2009 NISSAN LATIO light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 3145 of 4331
Com-
ponent " .
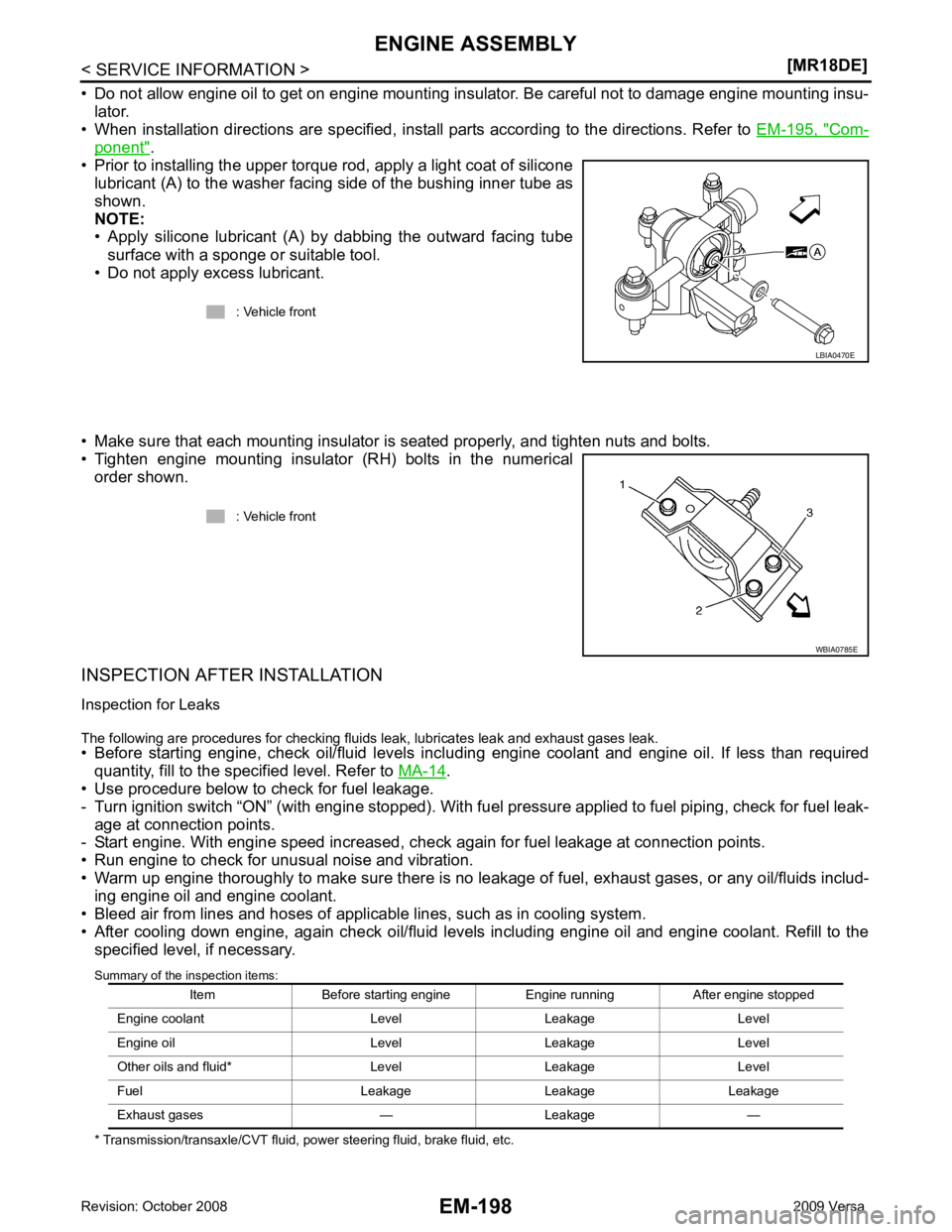
• Prior to installing the upper torque rod, apply a light coat of silicone lubricant (A) to the washer facing side of the bushing inner tube as
shown.
NOTE:
• Apply silicone lubricant (A) by dabbing the outward facing tube
surface with a sponge or suitable tool.
• Do not apply excess lubricant.
• Make sure that each mounting insulator is seated properly, and tighten nuts and bolts.
• Tighten engine mounting insulator (RH) bolts in the numerical order shown.
INSPECTION AFTER INSTALLATION
Inspection for Leaks
The following are procedures for checking fluids leak, lubricates leak and exhaust gases leak.
• Before starting engine, check oil/fluid levels incl uding engine coolant and engine oil. If less than required
quantity, fill to the specified level. Refer to MA-14 .
• Use procedure below to check for fuel leakage.
- Turn ignition switch “ON” (with engine stopped). With fuel pressure applied to fuel piping, check for fuel leak-
age at connection points.
- Start engine. With engine speed increased, che ck again for fuel leakage at connection points.
• Run engine to check for unusual noise and vibration.
• Warm up engine thoroughly to make sure there is no leak age of fuel, exhaust gases, or any oil/fluids includ-
ing engine oil and engine coolant.
