2013 SSANGYONG NEW ACTYON SPORTS turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 2 of 751

01-4
Detailed Dimensions ▶
Unit:mm
Headlamp
Front fog lamp
Side repeater
Tun signal lamp (front)
Position lamp 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.Stop/Tail lamp
Back-up lamp
License plate lamp
Turn signal lamp (rear)
Reflector 6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Page 101 of 751
03-24
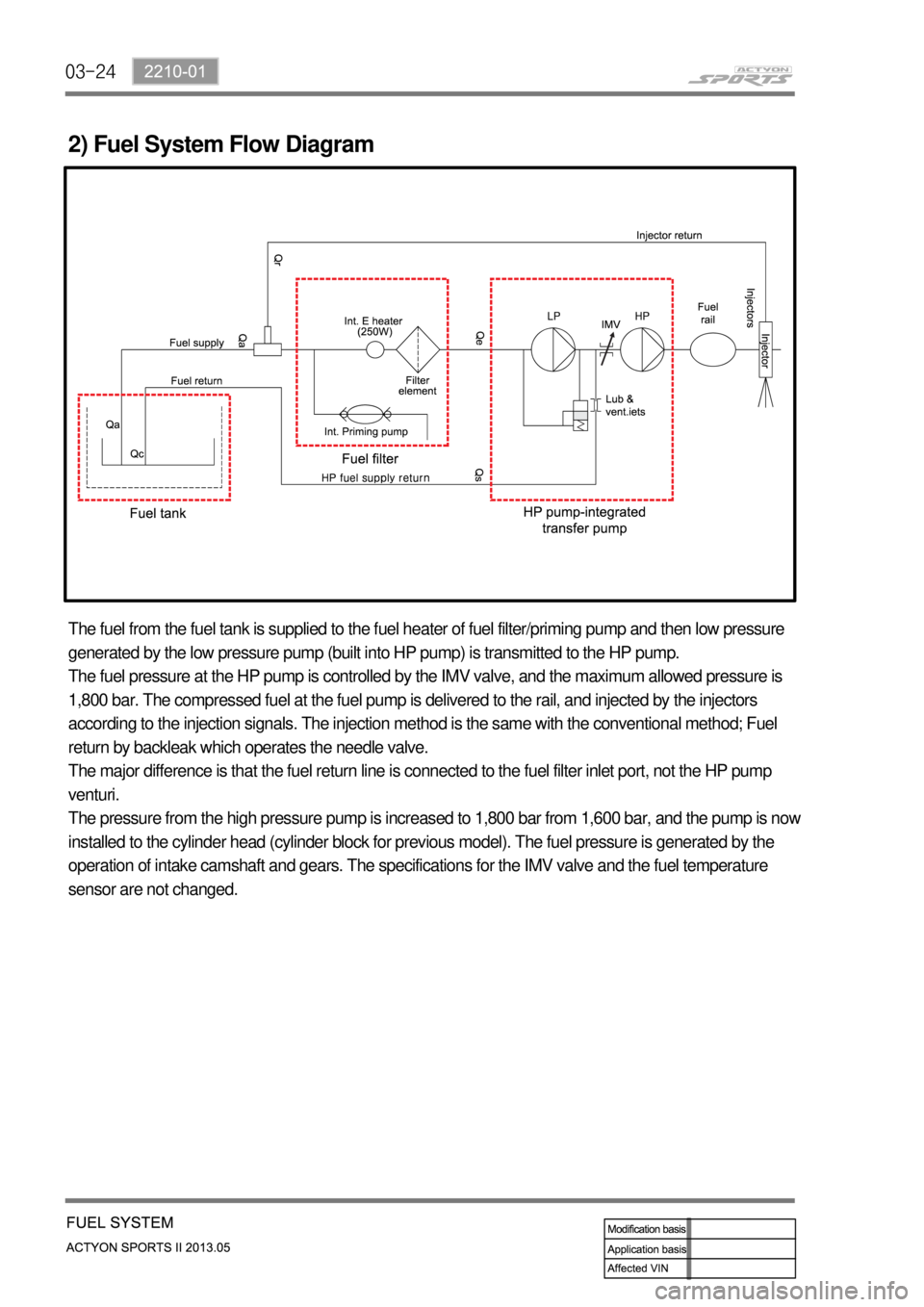
2) Fuel System Flow Diagram
The fuel from the fuel tank is supplied to the fuel heater of fuel filter/priming pump and then low pressure
generated by the low pressure pump (built into HP pump) is transmitted to the HP pump.
The fuel pressure at the HP pump is controlled by the IMV valve, and the maximum allowed pressure is
1,800 bar. The compressed fuel at the fuel pump is delivered to the rail, and injected by the injectors
according to the injection signals. The injection method is the same with the conventional method; Fuel
return by backleak which operates the needle valve.
The major difference is that the fuel return line is connected to the fuel filter inlet port, not the HP pump
venturi.
The pressure from the high pressure pump is increased to 1,800 bar from 1,600 bar, and the pump is now
installed to the cylinder head (cylinder block for previous model). The fuel pressure is generated by the
operation of intake camshaft and gears. The specifications for the IMV valve and the fuel temperature
sensor are not changed.
Page 107 of 751

