2007 MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1122 of 1449

STEERING -On-vehicle Service37A-8
2. Move ball joint stud several times and install nut on stud.
Measure ball joint turning torque with special tool.
Standard value: 1.0 - 3.0 N·m
3. When the turning torque exceeds the standard value,
replace tie rod end.
4. When the turning torque is under the standard value,
check ball joint for end play or ratcheting. If none of these,
the joint is still serviceable.
STATIONARY STEERING EFFORT CHECK
1. With the vehicle stopped on a flat, paved surface, turn
the steering wheel to the straight ahead position.
2. Start the engine and set it to 1,000±100 r/min.
3. Attach a spring balance to the outer circumference of
the steering wheel and measure the steering force
required to turn the steering wheel from the straight ahead
position to the left and right (within a range of 0.9 turns).
Also check to be sure that there is no significant fluctuation
of the required steering force.
Standard value:
Steering effort32 N or less
Fluctuation allowance6.0 N or less
4. If the standard values are not met, check and adjust
the related parts.
CHECKING STEERING WHEEL RETURN TO
CENTRE
To make this test, conduct a road test and check as follows.
1. Make both gradual and sudden turns and check the
steering “feeling” to be sure that there is not difference
in the steering force required and the wheel return between
left and right turns.
2. At a speed of 35 km/h, turn the steering wheel 90_and
release the steering wheel after 1 or 2 seconds. If the
steering wheel then returns 70_or more, the return can
be judged to be satisfactory.
NOTE
There will be a momentary feeling or “heaviness” when
the wheel is turned quickly, but this is not abnormal. (This
is because the oil pump discharge amount is especially
apt to be insufficient during idling.)
DRIVE BELT TENSION CHECK
Refer to GROUP 11A - On-vehicle Service.
MB990326
70_70_
Page 1123 of 1449

STEERING -On-vehicle Service37A-9
POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL CHECK
1. Park the vehicle on a flat, level surface, start the engine,
and then turn the steering wheel several times to raise
the temperature of the fluid to approximately 50 - 60_C.
2. With the engine running, turn the wheel all the way to
the left and right several times.
3. Check the fluid in the oil reservoir for foaming or milkiness.
Check the difference of the fluid level when the engine
is stopped, and while it is running. If the change of the
fluid level is 5 mm or more, air bleeding should be done.
POWER STEERING FLUID REPLACEMENT
1. Raise the front wheels on a jack, and then support them
with rigid racks.
2. Disconnect the return hose connection.
3. Connect a vinyl hose to the return hose, and drain the
oil into a container.
4. Disconnect the ignition coil connectors. (Refer to
GROUP16 - Ignition System.)
5. While operating the starting motor intermittently, turn the
steering wheel all the way to the left and right several
times to drain all of the fluid.
6. Connect the return hoses securely, and then secure it
with the clip.
7. Fill the oil reservoir with specified fluid up to the lower
position of the filter, and then bleed air.
Specified fluid:
Automatic transmission fluid DEXRONII
Caution
Do not use ATF-SPIIM and ATF-SPIII.
POWER STEERING SYSTEM BLEEDING
1. Jack up the vehicle and support the front wheels with
rigid racks.
2. Disconnect the ignition coil connectors. (Refer to
GROUP16 - Ignition System.)
3. Cranking the engine with the starter several times
intermittently (during 15 to 20 seconds), turn the steering
wheel left and right fully five or six times.
Caution
(1) During the bleeding, refill the fluid so that the
level never falls below the lower position of the
filter.
(2) Be sure to bleed air only while cranking. If the
bleeding is done with the engine running, the air
will be broken up and absorbed into the fluid.
4. Connect the ignition coil connectors and idle the engine.
5. Turn the steering wheel left and right fully until no bubbles
comes out in the oil reservoir.
6. See that the fluid is not milky and that the fluid level
is up to the specified position on the level gauge.
7. See that the fluid level changes little when the steering
wheel is turned left and right.
8. Check difference in fluid levels between the engine
stopped and running.