• Bleed air from lines and hoses of applicable lines, such as in cooling system.
• After cooling down engine, again check oil/fluid levels including engine oil and engine coolant. Refill to the specified level, if necessary.
Summary of the inspection items:
* Transmission/transaxle/CVT fluid, power steering fluid, brake fluid, etc. : Vehicle front
Page 3149 of 4331
Inspection After Disassembly " .
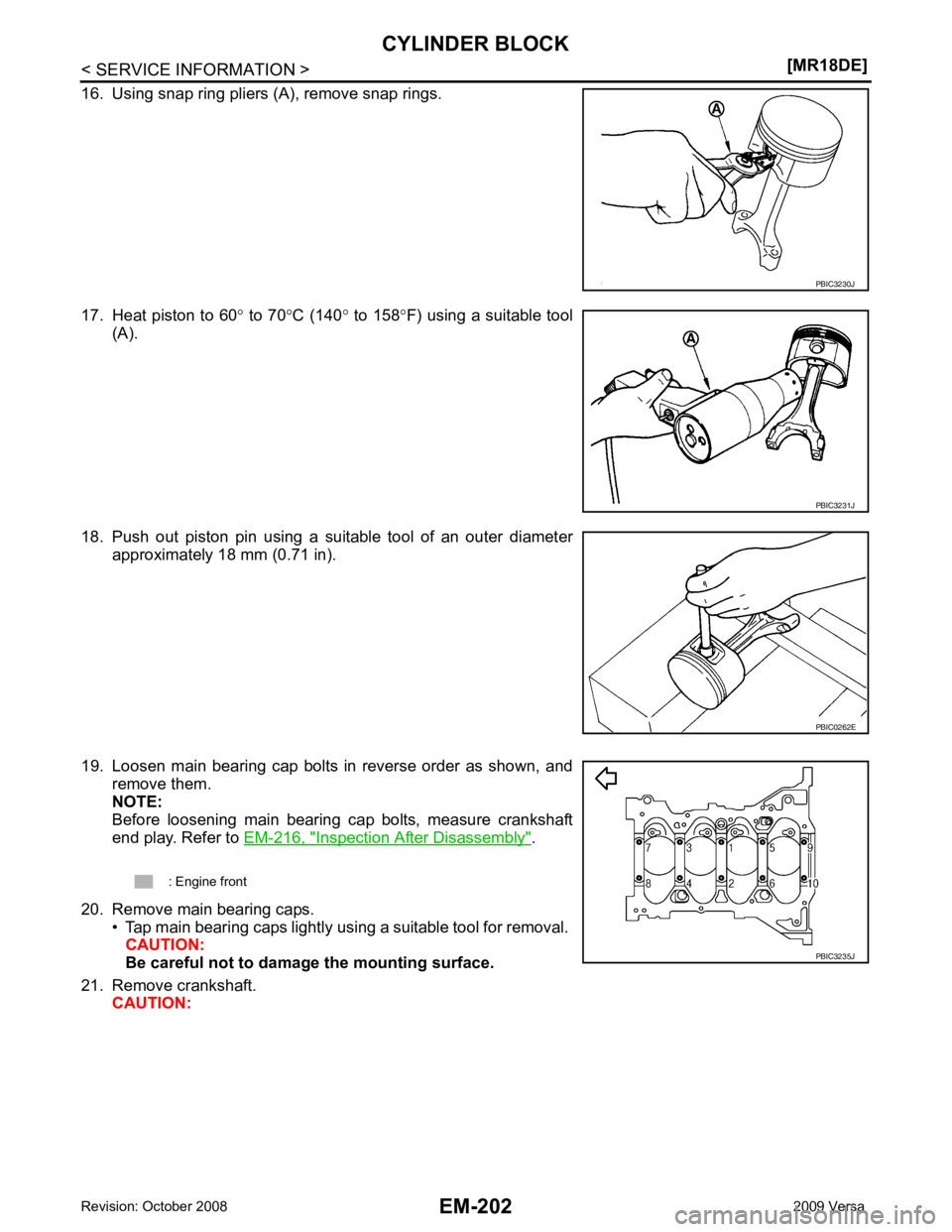
20. Remove main bearing caps. • Tap main bearing caps lightly using a suitable tool for removal. CAUTION:
Be careful not to damage the mounting surface.
