2009 SUBARU TRIBECA fuel pump
[x] Cancel search: fuel pumpPage 1612 of 2453
FU(H6DO)-51
Fuel System Trouble in General
FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEMS)
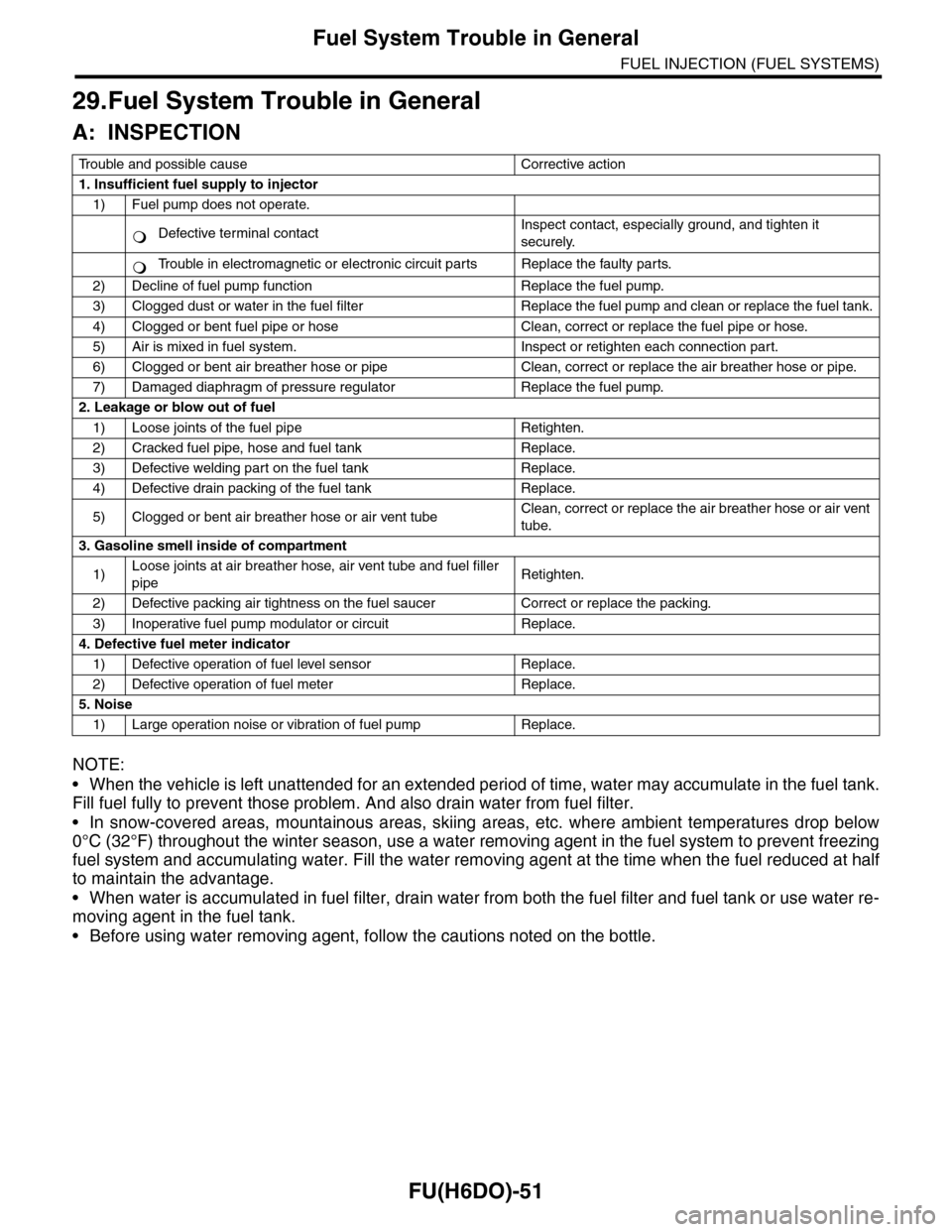
29.Fuel System Trouble in General
A: INSPECTION
NOTE:
•When the vehicle is left unattended for an extended period of time, water may accumulate in the fuel tank.
Fill fuel fully to prevent those problem. And also drain water from fuel filter.
•In snow-covered areas, mountainous areas, skiing areas, etc. where ambient temperatures drop below
0°C (32°F) throughout the winter season, use a water removing agent in the fuel system to prevent freezing
fuel system and accumulating water. Fill the water removing agent at the time when the fuel reduced at half
to maintain the advantage.
•When water is accumulated in fuel filter, drain water from both the fuel filter and fuel tank or use water re-
moving agent in the fuel tank.
