2009 SUBARU TRIBECA monitor
[x] Cancel search: monitorPage 1733 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-121
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
CB:DTC P0420 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD (BANK 1)
1. OUTLINE OF DIAGNOSIS
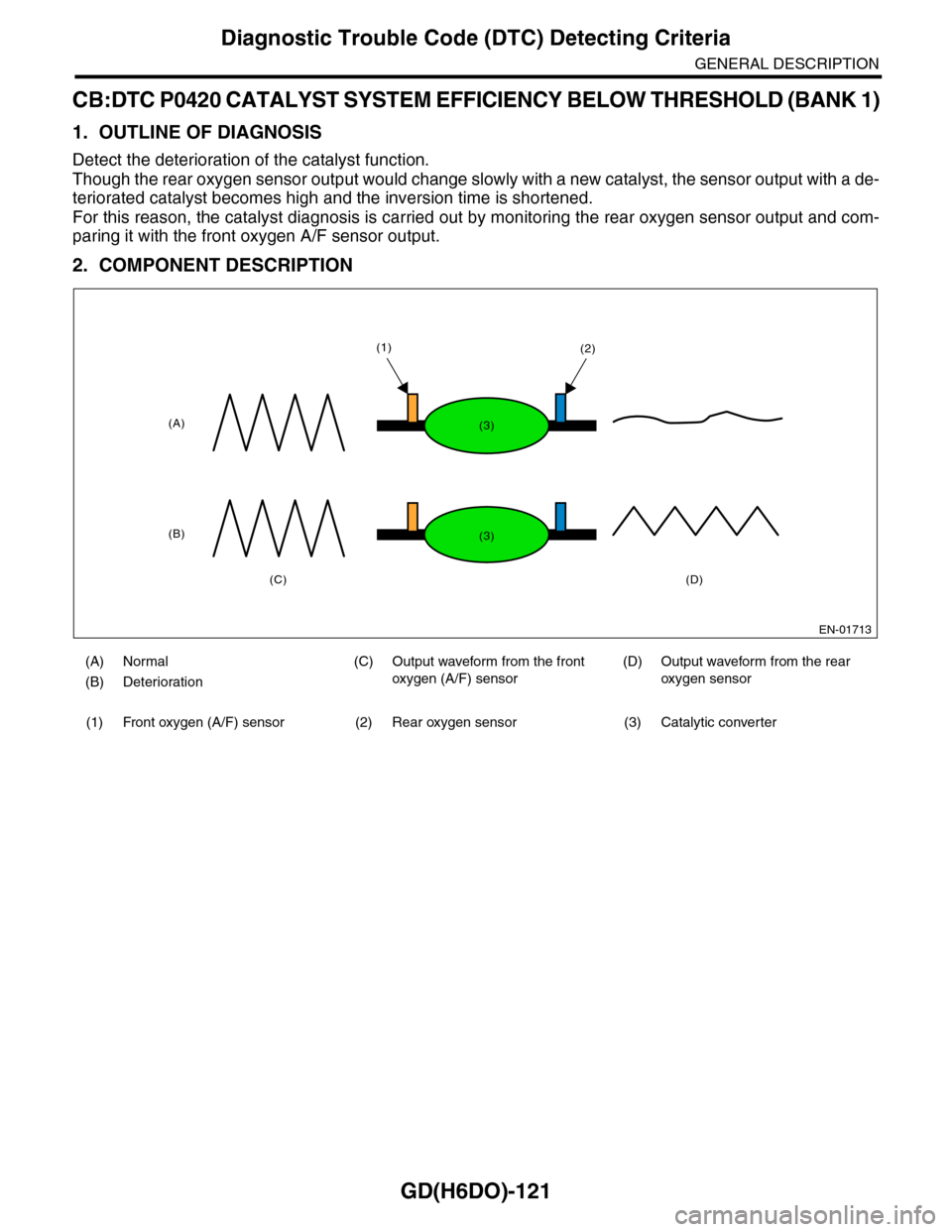
Detect the deterioration of the catalyst function.
Though the rear oxygen sensor output would change slowly with a new catalyst, the sensor output with a de-
teriorated catalyst becomes high and the inversion time is shortened.
For this reason, the catalyst diagnosis is carried out by monitoring the rear oxygen sensor output and com-
paring it with the front oxygen A/F sensor output.
2. COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
(A) Normal (C) Output waveform from the front
oxygen (A/F) sensor
(D) Output waveform from the rear
oxygen sensor(B) Deterioration
(1) Front oxygen (A/F) sensor (2) Rear oxygen sensor (3) Catalytic converter
EN-01713
(A)
(B)
(C)(D)
(1)(2)
(3)
(3)
Page 1736 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-124
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
CC:DTC P0442 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM LEAK DETECT-
ED (SMALL LEAK)
1. OUTLINE OF DIAGNOSIS
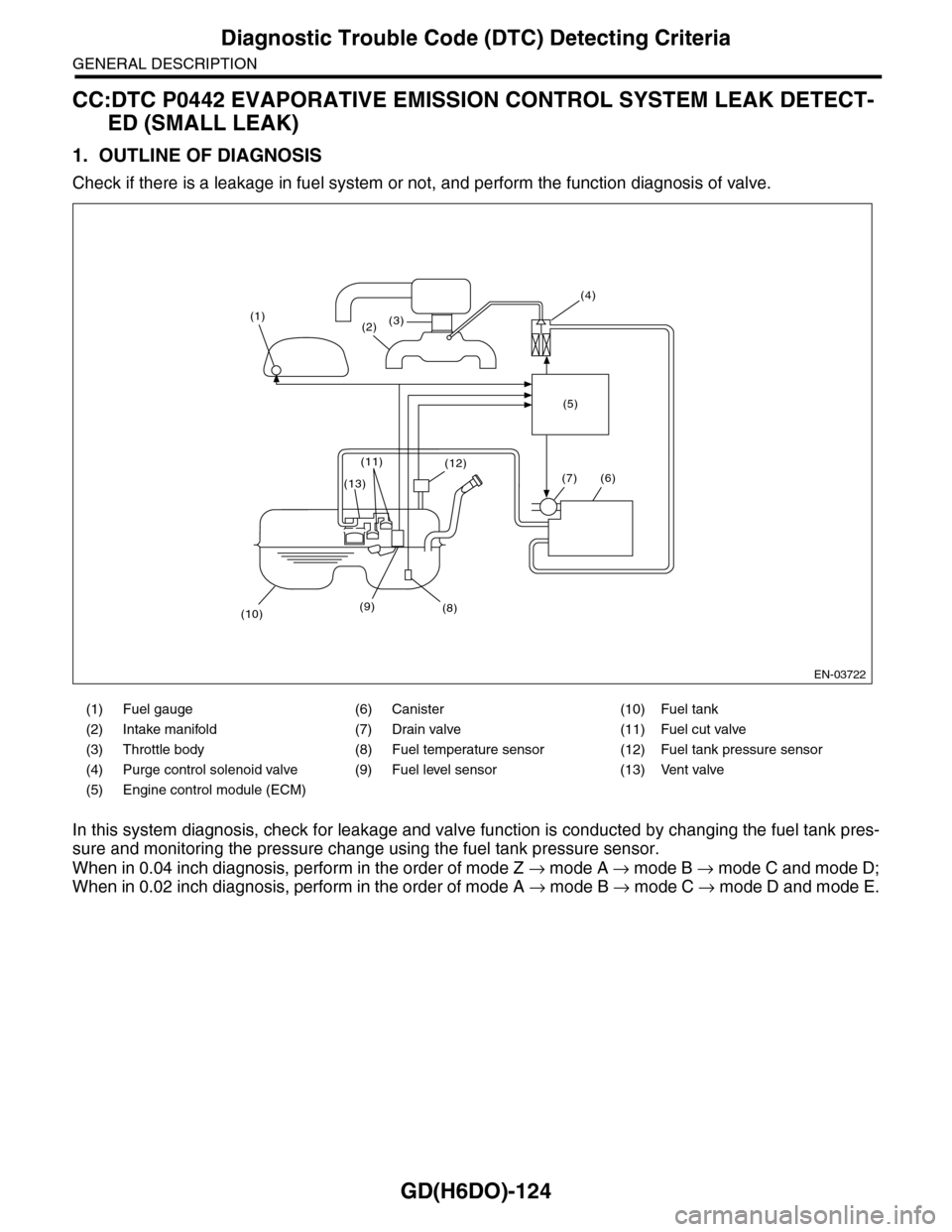
Check if there is a leakage in fuel system or not, and perform the function diagnosis of valve.
In this system diagnosis, check for leakage and valve function is conducted by changing the fuel tank pres-
sure and monitoring the pressure change using the fuel tank pressure sensor.
When in 0.04 inch diagnosis, perform in the order of mode Z → mode A → mode B → mode C and mode D;
When in 0.02 inch diagnosis, perform in the order of mode A → mode B → mode C → mode D and mode E.
