2008 NISSAN TEANA Trans
[x] Cancel search: TransPage 2527 of 5121

GI-34
< BASIC INSPECTION >
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
BASIC INSPECTION
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Work FlowINFOID:0000000003852793
WORK FLOW
Control Units and Electrical PartsINFOID:0000000003852794
PRECAUTIONS
Never reverse polarity of battery terminals.
Install only parts specified for a vehicle.
Before replacing the control unit, check the input and output and functions of the component parts.
Do not apply excessive force when disconnecting a connector.
SGI838
STEP DESCRIPTION
STEP 1Get detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the incident occurred.
The following are key pieces of information required to make a good analysis:
WHATVehicle Model, Engine, Transmission/Transaxle and the System (i.e. Radio).
WHENDate, Time of Day, Weather Conditions, Frequency.
WHERERoad Conditions, Altitude and Traffic Situation.
HOWSystem Symptoms, Operating Conditions (Other Components Interaction).
Service History and if any After Market Accessories have been installed.
STEP 2Operate the system, road test if necessary.
Verify the parameter of the incident.
If the problem cannot be duplicated, refer to “Incident Simulation Tests”.
STEP 3Get the proper diagnosis materials together including:
Power Supply Routing
System Operation Descriptions
Applicable Service Manual Sections
Check for any Service Bulletins
Identify where to begin diagnosis based upon your knowledge of the system operation and the customer comments.
STEP 4Inspect the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage.
Determine which circuits and components are involved and diagnose using the Power Supply Routing and Harness Lay-
outs.
STEP 5 Repair or replace the incident circuit or component.
STEP 6Operate the system in all modes. Verify the system works properly under all conditions. Make sure you have not inad-
vertently created a new incident during your diagnosis or repair steps.
Page 2528 of 5121

SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-35
< BASIC INSPECTION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
Do not apply excessive shock to the control unit by dropping or hit-
ting it.
Be careful to prevent condensation in the control unit due to rapid
temperature changes and do not let water or rain get on it. If water
is found in the control unit, dry it fully and then install it in the vehi-
cle.
Be careful not to let oil to get on the control unit connector.
Avoid cleaning the control unit with volatile oil.
Do not disassemble the control unit, and do not remove the upper
and lower covers.
When using a DMM, be careful not to let test probes get close to
each other to prevent the power transistor in the control unit from
damaging battery voltage because of short circuiting.
When checking input and output signals of the control unit, use the
specified check adapter.
Intermittent IncidentINFOID:0000000003852795
DESCRIPTION
Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought in for service. If possible, re-create the
conditions present at the time of the incident. Doing so may help avoid a No Trouble Found Diagnosis. The fol-
lowing section illustrates ways to simulate the conditions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics: Vehicle vibration
Heat sensitive
Freezing
Water intrusion
Electrical load
Cold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is important for simulating the conditions of the
problem.
VEHICLE VIBRATION
The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough road or when engine is vibrating (idle with
A/C on). In such a case, you will want to check for a vibration related condition. Refer to the following illustra-
tion.
Connector & Harness
SAIA0255E
SEF348N
Page 2536 of 5121

CONSULT-III/GST CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-43
< BASIC INSPECTION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
PCONSULT-III/GST CHECKING SYSTEM
DescriptionINFOID:0000000003852797
When CONSULT-III/GST is connected with a data link connector
(A) equipped on the vehicle side, it will communicate with the con-
trol unit equipped in the vehicle and then enable various kinds of
diagnostic tests.
Refer to “CONSULT-III Software Operation Manual” for more infor-
mation.
CONSULT-III Function and System Application*1INFOID:0000000003852798
x: Applicable
*1: If GST application is equipped, functions in accordance with SAE J1979 and ISO 15031-5 can be used.
CONSULT-III/GST Data Link Connector (DLC) CircuitINFOID:0000000003852799
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
If the CONSULT-III/GST cannot diagnose the system properly, check the following items.
1 : Instrument driver lower panel
JPAIA0313GB
Diagnostic test mode Function
ENGINE
TRANSMISSION
AIR BAG
METER/M&A
BCM
AUTO DRIVE POS.
