2007 MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION Leak
[x] Cancel search: LeakPage 529 of 1449

ENGINE LUBRICATION -On-vehicle Service12-5
OIL FILTER REPLACEMENT
1. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until the
temperature of the coolant reaches 80_Cto90_C.
2. Remove the engine oil filler cap.
3. Remove the drain plug to drain oil.
Caution
Use care as oil could be hot.
4. Remove the under cover.
5. Use the respective tool in the following table to remove
the engine oil filter.
6. Clean the filter bracket side mounting surface.
7. Apply a small amount of engine oil to the O-ring of the new
oil filter.
8. Once the O-ring of the oil filter is touching the flange,
use the generic tool to turn for approximately 3/4 round
and tighten to (14±2 N·m).
9. Install the drain plug and refill the engine oil.
(Refer to Engine Oil Replacement P.12-4.)
10. Race the engine 2 - 3 times, and check to be sure that
no engine oil leaks from installation section of the oil
filter.
OIL PRESSURE CHECK
1. Check engine oil quantity.
2. Remove the oil pressure switch terminal.
3. Use the special tool (oil pressure switch wrench) to remove
the oil pressure switch.
Caution
Since sealant is applied to the thread of oil pressure
switch, take care not to damage the oil pressure switch
when removing it.
Commercially-
available tool
O-ring
Oil pressure switch
Oil filter bracket
MD998054
Page 538 of 1449
MPI -Service Specifications/Sealant13A-6
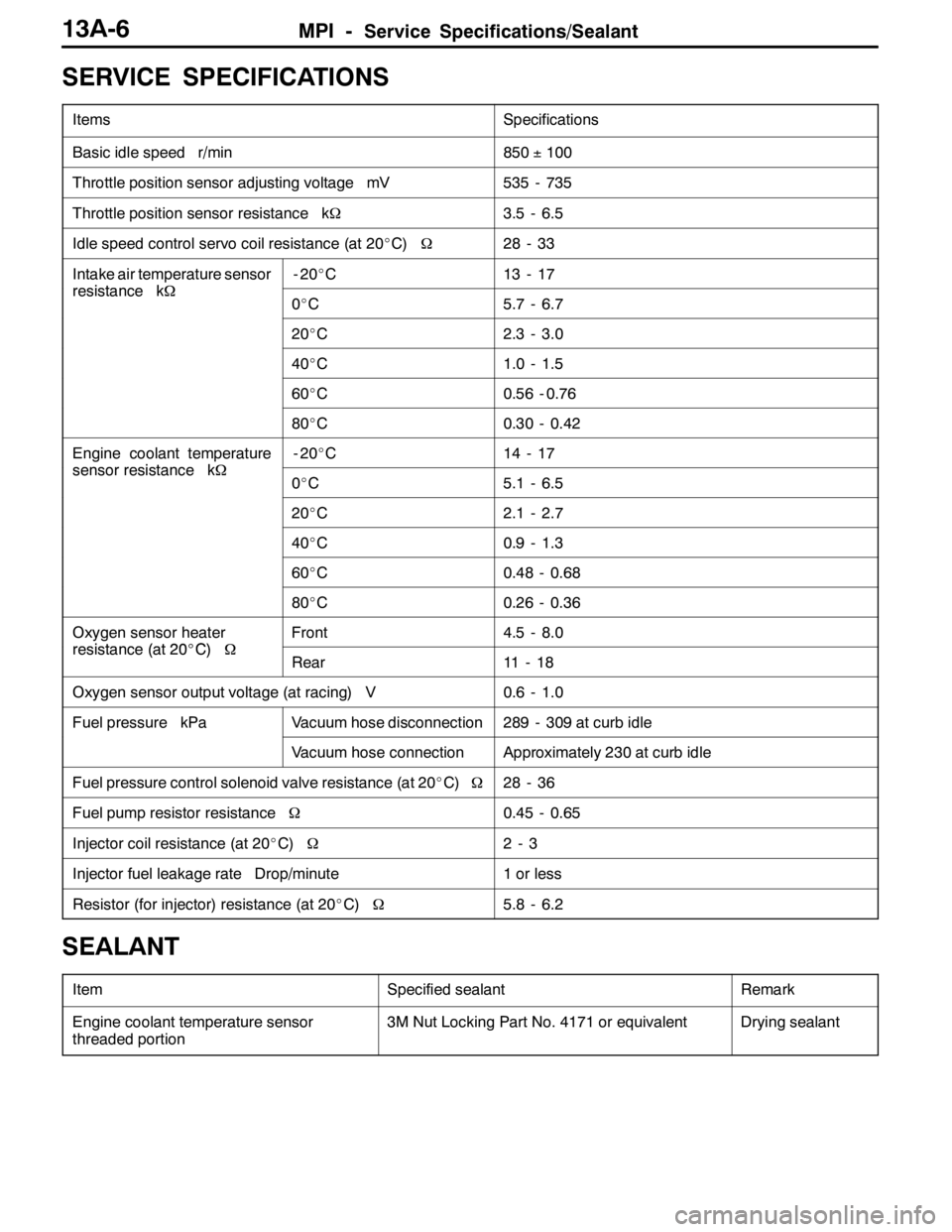
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsSpecifications
Basic idle speed r/min850±100
Throttle position sensor adjusting voltage mV535 - 735
Throttle position sensor resistance kΩ3.5 - 6.5
Idle speed control servo coil resistance (at 20_C)Ω28 - 33
Intake air temperature sensor
resistancekΩ
-20_C13 - 17
resistance kΩ0_C5.7 - 6.7
20_C2.3 - 3.0
40_C1.0 - 1.5
60_C0.56 - 0.76
80_C0.30 - 0.42
Engine coolant temperature
sensorresistancekΩ
-20_C14 - 17
sensor resistance kΩ0_C5.1 - 6.5
20_C2.1 - 2.7
40_C0.9 - 1.3
60_C0.48 - 0.68
80_C0.26 - 0.36
Oxygen sensor heater
resistance(at20_C)Ω