•Before using water removing agent, follow the cautions noted on the bottle.
Tr o u b l e a n d p o s s i b l e c a u s e C o r r e c t i v e a c t i o n
1. Insufficient fuel supply to injector
1) Fuel pump does not operate.
Defective terminal contactInspect contact, especially ground, and tighten it
securely.
Tr o u b l e i n e l e c t r o m a g n e t i c o r e l e c t r o n i c c i r c u i t p a r t s R e p l a c e t h e f a u l t y p a r t s .
2) Decline of fuel pump function Replace the fuel pump.
3) Clogged dust or water in the fuel filter Replace the fuel pump and clean or replace the fuel tank.
4) Clogged or bent fuel pipe or hose Clean, correct or replace the fuel pipe or hose.
5) Air is mixed in fuel system. Inspect or retighten each connection part.
6) Clogged or bent air breather hose or pipe Clean, correct or replace the air breather hose or pipe.
7) Damaged diaphragm of pressure regulator Replace the fuel pump.
2. Leakage or blow out of fuel
1) Loose joints of the fuel pipe Retighten.
2) Cracked fuel pipe, hose and fuel tank Replace.
3) Defective welding part on the fuel tank Replace.
4) Defective drain packing of the fuel tank Replace.
5) Clogged or bent air breather hose or air vent tubeClean, correct or replace the air breather hose or air vent
tube.
3. Gasoline smell inside of compartment
1)Loose joints at air breather hose, air vent tube and fuel filler
pipeRetighten.
2) Defective packing air tightness on the fuel saucer Correct or replace the packing.
3) Inoperative fuel pump modulator or circuit Replace.
4. Defective fuel meter indicator
1) Defective operation of fuel level sensor Replace.
2) Defective operation of fuel meter Replace.
5. Noise
1) Large operation noise or vibration of fuel pump Replace.
�
Page 1616 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-4
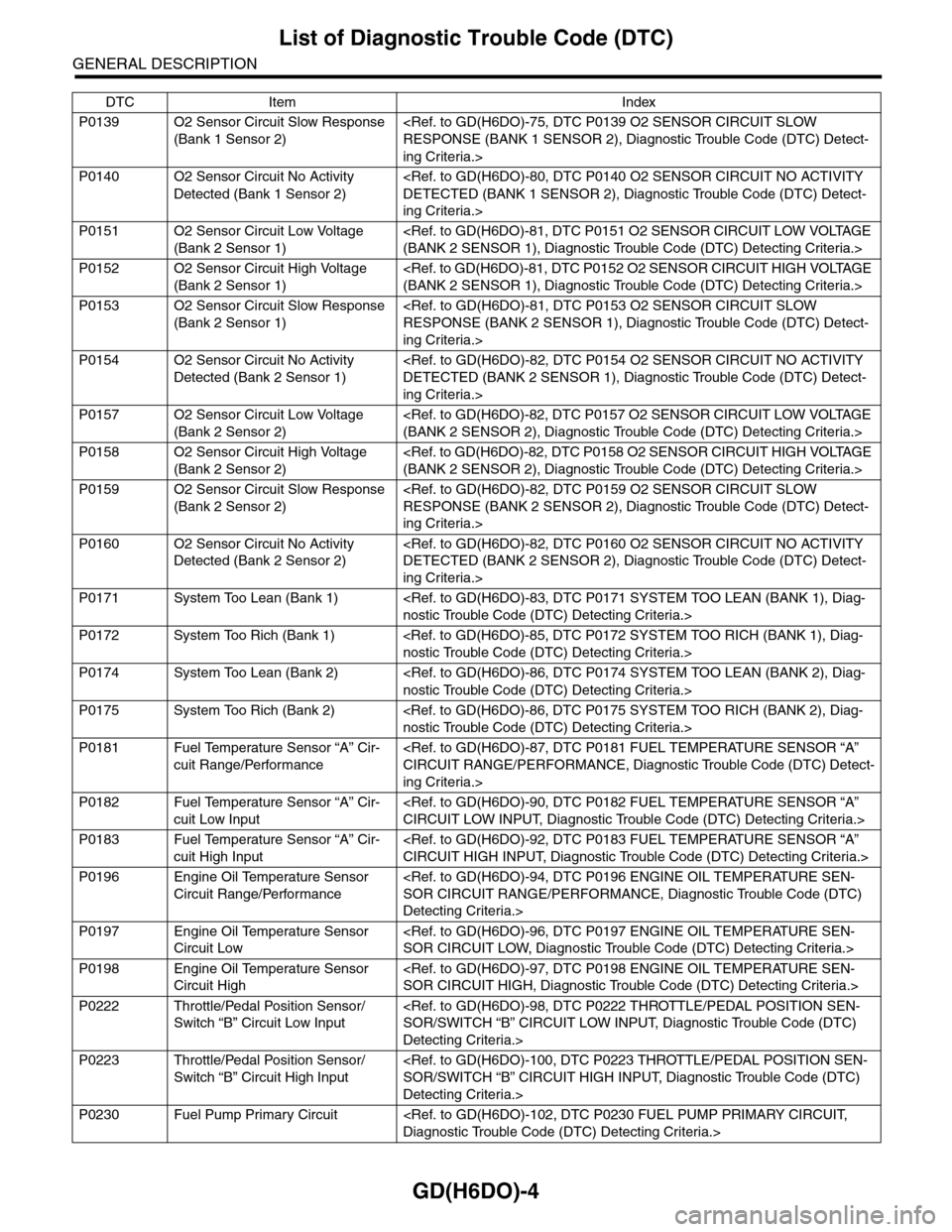
List of Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