ABS
ABS (Including VDC)
IPDM E/R
HEAD LAMP LEVELIZER
MULTI AV
HVAC
Work SupportThis mode enables a technician to adjust some devices
faster and more accurately.xx- -xx-x-x-x
Self-Diagnostic Results Retrieve DTC from ECU and display diagnostic items. x x x x x x x x x x x x
Data MonitorMonitor the input/output signal of the control unit in real
time.xx - xxxxxxxxx
CAN DiagnosisThis mode displays a network diagnosis result about
CAN by a diagram.xx - xxxxxx - xx
CAN Diagnosis Support
MonitorIt monitors the status of CAN communication. x x - x x x x x x - x -
Active TestSend the drive signal from CONSULT-III to the actua-
tor. The operation check can be performed.x - - - xxxxxx - x
DTC & SRT confirma-
tionThe status of system monitoring tests and the self-diag-
nosis status/result can be confirmed.x-----------
ECU IdentificationDisplay the ECU identification number (part number
etc.) of the selected system.xx - - xxxxxxxx
Function TestThis mode can show results of self-diagnosis of ECU
with either "OK" or "NG". For engine, more practical
tests regarding sensors/switches and/or actuators are
available.xxx---xx----
Configuration Function to READ/WRITE vehicle configuration - - - - x - - - - x - -
Special FunctionOther results or histories, etc. that are recorded in ECU
are displayed.-xxx--------
Page 2548 of 5121

SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
GW-5
< SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
GW
N
O
P
Again, pressing on the components to stop the noise while duplicating the conditions can isolate most of these
incidents. Repairs usually consist of insulating with felt cloth tape.
SEATS
When isolating seat noise it is important to note the position the seat is in and the load placed on the seat
when the noise occurs. These conditions should be duplicated when verifying and isolating the cause of the
noise.
Cause of seat noise include:
1. Headrest rods and holder
2. A squeak between the seat pad cushion and frame
3. Rear seatback lock and bracket
These noises can be isolated by moving or pressing on the suspected components while duplicating the con-
ditions under which the noise occurs. Most of these incidents can be repaired by repositioning the component
or applying urethane tape to the contact area.
UNDERHOOD
Some interior noise may be caused by components under the hood or on the engine wall. The noise is then
transmitted into the passenger compartment.
Causes of transmitted underhood noise include:
1. Any component mounted to the engine wall
2. Components that pass through the engine wall
3. Engine wall mounts and connectors