Front4.5 - 8.0
resistance (at 20_C)ΩRear11 - 1 8
Oxygen sensor output voltage (at racing) V0.6 - 1.0
Fuel pressure kPaVacuum hose disconnection289 - 309 at curb idle
Vacuum hose connectionApproximately 230 at curb idle
Fuel pressure control solenoid valve resistance (at 20_C)Ω28 - 36
Fuel pump resistor resistanceΩ0.45 - 0.65
Injector coil resistance (at 20_C)Ω2-3
Injector fuel leakage rate Drop/minute1 or less
Resistor (for injector) resistance (at 20_C)Ω5.8 - 6.2
SEALANT
ItemSpecified sealantRemark
Engine coolant temperature sensor
threaded portion3M Nut Locking Part No. 4171 or equivalentDrying sealant
Page 602 of 1449

MPI -Troubleshooting13A-70
Inspection Procedure 12
Shock during acceleration
Probable cause
The occurrence of ignition leaks, etc., due to the rise in voltage required for the spark
plugs during acceleration is a probable cause.DIgnition system malfunction
OK
Check and repair the harness and connector between each
cylinder’s ignition coil and body earth and between the engine-
ECU and ignition coil for disconnection, short-circuit and damage.
OK
Check the ignition coil parts.
(Refer to GROUP 16 - Ignition Device.)NGReplace the ignition coil.
OK
Check the following connectors:B-114, B-119NG
Repair
OK
Check the spark plug.
(Refer to GROUP 16 - Ignition Device.)NGReplace the spark plug.
NO
Check the spark plug cable.
(Refer to GROUP 16 - Ignition Device.)NGReplace the spark plug cable.
MUT-IISelf-Diag code
DIs a diagnosis code output?YESINSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSIS CODE
(Refer to P.13A-12.)
Page 607 of 1449

MPI -Troubleshooting13A-75
Inspection Procedure 17
Abnormal odor, white smoke, black smoke, high CO or HC
concentration when idling
Probable cause
Causes shown on right are suspected.DAir/fuel ratio control system malfunction
DIgnition system malfunction
DFuel system malfunction
DIntake and exhaust system malfunction
DExhaust gas purifier system malfunction
DImproper compression pressure
DCatalyst defect
DEngine-ECU malfunction
OK
To the next page
OK
Check the fuel pressure. (Refer to P.13A-128.)
