Page 527 of 751
06-2
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Location Front Axle Rear Axle
GearType Hypoid←←←
SizeØ182.8 mm ← Ø228.6 mm ←
Offset28.58 mm
(DYMOS)
35 mm(Tongil)←30 mm -
Housing Steel←Steel casting←
OilTypeSAE 80W/90, API
GL-5←SAE 80W/90, API
GL-5←
Capacity 1.4 L←
2.0L
←
Length 448.0 mm←469.0 mm←
Witdh 681.9 mm←1,717.7 mm←
Weight 45 kg←90 kg←
Specification M/T A/T M/T A/T
Gear ratio4.55R(5MT DSL)
4.89R(5MT GSL)3.54(5AT DSL)
3.91(6AT DSL)4.55R(5MT DSL)
4.89R(5MT GSL)3.54(5AT DSL)
3.91(6AT DSL)
Page 528 of 751
07-33240-01
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Description Specifications
Type Part-time transfer case
Total length 343 mm
Mating surface of front flange 40 mm
Weight 32.4 kg (including oil)
Oil capacity 1.4 L
Oil type ATF DEXRON III
Location Transfer case
Major element Housing Part-time & TOD
Bolt 11 ea, M8 x 1.25
Input shaft A/T: outer spline
M/T: inner spline
Page 547 of 751
08-10
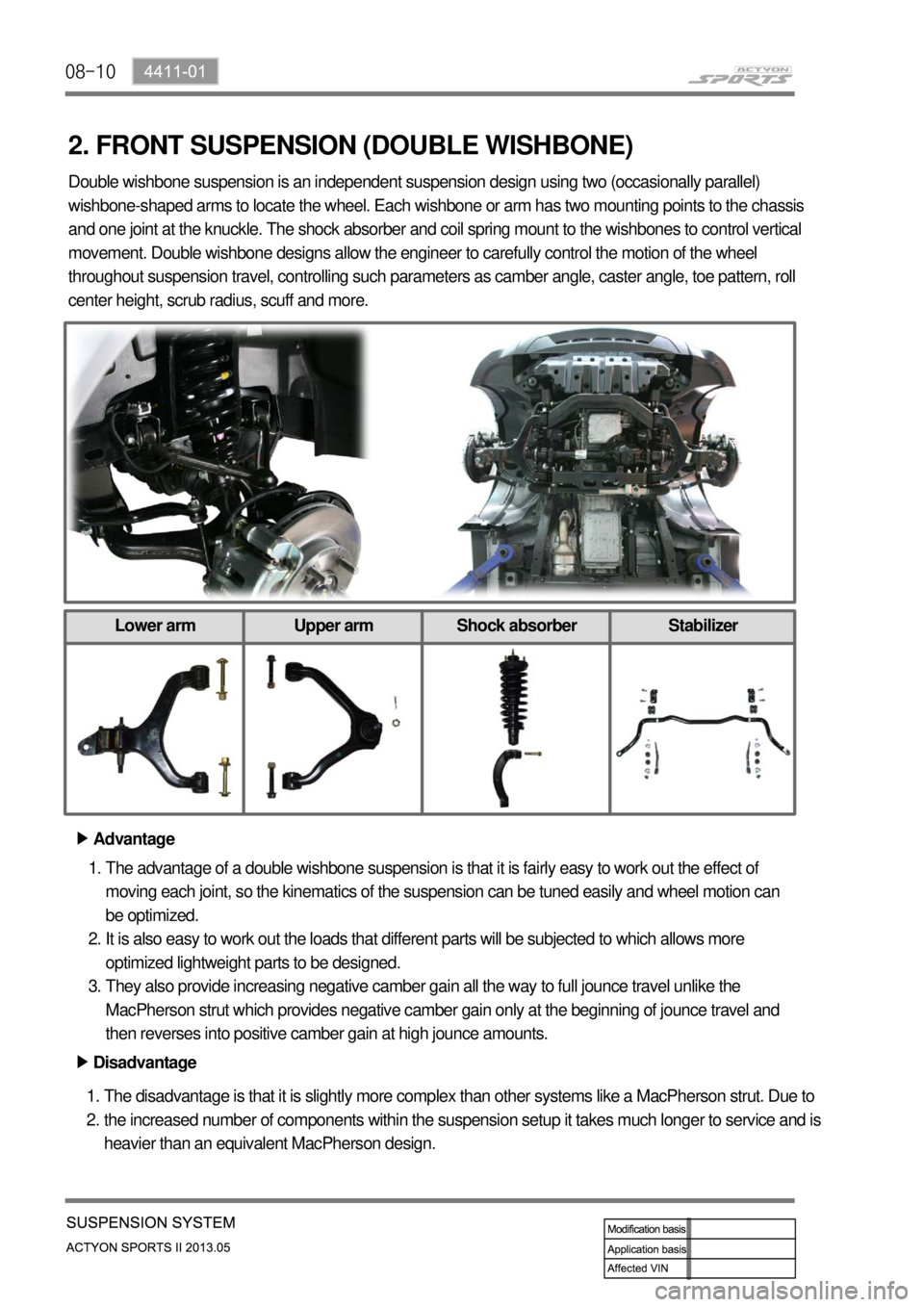
2. FRONT SUSPENSION (DOUBLE WISHBONE)
Advantage ▶
The advantage of a double wishbone suspension is that it is fairly easy to work out the effect of
moving each joint, so the kinematics of the suspension can be tuned easily and wheel motion can
be optimized.
It is also easy to work out the loads that different parts will be subjected to which allows more
optimized lightweight parts to be designed.
