2008 GREAT WALL FLORID lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 114 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 107Brake System
Anti-lock Brake System
ABS/EBD introduction
1. Operation
The vehicle's Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) is a type of increasingly popular brake safety device. It detects the
wheel's speed using wheel speed sensor detection. After signal processing, the wheel speed will be transferred
to the computer, which controls the solenoid valve’s operating condition and the pressure inside the brake wheel
cylinder to avoid wheel locking by using certain calculations and control methods based on the wheel speed.
ABS helps the vehicle to avoid sliding, deviation, fishtailing, and losing steering control capacity. ABS improves
the vehicle’s handling capability, stability and shortens braking distance. It also helps the vehicle to avoid the
partial wear and tear of wheels, hence improves the tire's useful life.
Electronic Brake Distribution (EBD) is used to adjust the vehicle's rear wheel brake pressure by using the ABS
components when the ABS does not respond to vehicle braking. It is also used to balance the vehicle’s front and
rear wheel brake pressure, maximizing the vehicle's braking efficiency. EBD uses the ABS components, yet its
controlling logic is independent from the ABS. After the ABS responds, the EBD will disengage.
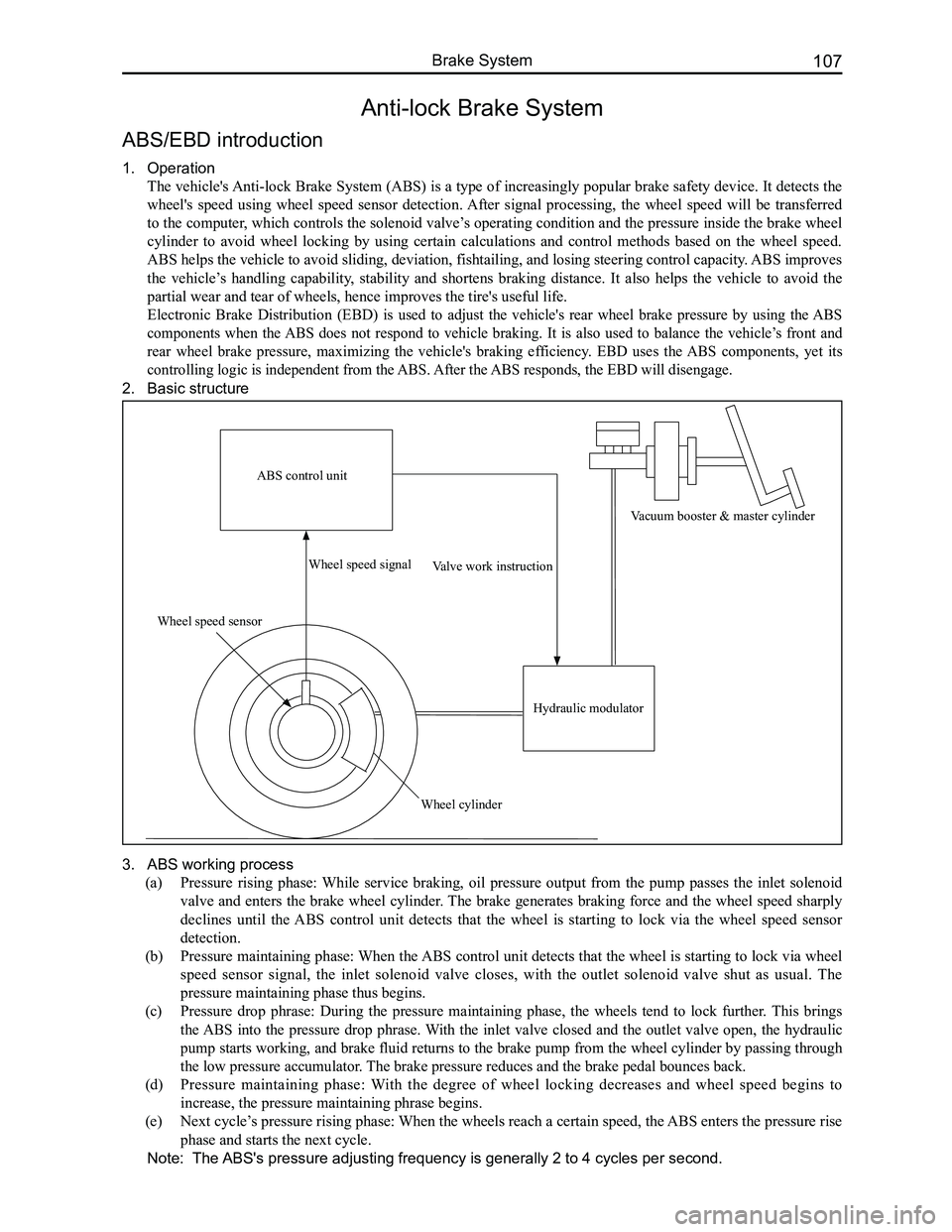
2. Basic structure
3. ABS working process
(a) Pressure rising phase: While service braking, oil pressure output from the pump passes the inlet solenoid
valve and enters the brake wheel cylinder. The brake generates braking force and the wheel speed sharply
declines until the ABS control unit detects that the wheel is starting to lock via the wheel speed sensor
detection.
