 Repair Manual CHASSIS ELECTRlCiL 6-23
93156P57 Fig. 98 The back-up lamp socket assembly Fig. 99 Twist the bulb socket to release the
is located on the underside of the trunk lid locking tabs from the lens *1W5y] MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900 Repair Manual CHASSIS ELECTRlCiL 6-23
93156P57 Fig. 98 The back-up lamp socket assembly Fig. 99 Twist the bulb socket to release the
is located on the underside of the trunk lid locking tabs from the lens *1W5y]](/manual-img/19/57096/w960_57096-225.png)
CHASSIS ELECTRlCiL 6-23
93156P57 Fig. 98 The back-up lamp socket assembly Fig. 99 Twist the bulb socket to release the
is located on the underside of the trunk lid locking tabs from the lens *1W5y] Fig 100 Pull the bulb assembly straight out
of the socket to remove it
Back-up light
u See Figures 98, 99, and 100
1 I Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Open the trunk lid.
3. If equipped, remove the trim on the underside
of the trunk lid.
4. Turn the socket counterclockwise ‘14 of a turn
to release it from the lens.
5. Pull the bulb out to remove it from the socket,
6. The installation is the reverse of removal.
7. Connect the negative battery cable.
8. Verify the operation of the lamp.
Side Marker light
# See Figures 101, lOi, 103, and 104 I. Remove the two retaining screws from the 2. Open the trunk lid and detach the electrical
lens. connector from the lamp assembly.
2. Remove the lens from the rear fascia. 3. Remove the retaining screw holding the lamp
’ 3. Grasp the bulb socket and rotate it counter- assembly.
clockwise to remove it from the lamp. 4. Lower the lamp assembly from the lamp lens.
4. Pull the bulb out to remove it from the’socket. 5. Rotate the bulb clockwise while pushing it
5. Installation is the reverse of removal. gently inward to remove it from the socket.
6. The installation is the reverse of removal. .
High-mount Brake light
199fH6 MIllAGE, 1990-93 GALANT, AND
799446 GALANT 7992-96 DlAMANTE
p See Figures 105, 106, 107, 108, and 109 1, Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. On the Mirage and Galant, remove the square
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
*The lamp assembly is accessible from the
trunk underneath the package shelf. retainer clips or bolts from the high-mount brake
light cover and remove the cover.
3. On the Diamante, press gently inward on the
sides of the liaht cover and remove it from the lamp.
1 taining screw . ~ . 93156p73 1 Fig 101 Remove the side marker light re-
93156p75 1 / ;;x,;;:,sdhen puii the lens awaG;:: 1 1 fror;l the iens Fig 103 Twist the bulb socket to release it
Fig. 104 Pull the bulb assembly straight out
of the socket to remove Fig. 105 Detach the high-mount brake
light electrical connector Fig. 106 Remove the lamp retaining screws
. a *
Page 227 of 408

.
6-24 CHASSIS ELECTRICAL
Fig. 107
. . . then lower the lamp assembly
for access to the bulbs
4. Rotate the bulb clockwise while pushing it
.,
gently inward to remove it from the socket.
5. The installation is the reverse of removal.
1997-00 MIRAGE, 1994-00 GALANT, AND
f 997-90 DIAMANTE
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
*The bulb socket is accessible from the
trunk underneath the package shelf.
2. Ooen the trunk lid
and detach the elwtrical connector from the bulb socket,
3. Rotate the socket counterclockwise and re-
move it from the lamp assembly.
4. Rotate the bulb clockwise while pushing
it gently inward to remove it from the socket. Fig. 108 Rotate the bulb assembly. . .
License Plate lights
p See Figures 110,111, and 112
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the two retaining screws for the lamp
lens.
3. Lower the lens from the trunk lid.
4. Grasp the bulb and remove it from the termi-
nals on the lens.
To install:
5. Place the bulb into place on the lens and
lightly press into the terminals on the lens.