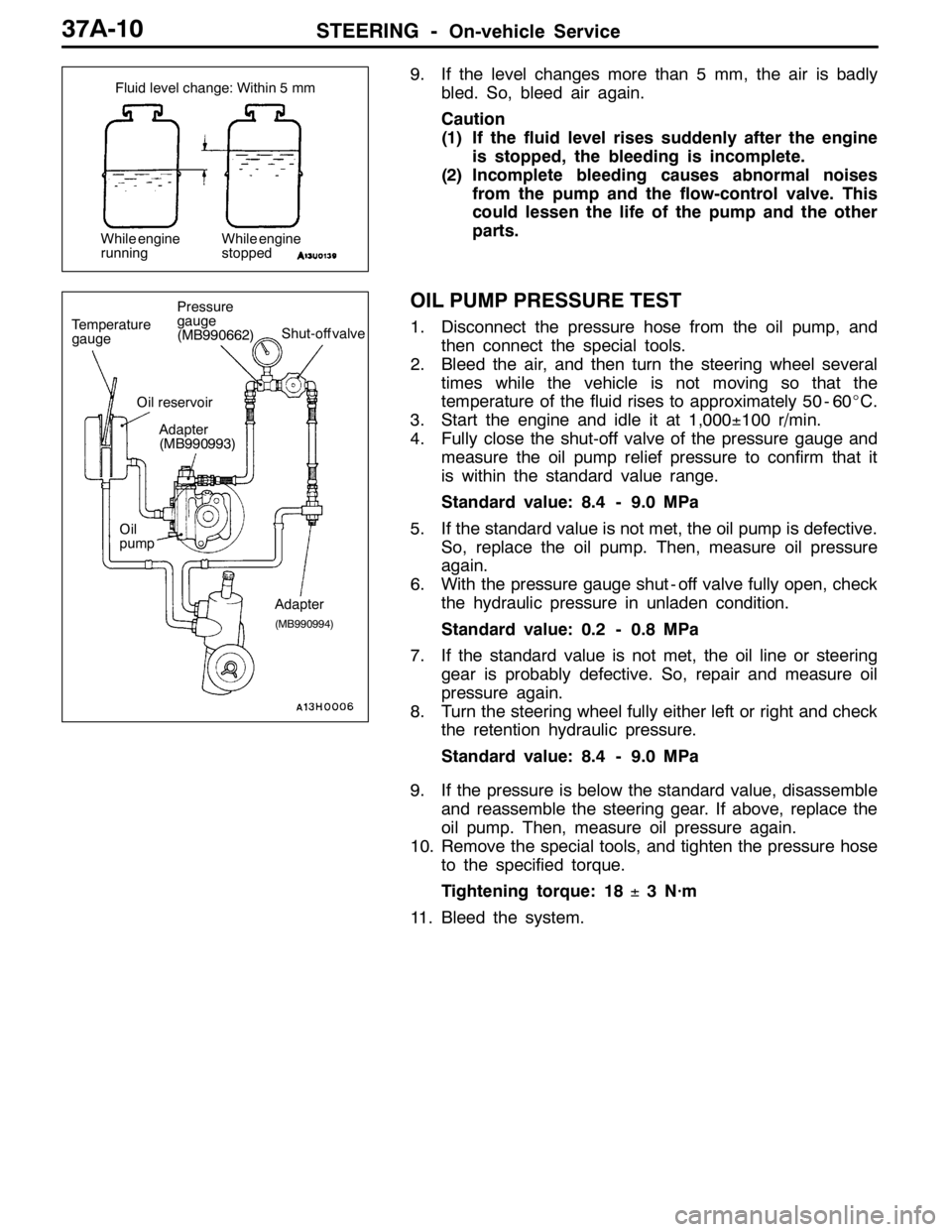
Fluid level change: Within 5 mm
While engine
runningWhile engine
stopped
Return hose
Vinyl hose
Page 1124 of 1449
STEERING -On-vehicle Service37A-10
9. If the level changes more than 5 mm, the air is badly
bled. So, bleed air again.
Caution
(1) If the fluid level rises suddenly after the engine
is stopped, the bleeding is incomplete.
(2) Incomplete bleeding causes abnormal noises
from the pump and the flow-control valve. This
could lessen the life of the pump and the other
parts.