P0139 O2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
ing Criteria.>
P0140 O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity
Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
ing Criteria.>
P0151 O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
(Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0152 O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage
(Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0153 O2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response
(Bank 2 Sensor 1)
ing Criteria.>
P0154 O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity
Detected (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
ing Criteria.>
P0157 O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
(Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0158 O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage
(Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0159 O2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response
(Bank 2 Sensor 2)
ing Criteria.>
P0160 O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity
Detected (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
ing Criteria.>
P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1)
P0172 System Too Rich (Bank 1)
P0174 System Too Lean (Bank 2)
P0175 System Too Rich (Bank 2)
P0181 Fuel Temperature Sensor “A” Cir-
cuit Range/Performance
ing Criteria.>
P0182 Fuel Temperature Sensor “A” Cir-
cuit Low Input
P0183 Fuel Temperature Sensor “A” Cir-
cuit High Input
P0196 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor
Circuit Range/Performance
Detecting Criteria.>
P0197 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor
Circuit Low
P0198 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor
Circuit High
P0222 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/
Switch “B” Circuit Low Input
Detecting Criteria.>
P0223 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/
Switch “B” Circuit High Input
Detecting Criteria.>
P0230 Fuel Pump Primary Circuit
DTC Item Index
Page 1714 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-102
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
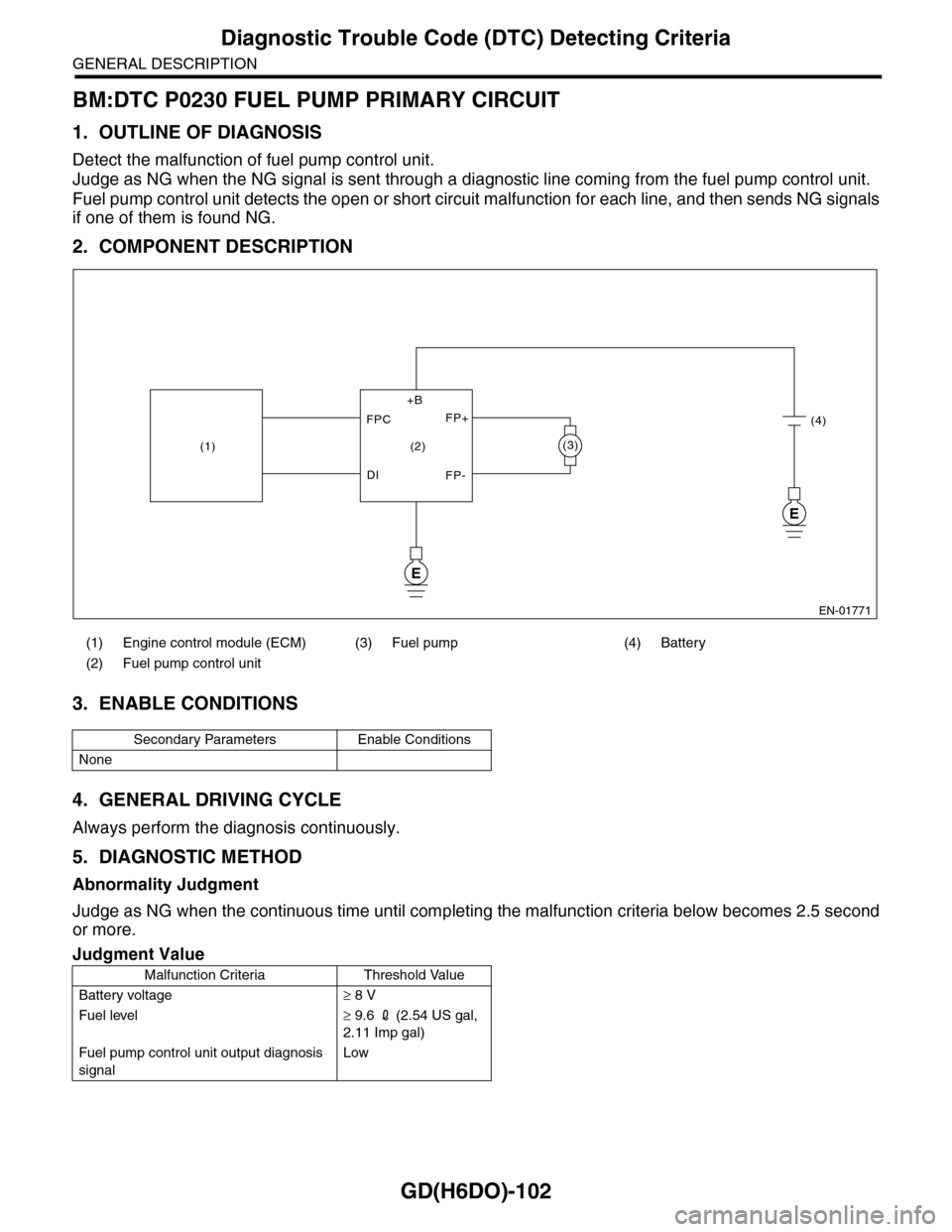
BM:DTC P0230 FUEL PUMP PRIMARY CIRCUIT
1. OUTLINE OF DIAGNOSIS
Detect the malfunction of fuel pump control unit.
Judge as NG when the NG signal is sent through a diagnostic line coming from the fuel pump control unit.
Fuel pump control unit detects the open or short circuit malfunction for each line, and then sends NG signals
if one of them is found NG.
2. COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
3. ENABLE CONDITIONS
4. GENERAL DRIVING CYCLE
Always perform the diagnosis continuously.
5. DIAGNOSTIC METHOD
Abnormality Judgment
Judge as NG when the continuous time until completing the malfunction criteria below becomes 2.5 second
or more.
(1) Engine control module (ECM) (3) Fuel pump (4) Battery
(2) Fuel pump control unit
Secondary Parameters Enable Conditions
None
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value
Battery voltage≥ 8 V
Fuel level≥ 9.6 2 (2.54 US gal,
2.11 Imp gal)
Fuel pump control unit output diagnosis
signal
Low
EN-01771
E
E
(3)
(4)
(2)
FPC
DI
FP+
FP-
+B
(1)
Page 1715 of 2453

GD(H6DO)-103
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 2.5 seconds
Malfunction Indicator Light Illumination: Illuminates when malfunctions occur in 2 continuous driving cy-
cles.
Normality Judgment
Judge as OK and clear the NG when the malfunction criteria below are met.
6. DTC CLEAR CONDITION
•When the OK idling cycle is completed 40 times in a row
•When “Clear Memory” is performed
7. MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LIGHT CLEAR CONDITIONS
•When the OK driving cycle is completed 3 times in a row
•When “Clear Memory” is performed
8. FAIL SAFE
OFF setting may be needed depending on the NG portion.