21. Remove crankshaft. CAUTION: PBIC3231J
PBIC0262E
Page 3170 of 4331
EM
NP
O
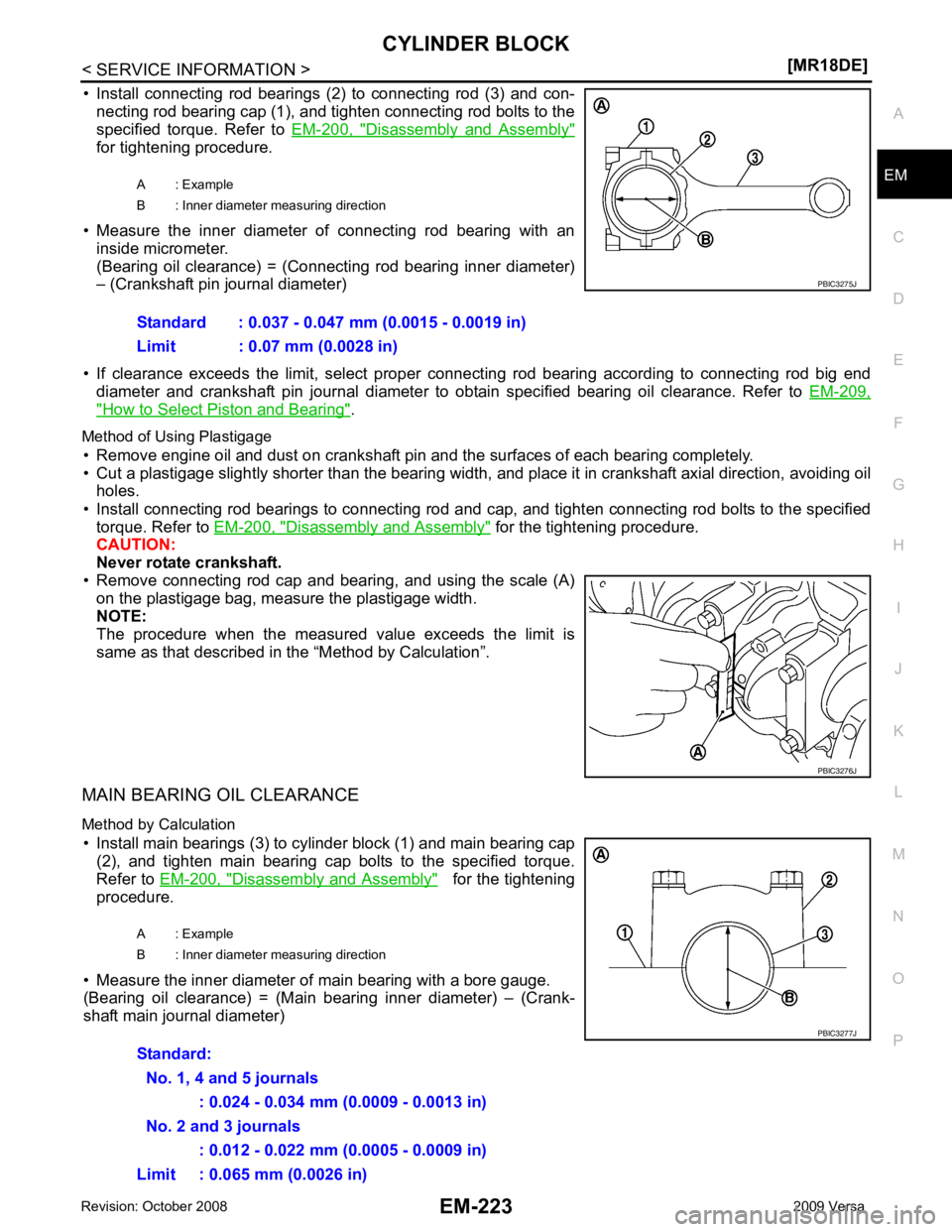
• Install connecting rod bearings (2) to connecting rod (3) and con-
necting rod bearing cap (1), and tighten connecting rod bolts to the
specified torque. Refer to EM-200, " Disassembly and Assembly "
for tightening procedure.
• Measure the inner diameter of connecting rod bearing with an inside micrometer.
(Bearing oil clearance) = (Connecting rod bearing inner diameter)
– (Crankshaft pin journal diameter)
• If clearance exceeds the limit, select proper c onnecting rod bearing according to connecting rod big end
diameter and crankshaft pin journal diameter to obtain specified bearing oil clearance. Refer to EM-209," How to Select Piston and Bearing " .
Method of Using Plastigage • Remove engine oil and dust on crankshaft pin and the surfaces of each bearing completely.
• Cut a plastigage slightly shorter than the bearing width, and place it in crankshaft axial direction, avoiding oil
holes.
• Install connecting rod bearings to connecting rod and c ap, and tighten connecting rod bolts to the specified
torque. Refer to EM-200, " Disassembly and Assembly " for the tightening procedure.
CAUTION:
Never rotate crankshaft.
• Remove connecting rod cap and bearing, and using the scale (A) on the plastigage bag, measure the plastigage width.
NOTE:
The procedure when the measured value exceeds the limit is
same as that described in the “Method by Calculation”.
MAIN BEARING OIL CLEARANCE
Method by Calculation • Install main bearings (3) to cylinder block (1) and main bearing cap (2), and tighten main bearing cap bolts to the specified torque.
Refer to EM-200, " Disassembly and Assembly " for the tightening
procedure.
• Measure the inner diameter of main bearing with a bore gauge.