4. Loose radiator mounting pins
5. Hood bumpers out of adjustment
6. Hood striker out of adjustment
These noises can be difficult to isolate since they cannot be reached from the interior of the vehicle. The best
method is to secure, move or insulate one component at a time and test drive the vehicle. Also, engine RPM
or load can be changed to isolate the noise. Repairs can usually be made by moving, adjusting, securing, or
insulating the component causing the noise.
Page 2576 of 5121
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
HA-7
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
HA
N
O
P
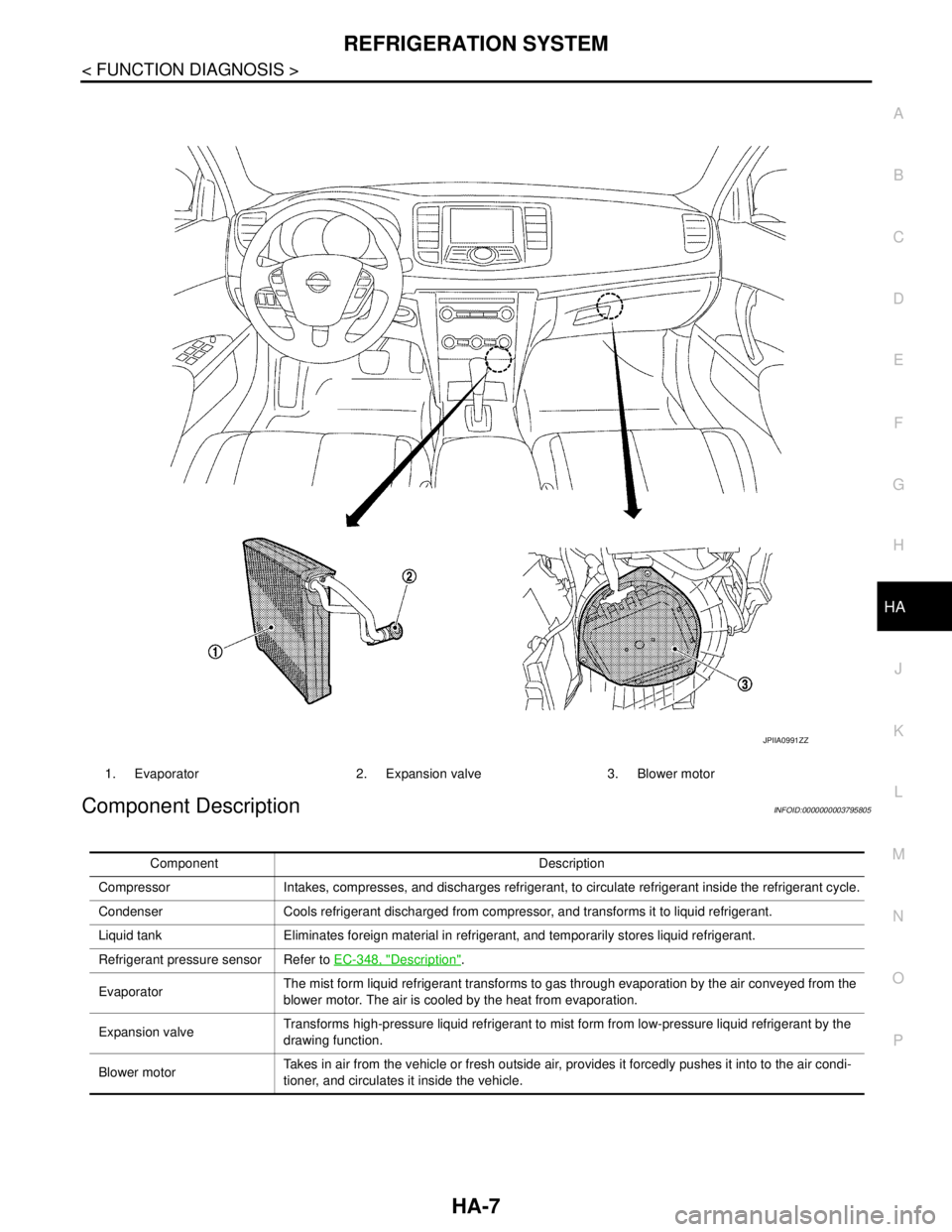
Component DescriptionINFOID:0000000003795805
1. Evaporator 2. Expansion valve 3. Blower motor
JPIIA0991ZZ
Component Description
Compressor Intakes, compresses, and discharges refrigerant, to circulate refrigerant inside the refrigerant cycle.
Condenser Cools refrigerant discharged from compressor, and transforms it to liquid refrigerant.
Liquid tank Eliminates foreign material in refrigerant, and temporarily stores liquid refrigerant.
Refrigerant pressure sensor Refer to EC-348, "
Description".
EvaporatorThe mist form liquid refrigerant transforms to gas through evaporation by the air conveyed from the
blower motor. The air is cooled by the heat from evaporation.
Expansion valveTransforms high-pressure liquid refrigerant to mist form from low-pressure liquid refrigerant by the
drawing function.
Blower motorTakes in air from the vehicle or fresh outside air, provides it forcedly pushes it into to the air condi-
tioner, and circulates it inside the vehicle.
Page 2650 of 5121
![NISSAN TEANA 2008 Service Manual HAC-22
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >[WITHOUT 7 INCH DISPLAY]
AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONER SYSTEM
AIR CONDITIONER LAN CONTROL SYSTEM
The LAN (Local Area Network) system consists of the A/C auto amp., the mode do NISSAN TEANA 2008 Service Manual HAC-22
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >[WITHOUT 7 INCH DISPLAY]
AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONER SYSTEM
AIR CONDITIONER LAN CONTROL SYSTEM
The LAN (Local Area Network) system consists of the A/C auto amp., the mode do](/manual-img/5/57391/w960_57391-2649.png)
HAC-22
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >[WITHOUT 7 INCH DISPLAY]
AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONER SYSTEM
AIR CONDITIONER LAN CONTROL SYSTEM
The LAN (Local Area Network) system consists of the A/C auto amp., the mode door motor, the air mix door
motors and the intake door motor.