9. ECM OPERATION AT DTC SETTING
Memorize the freeze frame data. (For test mode $02)
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value
Battery voltage≥ 8 V
Fuel level≥ 9.6 2 (2.54 US gal,
2.11 Imp gal)
Fuel pump control unit output diagnosis
signal
High
Page 1892 of 2453
ME(H6DO)-26
Fuel Pressure
MECHANICAL
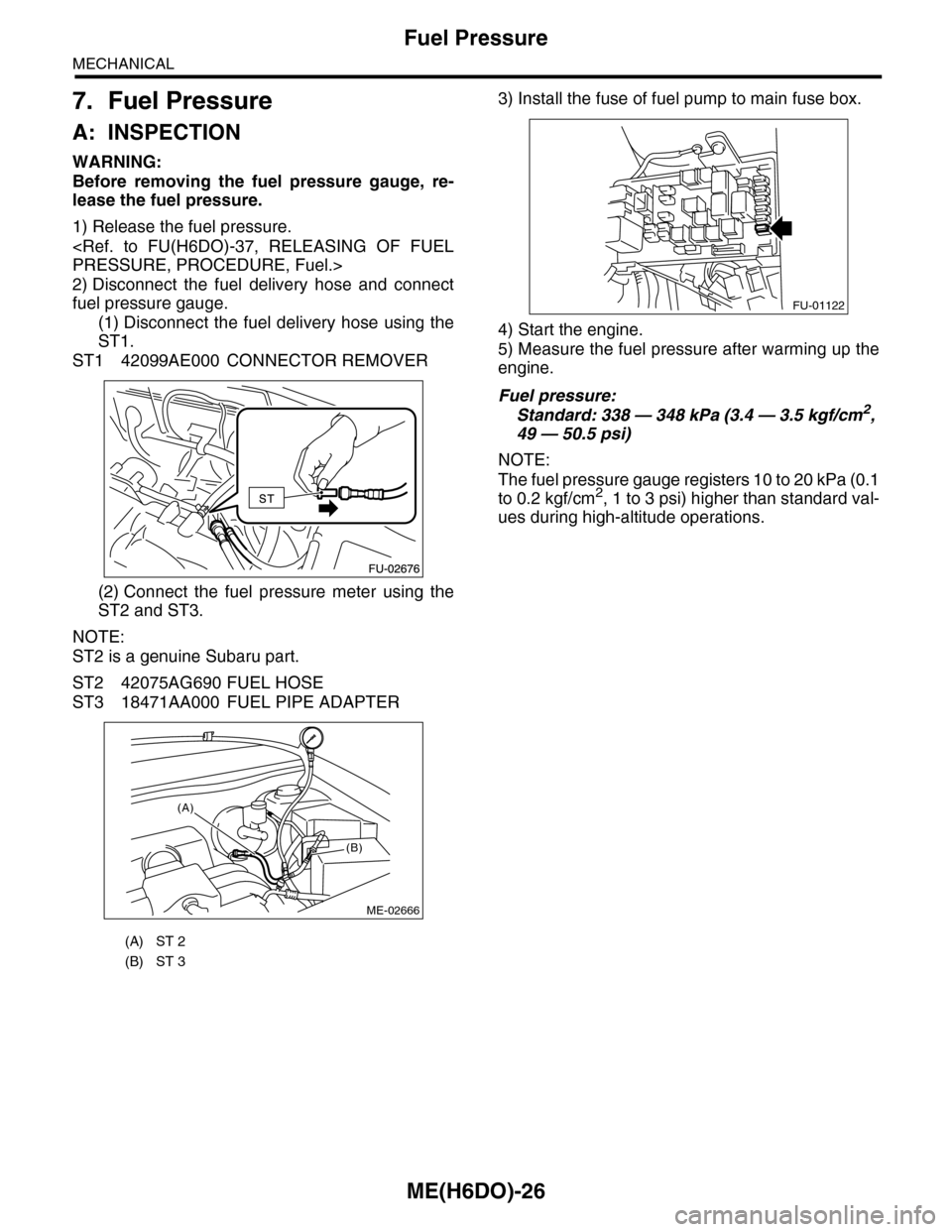
7. Fuel Pressure
A: INSPECTION
WARNING:
Before removing the fuel pressure gauge, re-
lease the fuel pressure.
1) Release the fuel pressure.
2) Disconnect the fuel delivery hose and connect
fuel pressure gauge.
(1) Disconnect the fuel delivery hose using the
ST1.
ST1 42099AE000 CONNECTOR REMOVER
(2) Connect the fuel pressure meter using the
ST2 and ST3.
NOTE:
ST2 is a genuine Subaru part.
ST2 42075AG690 FUEL HOSE
ST3 18471AA000 FUEL PIPE ADAPTER
3) Install the fuse of fuel pump to main fuse box.
4) Start the engine.
5) Measure the fuel pressure after warming up the
engine.
Fuel pressure:
Standard: 338 — 348 kPa (3.4 — 3.5 kgf/cm2,
49 — 50.5 psi)
NOTE:
The fuel pressure gauge registers 10 to 20 kPa (0.1
to 0.2 kgf/cm2, 1 to 3 psi) higher than standard val-
ues during high-altitude operations.