(Bearing oil clearance) = (Main bearing inner diameter) – (Crank-
shaft main journal diameter) A : Example
B : Inner diameter measuring direction
Standard : 0.037 - 0.047 mm (0.0015 - 0.0019 in)
Limit : 0.07 mm (0.0028 in)
Page 3171 of 4331
How to Select
Piston and Bearing " .
Method of Using Plastigage
• Remove engine oil and dust on crankshaft main journal and the surfaces of each bearing completely.
• Cut a plastigage slightly shorter than the bearing width, and place it in crankshaft axial direction, avoiding oil
holes.
• Install main bearings to cylinder block and main bearing cap, and tighten main bearing cap bolts to the spec- ified torque. Refer to EM-200, " Disassembly and Assembly " for the tightening procedure.
CAUTION:
Never rotate crankshaft.
• Remove main bearing cap and bearings, and using the scale (A) on the plastigage bag, measure the plastigage width.
NOTE:
The procedure when the measured value exceeds the limit is
same as that described in the “Method by Calculation”.
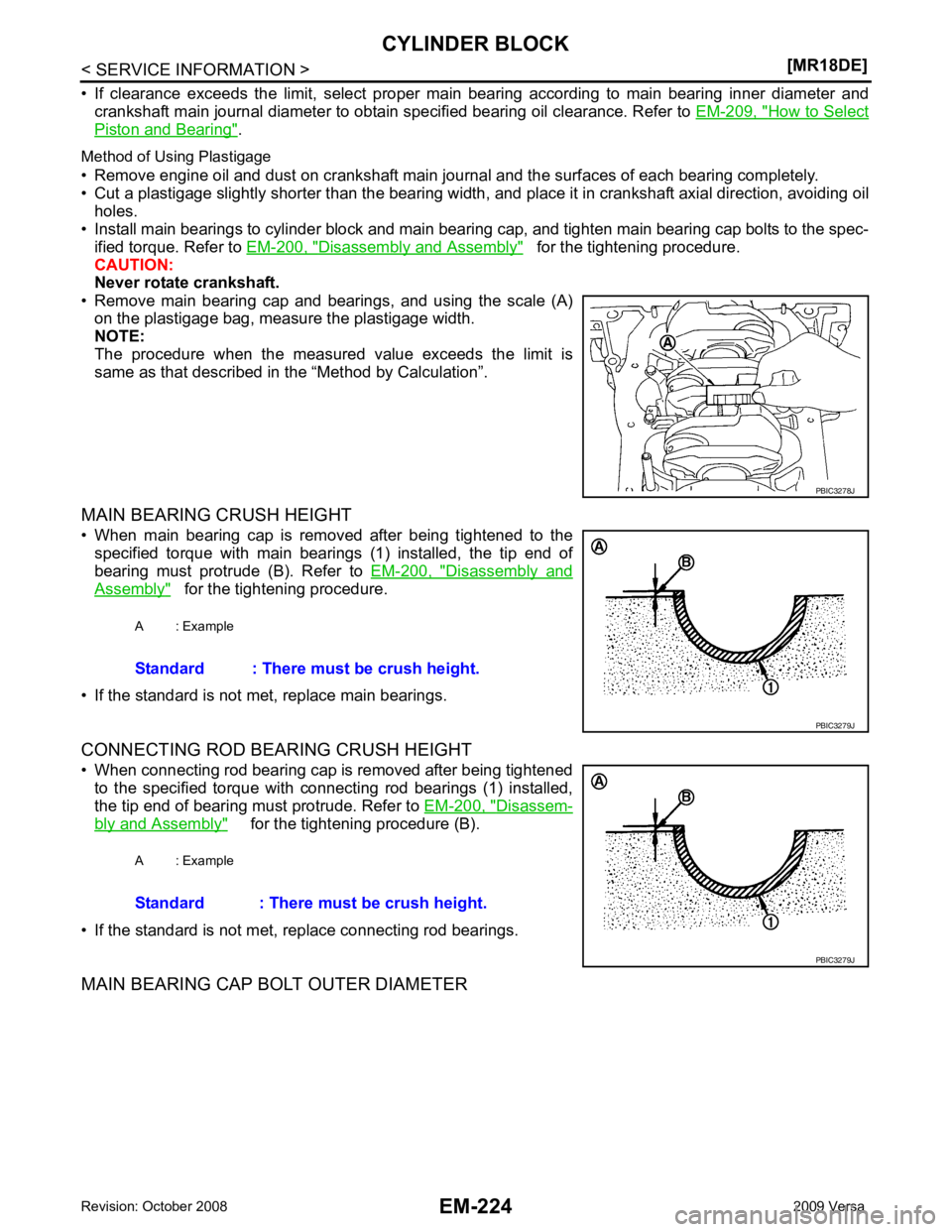
MAIN BEARING CRUSH HEIGHT
• When main bearing cap is removed after being tightened to the specified torque with main bearings (1) installed, the tip end of
bearing must protrude (B). Refer to EM-200, " Disassembly and
Assembly " for the tightening procedure.
• If the standard is not met, replace main bearings.