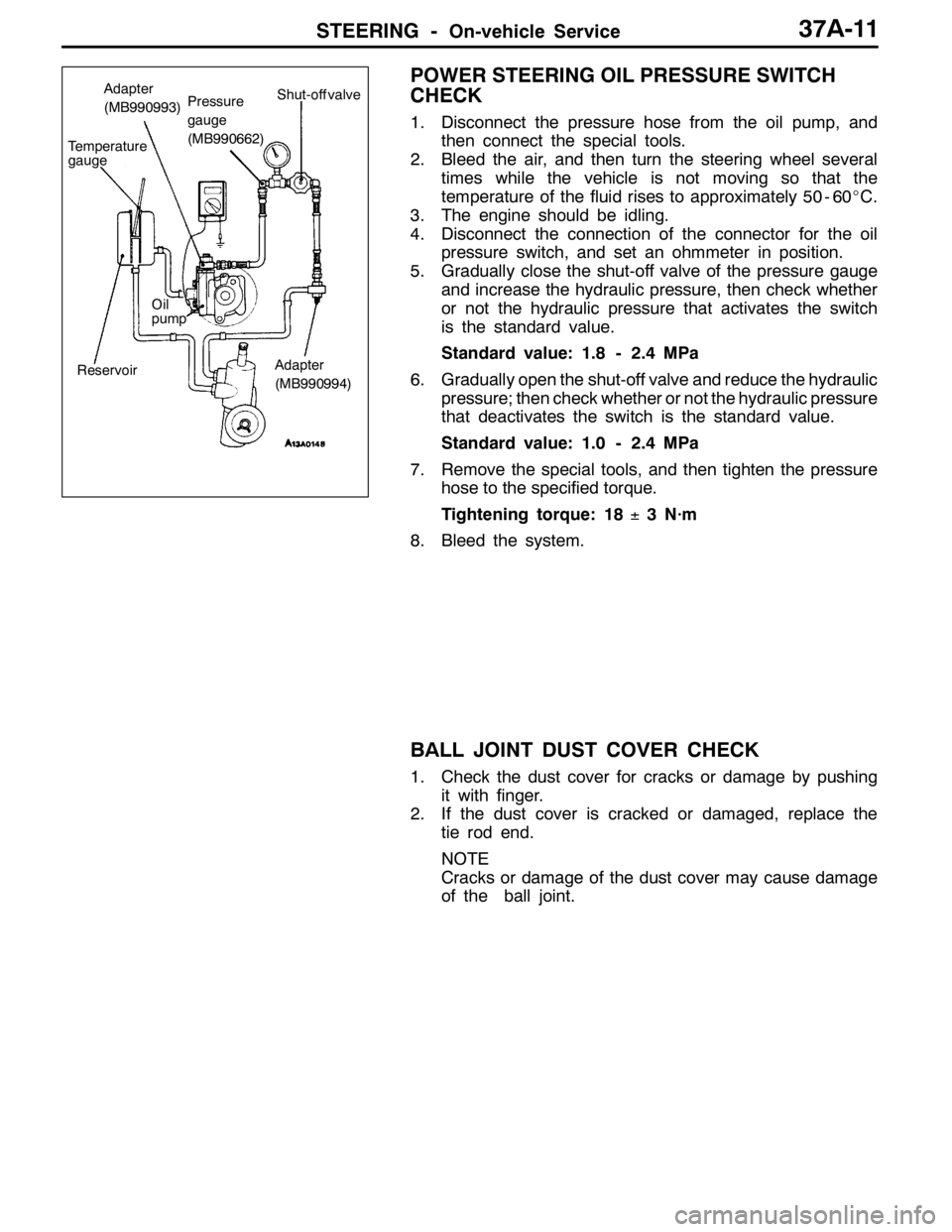
OIL PUMP PRESSURE TEST
1. Disconnect the pressure hose from the oil pump, and
then connect the special tools.
2. Bleed the air, and then turn the steering wheel several
times while the vehicle is not moving so that the
temperature of the fluid rises to approximately 50 - 60_C.
3. Start the engine and idle it at 1,000±100 r/min.
4. Fully close the shut-off valve of the pressure gauge and
measure the oil pump relief pressure to confirm that it
is within the standard value range.
Standard value: 8.4 - 9.0 MPa
5. If the standard value is not met, the oil pump is defective.
So, replace the oil pump. Then, measure oil pressure
again.
6. With the pressure gauge shut - off valve fully open, check
the hydraulic pressure in unladen condition.
Standard value: 0.2 - 0.8 MPa
7. If the standard value is not met, the oil line or steering
gear is probably defective. So, repair and measure oil
pressure again.
8. Turn the steering wheel fully either left or right and check
the retention hydraulic pressure.
Standard value: 8.4 - 9.0 MPa
9. If the pressure is below the standard value, disassemble
and reassemble the steering gear. If above, replace the
oil pump. Then, measure oil pressure again.
10. Remove the special tools, and tighten the pressure hose
to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 18±3 N·m
11. Bleed the system.
Fluid level change: Within 5 mm
While engine
runningWhile engine
stopped
Temperature
gaugePressure
gauge
(MB990662)Shut-off valve
Oil
pumpOil reservoir
Adapter
(MB990994)
Adapter
(MB990993)
Page 1125 of 1449
STEERING -On-vehicle Service37A-11
POWER STEERING OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
CHECK
1. Disconnect the pressure hose from the oil pump, and
then connect the special tools.
