2010 JAGUAR XFR turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 537 of 3039

bus allows the DLM to communicate with other systems on the vehicle.
A certain amount of differential slip is required to allow the vehicle to turn corners and to remain stable under control of the
ABS. The ADM monitors the driver's demands through primary vehicle controls and automatically sets the slip torque in the differential. The system is completely automatic and does not require any special driver input.
The differential strategy in the ADM includes:
A pre-loading function, increasing locking torque with increased driving torque.
A slip controller to decrease locking torque for optimum comfort, e.g. parking.
The ADM memorizes the position of the motor when the ignition is switched off.
CAN bus messages used by the ADM include wheel speed, steering angle, automatic transmission speed, temperature information, car configuration, axle ratios and mode inputs.
The ADM also sends messages via the CAN bus to tell other control modules on the network the status of the electronic differential. The clutch torque and default mode status are some of the main signals sent out by the ADM.
If the DLM or ADM are replaced, a Jaguar approved diagnostic system must be connected to the vehicle and the differential
self-calibration procedure must be performed. This procedure must also be performed if the motor or electronic differential is
replaced.
If a fault occurs with the electronic differential, the ADM, the DLM, or one of the required input signals, the ADM records an
error code and displays a warning in the message center.
The following messages can be displayed:
Message Description Chime E-DIFF NOT
AVAILABLE Differential temperature has reached the overheat threshold. System deactivated until temperature
returns within limits. Single E-DIFF FAULT Fault has occurred with electronic differential. System deactivated until fault rectified. Single
Page 697 of 3039

DSC becomes active whenever the engine is running. A momentary press of the switch allows the driver to toggle between the
standard DSC settings and the optimized 'Trac DSC' settings. The message 'Trac DSC' or 'DSC on' will temporarily be displayed
in the instrument cluster message center. The amber DSC warning indicator in the instrument cluster remains illuminated while
'Trac DSC' is selected.
The DSC can be switched off by pressing and holding the switch for more than 10 seconds.
In each case the message 'DSC OFF' will be displayed in the instrument cluster message center to confirm DSC has been
switched off. The amber DSC warning indicator in the instrument cluster will remain illuminated. The system can be switched
back on again by simply pressing and releasing the switch. The message 'DSC ON' will then temporarily appear in the
instrument cluster message center to confirm the system is on.
NOTE: Switch requests may be delayed if the switch is pressed while a DSC operation is taking place. The switch request
will be displayed in the instrument cluster but the ABS module will not initiate any stability changes until it is safe to do so.
If a fault is detected with the DSC switch, the ABS module defaults to the 'DSC ON' setting and any switch requests are ignored.
WARNING: It is recommended that when using snow chains, Trac DSC is switched off and JaguarDrive control winter mode
is selected.
Wheel Speed Sensors
Item Description 1 Front wheel speed sensor 2 Rear wheel speed sensor An active wheel speed sensor is installed in each wheel hub to provide the ABS module with a rotational speed signal from each road wheel. The head of each front wheel speed sensor is positioned close to a magnetic encoder ring incorporated into
the inboard seal of the wheel bearing. The head of each rear wheel speed sensor is positioned close to a magnetic encoder
ring incorporated into the rear wheel bearing assembly. Each encoder ring contains 46 north and south poles. A fly lead
connects each sensor to the vehicle harness.
The wheel speed sensors each have a signal and a return connection with the ABS module. When the ignition is ON the ABS module supplies a signal feed to the wheel speed sensors and monitors the return signals. Any rotation of the road wheels
induces current fluctuations in the return signals, which are converted into individual wheel speeds and overall vehicle speed
by the ABS module. The ABS module broadcasts the individual wheel speeds and the vehicle speed on the high speed CAN bus for use by other
Page 698 of 3039

center and an amber warning indicator will illuminate.
Refer to: Information and Message Center (413-08 Information and Message Center, Description and Operation).
As the wheel speed sensors are active devices, a return signal is available when the road wheels are not rotating. This enables
the ABS module to check the condition of the speed sensors while the vehicle is stationary.
Steering Angle Sensor
The steering angle sensor measures the steering wheel angle and the rate of change of the steering wheel angle. These
measurements are received by the ABS module and broadcast on the high speed CAN bus for use by other systems.
The steering angle sensor is mounted on the steering column upper shroud mounting bracket, immediately behind the
multifunction switches, and is secured by 2 screws. A fly lead connects the sensor to the passenger compartment wiring
harness via a 4 pin multiplug.