CONNECTING ROD BEARING CRUSH HEIGHT
• When connecting rod bearing cap is removed after being tightened to the specified torque with connecting rod bearings (1) installed,
the tip end of bearing must protrude. Refer to EM-200, " Disassem-
bly and Assembly " for the tightening procedure (B).
• If the standard is not met, replace connecting rod bearings.
MAIN BEARING CAP BOLT OUTER DIAMETER
Page 3202 of 4331
FAX
N
O P
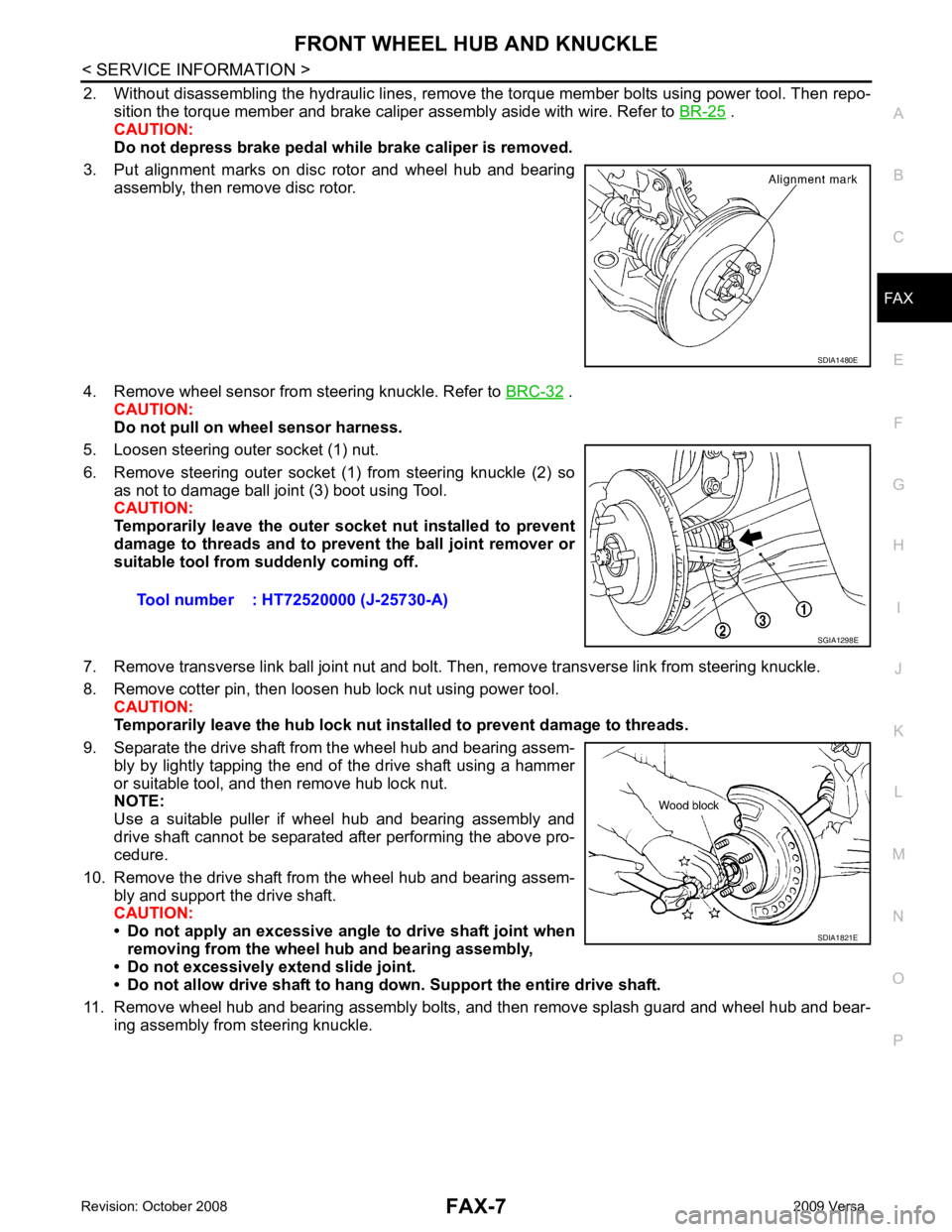
2. Without disassembling the hydraulic lines, remove the torque member bolts using power tool. Then repo-
sition the torque member and brake caliper assembly aside with wire. Refer to BR-25 .
CAUTION:
Do not depress brake pedal while brake caliper is removed.
3. Put alignment marks on disc rotor and wheel hub and bearing assembly, then remove disc rotor.
4. Remove wheel sensor from steering knuckle. Refer to BRC-32 .
CAUTION:
Do not pull on wheel sensor harness.
5. Loosen steering outer socket (1) nut.
6. Remove steering outer socket (1) from steering knuckle (2) so as not to damage ball joint (3) boot using Tool.
CAUTION:
Temporarily leave the outer so cket nut installed to prevent
damage to threads and to pr event the ball joint remover or
suitable tool from suddenly coming off.