(1) Fuel gauge (6) Canister (10) Fuel tank
(2) Intake manifold (7) Drain valve (11) Fuel cut valve
(3) Throttle body (8) Fuel temperature sensor (12) Fuel tank pressure sensor
(4) Purge control solenoid valve (9) Fuel level sensor (13) Vent valve
(5) Engine control module (ECM)
EN-03722
(1)(2)(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(8)
(12)
(9)(10)
(13)
(11)
(7)
Page 1741 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-129
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3. GENERAL DRIVING CYCLE
0.04-inch Diagnosis
Perform the diagnosis only once in 851 seconds or more after starting the engine, at a constant speed of 32
km/h (20 MPH) or more.
Pay attention to the fuel temperature and fuel level.
0.02-inch Diagnosis
Perform the diagnosis after 120 seconds or more after starting the engine, at a constant engine RPM of 30
km/h (19 MPH) or higher, to judge as NG or OK.
If OK/NG judgment is not possible, repeat the diagnosis.
Pay attention to the fuel temperature and fuel level.
4. DIAGNOSTIC METHOD
0.04-inch Diagnosis
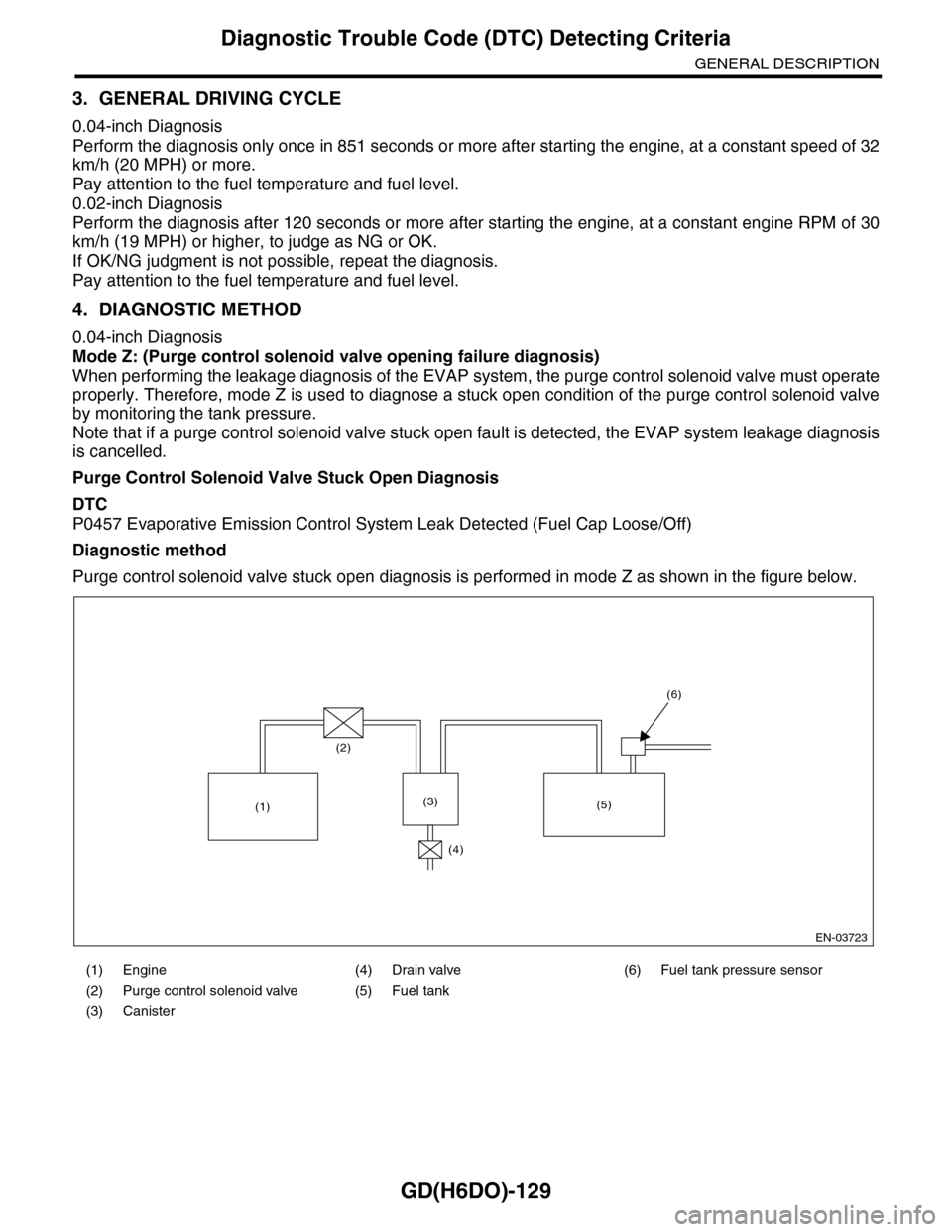
Mode Z: (Purge control solenoid valve opening failure diagnosis)
When performing the leakage diagnosis of the EVAP system, the purge control solenoid valve must operate
properly. Therefore, mode Z is used to diagnose a stuck open condition of the purge control solenoid valve
by monitoring the tank pressure.