The sensor is housed in a 'U' shaped plastic casing and contains two offset LED (light emitting diode)s facing two detectors.
An encoder ring is mounted on the inner steering column shaft and intersects the LEDs and detectors. The encoder ring contains 60 slots which break and restore the light beams between the LEDs and the detectors as the steering wheel is
Page 744 of 3039

1 Return fluid control groove 2 Radial groove 3 Feed fluid control groove 4 Radial groove 5 Axial groove 6 Feed fluid control edge 7 Feed fluid radial groove 8 Return fluid control edge 9 Return fluid chamber 10 Cut-off valve 11 Radial groove 12 Servotronic transducer valve 13 Feed fluid radial groove 14 Radial groove 15 Orifice 16 Balls 17 Compression spring 18 Torsion bar 19 Power steering fluid reservoir 20 Valve rotor 21 Reaction piston 22 Reaction chamber 23 Centering piece 24 Pressure relief/flow limiting valve 25 Power steering pump 26 Inner tie-rod 27 Pinion 28 Valve sleeve 29 Steering gear rack 30 Steering gear housing 31 Power assist cylinder - right 32 Piston 33 Power assist cylinder - left When the steering wheel is turned to the right, the steering rack and piston moves to the left in the piston bore. The valve
rotor is rotated to the right (clockwise) and pressurized fluid is directed over the further opened feed fluid control edges and to
the associated axial grooves, the radial groove and via an external pipe to the left power assist cylinder chamber. The pressure
applied to the piston from the left power assist cylinder chamber provides the hydraulic assistance.
An adaptable pressure build-up is achieved by the partially or fully closed feed fluid control edges restricting or preventing a
connection between the fluid pressure inlet and the other axial grooves connected to the radial groove.
Simultaneously, the fluid pressure outlet to the pressurized axial grooves are restricted or partially restricted by the closing
return fluid control edges. The fluid displaced by the piston from the right power assist cylinder chamber, flows through an
external pipe to the radial grooves. From there the fluid passes to the associated axial grooves and on to the return fluid
control grooves, via the further opened return fluid control edges.
The return flow of fluid to the reservoir passes via interconnecting bores which lead to the return fluid chamber. When the
steering wheel is turned to the left the operating sequence is as above but the pressure is applied to the opposite side of the
piston.
Servotronic Operation
The Servotronic software contains a number of steering maps which are selected via the car configuration file depending on the
vehicle mode and tire fitment.
If a failure of the Servotronic valve or software occurs, the system will suspend Servotronic assistance and only normal power
steering wheel be available. Fault codes relating to the fault are stored, but no warning lamps are illuminated and the driver
may be aware of the steering being 'heavier' than usual.
When the vehicle is manoeuvred into and out of a parking space (or other similar manoeuvre), the Servotronic software uses
road speed data from the ABS module to determine the vehicle speed, which in this case will be slow or stationary. The
Servotronic software analyses the signals and outputs an appropriate control current to the Servotronic transducer valve. The
Servotronic valve closes and prevents fluid flowing from the feed fluid radial groove to the reaction chamber. An orifice also
Page 747 of 3039

18 Pinion 19 Steering gear rack bar 20 Valve sleeve The valve unit is an integral part of the steering gear. The principle function of the valve unit is to provide power assistance
(i.e. when parking) to optimize the effort required to turn the steering wheel.
The pinion housing of the valve is an integral part of the main steering gear casting. The pinion housing has four machined
ports which provide connections for pressure feed from the power steering pump, return fluid to the reservoir and pressure
feeds to each side of the cylinder piston.
The valve unit comprises an outer sleeve, an input shaft, a torsion bar and a pinion shaft. The valve unit is co-axial with the
pinion shaft which is connected to the steering column via the input shaft. The valve unit components are located in the
steering gear pinion housing which is sealed with a cap.
The outer sleeve is located in the main bore of the pinion housing. Three annular grooves are machined on its outer diameter.
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) rings are located between the grooves and seal against the bore of the pinion housing. Holes
are drilled radially in each annular groove through the wall of the sleeve. The bore of the outer sleeve is machined to accept
the input shaft. Six equally spaced slots are machined in the bore of the sleeve. The ends of the slots are closed and do not
continue to the end of the outer sleeve. The radial holes in the outer sleeve are drilled into each slot.
