2008 NISSAN LATIO key
[x] Cancel search: keyPage 1855 of 2771
GI-4
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
PRECAUTIONS
• Use hand tools, power tools (disassembly only) and recommended
special tools where specified for safe and efficient service repairs.
• When repairing the fuel, oil, water, vacuum or exhaust systems,
check all affected lines for leaks.
• Before servicing the vehicle:
Protect fenders, upholstery and carpeting with appropriate covers.
Take caution that keys, buckles or buttons do not scratch paint.
WARNING:
To prevent ECM from storing the diagnostic trouble codes, do not carelessly disconnect the harness
connectors which are related to the engine control system and TCM (transmission control module)
system. The connectors should be disconnected only when working according to the WORK FLOW of
TROUBLE DIAGNOSES in EC and AT sections.
Precaution for Three Way CatalystINFOID:0000000001702425
If a large amount of unburned fuel flows into the catalyst, the catalyst temperature will be excessively high. To
prevent this, follow the instructions.
• Use unleaded gasoline only. Leaded gasoline will seriously damage the three way catalyst.
• When checking for ignition spark or measuring engine compression, make tests quickly and only when nec-
essary.
• Do not run engine when the fuel tank level is low, otherwise the engine may misfire, causing damage to the
catalyst.
Do not place the vehicle on flammable material. Keep flammable material off the exhaust pipe and the three
way catalyst.
Precaution for Fuel (Unleaded Regular Gasoline Recommended)INFOID:0000000001702426
Use unleaded regular gasoline with an octane rating of at least 87 AKI (Anti-Knock Index) number (Research
octane number 91).
CAUTION:
Do not use leaded gasoline. Using leaded gasoline will damage the three way catalyst. Do not use E-85
fuel (85% fuel ethanol, 15% unleaded gasoline) unless the vehicle is specifically designed for E-85 fuel
(i.e. Flexible Fuel Vehicle - FFV models). Using a fuel other than that specified could adversely affect
the emission control devices and systems, and could also affect the warranty coverage validity.
PBIC0190E
SGI234
Page 1861 of 2771

GI-10
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
3.Refer to Component Parts and Harness Connector Location for the Systems described in each
section for identification/location of components and harness connectors.
4.Refer to the Circuit Diagram for quick pinpoint check.
If you need to check circuit continuity between harness connectors in more detail, such as when a
sub-harness is used, refer to Wiring Diagram in each individual section and Harness Layout in PG
section for identification of harness connectors.
5.When checking circuit continuity, ignition switch should be OFF.
6.Before checking voltage at connectors, check battery voltage.
7.After accomplishing the Diagnostic Procedures and Electrical Components Inspection, make sure
that all harness connectors are reconnected as they were.
HOW TO FOLLOW TEST GROUPS IN TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
1.Work and diagnostic procedure
Start to diagnose a problem using procedures indicated in enclosed test groups.
2.Questions and required results
Questions and required results are indicated in bold type in test group.
The meaning of are as follows:
3.Symbol used in illustration
Symbols included in illustrations refer to measurements or procedures. Before diagnosing a problem,
familiarize yourself with each symbol. Refer to "Connector Symbols" in GI Section and "KEY TO SYM-
BOLS SIGNIFYING MEASUREMENTS OR PROCEDURES" below.
4.Action items
Next action for each test group is indicated based on result of each question. Test group number is shown
in the left upper portion of each test group.
HARNESS WIRE COLOR AND CONNECTOR NUMBER INDICATION
There are two types of harness wire color and connector number indication.
TYPE 1: Harness Wire Color and Connector Number are Shown in Illustration
SAIA0256E
a. Battery voltage → 11 - 14V or approximately 12V
b. Voltage : Approximately 0V → Less than 1V
Page 1863 of 2771

GI-12
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
KEY TO SYMBOLS SIGNIFYING MEASUREMENTS OR PROCEDURES
SAIA0750E
Page 1876 of 2771

SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-25
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
How to Perform Efficient Diagnosis for an Electrical IncidentINFOID:0000000001702441
WORK FLOW
INCIDENT SIMULATION TESTS
Introduction
Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought in for service. If possible, re-create the
conditions present at the time of the incident. Doing so may help avoid a No Trouble Found Diagnosis. The fol-
lowing section illustrates ways to simulate the conditions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics:
• Vehicle vibration
• Heat sensitive
• Freezing
• Water intrusion
• Electrical load
SGI838
STEP DESCRIPTION
STEP 1Get detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the incident occurred.
The following are key pieces of information required to make a good analysis:
WHATVehicle Model, Engine, Transmission/Transaxle and the System (i.e. Radio).
WHENDate, Time of Day, Weather Conditions, Frequency.
WHERERoad Conditions, Altitude and Traffic Situation.