(b) Pressure maintaining phase: When the ABS control unit detects that the wheel is starting to lock via wheel
speed sensor signal, the inlet solenoid valve closes, with the outlet solenoid valve shut as usual. The
pressure maintaining phase thus begins.
(c) Pressure drop phrase: During the pressure maintaining phase, the wheels tend to lock further. This brings
the ABS into the pressure drop phrase. With the inlet valve closed and the outlet valve open, the hydraulic
pump starts working, and brake fluid returns to the brake pump from the wheel cylinder by passing through
the low pressure accumulator. The brake pressure reduces and the brake pedal bounces back.
(d) Pressure maintaining phase: With the degree of wheel locking decreases and wheel speed begins to
increase, the pressure maintaining phrase begins.
(e) Next cycle’s pressure rising phase: When the wheels reach a certain speed, the ABS enters the pressure rise
phase and starts the next cycle.
Note: The ABS's pressure adjusting frequency is generally 2 to 4 cycles per second.
ABS control unit
Wheel speed sensor
Wheel speed signal
Wheel cylinder
Valve work instruction
Hydraulic modulator
Vacuum booster & master cylinder
Page 115 of 281
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual108
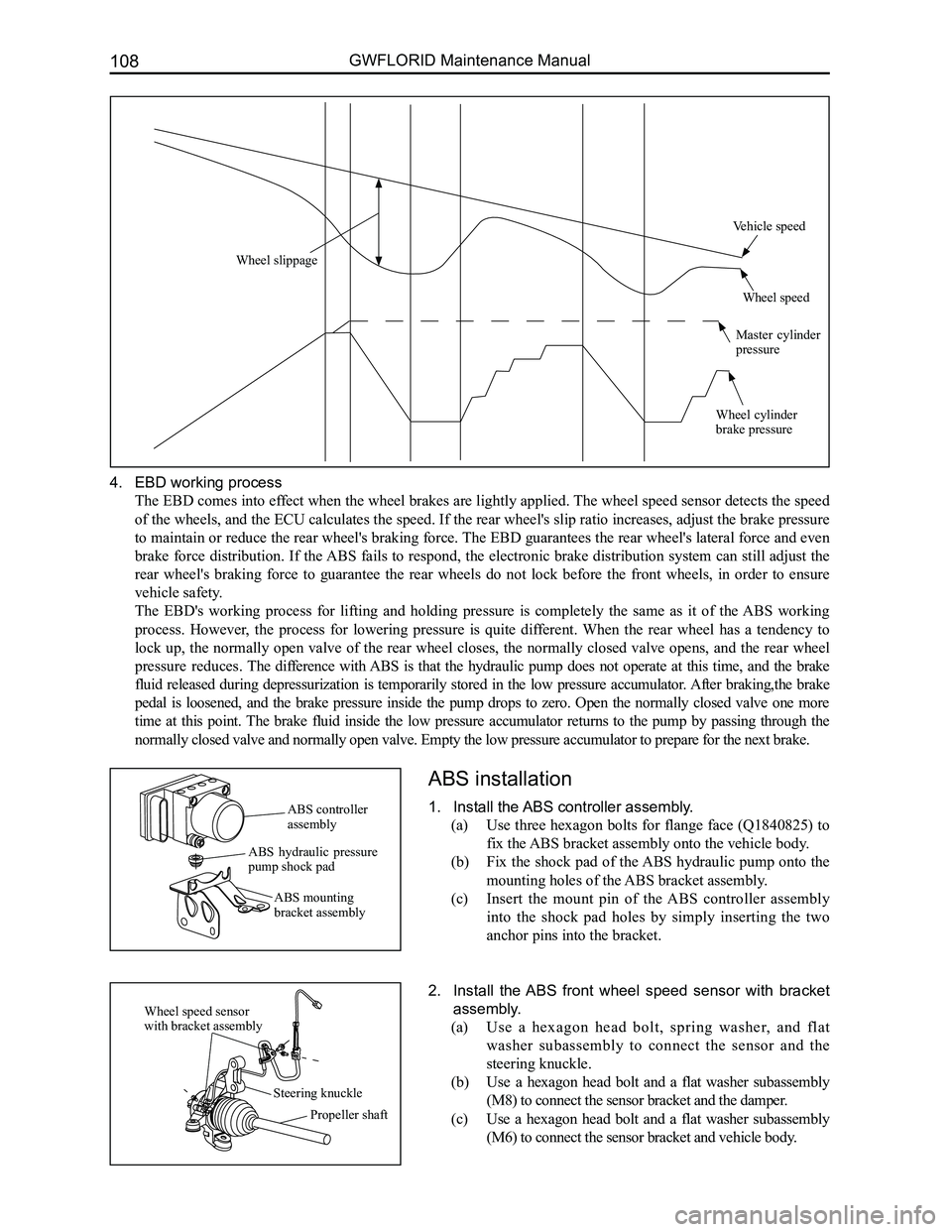
4. EBD working process
The EBD comes into effect when the wheel brakes are lightly applied. The wheel speed sensor detects the speed
of the wheels, and the ECU calculates the speed. If the rear wheel's slip ratio increases, adjust the brake pressure
to maintain or reduce the rear wheel's braking force. The EBD guarantees the rear wheel's lateral force and even
brake force distribution. If the ABS fails to respond, the electronic brake distribution system can still adjust the
rear wheel's braking force to guarantee the rear wheels do not lock before the front wheels, in order to ensure
vehicle safety.
The EBD's working process for lifting and holding pressure is completely the same as it of the ABS working
process. However, the process for lowering pressure is quite different. When the rear wheel has a tendency to