6. Place the lens into position on the trunk lid
and tighten the two retaining screws.
7. Connect the negative battery cable.
8. Verify the operation of the lamp. Dome/ Passenger Area lamps
p See Figures 113, 114, and 115
1, Using a small prytool, carefully remove the
cover lens from the lamp assembly.
2. Remove the bulb from its retaining clip con-
tacts. If the bulb has tapered ends, gently depress the
spring clip/metal contact and disengage the light
bulb, then pull it free of the two metal contacts.
To install:
3. Before installing the light bulb into the metal
contacts, ensure that all electrical conducting sur-
faces are free of corrosion or dirt.
4. Position the bulb between the two metal con-
tacts. If the contacts have small holes, be sure that
the tapered ends of the bulb are situated in them.
5. The installation is the reverse of removal.
Fig. 110 Remove the two lamp lens retain-
ing screws . . . Fig. ill . . .
then lower the lens to access
the bulb Fig. 112 Remove the bulb by pulling it from
the terminals on the lens
Page 228 of 408
CHASSIS ELECTRICAL 6-25
ove the socket from ig. 118 Pull the bulb straight out to remove
6. Install the cover lens until its retaining tabs are
properly engaged. ’
Light bulb application chart-1990-92 Mirage
Bulb Chart - Outaide
Instrument Cluster light bulbs
b See Figures 116,llf,ll8, and 119
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2: Remove the instrument cluster as outlined in
this section.
3. Turn the desired bulb socket counterclockwise
to remove it from the cluster.
, 4. Grasp the bulb and pull it straight out to re-
move it from the socket.
I 1 Lmelatel~hls
Fig. 119 On some of the bulbs, it is neces-
1 ;;tbqrlrnsferthe colore ’ ’ ” . .’ ’
1 EL&
!a OUID cover IO me
Bulb Chart-In
*__. . __.
, , JvR,,Is~,,o~
press i+ in+n n,app
II llll” ~“UVV.
To install:
5. If necessary, transfer the colored bulb cover to
the new bulb.
6. Place a new bulb into the socket and lightly
Place the socket into the cluster and turn the
,“. II pithpr it ic faldtv nr 9. Connect the negative battery cable.
I
Outside Inside
Page 229 of 408
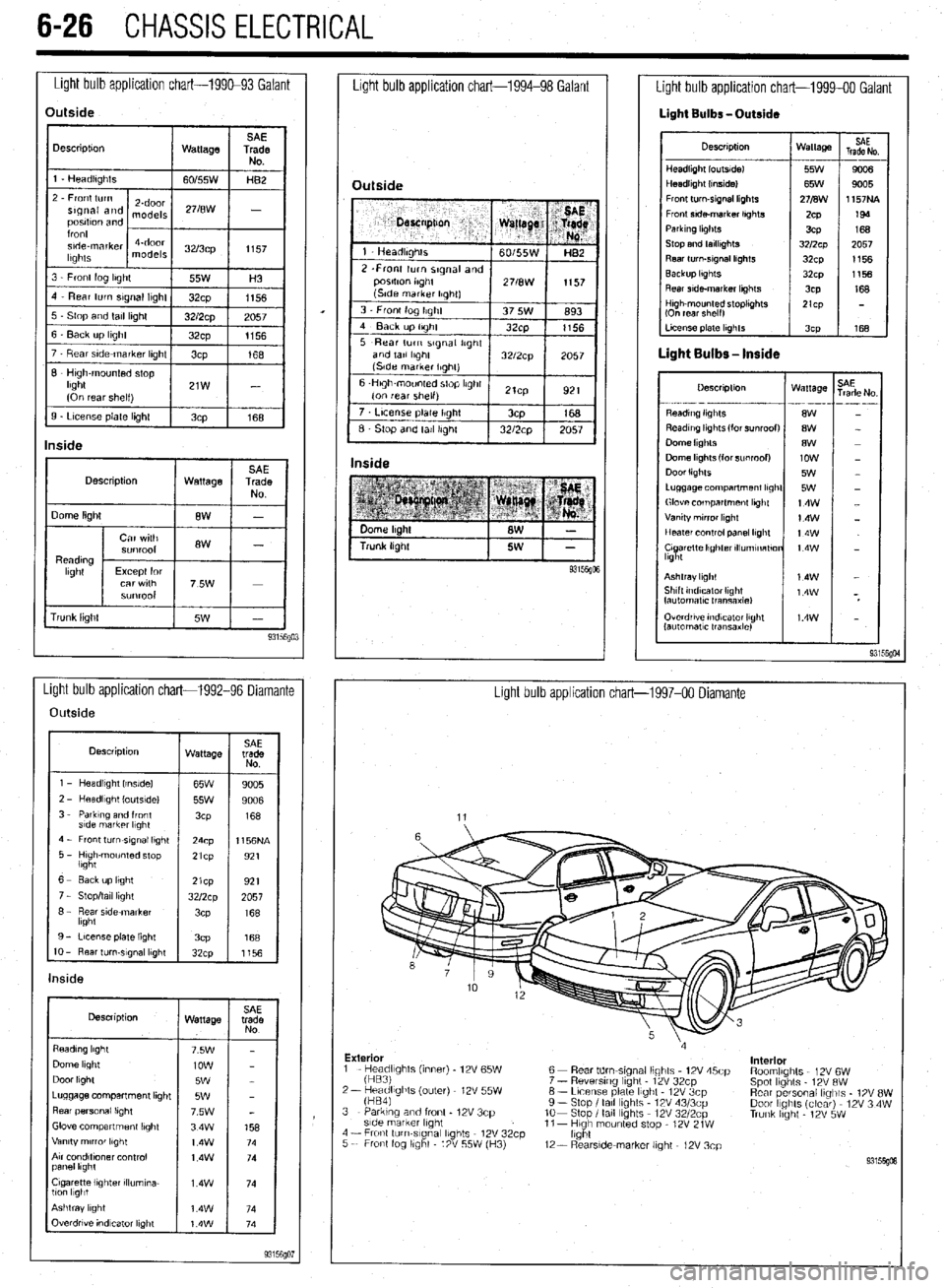
6-26 CHASSIS ELECTRICAL
Light bulb application chart-199&93 Galant
Light bulb application chart-1994-98 Galant
Description
1 Wattage 1
rrunk lrght Overdrwe rndvzator light
lautomatlc transaxle)
Light bulb application chart-1992-96 Diamante
Light bulb application chart-1997-00 Diamante
Outside
Description
wattage SAE
trade
NO
1 - Headlrght Irnslde)
65W
9005
l----if
2 - HeadlIght loutsldel
