2008 INFINITI FX35 length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 999 of 3924

BRAKE BOOSTERBR-15
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
G H
I
J
K L
M A
B
BR
N
O P
CAUTION:
Be careful not to splash brake fluid on painted areas; it may cause paint damage. If brake fluid is
splashed on painted surfaces of body, immediately wipe it off and them wash it away with water
immediately.
Be careful not to deform or bend brake tube while removing and installing brake booster.
Replace clevis pin if it is damaged.
Be careful not to damage brake booster stud bolt thr eads. If brake booster is tilted or inclined during
installation, dash panel may damage the threads.
Install the check valve in the correct direction.
1. Remove vacuum hose from brake booster. Refer to BR-16
.
2. Remove brake master cylinder. Refer to BR-12, "
Removal and Installation".
3. Disconnect harness connector from brake booster assembly. (ICC model)
4. Remove snap pin and clevis pin from inside the vehicle. Refer to BR-6, "
Component".
5. Remove nuts from brake booster and brake pedal bracket.
6. Remove brake booster assembly from engine room.
INSPECTION AFTER REMOVAL
Output Rod Length Inspection
1. Using a handy vacuum pump, apply a vacuum of –66.7 kPa (– 500 mmHg, –19.69 inHg) to brake booster.
2. Check output rod length.
INSTALLATION
1. Loosen lock nut to adjust input r od length so that the length “B”
(shown in the figure) satisfies the specified value.
2. After adjusting “B”, temporarily tighten lock nut to install brake booster assembly to the vehicle. At this time, make sure to
install a gasket between brake booster assembly and the engine
room.
3. Connect brake pedal with clevis of input rod.
4. Install brake pedal bracket mounting nuts and bolt and tighten them to the specified torque. BR-6, "
Component".
5. Install brake tube from brake master cylinder to ABS actuator. Refer to BR-10, "
Hydraulic Circuit".
6. Install master cylinder to booster assembly. Refer to BR-12, "
Removal and Installation".
7. Adjust the height and play of brake pedal. BR-5, "
Inspection and Adjustment".
8. Tighten lock nut of input rod to the specified torque. Refer to BR-14, "
Component".
9. Bleed air. Refer to BR-8, "
Bleeding Brake System".
Standard dimension when
applying a vacuum of
− 66.7 kPa ( −500 mmHg, −19.69 inHg):
15.6 − 15.9 mm (0.614 − 0.626 in)
SFIA2146E
Length “B” : 126.5 mm (4.98 in)
SGIA0060E
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 1014 of 3924
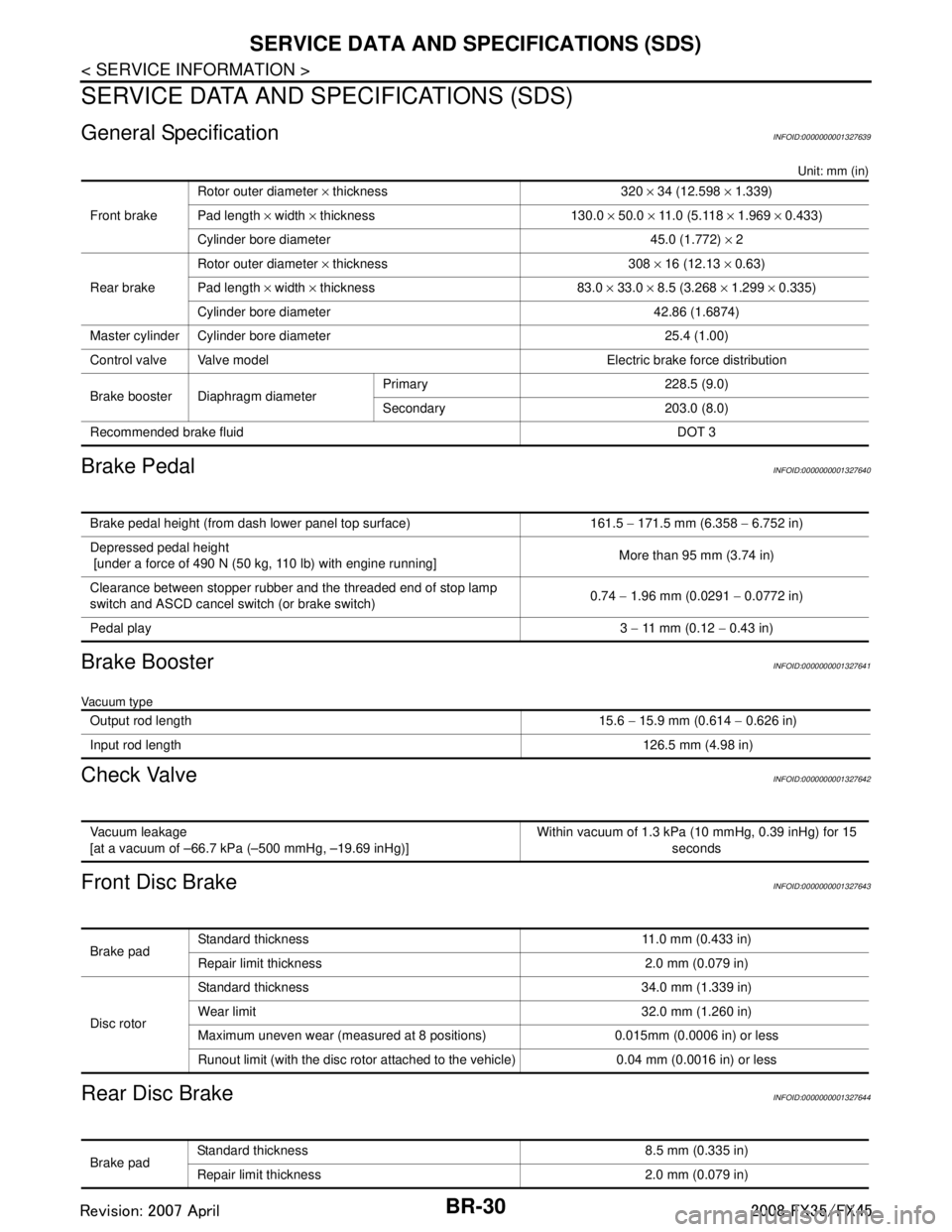
BR-30
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS)
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS)
General SpecificationINFOID:0000000001327639
Unit: mm (in)
Brake PedalINFOID:0000000001327640