A configuration of these components is as shown in the figure below.
SYSTEM CONSTRUCTION
A small network exists between the A/C auto amp., the mode door motor, the air mix door motor and the intake
door motor. The A/C auto amp. and motors are connected by data transmission lines and motor power supply
lines. The LAN network is built through the ground circuits of each door motor.
Addresses, motor opening angle signals, motor stop signals and error checking messages are all transmitted
through the data transmission lines connecting the A/C auto amp. and each door motor.
The following functions are contained in LCUs built into the mode door motor, the air mix door motors and the
intake door motor.
Address
Motor opening angle signals
Data transmission
Motor stop and drive decision
Opening angle sensor (PBR function)
Comparison
JSIIA1186GB
JSIIA1129GB
Page 2651 of 5121
![NISSAN TEANA 2008 Service Manual AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONER SYSTEM
HAC-23
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >[WITHOUT 7 INCH DISPLAY]
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
HAC
N
O
P
Decision (A/C auto amp. indicated value and motor opening angle comparison)
Op NISSAN TEANA 2008 Service Manual AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONER SYSTEM
HAC-23
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >[WITHOUT 7 INCH DISPLAY]
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
HAC
N
O
P
Decision (A/C auto amp. indicated value and motor opening angle comparison)
Op](/manual-img/5/57391/w960_57391-2650.png)
AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONER SYSTEM
HAC-23
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >[WITHOUT 7 INCH DISPLAY]
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
HAC
N
O
P
Decision (A/C auto amp. indicated value and motor opening angle comparison)
Operation
The A/C auto amp. receives data from each of the sensors. The A/C auto amp. sends mode door, the air mix
door and the intake door opening angle data to the mode door motor LCU, the air mix door motor LCUs and
the intake door motor LCU.
The mode door motor, the air mix door motors and the intake door motor read their respective signals accord-
ing to the address signal. Opening angle indication signals received from the A/C auto amp. and each of the
motor position sensors is compared by the LCUs in each door motor with the existing decision and opening
angles. Next, HOT/COLD, DEF/VENT, OPEN/SHUT or FRE/REC operation is selected. The new selection
data is returned to the A/C auto amp.
Transmission Data and Transmission Order
A/C auto amp. data is transmitted consecutively to each of the door motors following the form as shown in the
figure below.
START: Initial compulsory signal is sent to each of the door motors.
ADDRESS: Data sent from the A/C auto amp. is selected according to data-based decisions made by the mode door
motor, the air mix door motors and the intake door motor.
If the addresses are identical, the opening angle data and error check signals are received by the door motor
LCUs. The LCUs then make the appropriate error decision. If the opening angle data has no error, door con-
trol begins.
If an error exists, the received data is rejected and the corrected data received. Finally, door control is based
upon the corrected opening angle data.
OPENING ANGLE:
Data that shows the indicated door opening angle of each door motor.
ERROR CHECK: In this procedure, transmitted and received data is checked for errors. Error data is then compiled. The error
check prevents corrupted data from being used by the mode door motor, the air mix door motors and the
intake door motor. Error data can be related to the following symptoms.
- Malfunction of electrical frequency
- Poor electrical connections
- Signal leakage from transmission lines
- Signal level fluctuation
STOP SIGNAL:
JSIIA1130GB
JSIIA1131GB
Page 2652 of 5121
![NISSAN TEANA 2008 Service Manual HAC-24
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >[WITHOUT 7 INCH DISPLAY]
AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONER SYSTEM
At the end of each transmission, a stop operation, in-operation, or internal malfunction message is delivered
t NISSAN TEANA 2008 Service Manual HAC-24
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >[WITHOUT 7 INCH DISPLAY]
AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONER SYSTEM
At the end of each transmission, a stop operation, in-operation, or internal malfunction message is delivered
t](/manual-img/5/57391/w960_57391-2651.png)
HAC-24
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >[WITHOUT 7 INCH DISPLAY]
AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONER SYSTEM
At the end of each transmission, a stop operation, in-operation, or internal malfunction message is delivered
to the A/C auto amp. This completes one data transmission and control cycle.
Component Part LocationINFOID:0000000003846303
ENGINE COMPARTMENT
JSIIA1132GB