Note that if a purge control solenoid valve stuck open fault is detected, the EVAP system leakage diagnosis
is cancelled.
Purge Control Solenoid Valve Stuck Open Diagnosis
DTC
P0457 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Fuel Cap Loose/Off)
Diagnostic method
Purge control solenoid valve stuck open diagnosis is performed in mode Z as shown in the figure below.
(1) Engine (4) Drain valve (6) Fuel tank pressure sensor
(2) Purge control solenoid valve (5) Fuel tank
(3) Canister
EN-03723
(2)
(1)(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
Page 1742 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-130
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
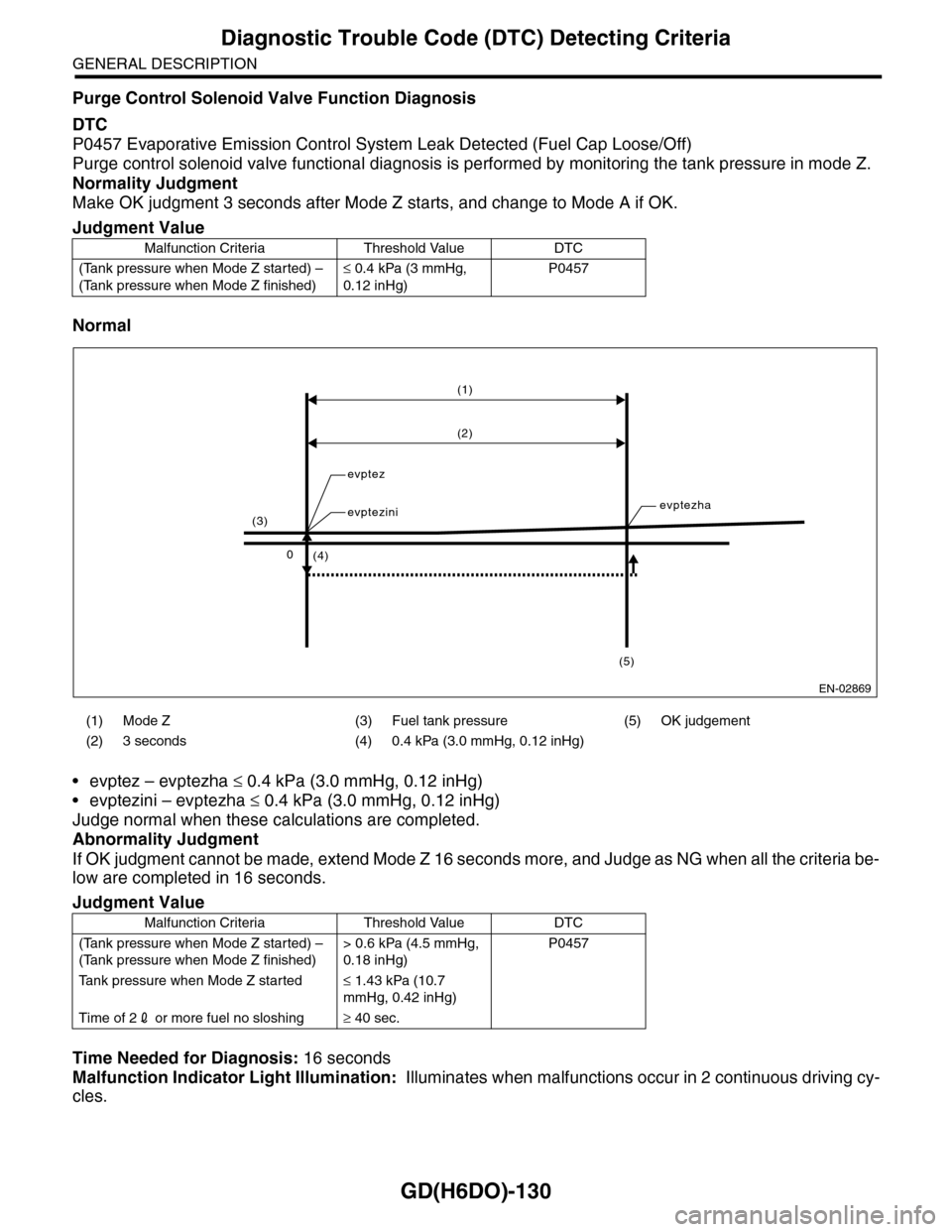
Purge Control Solenoid Valve Function Diagnosis
DTC
P0457 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Fuel Cap Loose/Off)
Purge control solenoid valve functional diagnosis is performed by monitoring the tank pressure in mode Z.