Brake BoosterINFOID:0000000001327641
Vacuum type
Check ValveINFOID:0000000001327642
Front Disc BrakeINFOID:0000000001327643
Rear Disc BrakeINFOID:0000000001327644
Front brakeRotor outer diameter
× thickness 320 × 34 (12.598 × 1.339)
Pad length × width × thickness 130.0 × 50.0 × 11.0 (5.118 × 1.969 × 0.433)
Cylinder bore diameter 45.0 (1.772) × 2
Rear brake Rotor outer diameter
× thickness 308 × 16 (12.13 × 0.63)
Pad length × width × thickness 83.0 × 33.0 × 8.5 (3.268 × 1.299 × 0.335)
Cylinder bore diameter 42.86 (1.6874)
Master cylinder Cylinder bore diameter 25.4 (1.00)
Control valve Valve model Electric brake force distribution
Brake booster Diaphragm diameter Primary 228.5 (9.0)
Secondary 203.0 (8.0)
Recommended brake fluid DOT 3
Brake pedal height (from dash lower panel top surface) 161.5 − 171.5 mm (6.358 − 6.752 in)
Depressed pedal height
[under a force of 490 N (50 kg, 110 lb) with engine running] More than 95 mm (3.74 in)
Clearance between stopper rubber and the threaded end of stop lamp
switch and ASCD cancel switch (or brake switch) 0.74
− 1.96 mm (0.0291 − 0.0772 in)
Pedal play 3 − 11 mm (0.12 − 0.43 in)
Output rod length 15.6 − 15.9 mm (0.614 − 0.626 in)
Input rod length 126.5 mm (4.98 in)
Vacuum leakage
[at a vacuum of –66.7 kPa (–500 mmHg, –19.69 inHg)]Within vacuum of 1.3 kPa (10 mmHg, 0.39 inHg) for 15
seconds
Brake padStandard thickness 11.0 mm (0.433 in)
Repair limit thickness 2.0 mm (0.079 in)
Disc rotor Standard thickness 34.0 mm (1.339 in)
Wear limit 32.0 mm (1.260 in)
Maximum uneven wear (measured at 8 positions) 0.015mm (0.0006 in) or less
Runout limit (with the disc rotor attached to the vehicle) 0.04 mm (0.0016 in) or less
Brake pad
Standard thickness 8.5 mm (0.335 in)
Repair limit thickness 2.0 mm (0.079 in)
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 1095 of 3924
![INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
CO-24
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
WATER PUMP
b. Screw M8 bolts [pitch: 1.25 mm (0.0492 in) length: approx. 50
mm (1.97 in)] into water pumps upper and lower mounting bolt
holes until they reach t INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
CO-24
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
WATER PUMP
b. Screw M8 bolts [pitch: 1.25 mm (0.0492 in) length: approx. 50
mm (1.97 in)] into water pumps upper and lower mounting bolt
holes until they reach t](/manual-img/42/57017/w960_57017-1094.png)
CO-24
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
WATER PUMP
b. Screw M8 bolts [pitch: 1.25 mm (0.0492 in) length: approx. 50
mm (1.97 in)] into water pumps upper and lower mounting bolt
holes until they reach timing chain case. Then, alternately
tighten each bolt for a half turn, and pull out water pump.
