Page 672 of 751

14-114170-09
1. OVERVIEW
A radial tire uses a cord angle of 90 degrees. That is, the cord material runs in a radial or direct line from
one bead to the other across the tread. In addition, a radial tire has a belt overwrap under the tread
surface to provide greater structural stability. The belt overwrap of a radial tire distortion while the radial
structure enables high speed driving.
Tire supports the weight of the vehicle, reduces the impact from the road and at the same time, transmits
<009b008f008c004700970096009e008c00990047009b009600470097009900960097008c0093005300470089009900880092008c004700880095008b0047009a009b008c008c00990047009600950047009b008f008c0047009900960088008b0055004700
70009b004700880093009a00960047008d009c0095008a009b>ions to maintain a vehicle’s
movement. In order to complete such tasks, a tire must be structured to be a resilient vessel of air.
There is wear limit mark on the tire, which protrudes as a strip shape located approximately 1.6 mm from
the groove bottom. This wear limit mark is not seen from the outside so there is additional "▲"
mark on the shoulder to let the driver find the wear mark easily. To measure the tire groove depth,
measure at any point other than the point which has a wear limit mark.
The tire is worn unevenly according to the driver's driving habit, improper servicing, low tire inflation
pressure, changed tire location, etc.
Page 678 of 751

14-174170-09
If weight is not equally distributed around the wheel, unbalance centrifugal force by the wheel rotation
produces vibration. As the centrifugal force is produced proportional to the square of the rotating speed,
the wheel weight should be balanced even at high speed. There are two types of the tire and wheel
balancing: static and dynamic. Abnormal vibration may also occur due to unbalanced rigidity or size of
tires.
Static Balance ▶
When the free rotation of the wheel is allowed,
the heavier part is stopped on the bottom if the
wheel weight is unbalanced and this is called
"Static Unbalance". Also, the state at which tire's
stop position is not same is called "Static
Balance" when the wheel is rotated again. If the
part A is heavier as shown in the figure 1, add
the balance weight of a weight corresponding to
unbalanced weight from B to A to maintain the
static balance. If the static balance is not
maintained, tramping, up and down vibration of
the wheels, occurs.
Dynamic Balance ▶
The static unbalance of the wheel creates the
vibration in the vertical direction, but the dynamic
unbalance creates the vibration in the lateral
direction. As shown in the figure 2 (a), if two
parts, (2) and (3), are heavier when the wheels
are under the static balance condition, dynamic
unbalance is created, resulting in shimmy, left
and right vibration of the wheels, and the torque
Fxa is applied in the axial direction. To correct
the dynamic unbalance, add the balance weight
of a same weight for two points of the