Normality Judgment
Make OK judgment 3 seconds after Mode Z starts, and change to Mode A if OK.
Normal
•evptez – evptezha ≤ 0.4 kPa (3.0 mmHg, 0.12 inHg)
•evptezini – evptezha ≤ 0.4 kPa (3.0 mmHg, 0.12 inHg)
Judge normal when these calculations are completed.
Abnormality Judgment
If OK judgment cannot be made, extend Mode Z 16 seconds more, and Judge as NG when all the criteria be-
low are completed in 16 seconds.
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 16 seconds
Malfunction Indicator Light Illumination: Illuminates when malfunctions occur in 2 continuous driving cy-
cles.
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value DTC
(Tank pressure when Mode Z started) –
(Tank pressure when Mode Z finished)
≤ 0.4 kPa (3 mmHg,
0.12 inHg)
P0457
(1) Mode Z (3) Fuel tank pressure (5) OK judgement
(2) 3 seconds (4) 0.4 kPa (3.0 mmHg, 0.12 inHg)
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value DTC
(Tank pressure when Mode Z started) –
(Tank pressure when Mode Z finished)
> 0.6 kPa (4.5 mmHg,
0.18 inHg)
P0457
Ta n k p r e s s u r e w h e n M o d e Z s t a r t e d≤ 1.43 kPa (10.7
mmHg, 0.42 inHg)
Time of 22 or more fuel no sloshing≥ 40 sec.
EN-02869
(1)
(2)
(4)
evptez
evptezinievptezha
0
(3)
(5)
Page 1744 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-132
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
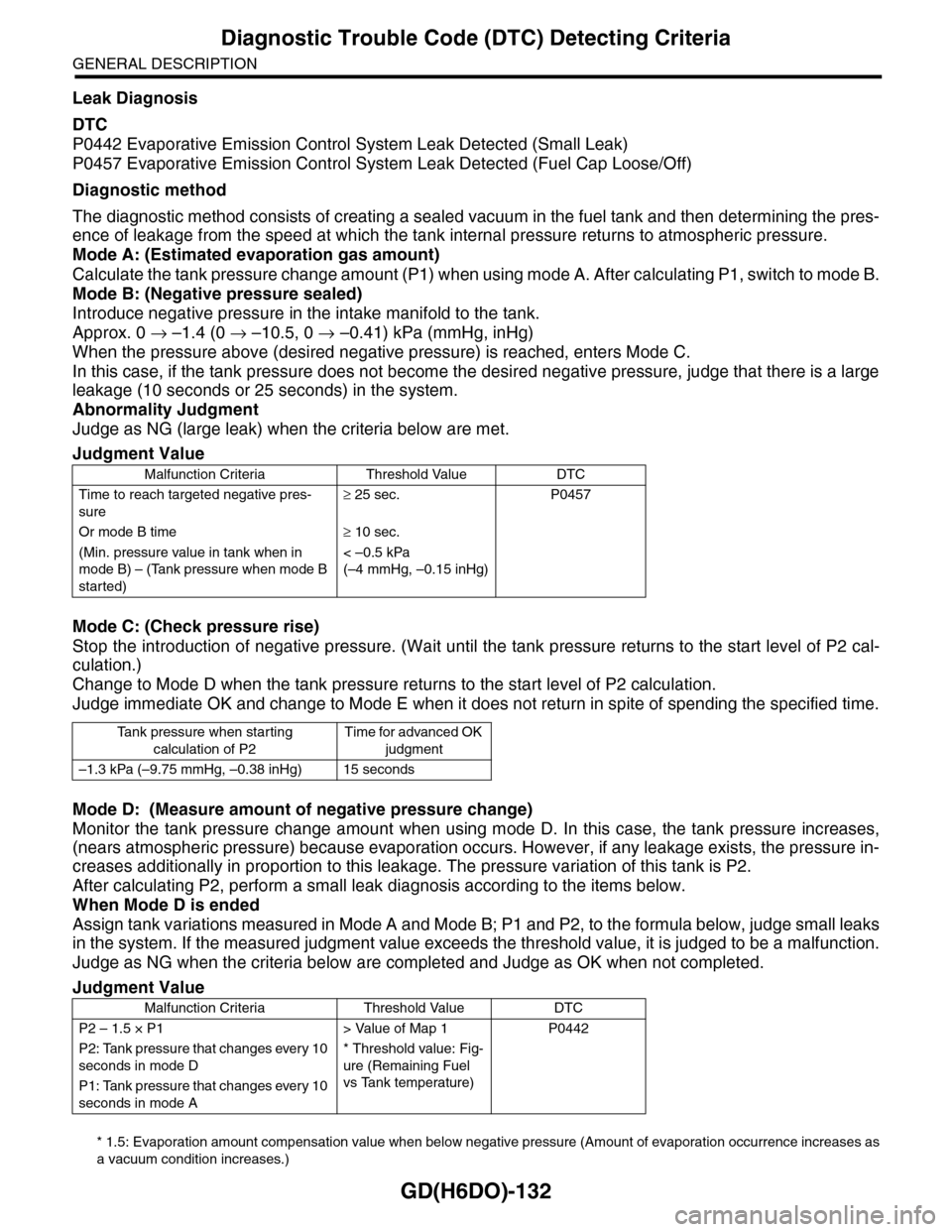
Leak Diagnosis
DTC
P0442 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
P0457 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Fuel Cap Loose/Off)
Diagnostic method
The diagnostic method consists of creating a sealed vacuum in the fuel tank and then determining the pres-
ence of leakage from the speed at which the tank internal pressure returns to atmospheric pressure.