The input shaft has two machined flats at its outer end which allow for the attachment of the steering column intermediate
shaft yoke. The flats ensure that the intermediate shaft is fitted in the correct position. The inner end of the input shaft forms
a dog-tooth which mates with a slot in the pinion shaft. The fit of the dog-tooth in the slot allows a small amount of relative
rotation between the input shaft and the pinion shaft before the dog-tooth contacts the wall of the slot. This ensures that, if
the power assistance fails, the steering can be operated manually without over stressing the torsion bar. The central portion of
the input shaft has equally spaced longitudinal slots machined in its circumference. The slots are arranged alternately around
the input shaft.
The torsion bar is fitted inside the input shaft and is an interference fit in the pinion shaft. The torsion bar is connected to the
input shaft by a drive pin. The torsion bar is machined to a smaller diameter in its central section. The smaller diameter allows
the torsion bar to twist in response to torque applied from the steering wheel in relation to the grip of the tyres on the road
surface.
The pinion shaft has machined teeth on its central diameter which mate with teeth on the steering gear rack. A slot, machined
in the upper end of the pinion shaft mates with the dog-tooth on the input shaft. The pinion shaft locates in the pinion
housing and rotates on ball and roller bearings.
Servotronic Valve
The Servotronic transducer valve is located in a port in the side of the steering gear valve housing. The valve is sealed in the
housing with an O-ring seal and is secured with two long screws into threaded holes in the housing. The Servotronic valve is a
transducer controlled valve which responds to control signals supplied from Servotronic software in the instrument cluster.
The Servotronic valve determines the hydraulic reaction at the steering gear rotary valve and controls the input torque required
to turn the steering wheel. The Servotronic system allows the steering to be turned with the optimum effort when the vehicle
is stationary or manoeuvred at slow speed. The hydraulic reaction changes proportional to the vehicle speed, with the required
steering effort increasing as the vehicle moves faster. At high speeds, the Servotronic system provides the driver with a good
feedback through the steering providing precise steering and improved stability.
The instrument cluster receives road speed signals from the ABS module and calculates the correct controlling signal for the Servotronic valve. The Servotronic software within the instrument cluster has a diagnostic capability which allows a Jaguar
approved diagnostic system to check the tune of the steering and retrieve fault codes relating to the Servotronic valve. Two
fault codes are stored relating to the valve for positive connection short to ground or battery and negative connection short to
ground or battery.
The Servotronic software within the instrument cluster also contains a number of steering maps which are selected via the car
configuration file depending on the vehicle model and tire fitment.