55w 9006
3 - Parktng and front
3cP 168
s!de markrr l,ght
4 - Front turn-srgnal light
24cp 1156NA
5 - Hugh-mounted stop
lbght 21cp
921
1 6- Eackuplrght
I 1921 21cp
7 - Stop/tall light
8 - Rear side marker
lkght
9 - License plate light
3cP 168
IO - Rear turn-slgnal lkght
32cp
1156
Description
Wattage
Dome light
Door light
Luggage compartment lrght
Rear personal lrght
Glove compartment lbght
Vanity mrrror lkght
Arr condltfoner control
panel lkght
Cigarette lighter rllumrna-
llcm l1gbt
Outside
7 t License plate Ilght / 3cp
168
6 Stop and tall Irghl 1 32/2cp 1 2057 I
Inside
Light bulb application chart-1999-00 Galant
Light Bulbs -Outside
Descrrptron Wattage
HeadlIght loutsldel 55W
Headlight (Inside1 65W
Front turn-srgnal lkghts 271B\1\1
Fronr srde-marker lrghts
ZCP
Parkrng hghts
3CP
Stop and tarllrghts 3212~~
Rear turn-srgnal lrghts
32cp
Backup lkghts
32~x1
Rear srde-marker lkghts
3CP SAE
Trade No
---
90a
9005
1157NA
199
168
2057
1156
1156
168
LI- 168
Descrrptron Wattage
- . ..-- -- --_ .---
8W
8W
8W
low
5W
5W
14w
14W
t4w
t4w
Ashtray light
Shtft tndrcaror Ilght
fautomatlc Iransaxlel
Exterior
interior
1 - He;;;fghts (inner) - 12V 65W
2- keadlights (outer) 12V 55W
fHB41 6 - Rear tdm-stgnal lights 12V 45cp
7 - Reversrng light - 12V 32cp
6 - Lrcense plate light 12V 3cp
9 - Stop I tall lights 12V 43/3cp
lo- Stop I tall Ibghts 12V 3212~~
11- Hugh mounted stop - 12V 21W
light RoomlIghts 12V 6W
Spot lights 12V RW
Rear personal lrglils - 1% 8W
Door IIghts (clear) 12V 3 4W
Trunk hght - 12V 5W 3 - Parking and front - 12V 3cp
side marker lrght
4 - Fronl turn-slgnal lights 12V 32cp
5 - Front fog llghl 12V 55W (H3)
12- RearsIde-marker light - 12V 3cp
Page 395 of 408

TROUBLESHOOTING 11-13
NOTE: When one shock fails, ft is recommended to replace front or rear
units as pairs.
3. Vehicle leans excessively in turns
a. Check for worn or leaking shock absorbers or strut assemblies and replace as neces-
sary.
b. Check for missing, damaged, or worn stabilizer links or bushings, and replace or in-
stall as necessary.
4. Vehicle ride quality seems excessively ha&h
a. Check for seized shock absorbers or strut assemblies and replace as necessary.
b. Check for excessively high tire pressures and adjust pressures to vehicle recommen-
dations.
5. Vehicle seems low or leans to one side
a. Check for a damaged, broken or weak spring. Replace defective parts and check for a
needed alignment.
b. Check for seized shock absorbers or strut assemblies and replace as necessary.
c. Check for worn or leaking shock absorbers or strut assemblies and replace as neces-