lock up, the normally open valve of the rear wheel closes, the normally closed valve opens, and the rear wheel
pressure reduces. The difference with ABS is that the hydraulic pump does not operate at this time, and the brake
fluid released during depressurization is temporarily stored in the low pressure accumulator. After braking,the brake
pedal is loosened, and the brake pressure inside the pump drops to zero. Open the normally closed valve one more
time at this point. The brake fluid inside the low pressure accumulator returns to the pump by passing through the
normally closed valve and normally open valve. Empty the low pressure ac\
cumulator to prepare for the next brake.
ABS installation
1. Install the ABS controller assembly.
(a) Use three hexagon bolts for flange face (Q1840825) to
fix the ABS bracket assembly onto the vehicle body.
(b) Fix the shock pad of the ABS hydraulic pump onto the
mounting holes of the ABS bracket assembly.
(c) Insert the mount pin of the ABS controller assembly
into the shock pad holes by simply inserting the two
anchor pins into the bracket.
2. Install the ABS front wheel speed sensor with bracket
assembly.
(a) Use a hexagon head bolt, spring washer, and flat
washer subassembly to connect the sensor and the
steering knuckle.
(b) Use a hexagon head bolt and a flat washer subassembly
(M8) to connect the sensor bracket and the damper.
(c) Use a hexagon head bolt and a flat washer subassembly
(M6) to connect the sensor bracket and vehicle body.
ABS controller assembly
ABS hydraulic pressure pump shock pad
ABS mounting bracket assembly
Wheel speed sensor with bracket assembly
Steering knuckle
Propeller shaft
Wheel slippage
Vehicle speed
Wheel speed
Master cylinder pressure
Wheel cylinder brake pressure
Page 125 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual118
Front Brake Caliper
Components
Disposable parts
Inner and outer brake pad assembly re-
placement
Remark: When applying the brake while driving, if the front
tires makes a continuous screeching sound, inspect the inner
and outer brake pad and friction limit alarm plate. If there
are traces of rubbing from the brake disc on the alarm plate,
the inner and outer brake pad assembly should be replaced.