7. Remove transverse link ball joint nut and bolt. Then, remove transverse link from steering knuckle.
8. Remove cotter pin, then loosen hub lock nut using power tool. CAUTION:
Temporarily leave the hub lock nut inst alled to prevent damage to threads.
9. Separate the drive shaft from the wheel hub and bearing assem- bly by lightly tapping the end of the drive shaft using a hammer
or suitable tool, and then remove hub lock nut.
NOTE:
Use a suitable puller if wheel hub and bearing assembly and
drive shaft cannot be separated after performing the above pro-
cedure.
10. Remove the drive shaft from the wheel hub and bearing assem- bly and support the drive shaft.
CAUTION:
• Do not apply an excessive angle to drive shaft joint when
removing from the wheel hub and bearing assembly,
• Do not excessively extend slide joint.
• Do not allow drive shaft to hang do wn. Support the entire drive shaft.
11. Remove wheel hub and bearing assembly bolts, and then remove splash guard and wheel hub and bear- ing assembly from steering knuckle.
Page 3204 of 4331
FAX
N
O P
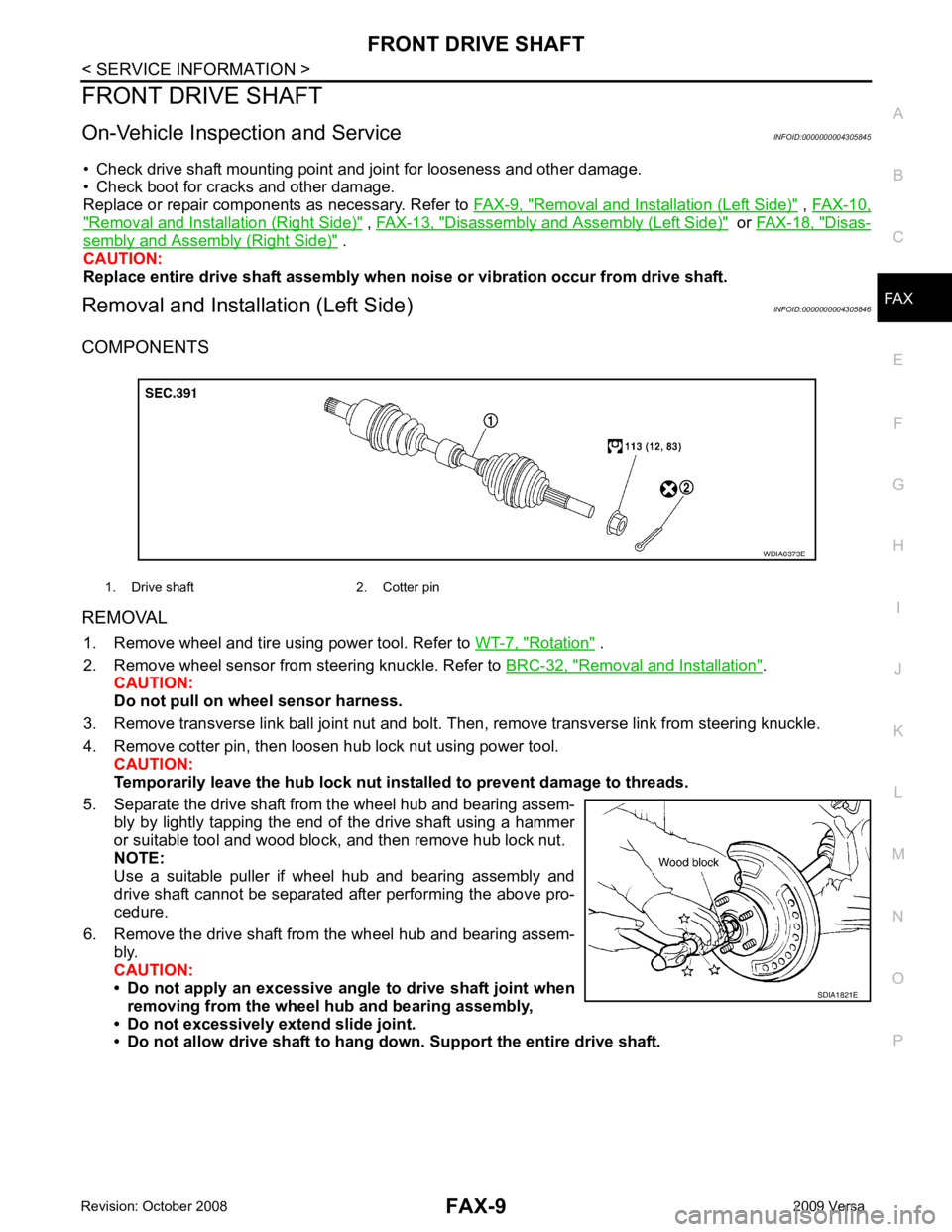
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT
On-Vehicle Inspection and Service INFOID:0000000004305845
• Check drive shaft mounting point and joint for looseness and other damage.
• Check boot for cracks and other damage.