04-6
1. OVERVIEW
The intake system for D20DTR engine is equipped with a throttle body which includes a flap. This flap is
controlled by an electrical signal to cut off the intake air entering to the engine when the ignition switch is
turned off. Because of this, the shape of the intake manifold has been changed and improved HFM
sensor is newly adopted to control the intake air volume more precisely.
2. COMPONENT
2330-01 Intercooler assembly
2313-15 HFM sensor
HFM sensor, version 6
*For more information, refer to Chapter "Engine
Control".
2313-01 Air cleaner assembly
Page 139 of 751

07-51543-00
1. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1) Overview
The lubrication system supplies oil to each lubrication section to prevent friction and wear and to remove
heat from the friction part. As the engine runs, frictional heat is generated on each lubrication section. If
this condition persists, the bearing can be burned and stuck.
In other words, it creates an oil film on each sliding surface to convert solid friction to liquid friction in order
to minimize wear and prevent temperature increasing on the friction part.
For the D20DTF engine with no oil pressure switch, the engine ECU receives the low engine oil level
signal from the oil level sensor and communicates with the instrument cluster through the CAN
communication to turn on the warning lamp.
2) Components
Oil coolerOil dipstick gaugeOil pump
Oil filter moduleOil pressure switchOil pan
Page 180 of 751

12-12
Do not move the shift lever to Neutral position while driving with the cruise control turned on.
Otherwise, it may result in system malfunction or accidents.
Always be prepared to use the brake or accelerator pedal for safe driving while the cruise control
system is running.
The actual speed can be different from the set speed momentarily when driving on a uphill or
downhill. So, it is recommended to disable the cruise control function on a uphill or downhill. hen
driving on a steep hill use the engine brake and foot brake properly to protect the vehicle system
and for a safe driving.
Ensure that the safe distance is maintained and use the brake pedal if needed. 1.
2.
3.
4.
(1) Abnormal Cancellation of the Cruise Control
When the rapid deceleration is applied without braking.
When the rapid acceleration is applied without acceleration pedal intervention.
When the cruise control lever is faulty.
When the brake switch and the brake light switch input signal are implausible. 1.
2.
3.
When the cruise control function is cancelled abnormally or intermittent problems occur, stop the vehicle
and turn off the ignition switch and remove the key to reset the system. After a while, turn on the ignition
switch again to operate the cruise control system.
Page 211 of 751