2. Bleed the air, and then turn the steering wheel several
times while the vehicle is not moving so that the
temperature of the fluid rises to approximately 50 - 60_C.
3. The engine should be idling.
4. Disconnect the connection of the connector for the oil
pressure switch, and set an ohmmeter in position.
5. Gradually close the shut-off valve of the pressure gauge
and increase the hydraulic pressure, then check whether
or not the hydraulic pressure that activates the switch
is the standard value.
Standard value: 1.8 - 2.4 MPa
6. Gradually open the shut-off valve and reduce the hydraulic
pressure; then check whether or not the hydraulic pressure
that deactivates the switch is the standard value.
Standard value: 1.0 - 2.4 MPa
7. Remove the special tools, and then tighten the pressure
hose to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 18±3 N·m
8. Bleed the system.
BALL JOINT DUST COVER CHECK
1. Check the dust cover for cracks or damage by pushing
it with finger.
2. If the dust cover is cracked or damaged, replace the
tie rod end.
NOTE
Cracks or damage of the dust cover may cause damage
of the ball joint.
Temperature
gaugeShut-off valve
Oil
pump
ReservoirAdapter
(MB990993)Pressure
gauge
(MB990662)
Adapter
(MB990994)
Page 1144 of 1449

STEERING - Power Steering Oil Pump/Power Steering Oil Hoses37A-30
"BAPRESSURE HOSE ASSEMBLY/SUCTION HOSE
REMOVAL
Install the pressure hose assembly and suction hose as
illustrated.
DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
21±3 N·m
3
4
2 1
39±5 N·m
: Automatic transmission fluid DEXRONII
NOTE
Disassembly steps
1. Suction connector
2. O-ring3. Connector
4. Gasket
POWER STEERING OIL HOSES
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Caution
1. Before removing the clock spring, always see GROUP 52B - Caution for Service and Air Bag
Module Clock Spring
2. If the vehicle is equipped with the Brembo disc brake, during maintenance, take care not to
contact the parts or tools to the caliper, because the paint of caliper will be scratched.
3. On the tightening section indicated in the mark (*), lightly tighten the nut first, and then finally
tighten it with the engine weight applied on the body.
Suction hose
Pressure hose
assembly
Marking
Notch
Page 1421 of 1449
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONER AND VENTILATION–On-vehicle Service HEATER, AIR CONDITIONER AND VENTILATION–On-vehicle Service55-19
8. Start the engine.
9. Operate the air conditioner and set at the lowest
temperature (MAX. COOL).
10. Fix the engine speed at 1,500 r/min.
11. Tighten the handle of the adaptor valve (valve open),
and replenish refrigerant while checking the quantity
through the sight glass.
Caution
If the service can is inverted, liquid refrigerant may
be draw into the compressor damaging it by liquid
compression. Keep the service can upright to ensure
that refrigerant is changed in gas state.
12. After replenishing is completed, turn the handle of the
adaptor valve all the way back (valve close), and remove
the quick joint.
NOTE
When there is remainder of refrigerant in the service can,
keep it for next use with the charge value and the valve
of the adaptor valve being closed.
DISCHARGING SYSTEM
Use the refrigerant recovery unit to discharge refrigerant gas
from the system.
NOTE : Refer to the Refrigerant Recovery and Recycling
Unit Instruction Manual for operation of the unit.
REFILLING OF OIL IN THE A/C SYSTEM
Too little oil will provide inadequate compressor lubrication
and cause a compressor failure. Too much oil will increase
discharge air temperature.
When a compressor is installed at the factory, it contains
130 cm
3of refrigerant oil. While the A/C system is in operation,
the oil is carried through the entire system by the refrigerant.
Some of this oil will be trapped and retained in various parts
of the system.
When the following system components are changed, it is
necessary to add oil to the system to replace the oil being
removed with the component.
Compressor oil: SUN PAG 56
Quantity
Condenser: 180 cm
3
Charging valve
Service can
(Refrigerant container)
Low-pressure
service valve
Page 1423 of 1449

HEATER, AIR CONDITIONER AND VENTILATION–On-vehicle Service55-21
REFRIGERANT LEAK REPAIR
LOST CHARGE
If the system has lost all charge due to a leak:
1. Evacuate the system. (See procedure.)
2. Charge the system with approximately one
pound of refrigerant.