Replace or repair components as necessary. Refer to FAX-9, " Removal and Installation (Left Side) " ,
FAX-10, " Removal and Installation (Right Side) " ,
FAX-13, " Disassembly and Assembly (Left Side) " or
FAX-18, " Disas-
sembly and Assembly (Right Side) " .
CAUTION:
Replace entire drive shaft assembly when noi se or vibration occur from drive shaft.
Removal and Installation (Left Side) INFOID:0000000004305846
COMPONENTS
REMOVAL 1. Remove wheel and tire using power tool. Refer to WT-7, " Rotation " .
2. Remove wheel sensor from steering knuckle. Refer to BRC-32, " Removal and Installation " .
CAUTION:
Do not pull on wheel sensor harness.
3. Remove transverse link ball joint nut and bolt. Then, remove transverse link from steering knuckle.
4. Remove cotter pin, then loosen hub lock nut using power tool. CAUTION:
Temporarily leave the hub lock nut inst alled to prevent damage to threads.
5. Separate the drive shaft from the wheel hub and bearing assem- bly by lightly tapping the end of the drive shaft using a hammer
or suitable tool and wood block, and then remove hub lock nut.
NOTE:
Use a suitable puller if wheel hub and bearing assembly and
drive shaft cannot be separated after performing the above pro-
cedure.
6. Remove the drive shaft from the wheel hub and bearing assem- bly.
CAUTION:
• Do not apply an excessive angle to drive shaft joint when
removing from the wheel hub and bearing assembly,
• Do not excessively extend slide joint.
• Do not allow drive shaft to hang do wn. Support the entire drive shaft.
1. Drive shaft 2. Cotter pin
Page 3206 of 4331
FAX
N
O P
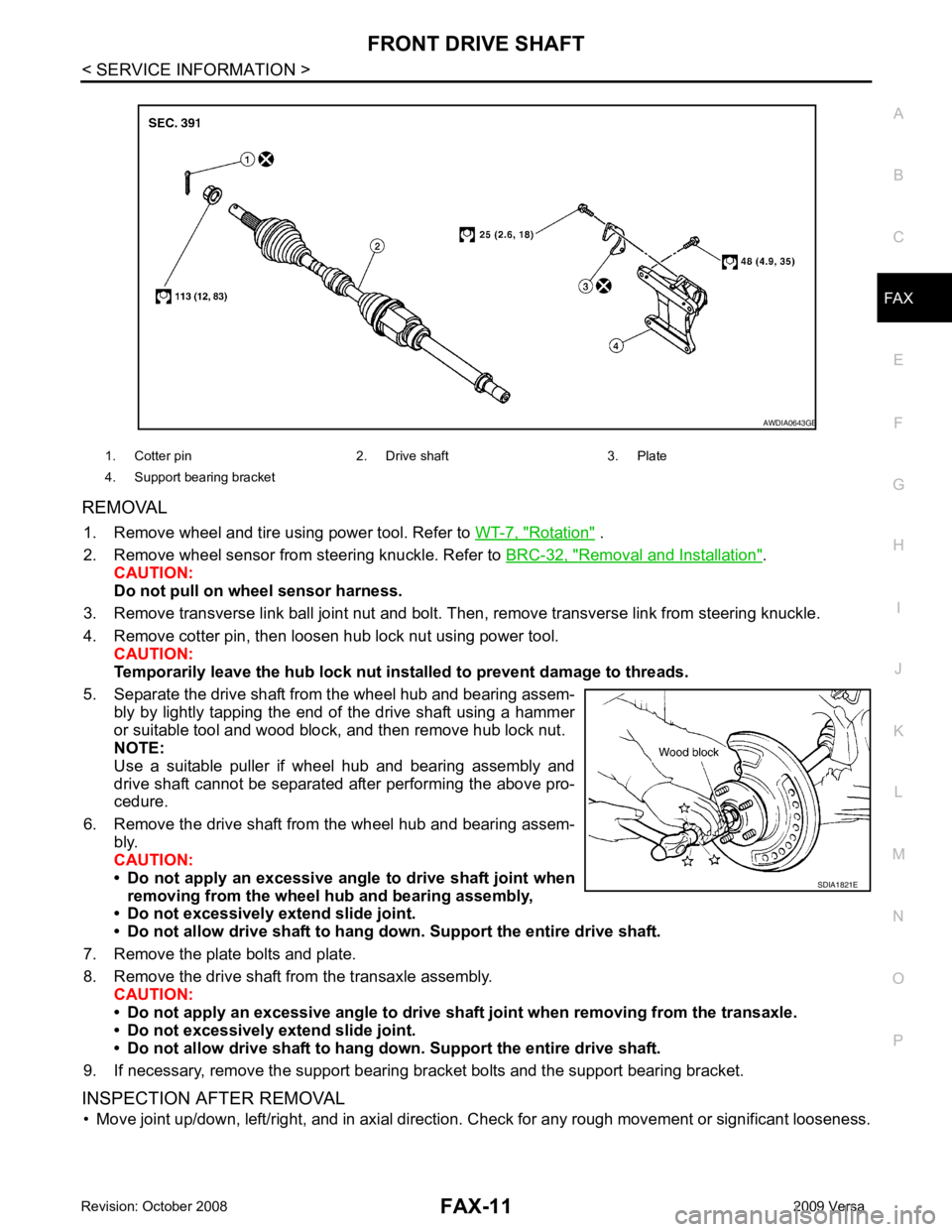
REMOVAL
1. Remove wheel and tire using power tool. Refer to WT-7, " Rotation " .
2. Remove wheel sensor from steering knuckle. Refer to BRC-32, " Removal and Installation " .
CAUTION:
Do not pull on wheel sensor harness.