OK
MUT-IIData list
DNo. 59: Oxygen sensor (rear)
(Refer to P.13A-105.)NGCheck the Code No. P0136: Oxygen sensor (rear) system.
(Refer to P.13A-27.)
OK
MUT-IIData list
DNo. 11: Oxygen sensor (front) (Refer to P.13A-102.)NGCheck the Code No. P0130: Oxygen sensor (front) system.
(Refer to P.13A-24.)
OK
Check for exhaust gas leaks from exhaust manifold.NG
Repair
OK
Check the air intake from the intake hose and intake manifold.NG
Repair
OK
MUT-IIData list
DNo. 12: Air flow sensor
DNo. 13: Intake air temperature sensor
DNo. 21: Engien coolant temperature sensor
DNo. 25: Barometric pressure sensor
(Refer to P.13A-102.)
Proceed to OK if all service data values are correct.
Proceed to NG if there is even one abnormal service data value.NGRefer to inspections for diagnosis code of sensor showing
abnormal service data. (Refer to P.13A-102.)
OK
Check the ignition timing.
(Refer to GROUP 11 - Engine Adjustment.)NGCheck the Inspection Procedure 15: Deviation of ignition interval
(Refer to P.13A-73.)
NO
MUT-IIActuator test
DNo. 01: No. 1 injector
DNo. 02: No. 2 injector
DNo. 03: No. 3 injector
DNo. 04: No. 4 injector
OK:The idling state changes.
DProceed to NG if the cylinder (NG cylinder) for which the idling
state did not change when injector was stopped is pinpointed.
DProceed to OK if all cylinders are OK, or if the NG cylinder
cannot be pinpointed.NGCheck the Code No. P0201: No. 1 injector system, P0202: No. 2
injector system, P0203: No. 3 injector system and P0204: No. 4
injector system. (Refer to P.13A-30, 31, 32, 33.)
MUT-IISelf-Diag code
DIs a diagnosis code output?YESINSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSIS CODE
(Refer to P.13A-12.)
Page 611 of 1449

MPI -Troubleshooting13A-79
Inspection Procedure 19
Overheating
Probable cause
Causes shown on right are suspected.DEngine coolant insufficient or deteriorated
DFan controller malfunction
DEngine coolant temperature sensor malfunction
DThermostat malfunction
DWater pump malfunction
DCondenser fan relay malfunction
DRadiator core malfunction
DEngine-ECU malfunction
NO
NG
Replace or replenish the engine coolant.
OK
Replace the radiator core.
OK
Check the water pump. (Refer to GROUP 14 - Water pump.)NGReplace the water pump.
OK
Check the thermostat. (Refer to GROUP 14 - Thermostat.)NGReplace the thermostat.
OK
MUT-IIData list
DNo. 21: Engine coolant temperaure sensor
OK:Approximately the same as the ambient temperature
when cooled.
Between 80 - 120_C when hot.NGCheck the Code No. P0115: Engine coolant temperature
sensor system. (Refer to P.13A-19.)
MUT-IIData list
21 Engine coolant temperature sensor (Refer to P.13A-102.)
OK
MUT-IIActuator Test
DNo. 37: Condenser fan (HI)
DNo. 38: Condenser fan (LOW)
DIgnition switch: ON
OK:Condenser fan rotates (low speed).
OK:Condenser fan rotates (high speed).NGCheck the Inspection Procedure 25: Condenser fan control
relay system. (Refer to P.13A-89.)
MUT-IIActuator Test
DNo. 21: Fan controller
DIgnition switch: ON
OK:Radiator fan rotates.NGCheck the Inspection Procedure 24: Radiator fan control relay
system. (Refer to P.13A-87.)
OK
Check the engine coolant.
(Refer to GROUP 14 - On-vehicle Service.)
If the engine coolant level is low, check whether the engine
coolant has leaked, and repair if required.