HOWSystem Symptoms, Operating Conditions (Other Components Interaction).
Service History and if any After Market Accessories have been installed.
STEP 2Operate the system, road test if necessary.
Verify the parameter of the incident.
If the problem cannot be duplicated, refer to “Incident Simulation Tests”.
STEP 3Get the proper diagnosis materials together including:
• Power Supply Routing
• System Operation Descriptions
• Applicable Service Manual Sections
• Check for any Service Bulletins
Identify where to begin diagnosis based upon your knowledge of the system operation and the customer comments.
STEP 4Inspect the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage.
Determine which circuits and components are involved and diagnose using the Power Supply Routing and Harness Lay-
outs.
STEP 5 Repair or replace the incident circuit or component.
STEP 6Operate the system in all modes. Verify the system works properly under all conditions. Make sure you have not inad-
vertently created a new incident during your diagnosis or repair steps.
Page 1880 of 2771
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-29
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
• Close the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
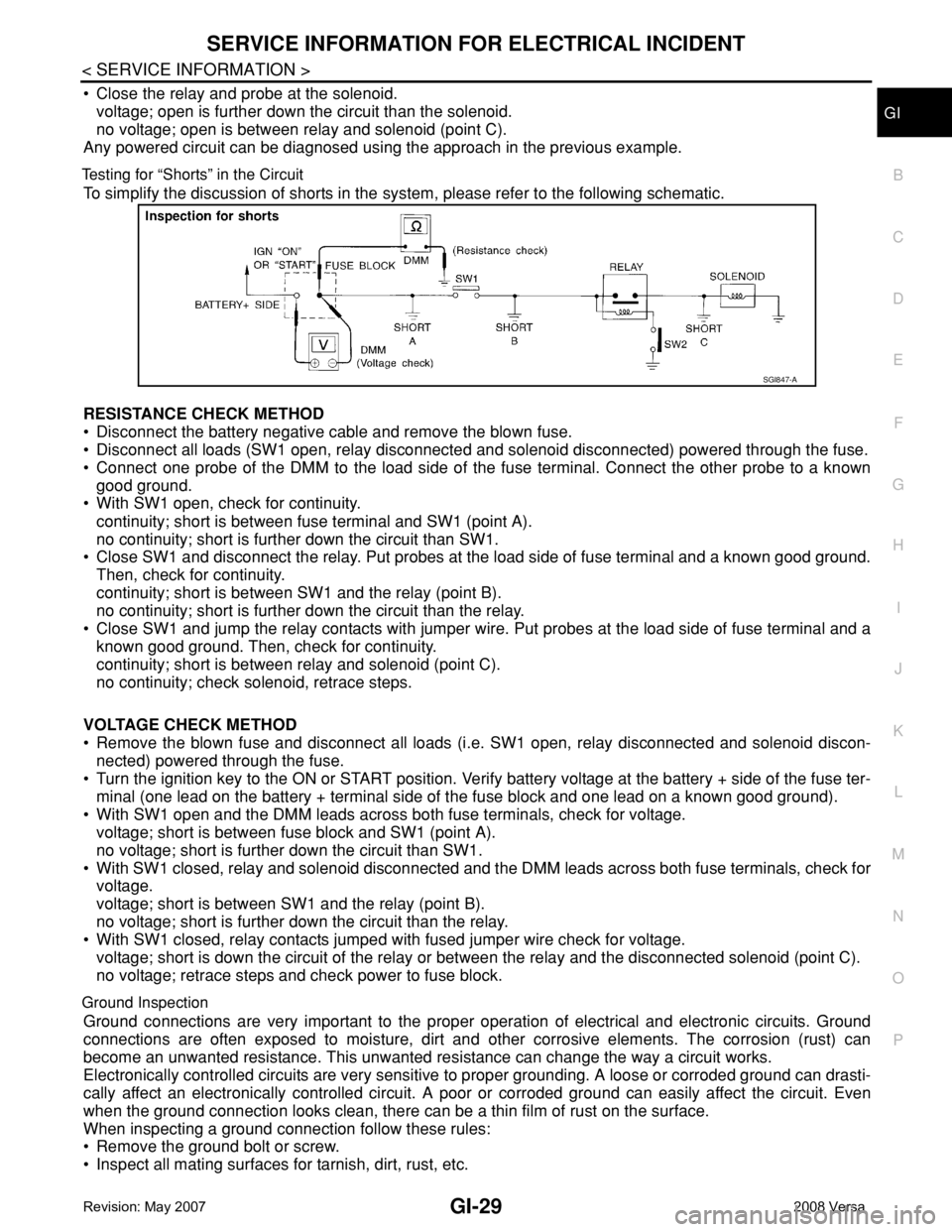
Testing for “Shorts” in the Circuit
To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system, please refer to the following schematic.