If a failure of the Servotronic valve or software occurs, the system will suspend Servotronic assistance and only a default level
of assistance will be available. Fault codes relating to the fault are stored in the instrument cluster. No warning lamps are
illuminated and the driver may be aware of the steering being 'heavier' than usual.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 782 of 3039
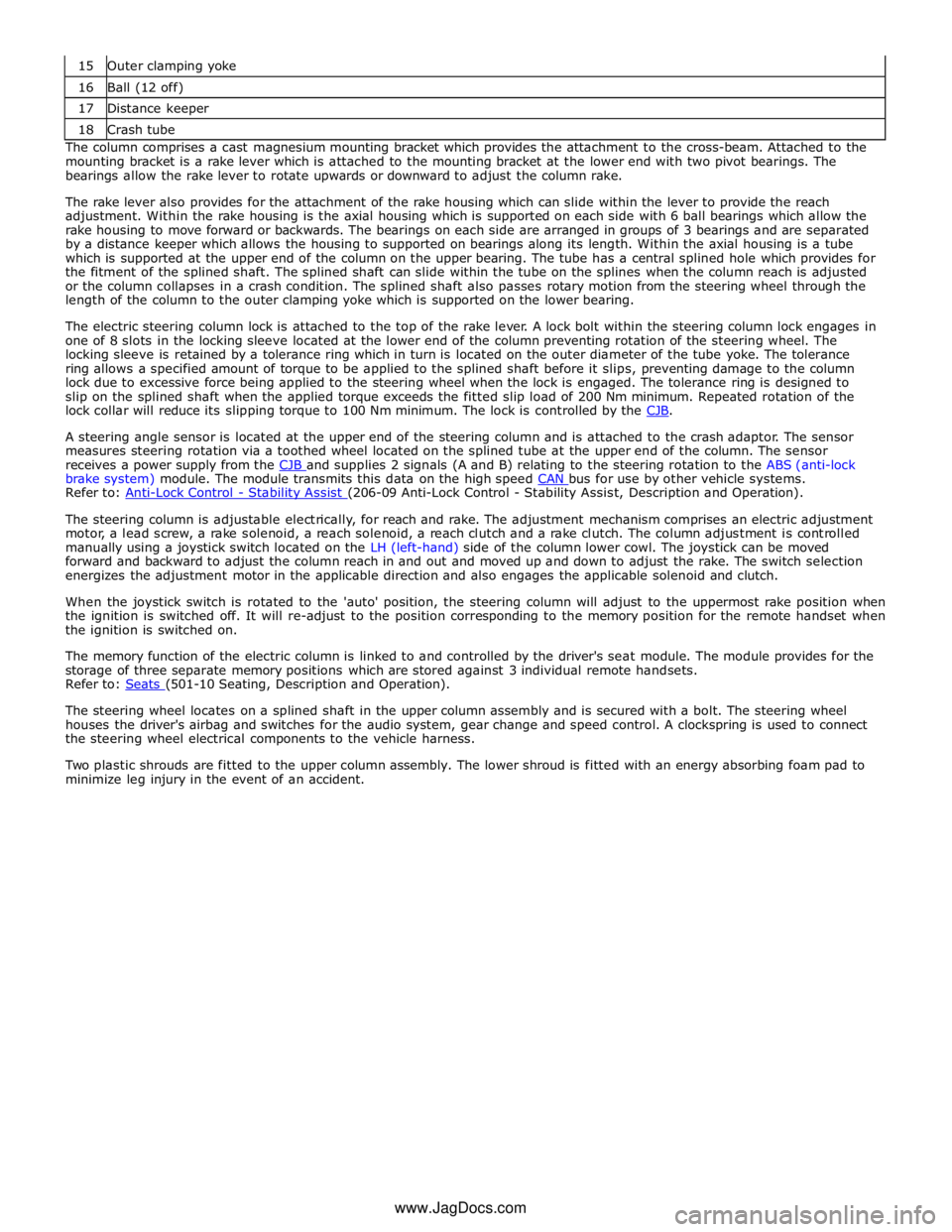
16 Ball (12 off) 17 Distance keeper 18 Crash tube The column comprises a cast magnesium mounting bracket which provides the attachment to the cross-beam. Attached to the
mounting bracket is a rake lever which is attached to the mounting bracket at the lower end with two pivot bearings. The
bearings allow the rake lever to rotate upwards or downward to adjust the column rake.
The rake lever also provides for the attachment of the rake housing which can slide within the lever to provide the reach
adjustment. Within the rake housing is the axial housing which is supported on each side with 6 ball bearings which allow the
rake housing to move forward or backwards. The bearings on each side are arranged in groups of 3 bearings and are separated
by a distance keeper which allows the housing to supported on bearings along its length. Within the axial housing is a tube
which is supported at the upper end of the column on the upper bearing. The tube has a central splined hole which provides for
the fitment of the splined shaft. The splined shaft can slide within the tube on the splines when the column reach is adjusted
or the column collapses in a crash condition. The splined shaft also passes rotary motion from the steering wheel through the
length of the column to the outer clamping yoke which is supported on the lower bearing.
The electric steering column lock is attached to the top of the rake lever. A lock bolt within the steering column lock engages in
one of 8 slots in the locking sleeve located at the lower end of the column preventing rotation of the steering wheel. The
locking sleeve is retained by a tolerance ring which in turn is located on the outer diameter of the tube yoke. The tolerance
ring allows a specified amount of torque to be applied to the splined shaft before it slips, preventing damage to the column
lock due to excessive force being applied to the steering wheel when the lock is engaged. The tolerance ring is designed to
slip on the splined shaft when the applied torque exceeds the fitted slip load of 200 Nm minimum. Repeated rotation of the
lock collar will reduce its slipping torque to 100 Nm minimum. The lock is controlled by the CJB.
A steering angle sensor is located at the upper end of the steering column and is attached to the crash adaptor. The sensor
measures steering rotation via a toothed wheel located on the splined tube at the upper end of the column. The sensor
receives a power supply from the CJB and supplies 2 signals (A and B) relating to the steering rotation to the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module. The module transmits this data on the high speed CAN bus for use by other vehicle systems. Refer to: Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist (206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist, Description and Operation).