CAUTION:
Pull straight out while pr eventing vane from contacting
socket in installation area.
Remove water pump without causing sprocket to contact timing chain.
c. Remove M8 bolts and O-rings from water pump. CAUTION:
Do not disassemble water pump.
INSPECTION AFTER REMOVAL
Check for badly rusted or corroded water pump body assembly.
Check for rough operation due to excessive end play.
If anything is found, replace water pump.
INSTALLATION
1. Install new O-rings to water pump. Apply engine oil and engine coolant to O-rings as shown in the
figure.
Locate O-ring with white paint mark to engine front side.
2. Install water pump. CAUTION:
Do not allow cylinder block to nip O-rings when installing
water pump.
Make sure timing chain and water pump sprocket are engaged.
Insert water pump by tightening mounting bolts alternately and evenly.
3. Install timing chain tensioner (primary) as follows:
JLC357B
SLC943A
PBIC1397E
PBIC1058E
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 1272 of 3924
![INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
EC-32
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
*1: This sensor is not used to control the engine system under normal conditions.
*2: This signal is sent to the ECM through CAN communicat INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
EC-32
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
*1: This sensor is not used to control the engine system under normal conditions.
*2: This signal is sent to the ECM through CAN communicat](/manual-img/42/57017/w960_57017-1271.png)
EC-32
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
*1: This sensor is not used to control the engine system under normal conditions.
*2: This signal is sent to the ECM through CAN communication line.
*3: ECM determines the start signal status by the signals of engine speed and battery voltage.
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The amount of fuel injected from the fuel injector is
determined by the ECM. The ECM controls the length of
time the valve remains open (injection pulse duration). T he amount of fuel injected is a program value in the
ECM memory. The program value is preset by engi ne operating conditions. These conditions are determined
by input signals (for engine speed and intake air) from both the crankshaft position sensor and the mass air
flow sensor.
VARIOUS FUEL INJECTION I NCREASE/DECREASE COMPENSATION
In addition, the amount of fuel injected is compens ated to improve engine performance under various operat-
ing conditions as listed below.
When starting the engine
During acceleration
Hot-engine operation
When selector lever is changed from N to D
High-load, high-speed operation
During high engine speed operation
MIXTURE RATIO FEEDBACK CONTROL (CLOSED LOOP CONTROL)
The mixture ratio feedback system prov ides the best air-fuel mixture ratio for driveability and emission control.
The three way catalyst 1 can then better reduce CO, HC and NOx emissions. This system uses air fuel ratio
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM function Actuator
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed*
3
Piston position
Fuel injection
& mixture ratio
controlFuel injector
Camshaft position sensor (PHASE)
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Air fuel ratio (A/F) sensor 1 Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
Throttle position sensor Throttle position
Accelerator pedal position sensor Accelerator pedal position
Park/neutral position (PNP) switch Gear position
Knock sensor Engine knocking condition
Battery
Battery voltage*
3
Power steering pressure sensor Power steering operation
Heated oxygen sensor 2*
1Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner operation*
2
Wheel sensorVehicle speed*2
PBIB3020E
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 1314 of 3924
![INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
EC-74
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
tified codes can be identified by using the CONSULT-II
I or GST. A DTC will be used as an example for how to
read a code.
A part INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
EC-74
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
tified codes can be identified by using the CONSULT-II
I or GST. A DTC will be used as an example for how to
read a code.