Mode A: (Estimated evaporation gas amount)
Calculate the tank pressure change amount (P1) when using mode A. After calculating P1, switch to mode B.
Mode B: (Negative pressure sealed)
Introduce negative pressure in the intake manifold to the tank.
Approx. 0 → –1.4 (0 → –10.5, 0 → –0.41) kPa (mmHg, inHg)
When the pressure above (desired negative pressure) is reached, enters Mode C.
In this case, if the tank pressure does not become the desired negative pressure, judge that there is a large
leakage (10 seconds or 25 seconds) in the system.
Abnormality Judgment
Judge as NG (large leak) when the criteria below are met.
Mode C: (Check pressure rise)
Stop the introduction of negative pressure. (Wait until the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 cal-
culation.)
Change to Mode D when the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 calculation.
Judge immediate OK and change to Mode E when it does not return in spite of spending the specified time.
Mode D: (Measure amount of negative pressure change)
Monitor the tank pressure change amount when using mode D. In this case, the tank pressure increases,
(nears atmospheric pressure) because evaporation occurs. However, if any leakage exists, the pressure in-
creases additionally in proportion to this leakage. The pressure variation of this tank is P2.
After calculating P2, perform a small leak diagnosis according to the items below.
When Mode D is ended
Assign tank variations measured in Mode A and Mode B; P1 and P2, to the formula below, judge small leaks
in the system. If the measured judgment value exceeds the threshold value, it is judged to be a malfunction.
Judge as NG when the criteria below are completed and Judge as OK when not completed.
* 1.5: Evaporation amount compensation value when below negative pressure (Amount of evaporation occurrence increases as
a vacuum condition increases.)
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value DTC
Time to reach targeted negative pres-
sure
≥ 25 sec. P0457
Or mode B time≥ 10 sec.
(Min. pressure value in tank when in
mode B) – (Tank pressure when mode B
started)
< –0.5 kPa
(–4 mmHg, –0.15 inHg)
Ta n k p r e s s u r e w h e n s t a r t i n g
calculation of P2
Time for advanced OK
judgment
–1.3 kPa (–9.75 mmHg, –0.38 inHg) 15 seconds