RESISTANCE CHECK METHOD
• Disconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
• Disconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the fuse.
• Connect one probe of the DMM to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a known
good ground.
• With SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
• Close SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good ground.
Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
• Close SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a
known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
• Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
• Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify battery voltage at the battery + side of the fuse ter-
minal (one lead on the battery + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
• With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
• With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for
voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
• With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
• Remove the ground bolt or screw.
• Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
SGI847-A
Page 1886 of 2771

CONSULT-III CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-35
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
PCONSULT-III CHECKING SYSTEM
DescriptionINFOID:0000000001806209
• CONSULT-III is a hand-held type tester. When it is connected with a diagnostic connector equipped on the
vehicle side, it will communicate with the control unit equipped in the vehicle and then enable various kinds
of diagnostic tests.
• Refer to CONSULT-III Operator's Manual for more information.
Function and System ApplicationINFOID:0000000001806219
x: Applicable.
*1: If equipped.
*2: This option is shown on vehicles equipped with continuously variable transmission (CVT).
*3: NVIS (NATS) [NISSAN Vehicle Immobilizer System (Nissan Anti-theft System)]. Diagnostic test mode Function
ENGINE
ABS*
1
AIR BAG
EPS
IPDM E/R
BCM
METER/M&A
INTELLIGENT KEY*
1
A/T*
1
TRANSMISSION*
2
NVIS (NATS)*
3
NVIS (NATS BCM OR S/ENT)*
3
NATS I-KEY
*3,5
Work supportThis mode enables a technician to adjust some devices faster
and more accurately by following indications on CONSULT-III.x----x-xxx--x
Self-diagnostic results Self-diagnostic results can be read and erased quickly. xxxxxxxxxxx - x
Trouble diagnostic
recordCurrent self-diagnostic results and all trouble diagnostic records
previously stored can be read.--x----------
Data monitor Input/Output data in the ECU can be read. xx - xx - xxxx - - -
CAN diagnostic support
monitorThe communication condition of CAN communication line can
be read.xx - xxxxxxx - - -
Calibration data*
2Shows unit calibration IDs, offsets and gains. This data is stored
in the ECU memory.---------x---
Active testDiagnostic Test Mode in which CONSULT-III drives actuators
apart from ECU shifting some parameters in a specified range.xx--x--x-----
Function testThis mode can show results of self-diagnosis of ECU with either
"OK" or "NG". For engines, more practical tests regarding sen-
sors/switches and/or actuators are available.xxx-----xx---
DTC & SRT confirmationThe results of SRT (System Readiness Test) and the self-diag-
nosis status/result can be confirmed.x------------
DTC work supportThe operating condition to confirm Diagnosis Trouble Codes
can be selected.x-------x----
ECM/ECU part number ECM/ECU part number can be read. x x - x - x - x x x - - -
ECU discriminated No.Classification number of a replacement ECU can be read to pre-
vent an incorrect ECU from being installed.--x----------
Passenger airbag Displays the STATUS (readiness) of front passenger air bag. --x----------
Configuration Sets control module parameters to match vehicle options. -----x-------
Steering lock release
*4,5Condition of steering lock release solenoid. -----------x-
Control unit initializa-
tion
*4,6All registered ignition key IDs in NATS components can be ini-
tialized and new IDs can be registered.----------x--
PIN Read
*4This mode enables technician to get BCM-specific 5-digit code.-----------x-
Page 1887 of 2771
GI-36
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
CONSULT-III CHECKING SYSTEM
*4: This system is shown with NVIS (NATS) using program card AEN06B or later.
*5: With Intelligent Key System.
*6: Without Intelligent Key System.