A part](/manual-img/42/57017/w960_57017-1313.png)
EC-74
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
tified codes can be identified by using the CONSULT-II
I or GST. A DTC will be used as an example for how to
read a code.
A particular trouble code can be identified by the number of four-digit numeral flashes. The “zero” is indicated
by the number of ten flashes. The “A” is indicated by the number of eleven flash. The length of time the
1,000th-digit numeral flashes on and off is 1.2 seconds consisting of an ON (0.6-second) - OFF (0.6-second)
cycle.
The 100th-digit numeral and lower digit numerals cons ist of a 0.3-second ON and 0.3-second OFF cycle.
A change from one digit numeral to another occurs at an inte rval of 1.0-second OFF. In other words, the later
numeral appears on the display 1.3 seconds after the former numeral has disappeared.
A change from one trouble code to another occu rs at an interval of 1.8-second OFF.
In this way, all the detected malfunctions are classi fied by their DTC numbers. The DTC 0000 refers to no mal-
function. (See EC-17
)
How to Erase Diagnostic Test Mode II (Self-diagnostic Results)
The DTC can be erased from the back up memory in t he ECM by depressing accelerator pedal. Refer to "How
to Set Diagnostic Test Mode II (Self-diagnostic Results)".
If the battery is disconnected, the DTC will be lost from the backup memory within 24 hours.
Be careful not to erase the stored memo ry before starting trouble diagnoses.
OBD System Operation ChartINFOID:0000000001325918
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MIL, 1ST TRIP DTC, DTC, AND DETECTABLE ITEMS
When a malfunction is detected for the 1st time, the 1st trip DTC and the 1st trip freeze frame data are
stored in the ECM memory.
When the same malfunction is detected in two consec utive trips, the DTC and the freeze frame data are
stored in the ECM memory, and the MIL will come on. For details, refer to EC-54, "
Two Trip Detection Logic".
The MIL will go off after the vehicle is driven 3 time s (drive pattern B) with no malfunction. The drive is
counted only when the recorded driving pattern is met (as stored in the ECM). If another malfunction occurs
while counting, the counter will reset.
The DTC and the freeze frame data will be stored until the vehicle is driven 40 times (driving pattern A) with-
out the same malfunction recurring (except for Misfire and Fuel Injection System). For Misfire and Fuel Injec-
tion System, the DTC and freez e frame data will be stored until the vehicle is driven 80 times (driving pattern
PBIB3005E
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 1792 of 3924
![INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
EC-552
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
FUEL INJECTOR
FUEL INJECTOR
Component DescriptionINFOID:0000000001326438
The fuel injector is a small, precise solenoid valve. When the ECM
supplies a ground to INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
EC-552
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
FUEL INJECTOR
FUEL INJECTOR
Component DescriptionINFOID:0000000001326438
The fuel injector is a small, precise solenoid valve. When the ECM
supplies a ground to](/manual-img/42/57017/w960_57017-1791.png)
EC-552
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VQ35DE]
FUEL INJECTOR
FUEL INJECTOR
Component DescriptionINFOID:0000000001326438
The fuel injector is a small, precise solenoid valve. When the ECM
supplies a ground to the fuel injector circuit, the coil in the fuel injec-
tor is energized. The energized coil pulls the Ball valve back and
allows fuel to flow through the fuel injector into the intake manifold.
The amount of fuel injected depends upon the fuel injection pulse
duration. Pulse duration is the length of time the fuel injector remains
open. The ECM controls the injection pulse duration based on
engine fuel needs.
CONSULT-III Reference Value in Data Monitor ModeINFOID:0000000001326439
Specification data are reference values.
SEF375Z
MONITOR ITEM CONDITION SPECIFICATION
B/FUEL SCHDL See EC-131
.
INJ PULSE-B1
INJ PULSE-B2 Engine: After warming up
Selector lever: P or N
Air conditioner switch: OFF
No load Idle 2.0 - 3.0 msec
2,000 rpm 1.9 - 2.9 msec
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 1850 of 3924
![INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
EC-610
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VK45DE]
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
*1: This sensor is not used to control the engine system under normal conditions.
*2: This signal is sent to the ECM through CAN communica INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
EC-610
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VK45DE]
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
*1: This sensor is not used to control the engine system under normal conditions.
*2: This signal is sent to the ECM through CAN communica](/manual-img/42/57017/w960_57017-1849.png)
EC-610
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VK45DE]
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
*1: This sensor is not used to control the engine system under normal conditions.