3. Check for leaks.
4. Discharge the system.
5. Repair leaks.
6. Replace receiver drier.
Caution
Replacement filter-drier units must be
sealed while in storage. The drier used in
these units will saturate water quickly upon
exposure to the atmosphere. When
installing a drier, have all tools and supplies
ready for quick reassembly to avoid keeping
the system open any longer than necessary.
7. Evacuate and charge system.
LOW CHARGE
If the system has not lost all of its refrigerant charge;
locate and repair all leaks. If it is necessary to
increase the system pressure to find the leak
(because of an especially low charge) add
refrigerant. If it is possible to repair the leak without
discharging the refrigerant system, use the
procedure for correcting low refrigerant level.HANDLING TUBING AND FITTINGS
Kinks in the refrigerant tubing or sharp bends in
the refrigerant hose lines will greatly reduce the
capacity of the entire system. High pressures are
produced in the system when it is operating.
Extreme care must be exercised to make sure that
all connections are pressure tight. Dirt and moisture
can enter the system when it is opened for repair
or replacement of lines or components. The
following precautions must be observed. The
system must be completely discharged before
opening any fitting of connection in the refrigeration
system. Open fittings with caution even after the
system has been discharged. If any pressure is
noticed as a fitting is loosened, allow trapped
pressure to bleed off very slowly.
Never attempt to rebend formed lines to fit. Use
the correct line for the installation you are servicing.
A good rule for the flexible hose lines is keep the
radius of all bends at least 10 times the diameter
of the hose.
Sharper bends will reduce the flow of refrigerant.
The flexible hose lines should be routed so that
they are at least 80 mm from the exhaust manifold.
It is good practice to inspect all flexible hose lines
at least once a year to make sure they are in good
condition and properly routed.
Unified plumbing connections with O-rings, these
O-rings are not reusable.
COMPRESSOR NOISE
You must first know the conditions when the noise
occurs. These conditions are: weather, vehicle
speed, in gear or neutral, engine temperature or
any other special conditions.
Noises that develop during A/C operation can often
be misleading. For example: what sounds like a
failed front bearing or connecting rod, may be
caused by loose bolts, nuts, mounting brackets,
or a loose clutch assembly. Verify accessory drive
belt tension (power steering or alternator).
Improper accessory drive belt tension can cause
a misleading noise when the compressor is
engaged and little or no noise when the compressor
is disengaged.
Drive belts are speed-sensitive. That is, at different
engine speeds, and depending upon belt tension,
belts can develop unusual noises that are often
mistaken for mechanical problems within the
compressor.ADJUSTMENT
1. Select a quiet area for testing. Duplicate
conditions as much as possible. Switch
compressor on and off several times to clearly
identify compressor noise. To duplicate high
ambient conditions (high head pressure),
restrict air flow through condenser. Install
manifold gauge set to make sure discharge
pressure doesn’t exceed 2,070 kPa.
2. Tighten all compressor mounting bolts, clutch
mounting bolt, and compressor drive belt.
Check to assure clutch coil is tight (no rotation
or wobble).
3. Check refrigerant hoses for rubbing or
interference that can cause unusual noises.
4. Check refrigerant charge. (See “Charging
System”.)
5. Recheck compressor noise as in Step 1.
6. If noise still exists, loosen compressor mounting
bolts and retorque. Repeat Step 1.
7. If noise continues, replace compressor and
repeat Step 1.
Page 1436 of 1449

HEATER, AIR CONDITIONER AND VENTILATION-Evaporator and Air Thermo Sensor55-34
EVAPORATOR AND AIR THERMO SENSOR
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Pre-removal and Post-installation Operations
DRefrigerant Draining and Refilling (Refer to P.55-16, 19.)
1 2
3
4
56
7 8
12±2 N·m
- Pipe coupling
O-ring
A/C compressor oil:
SUN PAG 56
1, 2
9
Disassembly steps
DGlove box (Refer to GROUP 52A –
Instrument Panel.)
DEngine-ECU (Refer to GROUP 14.)
AA"1. Suction pipe connection
AA"2. Liquid pipe B connection
AA"3. Expansion valve4. Expansion valve adapter
5. Joint duct
6. Evaporator cover
AB""AA7. Evaporator
8. Air thermo sensor clip
9. Air thermo sensor
REMOVAL SERVICE POINTS
AA"WHEN DISCONNECTING THE SUCTION PIPE,
LIQUID PIPE B, AND THE EXPANSION VALVE
To prevent the entry of dust or other foreign bodies, plug
the dismantled hose and the nipples of the expansion valves.
Caution
As the compressor oil and receiver are highly moisture
absorbent, use a non-porous material to plug the hose
and nipples.