The steering column is adjustable electrically, for reach and rake. The adjustment mechanism comprises an electric adjustment
motor, a lead screw, a rake solenoid, a reach solenoid, a reach clutch and a rake clutch. The column adjustment is controlled
manually using a joystick switch located on the LH (left-hand) side of the column lower cowl. The joystick can be moved
forward and backward to adjust the column reach in and out and moved up and down to adjust the rake. The switch selection
energizes the adjustment motor in the applicable direction and also engages the applicable solenoid and clutch.
When the joystick switch is rotated to the 'auto' position, the steering column will adjust to the uppermost rake position when
the ignition is switched off. It will re-adjust to the position corresponding to the memory position for the remote handset when
the ignition is switched on.
The memory function of the electric column is linked to and controlled by the driver's seat module. The module provides for the
storage of three separate memory positions which are stored against 3 individual remote handsets.
Refer to: Seats (501-10 Seating, Description and Operation).
The steering wheel locates on a splined shaft in the upper column assembly and is secured with a bolt. The steering wheel
houses the driver's airbag and switches for the audio system, gear change and speed control. A clockspring is used to connect
the steering wheel electrical components to the vehicle harness.
Two plastic shrouds are fitted to the upper column assembly. The lower shroud is fitted with an energy absorbing foam pad to
minimize leg injury in the event of an accident.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 797 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Steering Column Switches - Steering Column Switches - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
The steering column multifunction switch is situated on the steering column and consists of the wiper switch, the turn signal
indicator/lighting switch and the trip computer switch.
The RH (right-hand) multifunction switch controls the following windshield wiper functions:
Flick wipe
Intermittent wipe
Slow speed wipe
High speed wipe
Wash/Wipe
Headlamp powerwash
Rain sensing / variable wipe selection.
The LH (left-hand) multifunction switch controls the following functions:
Turn signal indicators
Side lamps
Headlamps
Auto lamps
High/low beam
Headlamp flash
Headlamp timer
Trip computer.
The steering column adjustment switch is located in the steering column lower shroud on the LH side. The switch is a 4 position 'joystick' which controls reach and rake adjustment.
The trip button allows the driver to cycle though an option menu and also reset trip cycle mileage calculations. The trip
computer information is displayed in the instrument cluster message centre.
Steering wheel mounted switches on the LH side of the driver's airbag, control the audio and telephone functions. Switches on the RH side of the driver's airbag, control the speed control functions. The steering wheel has an internal heating element. This is controlled by the driver via the Touch Screen Display (TSD). www.JagDocs.com
Page 799 of 3039
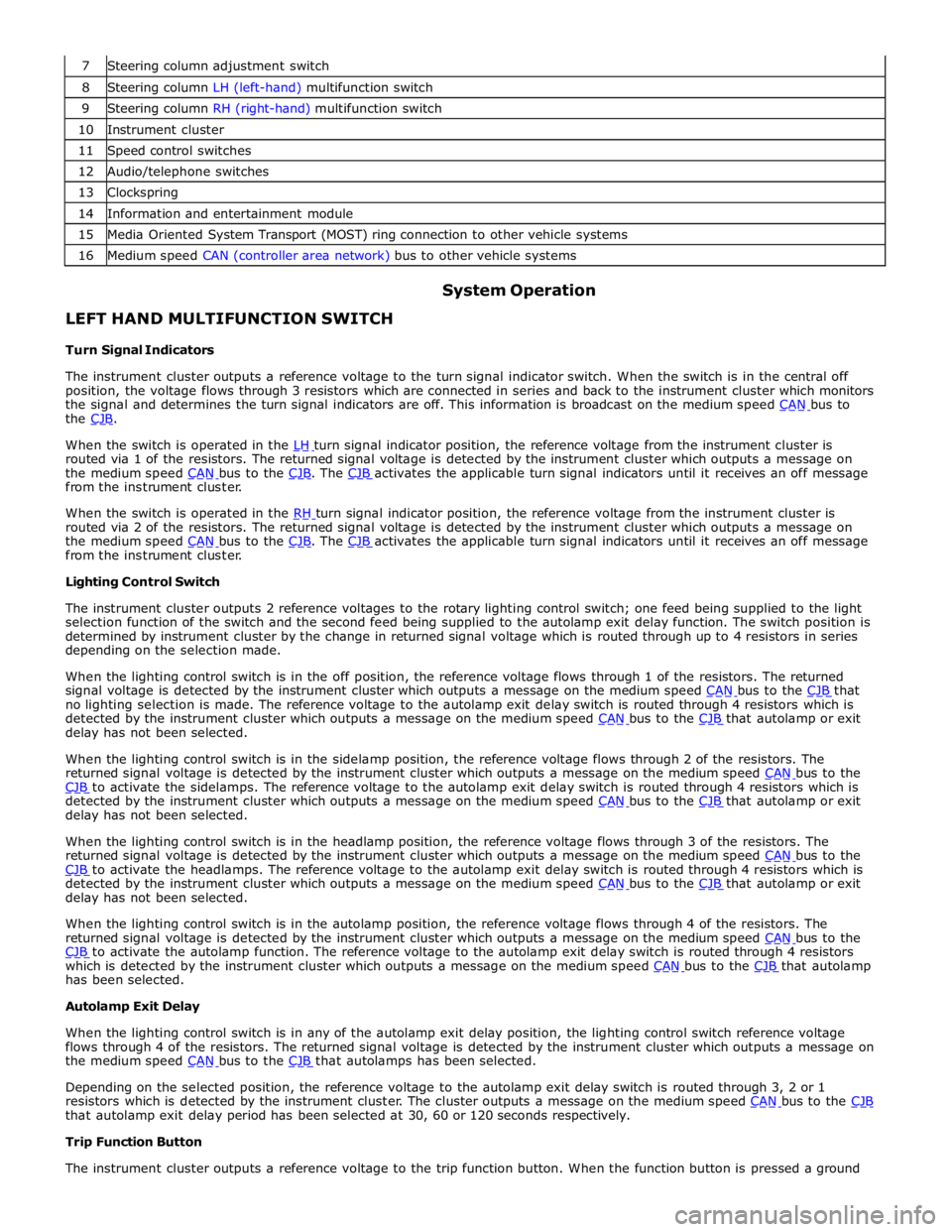
8 Steering column LH (left-hand) multifunction switch 9 Steering column RH (right-hand) multifunction switch 10 Instrument cluster 11 Speed control switches 12 Audio/telephone switches 13 Clockspring 14 Information and entertainment module 15 Media Oriented System Transport (MOST) ring connection to other vehicle systems 16 Medium speed CAN (controller area network) bus to other vehicle systems
LEFT HAND MULTIFUNCTION SWITCH
Turn Signal Indicators System Operation
The instrument cluster outputs a reference voltage to the turn signal indicator switch. When the switch is in the central off