15-110000-00
2) ECU Control
(1) Function
a. ECU Function
ECU receives and analyzes signals from various sensors and then modifies those signals into
permissible voltage levels and analyzes to control respective actuators.
ECU microprocessor calculates injection period and injection timing proper for engine piston speed and
crankshaft angle based on input data and stored specific map to control the engine power and emission
gas.
Output signal of the ECU microprocessor drives pressure control valve to control the rail pressure and
activates injector solenoid valve to control the fuel injection period and injection timing; so controls
various actuators in response to engine changes. Auxiliary function of ECU has adopted to reduce
emission gas, improve fuel economy and enhance safety, comforts and conveniences. For example,
there are EGR, booster pressure control, autocruise (export only) and immobilizer and adopted CAN
communication to exchange data among electrical systems (automatic T/M and brake system) in the
vehicle fluently. And Scanner can be used to diagnose vehicle status and defectives.
<00760097008c00990088009b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c0047009900880095008e008c00470096008d0047006c006a007c00470090009a0047009500960099009400880093009300a000470054005b005700
47009b009600470052005f005c00b6006a004700880095008b> protected from factors like oil,
water and electromagnetism and there should be no mechanical shocks.
To control the fuel volume precisely under repeated injections, high current should be applied instantly
so there is injector drive circuit in the ECU to generate necessary current during injector drive stages.
Current control circuit divides current applying time (injection time) into full-in-current-phase and hold-
current-phase and then the injectors should work very correctly under every working condition.
b. Control Function
Controls by operating stages
To make optimum combustion under every operating stage, ECU should calculate proper injection
volume in each stage by considering various factors.
Starting injection volume control
During initial starting, injecting fuel volume will be calculated by function of temperature and engine
cranking speed. Starting injection continues from when the ignition switch is turned to ignition
position to till the engine reaches to allowable minimum speed.
Driving mode control
If the vehicle runs normally, fuel injection volume will be calculated by accelerator pedal travel and
engine rpm and the drive map will be used to match the drivers inputs with optimum engine power. -
-
-
Page 275 of 751

02-6
1) Starting Mode
When the ignition is turned ON, the ECM turns the fuel pump relay on for 1 second. The fuel pump then
builds fuel pressure. The ECM also checks the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor and the
Throttle Position (TP) sensor and determines the proper air/fuel ratio for starting the engine. This ranges
from1.5 to 1 at -36 °C (-33 °F) coolant temperature to 14.7 to 1 at 94 °C (201 °F) coolant
temperature. The ECM controls the amountof fuel delivered in the starting mode by changing how long
the fuel injector is turned on and off. This is done by ''pulsing" the fuel injectors for very short times.
2) Run Mode
The run mode has two conditions called ''open loop" and ''closed loop".
3) Open Loop
When the engine is first started and it is above 690 rpm, the system goes into "open loop" operation. In
"open loop", the ECM ignores the signal from the HO2S and calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs
from the ECT sensor and the MAF sensor. The ECM stays in "open loop" until the following conditions
are met:
The O2 has a varying voltage output, showing that it is hot enough to operate properly.
The ECT sensor is above a specified temperature (22.5 °C).
A specific amount of time has elapsed after starting the engine. -
-
-
4) Closed Loop
The specific values for the above conditions vary with different engines and are stored in the
Electronically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM).
When these conditions are met, the system goes into "closed loop" operation. In "closed loop", the ECM
calculates the air/fuel ratio (fuel injector on- time) based on the signals from the O2 sensors. This allows
the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7 to 1.
5) Acceleration Mode
The ECM responds to rapid changes in throttle position and airflow and provides extra fuel.
6) Deceleration Mode
The ECM responds to changes in throttle position and airflow and reduces the amount of fuel. When
deceleration is very fast, the ECM can cut off fuel completely for short periods of time.
Page 288 of 751

06-8
The cooling fans are mounted behind the radiator in the engine compartment. The electric cooling fans
increase the flow of air across the radiator fins and across the condenser on air conditioned (A/C)-
equipped vehicles.
This helps to speed cooling when the vehicle is at idle or moving at low speeds.
All models have two fans. The main fan is 320 mm (12. 6 inches) in diameter with seven blades to aid
the airflow through the radiator and the condenser. An electric motor attached to the radiator support
drives the fan.
The auxiliary fan is 320 mm (12.6 inches) in diameter.
A/C Off or Non-AC Model ▶
The cooling fans are actuated by the engine control module (ECM) using a low-speed cooling
fan relay, a high-speed cooling fan relay and a cooling fan motor relay.
The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed when the coolant temperature reaches
95°C(203°F) and at high speed when the coolant temperature reaches 105°C(221°F).
The ECM will change the cooling fans from high peed to low speed at 100°C(212°F) and
will turn the cooling fans off at 90°C (194°F). -
-
-
A/C On ▶
The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed when the A/C system is on. The ECM will
change to high speed when the high side A/C pressure reaches 1860 kPa (269.8 psi).
The cooling fans will return to low speed when the high side A/C pressure reaches 1378 kPa
(199.8 psi). -
-
7) Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor uses a temperature to control the signal voltage to the
Engine Control Module (ECM).
8) Coolant Temperature Gauge
The coolant temperature gauge controls the instrument panel temperature indicator. The coolant
temperature gauge is located with ECT sensor.