1. Remove the front wheel.
2. Inspect the inner and outer brake pad's friction material
thickness.
By looking through the caliper's observation ports, inspect
the inner and outer brake pad friction material thickness. If it
is no longer within the specified range, it should be replaced.
Minimum thickness: 2.0 mm
Bleed screw cap
Air bleed screw
Caliper
Rectangular sealing ring
Piston
P iston dust cover
Inner muffler plate subassembly
Alarm plate
Inner brake pad assembly
Outer brake pad assembly
Outer muffler plate subassembly
Guide pin
Guide pin dust cover
Caliper frame
Brake block yoke spring plate
Brake block yoke spring plate
30 ± 5
: Specified torqueN·m
10 ± 2
Q1840820
Rubber grease
Page 126 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 119Brake System
3. Remove the caliper assembly.
(a) Remove the hexagon bolt for flange face connecting
the caliper and caliper frame's lower end.
(b) Lift the caliper assembly and use a rope to hang it up to
protect the brake pipeline.
Remark: Do not unscrew the brake pipeline and bleed screw.
4. Remove the following parts.
(a) The group of inner and outer shims B.
(b) The group of inner and outer shims A.
(c) The group of inner and outer brake discs.
(d) One pair of yoke springs.
5. Measure the brake disc thickness.
(See steering knuckle and hub brake assembly examination and
disassembly step 4).
6. Measure the brake disc radial runout.
(See steering knuckle and hub brake assembly examination and
disassembly step 3).
7. Install the yoke spring.
Install the brake block yoke spring plate to the caliper frame.
Outer shim B
Outer shim AInner brake disc
Warning device
Inner shim B
Inner shim A
Outer brake disc
Yoke spring
Page 128 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 121Brake System
2. Remove the caliper assembly.
(a) Remove the two hexagon bolts for flange face connecting
the caliper and caliper frame.
(b) Remove the caliper assembly from the caliper frame.
3. Remove the following parts.
(a) The group of inner and outer shims B.
(b) The group of inner and outer shims A.
(c) The group of inner and outer brake discs.
(d) One pair of yoke springs.
4. Remove the piston and piston dust cover from the
caliper.
(a) Place a block in the middle of the caliper.
(b) Use an airgun or air pipe to align the brake pipeline
holes. Remove the piston from the caliper, and at the
same time remove the piston dust cover.
(c) Use a clean rag or other soft cloth to extract the piston.
Warning: When using compressed air, be sure not to
place fingers in front of the piston.
5. Remove the rectangular sealing ring from the caliper.
Use a paperclip to remove the rectangular sealing ring from
the caliper.
Caution: The tools being used should not be sharp, in
order to avoid tearing the rectangular sealing ring.
Inner and outer brake pad assembly exami-
nation
Measure the inner and outer brake pad assembly's thickness.
Standard thickness: 8.5 mm
Minimum thickness: 2.0 mm
If it is smaller than the minimum level of thickness or there
are traces of uneven wear and tear, the brake pad should be
replaced.
Page 129 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual122
Front brake caliper assembly installation
1. Preparations
Make sure all parts are clean and free of foreign materials
before installation.When installing, apply an appropriate
amount of rubber grease to the guide pin and piston's
working surface, as well as the rectangular sealing ring and
the piston protective cover's working surface.
2. Install the rectangular sealing ring to the caliper.
(a) Screw the bleed screw into the caliper's vent holes.
Tightening torque: 10±2 N·m
(b) After applying an appropriate amount of rubber grease
on the rectangular sealing ring's working surface, install
them into the caliper's seal groove.
3. Install the piston with piston dust cover on the caliper.
(a) Place the piston dust cover on the piston.
(b) Stretch the piston dust cover, until its card holder
exposes the bottom of the piston. Use tools (for
example, about Ф2 mm of iron wire) to assist by
stuffing the card holder into the cylinder bore card
holder's groove.
Caution: The tools being used should not be sharp, as
to avoid tearing the dust cover.
(c) Then manually press the piston into the bottom of the
cylinder bore.
4. Install the guide pin and guide pin dust cover onto the
caliper frame.
(a) Install the guide pin dust cover onto the guide pin.