MUT-IISelf-Diag Code
Is a diagnosis code output?YESINSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSIS CODE (Refer to
P.13A-12.)
Page 649 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-117
Examples of Abnormal Wave Patterns
DExample 1
Cause of problem
Sensor interface malfunction
Wave pattern characteristics
Rectangular wave pattern is output even when the engine
is not started.
DExample 2
Cause of problem
Damaged rectifier or vortex generation column
Wave pattern characteristics
Unstable wave pattern with non-uniform frequency.
However, when an ignition leak occurs during acceleration,
the wave pattern will be distorted temporarily, even if the air
flow sensor is normal.
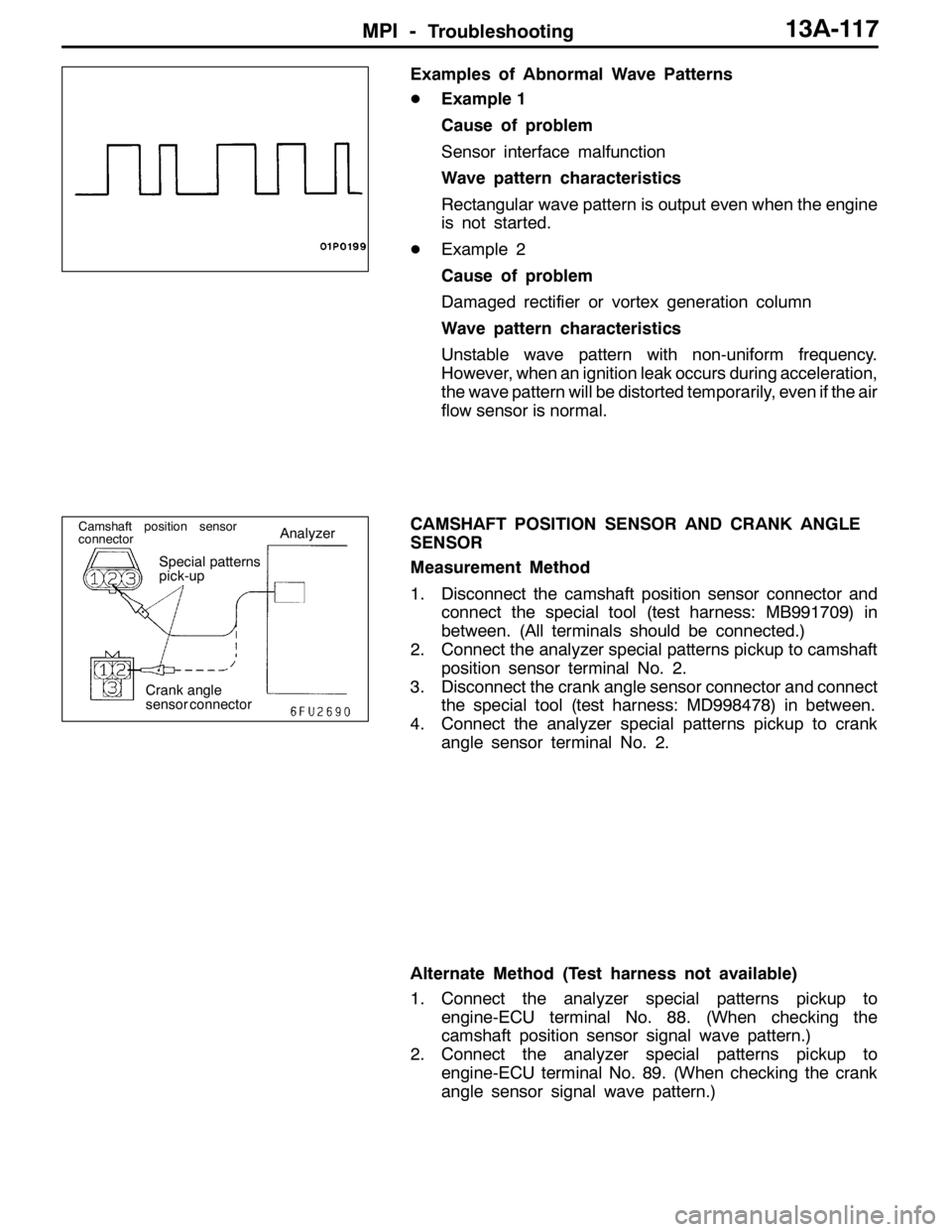
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR AND CRANK ANGLE
SENSOR
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the camshaft position sensor connector and
connect the special tool (test harness: MB991709) in
between. (All terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to camshaft
position sensor terminal No. 2.