(A) ST 2
(B) ST 3
ME-02666
(A)
(B)
FU-01122
Page 1903 of 2453
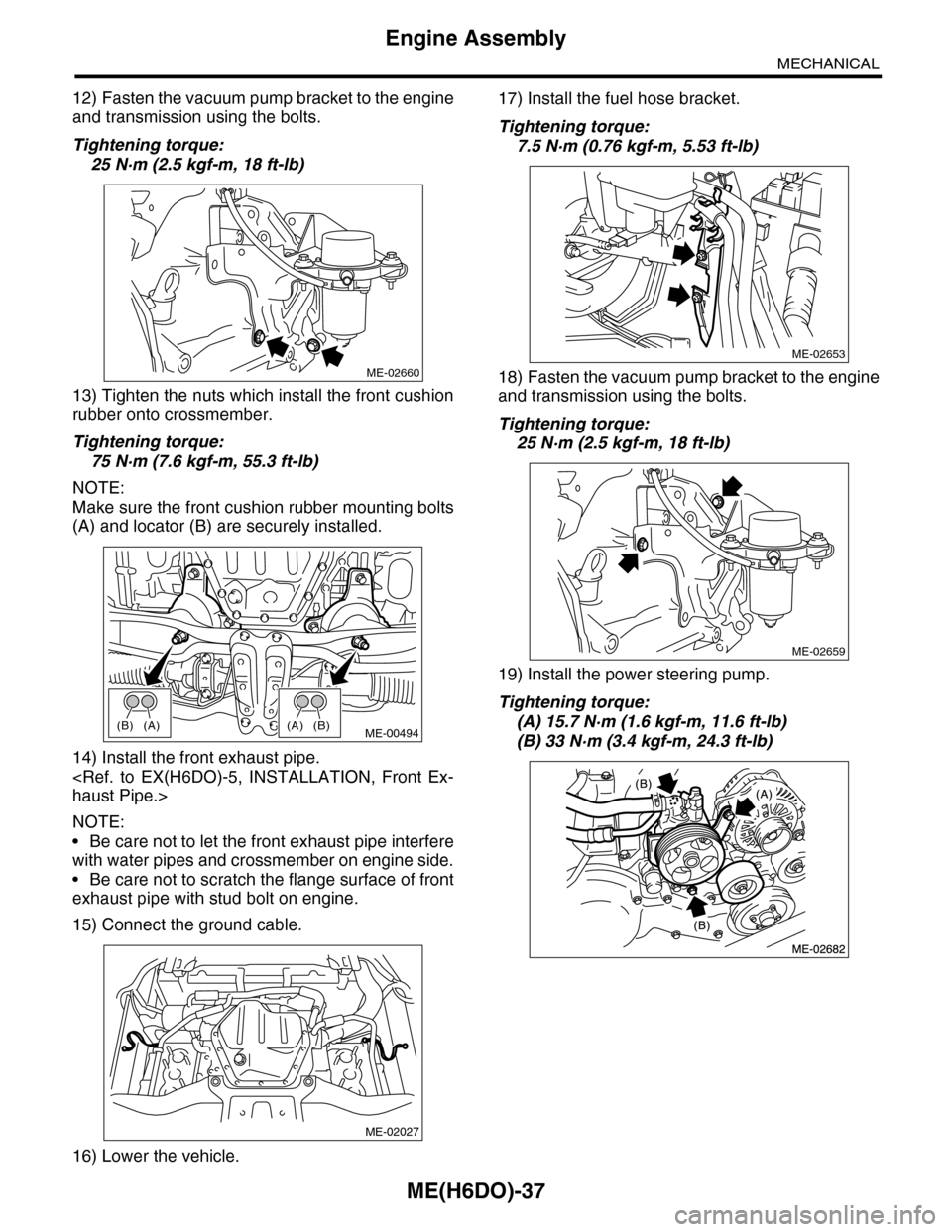
ME(H6DO)-37
Engine Assembly
MECHANICAL
12) Fasten the vacuum pump bracket to the engine
and transmission using the bolts.
Tightening torque:
25 N·m (2.5 kgf-m, 18 ft-lb)
13) Tighten the nuts which install the front cushion
rubber onto crossmember.
Tightening torque:
75 N·m (7.6 kgf-m, 55.3 ft-lb)
NOTE:
Make sure the front cushion rubber mounting bolts
(A) and locator (B) are securely installed.
14) Install the front exhaust pipe.
NOTE:
•Be care not to let the front exhaust pipe interfere
with water pipes and crossmember on engine side.
•Be care not to scratch the flange surface of front
exhaust pipe with stud bolt on engine.
15) Connect the ground cable.
16) Lower the vehicle.
17) Install the fuel hose bracket.
Tightening torque:
7.5 N·m (0.76 kgf-m, 5.53 ft-lb)
18) Fasten the vacuum pump bracket to the engine
and transmission using the bolts.
Tightening torque:
25 N·m (2.5 kgf-m, 18 ft-lb)
19) Install the power steering pump.