3. Remove transverse link ball joint nut and bolt. Then, remove transverse link from steering knuckle.
4. Remove cotter pin, then loosen hub lock nut using power tool. CAUTION:
Temporarily leave the hub lock nut inst alled to prevent damage to threads.
5. Separate the drive shaft from the wheel hub and bearing assem- bly by lightly tapping the end of the drive shaft using a hammer
or suitable tool and wood block, and then remove hub lock nut.
NOTE:
Use a suitable puller if wheel hub and bearing assembly and
drive shaft cannot be separated after performing the above pro-
cedure.
6. Remove the drive shaft from the wheel hub and bearing assem- bly.
CAUTION:
• Do not apply an excessive angle to drive shaft joint when
removing from the wheel hub and bearing assembly,
• Do not excessively extend slide joint.
• Do not allow drive shaft to hang do wn. Support the entire drive shaft.
7. Remove the plate bolts and plate.
8. Remove the drive shaft from the transaxle assembly. CAUTION:
• Do not apply an excessive angle to drive shaf t joint when removing from the transaxle.
• Do not excessively extend slide joint.
• Do not allow drive shaft to hang do wn. Support the entire drive shaft.
9. If necessary, remove the support bearing bracket bolts and the support bearing bracket.
INSPECTION AFTER REMOVAL • Move joint up/down, left/right, and in axial direction. Check for any rough movement or significant looseness.
1. Cotter pin 2. Drive shaft 3. Plate
4. Support bearing bracket B
Page 3270 of 4331

GI
N
O P
Harness Indication 14 Wire color
• This shows a code for the color of the wire.
B = Black
W = White
R = Red
G = Green
L = Blue
Y = Yellow
LG = Light Green BR = Brown
OR or O = Orange
P = Pink
PU or V (Violet) = Purple
GY or GR = Gray
SB = Sky Blue
CH = Dark Brown
DG = Dark Green
When the wire color is striped, the base color is given first, followed by the stripe color as shown
below:
Example: L/W = Blue with White Stripe
15 Option description • This shows a description of the option abbreviation used on the page.
16 Switch • This shows that continuity exists between terminals 1 and 2 when the switch is in the A posi-
tion. Continuity exists between terminals 1 and 3 when the switch is in the B position.
17 Assembly parts • Connector terminal in component shows that it is a harness incorporated assembly.
18 Cell code • This identifies each page of the wiring diagram by section, system and wiring diagram page
number.
19 Current flow arrow • Arrow indicates electric current flow, especially where the direction of standard flow (vertically
downward or horizontally from left to right) is difficult to follow.
• A double arrow “ ” shows that current can flow in either direction depending on circuit operation.
20 System branch • This shows that the system branches to another system identified by cell code (section and
system).
21 Page crossing • This arrow shows that the circuit continues to another page identified by cell code.
• The C will match with the C on another page within the system other than the next or preceding pages.
22 Shielded line • The line enclosed by broken line circle shows shield wire.
23 Component box in
wave line • This shows that another part of the component is also shown on another page (indicated by
wave line) within the system.
24 Component name • This shows the name of a component.
25 Connector number • This shows the connector number.
• The letter shows which harness the connector is located in.
• Example: M: main harness. For detail and to locate the connector, refer to PG section "Main
Harness", “Harness Layout”. A coordinate grid is included for complex harnesses to aid in lo-
cating connectors.
26 Ground (GND) • The line spliced and grounded under wire color shows that ground line is spliced at the ground-
ed connector.
27 Ground (GND) • This shows the ground connection. For detailed ground distribution information, refer to
"Ground Distribution" in PG section.
28 Connector views • This area shows the connector faces of the components in the wiring diagram on the page.
29 Common component • Connectors enclosed in broken line show that these connectors belong to the same compo-
nent.
30 Connector color • This shows a code for the color of the connector. For code meaning, refer to wire color codes,
Number 14 of this chart.
31 Fusible link and fuse
box • This shows the arrangement of fusible link(s) and fuse(s), used for connector views of "POW-
ER SUPPLY ROUTING" in PG section.
The open square shows current flow in, and the shaded square shows current flow out.
32 Reference area • This shows that more information on the Super Multiple Junction (SMJ) and Joint Connectors
(J/C) exists on the PG section. Refer to "Reference Area" for details.
Num-
ber Item Description