3. Disconnect the crank angle sensor connector and connect
the special tool (test harness: MD998478) in between.
4. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to crank
angle sensor terminal No. 2.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 88. (When checking the
camshaft position sensor signal wave pattern.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 89. (When checking the crank
angle sensor signal wave pattern.)
Crank angle
sensor connector
Camshaft position sensor
connectorAnalyzer
Special patterns
pick-up
Page 661 of 1449
MPI -On-vehicle Service13A-129
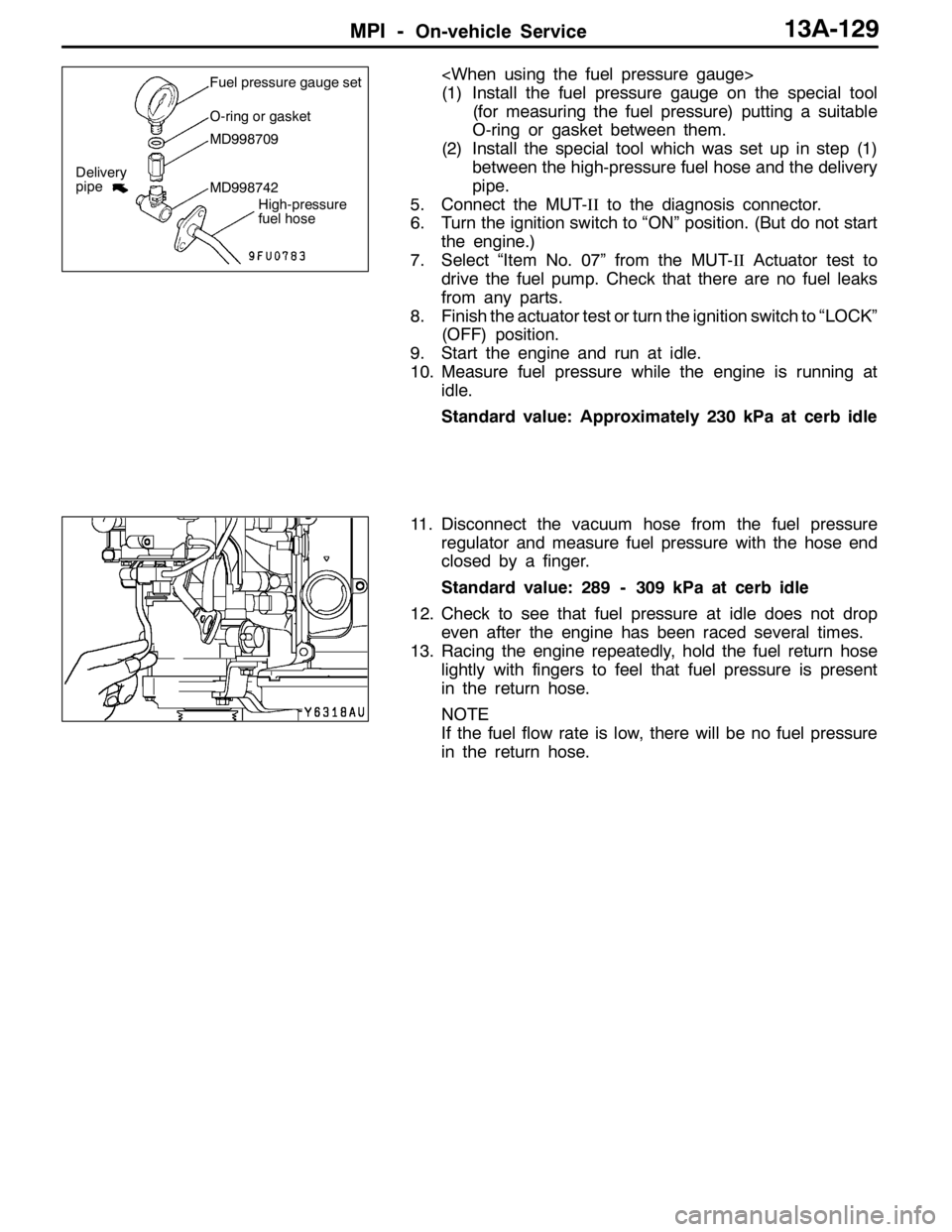
(1) Install the fuel pressure gauge on the special tool
(for measuring the fuel pressure) putting a suitable
O-ring or gasket between them.