*2: This signal is sent to the ECM through CAN communication line.
*3: ECM determines the start signal status by the signals of engine speed and battery voltage.
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The amount of fuel injected from the fuel injector is
determined by the ECM. The ECM controls the length of
time the valve remains open (injection pulse duration). T he amount of fuel injected is a program value in the
ECM memory. The program value is preset by engi ne operating conditions. These conditions are determined
by input signals (for engine speed and intake air) from t he crankshaft position sensor (POS), camshaft position
sensor (PHASE) and the ma ss air flow sensor.
VARIOUS FUEL INJECTION I NCREASE/DECREASE COMPENSATION
In addition, the amount of fuel injected is compens ated to improve engine performance under various operat-
ing conditions as listed below.
When starting the engine
During acceleration
Hot-engine operation
When selector lever is changed from N to D
High-load, high-speed operation
During high engine speed operation
MIXTURE RATIO FEEDBACK CONTROL (CLOSED LOOP CONTROL)
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM function Actuator
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed*
3
Piston position
Fuel injection
& mixture ratio
controlFuel injector
Camshaft position sensor (PHASE)
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Air fuel ratio (A/F) sensor 1 Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
Throttle position sensor Throttle position
Accelerator pedal position sensor Accelerator pedal position
Park/neutral position (PNP) switch Gear position
Battery
Battery voltage*
3
Knock sensor Engine knocking condition
Power steering pressure sensor Power steering operation
Heated oxygen sensor 2*
1Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
ABS actuator and electric unit (control unit) VDC/TCS operation command*
2
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner operation
Wheel sensorVehicle speed*
2
PBIB3020E
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 1892 of 3924
![INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
EC-652
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VK45DE]
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
tified codes can be identified by using the CONSULT-II
I or GST. A DTC will be used as an example for how to
read a code.
A par INFINITI FX35 2008 Service Manual
EC-652
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VK45DE]
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
tified codes can be identified by using the CONSULT-II
I or GST. A DTC will be used as an example for how to
read a code.
A par](/manual-img/42/57017/w960_57017-1891.png)
EC-652
< SERVICE INFORMATION >[VK45DE]
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
tified codes can be identified by using the CONSULT-II
I or GST. A DTC will be used as an example for how to
read a code.
A particular trouble code can be identified by the number of four-digit numeral flashes. The “zero” is indicated
by the number of ten flashes. The “A ” is indicated by the number of eleven flashes. The length of time the
1,000th-digit numeral flashes on and off is 1.2 seconds consisting of an ON (0.6-second) - OFF (0.6-second)
cycle.
The 100th-digit numeral and lower digit numerals cons ist of a 0.3-second ON and 0.3-second OFF cycle.
A change from one digit numeral to another occurs at an inte rval of 1.0-second OFF. In other words, the later
numeral appears on the display 1.3 seconds after the former numeral has disappeared.
A change from one trouble code to another occu rs at an interval of 1.8-second OFF.
In this way, all the detected malfunctions are classi fied by their DTC numbers. The DTC 0000 refers to no mal-
function. (See EC-595
)
How to Erase Diagnostic Test Mode II (Self-diagnostic Results)
The DTC can be erased from the back up memory in t he ECM by depressing accelerator pedal. Refer to "How
to Erase Diagnostic Test Mode II (Self-diagnostic Results)".
If the battery is disconnected, the DTC will be lost from the backup memory within 24 hours.
Be careful not to erase the stored memo ry before starting trouble diagnoses.
OBD System Operation ChartINFOID:0000000001326514
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MIL, 1ST TRIP DTC, DTC, AND DETECTABLE ITEMS
When a malfunction is detected for the first time, the 1st trip DTC and the 1st trip freeze frame data are
stored in the ECM memory.
When the same malfunction is detected in two consec utive trips, the DTC and the freeze frame data are
stored in the ECM memory, and the MIL will come on. For details, refer to EC-632, "
Two Trip Detection
Logic".
The MIL will go off after the vehicle is driven 3 time s (driving pattern B) with no malfunction. The drive is
counted only when the recorded driving pattern is met (as stored in the ECM). If another malfunction occurs
while counting, the counter will reset.
The DTC and the freeze frame data will be stored until the vehicle is driven 40 times (driving pattern A) with-
out the same malfunction recurring (except for Misfire and Fuel Injection System). For Misfire and Fuel Injec-
PBIB3005E
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C