Tightening torque:
(A) 15.7 N·m (1.6 kgf-m, 11.6 ft-lb)
(B) 33 N·m (3.4 kgf-m, 24.3 ft-lb)
ME-02660
(A)(B)(B)(A)ME-00494
ME-02027
ME-02653
ME-02659
Page 1949 of 2453
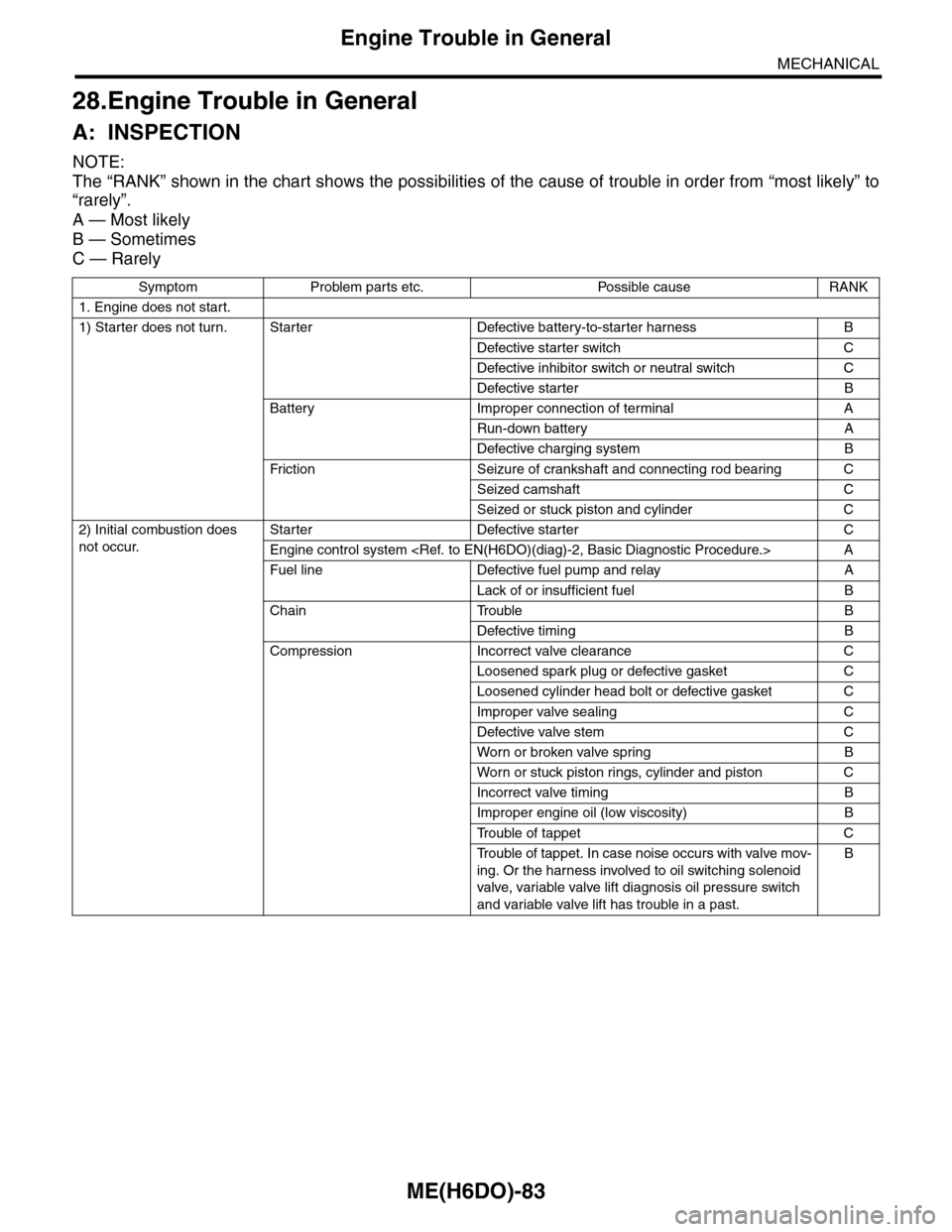
ME(H6DO)-83
Engine Trouble in General
MECHANICAL
28.Engine Trouble in General
A: INSPECTION
NOTE:
The “RANK” shown in the chart shows the possibilities of the cause of trouble in order from “most likely” to
“rarely”.
A — Most likely
B — Sometimes
C — Rarely
Symptom Problem parts etc. Possible cause RANK
1. Engine does not start.
1) Starter does not turn. Starter Defective battery-to-starter harness B
Defective starter switch C
Defective inhibitor switch or neutral switch C
Defective starter B
Battery Improper connection of terminal A
Run-down battery A
Defective charging system B
Fr iction Seizure of crankshaft and connecting rod bear ing C
Seized camshaft C
Seized or stuck piston and cylinder C
2) Initial combustion does
not occur.