sary.
Noises 1. Vehicle makes a clicking noises when driven
a. Check the noise to see if it varies with road speed. Verify if the noise is present when
coasting or with steering or throttle input. If the clicking noise frequency changes with
road speed and is not affected by steering or throttle input, check the tire treads for a
stone, piece of glass, nail or another hard object imbedded into the tire or tire tread.
Stones rarely cause a tire puncture and are easily removed. Other objects may create
an air leak when removed. Consider having these objects removed immediately at a
facility equipped to repair tire punctures.
b. If the clicking noise varies with throttle input and steering, check for a worn Constant
Velocity (CV-joint) joint, universal (U- joint) or flex joint.
2. Vehicle makes a clunking or knocking noise over bumps
a. A clunking noise over bumps is most often caused by excessive movement or clear-
ance in a suspension component. Check the suspension for soft, cracked, damaged or
worn bushings. Replace the bushings and check the vehicle’s alignment.
b. Check for loose suspension mounting bolts. Check the tightness on subframe bolts,
pivot bolts and suspension mounting bolts, and torque to specification.
c. Check the vehicle for a loose wheel bearing. Some wheel bearings can be adjusted for
looseness, while others must be replaced if loose. Adjust or replace the bearings as
recommended by the manufacturer.
d. Check the door latch adjustment. If the door is slightly loose, or the latch adjustment
is not centered, the door assembly may create noises over bumps and rough surfaces.
Properly adjust the door latches to secure the door. 3. Vehicle makes a low pitched rumbling noise when driven
a. A low pitched rumbling noise is usually caused by a drive train related bearing and is
most often associated with a wheel bearing which has been damaged or worn. The
damage can be caused by excessive brake temperatures or physical contact with a pot
hole or curb. Sometimes the noise will vary when turning. Left hand turns increase the
load on the vehicle’s right side, and right turns load the left side. A failed front wheel
bearing may also cause a slight steering wheel vibration when turning. A bearing
which exhibits noise must be replaced.
b. Check the tire condition and balance. An internally damaged tire may cause failure
symptoms similar to failed suspension parts. For diagnostic purposes, try a known
good set of tires and replace defective tires.