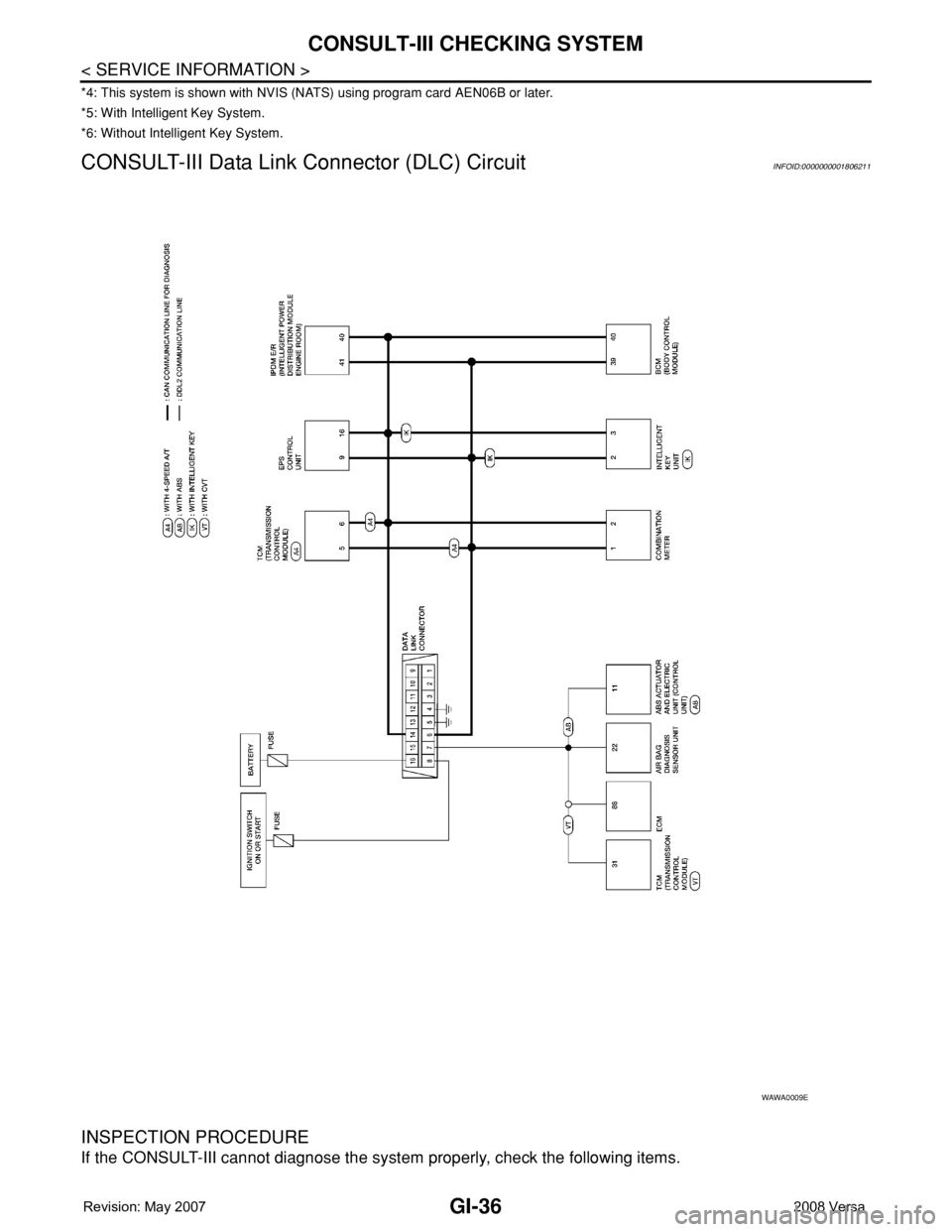
CONSULT-III Data Link Connector (DLC) CircuitINFOID:0000000001806211
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
If the CONSULT-III cannot diagnose the system properly, check the following items.
WAWA0009E
Page 1993 of 2771

LAN-2
DLC BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...........................35
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................35
EPS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...........................36
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................36
I-KEY BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ........................37
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................37
M&A BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................38
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................38
ABS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................39
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................39
TCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................40
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................40
IPDM-E BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT .....................41
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................41
CAN COMMUNICATION CIRCUIT ....................42
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................42
CAN SYSTEM (TYPE 1)
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS ........................
44
ECM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................44
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................44
BCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................45
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................45
DLC BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...........................46
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................46
EPS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...........................47
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................47
M&A BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................48
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................48
IPDM-E BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT .....................49
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................49
CAN COMMUNICATION CIRCUIT ....................50
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................50
CAN SYSTEM (TYPE 2)
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS ........................
52
ECM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................52
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................52
BCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................53
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................53
DLC BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...........................54
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................54
EPS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...........................55
Diagnosis Procedure ..............................................55
I-KEY BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ........................56
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................56
M&A BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................57
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................57
IPDM-E BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT .....................58
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................58
CAN COMMUNICATION CIRCUIT ...................59
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................59
CAN SYSTEM (TYPE 3)
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS .......................
61
MAIN LINE BETWEEN DLC AND ABS CIR-
CUIT ...................................................................
61
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................61
ECM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................62
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................62
BCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................63
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................63
DLC BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................64
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................64
EPS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...........................65
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................65
M&A BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................66
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................66
ABS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................67
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................67
IPDM-E BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT .....................68
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................68
CAN COMMUNICATION CIRCUIT ...................69
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................69
CAN SYSTEM (TYPE 4)
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS .......................
71
MAIN LINE BETWEEN DLC AND ABS CIR-
CUIT ...................................................................
71
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................71
ECM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................72
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................72
BCM BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................73
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................73
DLC BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ..........................74
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................74
EPS BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT ...........................75
Diagnosis Procedure ...............................................75
I-KEY BRANCH LINE CIRCUIT .....................