circumference of the rim, A and B, as shown in
the figure 2 (b), and apply the torque in the
opposite direction to the torque Fxa to offset in
order to ensure smooth rotation of the wheel.
Center
A
B
(a) (b)
[Figure 1]
[Figure 2]
3. WHEEL BALANCE
Page 679 of 751
14-18
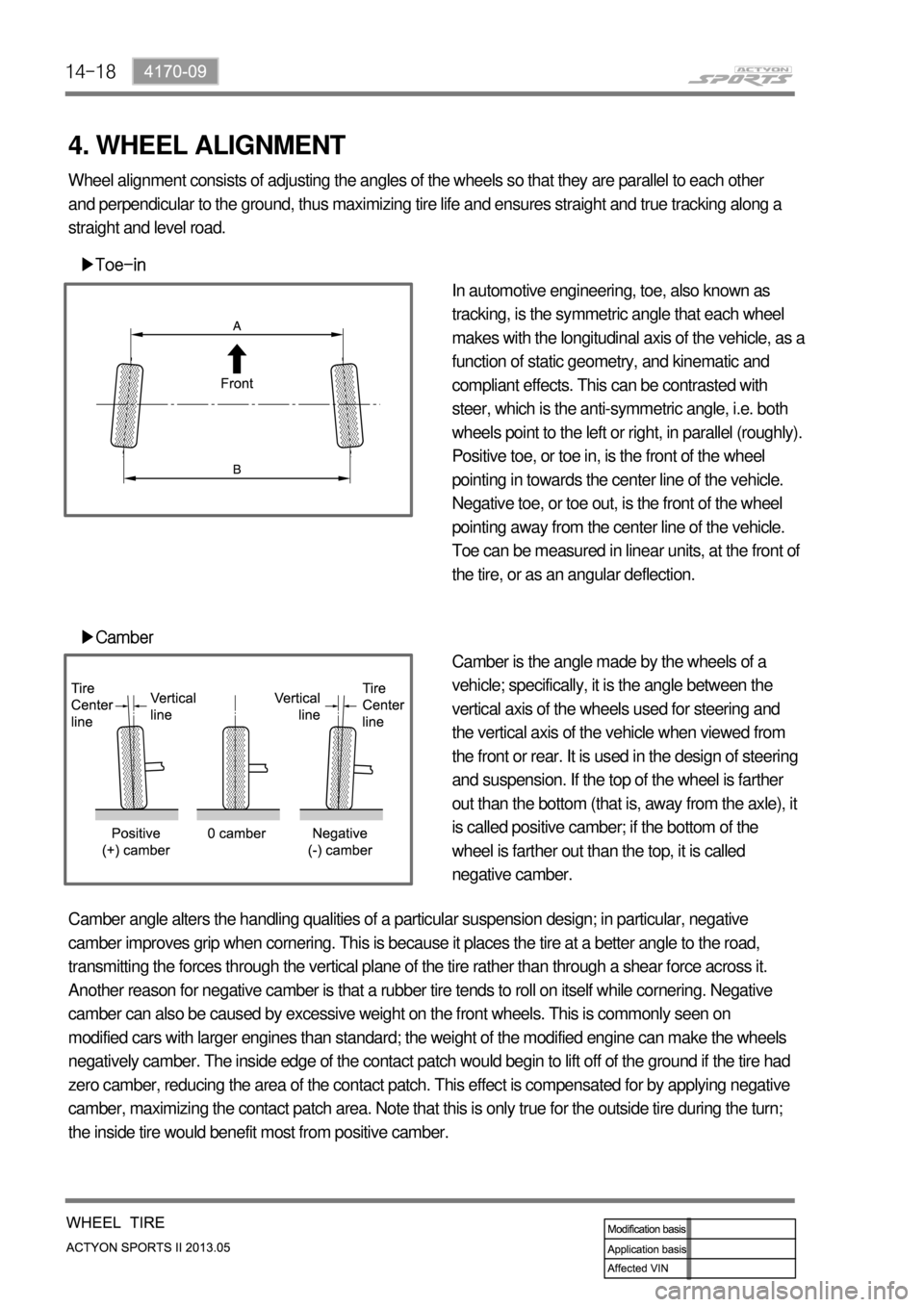
4. WHEEL ALIGNMENT
▶Toe-in
▶Camber
In automotive engineering, toe, also known as
tracking, is the symmetric angle that each wheel
makes with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle, as a
function of static geometry, and kinematic and
compliant effects. This can be contrasted with
steer, which is the anti-symmetric angle, i.e. both
wheels point to the left or right, in parallel (roughly).
Positive toe, or toe in, is the front of the wheel
pointing in towards the center line of the vehicle.
Negative toe, or toe out, is the front of the wheel
pointing away from the center line of the vehicle.
Toe can be measured in linear units, at the front of
the tire, or as an angular deflection.
Camber is the angle made by the wheels of a
vehicle; specifically, it is the angle between the
vertical axis of the wheels used for steering and
the vertical axis of the vehicle when viewed from
the front or rear. It is used in the design of steering
and suspension. If the top of the wheel is farther
out than the bottom (that is, away from the axle), it
is called positive camber; if the bottom of the
wheel is farther out than the top, it is called
negative camber. Wheel alignment consists of adjusting the angles of the wheels so that they are parallel to each other
and perpendicular to the ground, thus maximizing tire life and ensures straight and true tracking along a
straight and level road.
Camber angle alters the handling qualities of a particular suspension design; in particular, negative
camber improves grip when cornering. This is because it places the tire at a better angle to the road,
transmitting the forces through the vertical plane of the tire rather than through a shear force across it.
Another reason for negative camber is that a rubber tire tends to roll on itself while cornering. Negative
camber can also be caused by excessive weight on the front wheels. This is commonly seen on
modified cars with larger engines than standard; the weight of the modified engine can make the wheels
negatively camber. The inside edge of the contact patch would begin to lift off of the ground if the tire had
zero camber, reducing the area of the contact patch. This effect is compensated for by applying negative
camber, maximizing the contact patch area. Note that this is only true for the outside tire during the turn;
the inside tire would benefit most from positive camber.
Page 681 of 751
14-20
Even friction coefficient road Uneven friction coefficient road
Driving Force
Braking Force
Supporting the Vehicle Weight ▶Transferring the Driving Force & Braking Force to Road ▶
5. FUNCTIONS OF TIRE
Supporting the Vehicle Weight ▶
Page:
< prev 1-8 9-16 17-24