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value DTC
P2 – 1.5 × P1 > Value of Map 1 P0442
P2: Tank pressure that changes every 10
seconds in mode D
* Threshold value: Fig-
ure (Remaining Fuel
vs Tank temperature)
P1: Tank pressure that changes every 10
seconds in mode A
Page 1745 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-133
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
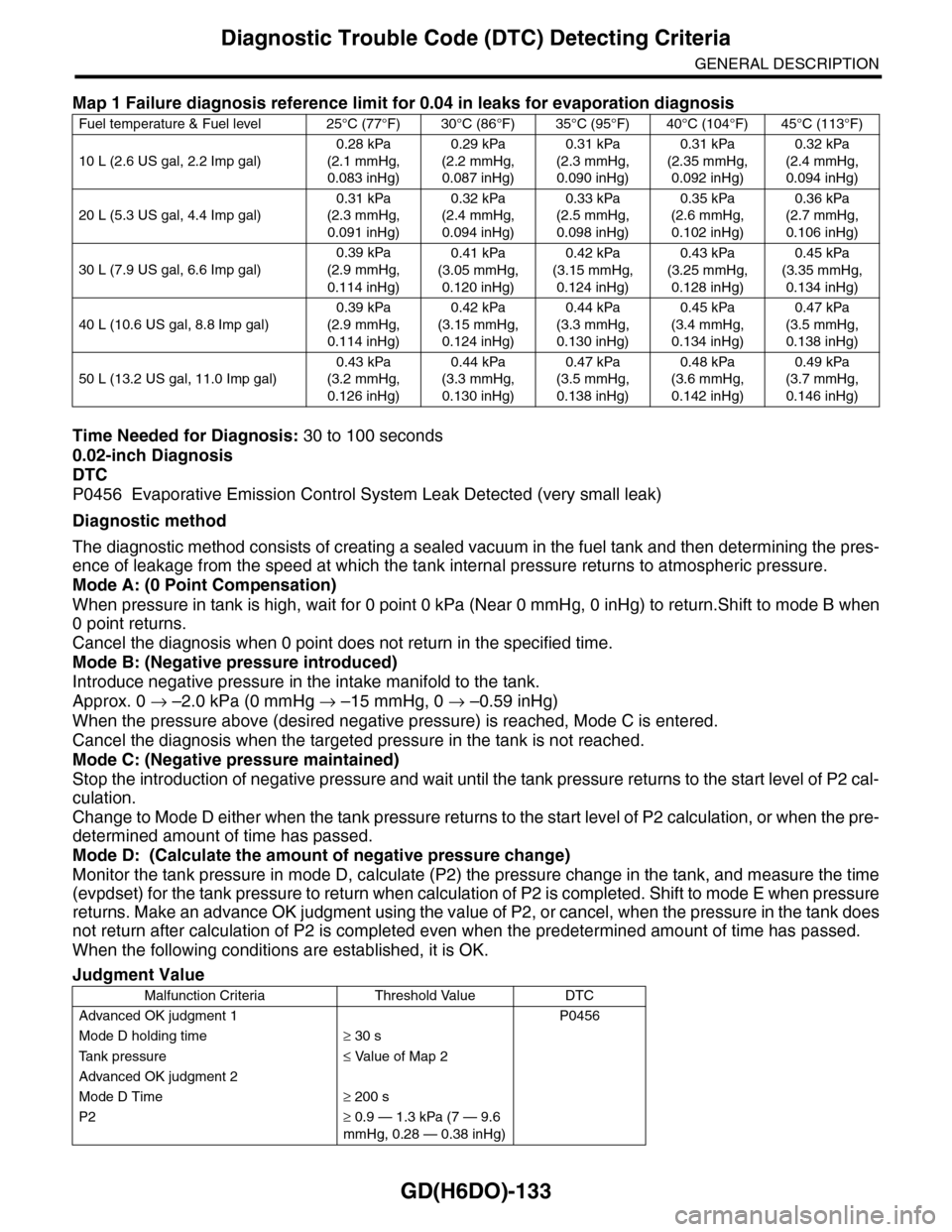
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 30 to 100 seconds
0.02-inch Diagnosis
DTC
P0456 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (very small leak)
Diagnostic method
The diagnostic method consists of creating a sealed vacuum in the fuel tank and then determining the pres-
ence of leakage from the speed at which the tank internal pressure returns to atmospheric pressure.
Mode A: (0 Point Compensation)
When pressure in tank is high, wait for 0 point 0 kPa (Near 0 mmHg, 0 inHg) to return.Shift to mode B when
0 point returns.
Cancel the diagnosis when 0 point does not return in the specified time.
Mode B: (Negative pressure introduced)
Introduce negative pressure in the intake manifold to the tank.
Approx. 0 → –2.0 kPa (0 mmHg → –15 mmHg, 0 → –0.59 inHg)
When the pressure above (desired negative pressure) is reached, Mode C is entered.
Cancel the diagnosis when the targeted pressure in the tank is not reached.
Mode C: (Negative pressure maintained)
Stop the introduction of negative pressure and wait until the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 cal-
culation.
Change to Mode D either when the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 calculation, or when the pre-
determined amount of time has passed.
Mode D: (Calculate the amount of negative pressure change)
Monitor the tank pressure in mode D, calculate (P2) the pressure change in the tank, and measure the time
(evpdset) for the tank pressure to return when calculation of P2 is completed. Shift to mode E when pressure
returns. Make an advance OK judgment using the value of P2, or cancel, when the pressure in the tank does
not return after calculation of P2 is completed even when the predetermined amount of time has passed.
When the following conditions are established, it is OK.