4. Vehicle makes a squeaking noise over bumps
a. Check the vehicle’s ball joints for wear, damaged or leaking boots. Replace a ball joint
if it is loose, the boot is damaged and leaking, or the ball joint is binding. When re-
placing suspension parts, check the vehicle for alignment.
b. Check for seized or deteriorated bushings. Replace bushings that are worn or dam-
aged and check the vehicle for alignment.
c. Check for the presence of sway bar or stabilizer bar bushings which wrap around the
bar. Inspect the condition of the bushings and replace if worn or damaged. Remove
the bushing bracket and apply a thin layer of suspension grease to the area where the
bushings wrap around the bar and reinstall the bushing brackets. ~
5. Vehicle vibrates when driven
a. Check the road surface. Roads which have rough or uneven surfaces may cause un-
usual vi brations.
b. Check the tire condition and balance. An internally damaged tire may cause failure
symptoms similar to failed suspension parts. For diagnostic purposes, try a known
good set of tires and replace defective tires immediately.
c. Check for a worn Constant Velocity (CV-joint) joint, universal (U- joint) or flex joint
and replace if loose, damaged or binding.
d. Check for a loose, bent, or out-of-balance axle or drive shaft. Replace damaged or
failed components.
NOTE: Diagnosing failures related to wheels, tires, steering and the sus-
pension system can often times be accomplished with a careful and thor-
ough test drive. Bearing noises are isolated by noting whether the noises
or symptoms vary when turning left or right, or occur while driving a
straight line. During a teft hand turn, the vehicle’s weight shifts to the
right, placing more force on the right side bearings, such that if a right side
wheel bearing is worn or damaged, the noise or vibration should increase
during light-to-heavy acceleration. Conversely, on right hand turns, the ve-
hicle tends to lean to the left, loading the left side bearings.
Knocking noises in the suspension when the vehicle is driven over rough roads, rail-
road tracks and speed bumps indicate worn suspension components such as bushings,
ball joints or tie rod ends, or a worn steering system.
1. One headlight only works on high or low beam
a. Check for battery voltage at headlight electrical connector. If battery voltage is present,
replace the headlight assembly or bulb if available separately. If battery voltage is not
present, refer to the headlight wiring diagram to troubleshoot.
2. Headlight does not work on high or low beam
a. Check for battery voltage and ground at headlight electrical connector. If battery volt-
age is present, check the headlight connector ground terminal for a proper ground. If
battery voltage and ground are present at the headlight connector, replace the head-
light assembly or bulb if available separately. If battery voltage or ground is not pre-
sent, refer to the headlight wiring diagram to troubleshoot.
b. Check the headlight switch operation. Replace the switch if the switch is defective or
ooerates intermittentlv. 1. Tail light, running light or side marker light inoperative
a. Check for battery voltage and ground at light’s electrical connector. If battery voltage is
present, check the bulb socket and electrical connector ground terminal for a proper
ground. If battery voltage and ground are present at the light connector, but not in the
socket, clean the socket and the ground terminal connector. If battery voltage and
ground are present in the bulb socket, replace the bulb. If battery voltage or ground is
not present, refer to the wiring diagram to troubleshoot for an open circuit.
b. Check the light switch operation and replace if necessary.
2. Tall light, running light or side marker light works intermittently
a. Check the bulb for a damaged filament, and replace if damaged.
b. Check the bulb and bulb socket for corrosion, and clean or replace the bulb and
socket.
w 3. Headlight(s) very dim
a. Check for battery voltage and ground at headlight electrical connector. If battery volt-
age is present, trace the ground circuit for the headlamp electrical connector, then
clean and repair as necessary. If the voltage at the headlight electrical connector is
significantly less than the voltage at the battery, refer to the headlight wiring diagram
to troubleshoot and locate the voltage drop. c. Check for loose, damaged or corroded wires and electrical terminals, and repair as
necessary.
d. Check the light switch operation and replace if necessary.