Starter Defective starter C
Engine control system
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay A
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Chain Trouble B
Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket C
Improper valve sealing C
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing B
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing B
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Page 1950 of 2453
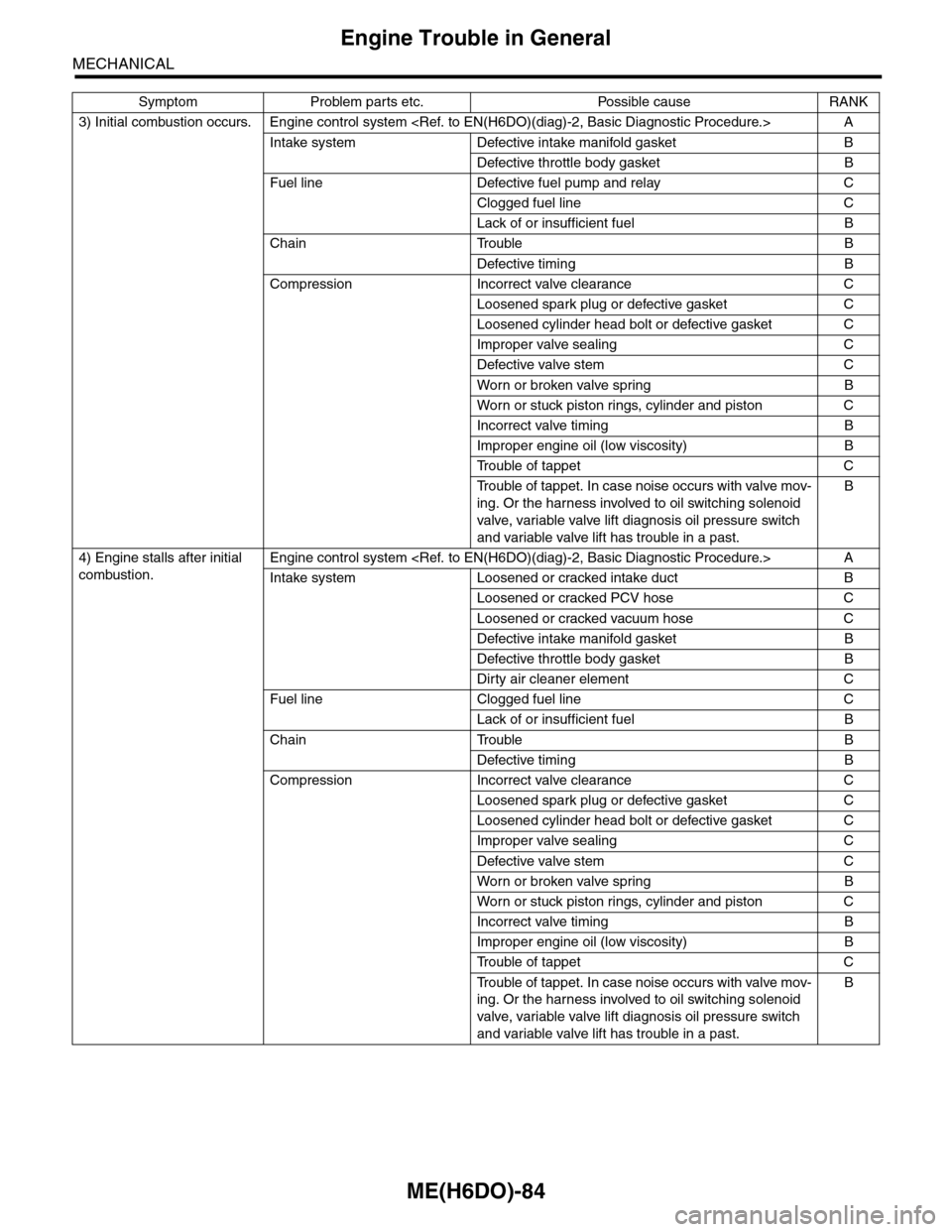
ME(H6DO)-84
Engine Trouble in General
MECHANICAL
3) Initial combustion occurs. Engine control system
Intake system Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay C
Clogged fuel line C
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Chain Trouble B
Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket C
Improper valve sealing C
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing B
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing B
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
4) Engine stalls after initial
combustion.
Engine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct B
Loosened or cracked PCV hose C
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose C
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Dirty air cleaner element C
Fuel line Clogged fuel line C
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Chain Trouble B
Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket C
Improper valve sealing C
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing B
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing B
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Symptom Problem parts etc. Possible cause RANK