Map 1 Failure diagnosis reference limit for 0.04 in leaks for evaporation diagnosis
Fuel temperature & Fuel level 25°C (77°F) 30°C (86°F) 35°C (95°F) 40°C (104°F) 45°C (113°F)
10 L (2.6 US gal, 2.2 Imp gal)
0.28 kPa
(2.1 mmHg,
0.083 inHg)
0.29 kPa
(2.2 mmHg,
0.087 inHg)
0.31 kPa
(2.3 mmHg,
0.090 inHg)
0.31 kPa
(2.35 mmHg,
0.092 inHg)
0.32 kPa
(2.4 mmHg,
0.094 inHg)
20 L (5.3 US gal, 4.4 Imp gal)
0.31 kPa
(2.3 mmHg,
0.091 inHg)
0.32 kPa
(2.4 mmHg,
0.094 inHg)
0.33 kPa
(2.5 mmHg,
0.098 inHg)
0.35 kPa
(2.6 mmHg,
0.102 inHg)
0.36 kPa
(2.7 mmHg,
0.106 inHg)
30 L (7.9 US gal, 6.6 Imp gal)
0.39 kPa
(2.9 mmHg,
0.114 inHg)
0.41 kPa
(3.05 mmHg,
0.120 inHg)
0.42 kPa
(3.15 mmHg,
0.124 inHg)
0.43 kPa
(3.25 mmHg,
0.128 inHg)
0.45 kPa
(3.35 mmHg,
0.134 inHg)
40 L (10.6 US gal, 8.8 Imp gal)
0.39 kPa
(2.9 mmHg,
0.114 inHg)
0.42 kPa
(3.15 mmHg,
0.124 inHg)
0.44 kPa
(3.3 mmHg,
0.130 inHg)
0.45 kPa
(3.4 mmHg,
0.134 inHg)
0.47 kPa
(3.5 mmHg,
0.138 inHg)
50 L (13.2 US gal, 11.0 Imp gal)
0.43 kPa
(3.2 mmHg,
0.126 inHg)
0.44 kPa
(3.3 mmHg,
0.130 inHg)
0.47 kPa
(3.5 mmHg,
0.138 inHg)
0.48 kPa
(3.6 mmHg,
0.142 inHg)
0.49 kPa
(3.7 mmHg,
0.146 inHg)
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value DTC
Advanced OK judgment 1 P0456
Mode D holding time≥ 30 s
Ta n k p r e s s u r e≤ Value of Map 2
Advanced OK judgment 2
Mode D Time≥ 200 s
P2≥ 0.9 — 1.3 kPa (7 — 9.6
mmHg, 0.28 — 0.38 inHg)
Page 1888 of 2453

ME(H6DO)-22
Idle Speed
MECHANICAL
3. Idle Speed
A: INSPECTION
1) Before checking the idle speed, check the fol-
lowing item:
(1) Check the air cleaner element is free from
clogging, ignition timing is correct, spark plugs
are in good condition, and hoses are connected
properly.
(2) Check the malfunction indicator light does
not illuminate.
2) Idle the engine.
3) Stop the engine, and turn the ignition switch to
OFF.
4) Insert the cartridge to Subaru Select Monitor.
5) Connect the Subaru Select Monitor to data link
connector.
6) Turn the ignition switch to ON and Subaru Select
Monitor switch to ON.
7) Select {Each System Check} in Main Menu.
8) Select {Engine} in Selection Menu.
9) Select {Current Data Display & Save} in Engine
Control System Diagnosis.
10) Select {Data Display} in Data Display Menu.
11) Start the engine, and read the engine idle
speed.
12) Check the idle speed when no-loaded. (Head-
light, heater fan, rear defroster, radiator fan, A/C
and etc. are OFF)
Idle speed [No load and gears in neutral]:
650±50 rpm
13) Check the idle speed when loaded. (Turn the A/
C switch to “ON” and operate the compressor for at
least one minute before measurement.)
Idle speed [A/C ON and gears in neutral]:
770±50 rpm
NOTE:
Idle speed cannot be adjusted manually, because
the idle speed is automatically adjusted. If the pre-
scribed idle speed cannot be maintained, refer to
General On-board Diagnosis Table under “Engine
Control System”.
Page 1889 of 2453

ME(H6DO)-23
Ignition Timing
MECHANICAL
4. Ignition Timing
A: INSPECTION
CAUTION:
After warming-up, engine becomes very hot. Be
careful not to burn yourself at measurement.
1) Before checking the ignition timing, check the
following item:
(1) Check the air cleaner element is free from
clogging, spark plugs are in good condition, and
hoses are connected properly.
(2) Check the malfunction indicator light does
not illuminate.
2) Idle the engine.
3) Stop the engine, and turn the ignition switch to
OFF.
4) Insert the cartridge to Subaru Select Monitor.
5) Connect the Subaru Select Monitor to data link
connector.
6) Turn the ignition switch to ON and Subaru Select
Monitor switch to ON.
7) Select {Each System Check} in Main Menu.
8) Select {Engine} in Selection Menu.
9) Select {Current Data Display & Save} in Engine
Control System Diagnosis.
10) Select {Data Display} in Data Display Menu.
11) Start the engine and check the ignition timing at
idle speed.
Ignition timing [BTDC/rpm]:
15°±8°/650
If the timing is not correct, check the ignition control
system. Refer to Engine Control System.