3. Tail light, running light or side marker light very dim
a. Check the bulb and bulb socket for corrosion and clean or replace the bulb and
socket.
Page 396 of 408

II-14 TROUBLESHOOTING
b. Check for low voltage at the bulb socket positive terminal or a poor ground. If voltage
is low, or the ground marginal, trace the wiring to, and check for loose, damaged or
corroded wires and electrical terminals; repair as necessary.
c. Check the light switch operation and replace if necessary.
1. Interior light inoperative
a. Verify the interior light switch location and position(s), and set the switch in the cor-
rect position.
b. Check for battery voltage and ground at the interior light bulb socket. If battery voltage
and ground are present, replace the bulb. If voltage is not present, check the interior
light fuse for battery voltage. If the fuse is missing, replace the fuse. If the fuse has
blown, or if battery voltage is present, refer to the wiring diagram to troubleshoot the
cause for an open or shorted circuit. If ground is not present, check the door switch
contacts and clean or repair as necessary.
2. Interior light works intermittent/y
a. Check the bulb for a damaged filament, and replace if damaged.
b. Check the bulb and bulb socket for corrosion, and clean or replace the bulb and
socket.
c. Check for loose, damaged or corroded wires and electrical terminals; repair as neces-
sary.
d. Check the door and light switch operation, and replace if necessary.
3. Interior light very dim
a. Check the bulb and bulb socket for corrosion, and clean or replace the bulb and
socket.
b. Check for low voltage at the bulb socket positive terminal or a poor ground. If voltage
is low, or the ground marginal, trace the wiring to, and check for loose, damaged or
corroded wires and electrical terminals; repair as necessary.
c. Check the door and light switch operation, and replace if necessary.
1. One brake light inoperative
a. PressPress the brake pedal and check for battery voltage and ground at the brake light
bulb socket. If present, replace the bulb. If either battery voltage or ground is not pre-
sent, refer to the wiring diagram to troubleshoot.
2. Both brake lights inoperative
a. Press the brake pedal and check for battery voltage and grou’nd at the brake light bulb
socket. If present, replace both bulbs. If battery voltage is not present, check the brake
light switch adjustment and adjust as necessary. If the brake light switch is properly
adjusted, and battery voltage or the ground is not present at the bulb sockets, or at the
bulb electrical connector with the brake pedal pressed, refer to the wiring diagram to
troubleshoot the cause of an open circuit.
3. One or both brake lights very dim
a. Press the brake pedal and measure the voltage at the brake light bulb socket. If the
measured voltage is close to the battery voltage, check for a poor ground caused by a
loose, damaged, or corroded wire, terminal, bulb or bulb socket. If the ground is
bolted to a painted surface, it may be necessary to remove the electrical connector and
clean the mounting surface, so the connector mounts on bare metal. If battery voltage
is low, check for a poor connection caused by either a faulty brake light switch, a
loose, damaged, or corroded wire, terminal or electrical connector. Refer to the wiring
diagram to troubleshoot the cause of a voltage drop.
1. Warning light(s) stay on when the engine is started
Ignition, Battery or Alternator Warning light a. Check the alternator output and voltage regulator operation, and replace as necessary.
b. Check the warning light wiring for a shorted wire.
Check Engine Light a. Check the engine for routine maintenance and tune-up status. Note the engine tune-up
specifications and verify the spark plug, air filter and engine oil condition; replace
and/or adjust items as necessary.
b. Check the fuel tank for low fuel level, causing an intermittent lean fuel mixtur
e. Top off fuel tank and reset check engine light.
c. Check for a failed or disconnected engine fuel or ignition component, sensor or con-
trol unit and repair or replace as necessary.
d. Check the intake manifold and vacuum hoses for air leaks and repair as
necessary.
e. Check the engine’s mechanical condition for excessive oil consumption.
Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) Light a. Check the wheel sensors and sensor rings for debris, and clean as necessary.
b. Check the brake master cylinder for fluid leakage or seal failure and replace as neces-
sary.
c, Check the ABS control unit, pump and proportioning valves for proper operation; re-
place as necessary.
d. Check the sensor wiring at the wheel sensors and the ABS control unit for a loose or
shorted wire, and repair as necessary.
brake Warning Light a. Check the brake fluid level and check for possible leakage from the hydraulic lines and
seals. Top off brake fluid and repair leakage as necessary.
b. Check the brake linings for wear and replace as necessary.
c. Check for a loose or shot-ted brake warning light sensor or wire, and replace or repair
as necessary.
Oil Pressure Warning Light a. Stop the engine immediately. Check the engine oil level and oil filter condition, and
top off or change the oil as necessary.
b. Check the oil pressure sensor wire for being shorted to ground. Disconnect the wire
from the oil pressure sensor and with the ignition in the ON position, but not running,
the oil pressure light should not be working. If the light works with the wire discon-
nected, check the sensor wire for being shorted to ground. Check the wire routing to
make sure the wire is not pinched and check for insulation damage. Repair or replace
the wire as necessary and recheck before starting the engine.
c. Remove the oil pan and check for a clogged oil pick-up tube screen.
d. Check the oil pressure sensor operation by substituting a known good sensor.
e. Check the oil filter for internal restrictions or leaks, and replace as necessary.
WARNING: If the engine is operated with oil pressure below the manufac-
turer’s specification, severe (and costly) engine damage could occur. Low
oil pressure can be caused by excessive internal wear or damage to the en-
gine bearings, oil pressure relief valve, oil pump or oil pump drive mecha-
nism.
Before starting the engine, check for possible causes of rapid oil loss, such as leaking
oil lines or a loose, damaged, restricted, or leaking oil filter or oil pressure sensor. If the
engine oil level and condition are acceptable, measure the engine’s oil pressure using a
pressure gauge, or determine the cause for the oil pressure warning light to function
when the engine is running, before operating the engine for an extended period of time.
Another symptom of operating an engine with low oil pressure is the presence of severe
knocking and tapping noises.
Parking Brake Warning Light a. Check the brake release mechanism and verify the parking brake has been fully re-
leased.
b. CheckCheck the parking brake light switch for looseness or misalignment.
c. CheckCheck for a damaged switch or a loose or shorted brake light switch wire, and
replace or repair as necessary.
2. Warning light(s) flickers on and off when driving
Ignition, Battery or Alternator Warning Light a. Check the alternator output and voltage regulator operation. An intermittent condition
may indicate worn brushes, an internal short, or a defective voltage regulator. Replace
the alternator or failed component.
b. Check the warning light wiring for a shorted, pinched or damaged wire and repair as
necessary.
Check Engine Light a. Check the engine for required maintenance and tune-up status. Verify engine tune-up
specifications, as well as spark plug, air filter and engine oil condition; replace and/or
adjust items as necessary.
b. Check the fuel tank for low fuel level causing an intermittent lean fuel mixture. Top off
fuel tank and reset check engine light.
c. Check for an intermittent failure or partially disconnected engine fuel and ignition
component, sensor or control unit; repair or replace as necessary.
d. Check the intake manifold and vacuum hoses for air leaks, and repair as necessary.
e. Check the warning light wiring for a shorted, pinched or damaged wire and repair as
necessary.
Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) Light a. Check the wheel sensors and sensor rings for debris, and clean as necessary.
b. Check the brake master cylinder for fluid leakage or seal failure and replace as neces-
sary.
c. Check the ABS control unit, pump and proportioning valves for proper operation, and
replace as necessary.