position, the voltage flows through 3 resistors which are connected in series and back to the instrument cluster which monitors
the signal and determines the turn signal indicators are off. This information is broadcast on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB.
When the switch is operated in the LH turn signal indicator position, the reference voltage from the instrument cluster is routed via 1 of the resistors. The returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on
the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB. The CJB activates the applicable turn signal indicators until it receives an off message from the instrument cluster.
When the switch is operated in the RH turn signal indicator position, the reference voltage from the instrument cluster is routed via 2 of the resistors. The returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on
the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB. The CJB activates the applicable turn signal indicators until it receives an off message from the instrument cluster.
Lighting Control Switch
The instrument cluster outputs 2 reference voltages to the rotary lighting control switch; one feed being supplied to the light
selection function of the switch and the second feed being supplied to the autolamp exit delay function. The switch position is
determined by instrument cluster by the change in returned signal voltage which is routed through up to 4 resistors in series
depending on the selection made.
When the lighting control switch is in the off position, the reference voltage flows through 1 of the resistors. The returned
signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that no lighting selection is made. The reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 4 resistors which is
detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamp or exit delay has not been selected.
When the lighting control switch is in the sidelamp position, the reference voltage flows through 2 of the resistors. The
returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the sidelamps. The reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 4 resistors which is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamp or exit delay has not been selected.
When the lighting control switch is in the headlamp position, the reference voltage flows through 3 of the resistors. The
returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the headlamps. The reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 4 resistors which is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamp or exit delay has not been selected.
When the lighting control switch is in the autolamp position, the reference voltage flows through 4 of the resistors. The
returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the autolamp function. The reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 4 resistors which is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamp has been selected.
Autolamp Exit Delay
When the lighting control switch is in any of the autolamp exit delay position, the lighting control switch reference voltage
flows through 4 of the resistors. The returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on
the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamps has been selected.
Depending on the selected position, the reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 3, 2 or 1
resistors which is detected by the instrument cluster. The cluster outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamp exit delay period has been selected at 30, 60 or 120 seconds respectively.
Trip Function Button
The instrument cluster outputs a reference voltage to the trip function button. When the function button is pressed a ground