(2) Install the special tool which was set up in step (1)
between the high-pressure fuel hose and the delivery
pipe.
5. Connect the MUT-IIto the diagnosis connector.
6. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position. (But do not start
the engine.)
7. Select “Item No. 07” from the MUT-IIActuator test to
drive the fuel pump. Check that there are no fuel leaks
from any parts.
8. Finish the actuator test or turn the ignition switch to “LOCK”
(OFF) position.
9. Start the engine and run at idle.
10. Measure fuel pressure while the engine is running at
idle.
Standard value: Approximately 230 kPa at cerb idle
11. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure
regulator and measure fuel pressure with the hose end
closed by a finger.
Standard value: 289 - 309 kPa at cerb idle
12. Check to see that fuel pressure at idle does not drop
even after the engine has been raced several times.
13. Racing the engine repeatedly, hold the fuel return hose
lightly with fingers to feel that fuel pressure is present
in the return hose.
NOTE
If the fuel flow rate is low, there will be no fuel pressure
in the return hose.Fuel pressure gauge set
O-ring or gasket
MD998709
MD998742
High-pressure
fuel hose
Delivery
pipe
Page 662 of 1449
MPI -On-vehicle Service13A-130
14. If any of fuel pressure measured in steps 10 to 13 is out of
specification, troubleshoot and repair according to the
table below.
SymptomProbable causeRemedy
DFuel pressure too low
DFuelpressuredropsafterracing
Clogged fuel filterReplace fuel filter
DFuelpressuredrops after racing
DNo fuel pressure in fuel return
hose
Fuel leaking to return side due to poor
fuel regulator valve seating or settled
springReplace fuel pressure regulator
Low fuel pump delivery pressureReplace fuel pump
Fuel pressure too highBinding valve in fuel pressure
regulatorReplace fuel pressure regulator
Clogged fuel return hose or pipeClean or replace hose or pipe
Same fuel pressure when vacuum
hose is connected and when
disconnected
Damaged vacuum hose or clogged
nippleReplace vacuum hose or clean nipple
disconnectedFuel pressure control system
malfunctionCheck the fuel pressure control
system
15. Stop the engine and check change of fuel pressure gauge
reading. Normal if the reading does not drop within 2
minutes. If it does, observe the rate of drop and
troubleshoot and repair according to the table below.
SymptomProbable causeRemedy
Fuel pressure drops gradually after
engineisstopped
Leaky injectorReplace injector
engineisstopped
Leaky fuel regulator valve seatReplace fuel pressure regulator
Fuel pressure drops sharply
immediately after engine is stoppedCheck valve in fuel pump is held openReplace fuel pump
16. Release residual pressure from the fuel pipe line.
(Refer to P.13A-125.)
17. Remove the fuel pressure gauge and special tool from
the delivery pipe.
Caution
Cover the hose connection with rags to prevent splash
of fuel that could be caused by some residual pressure
in the fuel pipe line.
18. Replace the O-ring at the end of the fuel high pressure
hose with a new one. Furthermore, apply engine oil to
the new O-ring before replacement.
19. Fit the fuel high pressure hose over the delivery pipe
and tighten the bolt to specified torque.
Tightening torque: 5.0±1.0 N·m
20. Check for any fuel leaks by following the procedure in
step 7.
21. Disconnect the MUT-II.