They also provide increasing negative camber gain all the way to full jounce travel unlike the
MacPherson strut which provides negative camber gain only at the beginning of jounce travel and
then reverses into positive camber gain at high jounce amounts. 1.
2.
3.
Disadvantage ▶
The disadvantage is that it is slightly more complex than other systems like a MacPherson strut. Due to
the increased number of components within the suspension setup it takes much longer to service and is
heavier than an equivalent MacPherson design. 1.
2. Double wishbone suspension is an independent suspension design using two (occasionally parallel)
wishbone-shaped arms to locate the wheel. Each wishbone or arm has two mounting points to the chassis
and one joint at the knuckle. The shock absorber and coil spring mount to the wishbones to control vertical
movement. Double wishbone designs allow the engineer to carefully control the motion of the wheel
throughout suspension travel, controlling such parameters as camber angle, caster angle, toe pattern, roll
center height, scrub radius, scuff and more.
Lower arm Upper arm Shock absorber Stabilizer
Page 548 of 751
08-114411-01
3. REAR SUSPENSION (MULTI LINK TYPE)
Multi-link (5-Link) type suspension is the independent suspension. It provides good ride comfort and
drivability by reducing the coil spring weight. Also, it increases the space for passenger compartment by
lowering the floor. This type of suspension consists of multiple links such as coil spring, shock absorber,
upper and lower arms, lateral rod and stabilizer bar.
Shock absorber Stabilizer bar Rear coil spring
Lower arm Upper arm Lateral rod
Page 594 of 751

10-14
2) Basic Theory of ABS Function
To give you a better understanding of the tasks and functions of ABS, we will first look at the physics
principles.
(1) Stopping distance
(2) Brake force on a wheel
The maximum possible brake force on a wheel depends on the wheel load and the adhesion coefficient
between tire and carriageway. With a low adhesion coefficient the brake force, which can be obtained is
very low. You are bound to know the result already from driving on winter roads. With a high adhesion
coefficient on a dry road, the brake force, which can be obtained, is considerably higher. The brake
force, which can be obtained, can be calculated from below formula:
Maximum brake force ▶
FBmax = wheel load FR x coefficient of
frictionMh
The braking process cannot be described
sufficiently accurately with the brake forces
calculated. The values calculated only apply if
the wheel is not locked. In the case of a locking
wheel, the static friction turns into lower sliding
friction, with the result that the stopping distance
is increased. This loss of friction is termed "slip"
in specialist literature.
The stopping distance depends on the vehicle weight and initial speed when braking starts. This also
applies for vehicle with ABS, where ABS always tries to set an optimum brake force on each wheel. As
great forces are exerted between the tires and the carriageway when braking, even with ABS the wheels
may scream and rubber is left on the road. With an ABS skid mark one may be able to clearly recognize
the tire profile. The skid mark of an ABS vehicle does not however leave any hint of the speed of the
vehicle in the case of an accident, as it can only be clearly drawn at the start of braking.
Page 653 of 751
13-34620-01
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Item Item Specification
SSPS solenoid valveRated voltage DC 12 V
Rated voltage 1.0 A
Resistance6.7 ±1 Ω
Power steering oil pump
(with SSPS)Operating temperature-40℃~150℃
Release pressure 90 bar
Displacement 9.3 cc/rev
Flow velocity 9.75~6 l/mn
Pulley sizeØ115
Pulley type 6 groove
Housing material Aluminium
Power steering fluid reservoir
(with SSPS)Fracture pressuremin 8kgf/㎠
Air leakage2 kgf/㎠×min
Cap open torque 9.8 to 14.2 Nm
Oil capacity FULL 550cc
Power steering gear box
(with SSPS)Gear type Rack & pinion type
Gear ratio 40.245
Fixed rack 3.78
Gear weight 12.800 kg
Steering angleInner36.2°
Outer32.4°
Page 664 of 751
14-34170-09
1. SPECIFICATIONS
2. MAJOR CHANGES
Wheel assembly
16-inches silver 18-inches silver 18-inches hyper silver
PN: 41730-32000 PN: 41730-32200 PN: 41730-32300
- Added 18-inches hyper silver to wheel assembly
- Wheel offset and tire size are identical with existing specifications
Existing specifications New specifications
Description Specification
Tire 16 inch 225/75R 16
18 inch 255/60R 18
Tire inflation pressure Front: 32 psi
Rear: 32 psi (44 psi: when the vehicle is fully laden
with luggage)
Wheel 16 inch 6.5J x 16
18 inch 7.5J x 18
Balance weight 16 inch Inner: Attachment type
Outer: Clip type
18 inch Inner: Attachment type
Outer: Attachment type
Tightening torquse of wheel bolt 127.4 ~ 156.8 Nm
Page 670 of 751
14-94170-09
Wheel balance 5.
Check the wheel balance when the wheel
is unbalanced or the tire is repaired.
The total weight of the wheel weight
should not exceed 150 g.
Ensure that the balance weight installed is
not projected over 3mm from the wheel
surface.
Use the specified aluminum wheel balance
weights for aluminum wheels.
Weight balance can be added by 5 g.
There are two types of weight balance,
tape type and adhesion type. -
-
-
-
-
-
Make sure to read the manual of the
manufacturer thoroughly before using
wheel balance tester. -
Change tire location
To avoid uneven wear of tires and to prolong
tire life, inspect and rotate your tires every
5,000 km. 6.
Mixing tires could cause to lose control while driving. Be sure to use the same size and type tires of
the same manufacturer on all wheels. -