(b) Screw the guide pin into the caliper frame.
Caution: Do not damage the guide pin dust cover.
5. Install an inner and outer brake pad assembly and
inner and outer muffler plate subassembly.
6. Install the brake block yoke spring plate as well as the
inner and outer brake pad assembly and inner and
outer muffler plate subassembly on the caliper frame.
Guide pin
Guide pin dust cover
Caliper frameBrake block yoke spring plate
Air bleed screw cap
Air bleed screw Caliper
Inner muffler plate subassembly
Alarm plate
Inner brake pad assembly
Outer brake pad assembly
Outer muffler plate subassembly
Page 131 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual124
Rear Brake
Components
4. Remove the rear brake drum.
Remark: If it is difficult to remove the rear brake drum,
follow the steps below:
Method one:
(a) Remove the rubber plug of the adjuster's observation
port, and insert a slotted screwdriver into the brake's
back plate assembly hole, and pry off the adjusting
paddle from the adjusting clearance wheel.
(b) Use another slotted screwdriver to toggle the adjusting
clearance wheel and loosen the brake's leading and
trailing shoe assembly's tension on the rear brake drum.
Disposable parts
Dust cover
Brake leading shoe assembly
Pressure spring
Pressure spring cap
Brake shoe tension spring
Rear brake drum
Lever rotating shaft
Retainer spring
Locking cap
Split ring
Brake lever
Brake trailing shoe assembly
Brake back plate assembly
Pressure spring bar
Rubber plug of the adjuster's observation port
Rubber plug of the observation port gap
Washer
Bleed screw cap
Bleed screwPiston
Ring cup
Piston spring
Wheel cylinder
Adjusting clearance shaft head
Adjusting clearance wheel
Adjusting clearance screw rod
Return springAdjusting paddle
Pin
Side spring
Dust cover
Piston
Ring cup
Rubber grease
: Specified torqueN·m
7.8-11.8
High temperature resistant grease
Rear brake removal
1. Inspecting the brake's friction plate thickness.
Remove the rubber plug of the observation port gap and
examine the friction plate thickness via the observation port.
If it's smaller than the minimum value, the brake's leading
and trailing shoe assemblies should be replaced.
Minimum thickness: 1.0 mm
2. Remove the rear wheel.
3. Release the brake fluid.
Caution: Be sure not to spill the brake fluid onto the
paint's surface. Otherwise it must be immediately
cleaned.
Page 137 of 281

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GWFLORID Maintenance Manual130
7. Install the brake cable connector on the brake trailing
shoe with brake lever assembly.
(a) Install the brake cable connector on the brake trailing
shoe with brake lever assembly.
(b) Insert the brake trailing shoe with brake lever assembly
and the shoe end of the brake leading shoe assembly
into the wheel cylinder assembly.
Remark: Do not let oil or grease drip on the brake shoe's
lining.
8. Install the retainer spring.
9. Install the brake leading and trailing shoe assemblies
onto the brake back plate assembly.
(a) Insert the pressure spring bar into the brake back plate
assembly and brake leading and trailing shoe assemblies.
(b) Put the pressure spring on the pressure spring bar,
put in the pressure spring cap, and use SST (Special
Service Tools) to lock the pressure spring cap onto the
pressure spring bar.
10. Inspect the operating procedures of the automatic ad-
juster.
(a) Refer to the diagram for directions, step on and off the
brake pedal, and make sure the self-adjusting screws
can rotate. If they are unable to rotate, inspect the rear
brake to try to determine the source of the problem.
(b) Adjust the adjusting mechanisms length and make it as
short as possible.
(c) Install the rear brake drum.
(d) Press the brake pedal towards the floor until a clicking
noise cannot be heard.
11. Inspect the space between the brake's friction plate
and rear brake drum.
(a) Remove the rear brake drum.
(b) Measure the rear brake drum's internal diameter and
the brake shoe friction plate's external diameter, and
inspect if the difference between the two diameters is
within the regulated clearance range.
Single sided clearance: 0.25 mm
If not correct, inspect the braking system.
12. Install the rear wheel.
Tightening torque: 100 N·m
13. Fill the brake fluid reservoir up with brake fluid and
exhaust the air out of the brake system.
14. Check for leaking brake fluid
SST