2007 KIA CARNIVAL engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 2 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
IDENTIFICATION NUMBER DESCRIPTION
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
1 : Geographic zone
- K = Korea
2 : Manufacturer
- N = Kia motor company
3 : Vehicle type
- A = Passenger car
4 - 5 : Vehicle Line/Series
- MB = VQ
- MC = EP
6 - 7: Body type
- 75 = Coach & GVW 2271 ~ 2720 kg
- 76 = Long coach & GVW 2271 ~ 2720 kg
8 : Engine type
- 1 = J2.9 Diesel
- 2 = µ 2.7
- 3 = λ3.8 Gasoline
9 : Transmission type
- 2 : Manual
- 5 : Automatic
10 : Model year
- 5 = 2005, 6 = 2006, 7 = 2007
11 : Plant location
- 6 = Soha plant
12 - 17 : Production sequential number
- 000001 ~ 999999
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
GASOLINE
1. Engine fuel
- G : Gasoline
2. Engine range
- 4 : 4 cycle 4 cylinder
- 6 : 4 cycle 6 cylinder
3. Engine development order
- D : Lambda engine
4. Engine capacity
- E : 2656 cc (µ- engine)
5. Production year
- 5 : 2005, 6 : 2006
6. Engine production sequence number
- 000001 ~ 999999
Page 3 of 1575

TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
AUTOMATIC
1.Modle
- U : A5HF1
2. Production year
- 5 : 2005, 6 : 2006, 7 : 2007
3. Gear ratio
- K : 3.333
4. Detailed chassification
- FD : 3.8D
5. Spare
6. Transaxle production sequence number
- 000001 ~ 999999
MANUAL
1. Model
- Y : M5HF2
2. Production year
- 5 : 2005, 6 : 2006, 7 : 2007
3. Transaxle production sequence number
- 000001 ~ 999999
LUBRICANTS
RECOMMENDED LUBRICANTS
Parts OIL & GREASE STANDARD
Engine Oil GasolineAPI SJ or SL
SAE 5W - 20
If 5W- 20 engine oil is not available, 5W- 30 or secondary
recommended engine oil for corresponding temperature range can be
used.
Transaxle Auto
DIAMOND ATF SP - III, SK ATF SP - III
Manual API Classification GL - 4 (SAE 75W/85)
Power Steering PSF - 3
Breake Steering DOT 3 or equivalent
Coolant Ethlyene glycol base for aluminium radiator
Transaxle linkage, parking breake cable
mechanism, hood, door latch, seat
adjuster,tailgate latch, door hinges, tailgate
hinge Multipurpose grease NIGL grade #2
Page 4 of 1575

Always use Genuine Kia parts and recommedended fluid.
Using any other type of parts and fluid can cause serious damaged if the vehicle.RECOMMENDED LUBRICANTS
LUBRICANTS CAPACITIES Description 2.7
Engine oil Oil pan 4.2 (4.44, 3.70)
Oil filter 0.3 (0.32, 0.26)
Total 4.5 (4.76, 0.26)
Cooling system 8.2~8.3
(8.66~8.77, 7.22~7.3)
Manual transaxle 1.85 (1.95, 1.62)
Automatic transaxle 10.7 (11.3, 9.41)
Power steering 1.0 (1.06, 0.88)
Capacities : [liter (U.S.qus, lmp.qts)]
SELECTION OF ENGINE OIL (Gasoline-2.7)
RECOMMENDED ILSAC classification : GF - 3 OR ABOVE
RECOMMENDED API classification : SL(SJ) OR ABOVE
RECOMMENDED SAE viscosity grades :
Page 6 of 1575

CHAPTER 2:
Engine Mechanical System
Page 9 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom Suspect area Remedy
Engine misfire with
abnormal internal
lower engine noises. Worn crankshaft bearings.
Loose or impropes engine drive plate.
Replace the crankshaft and bearings as
required.
Repair or replace the drive plate as required.
Worn piston rings.
(Oil consumption may or may not cause the
engine to misfire.) Inspect the cylinder for a loss of compression.
Repair or replace as required.
Worn crankshaft thrust bearings Replace the crankshaft and bearings as
required.
Engine misfire with
abnormal valve train
noise. Stuck valves.
(Carbon buildup on the valve stem)
Repair or replace as required.
Excessive worn or mis - aligned timing chain. Replace the timing chain and sprocket as
required.
Worn camshaft lobes. Replace the camshaft and valve lifters.
Engine misfire with
coolant consumption. a.
Faulty cylinder head gasket and/or
cranking or other damage to the cylinder
head and engine block cooling system.
b. Coolant consumption may or may not
cause the engine to overheat. a.
Inspect the cylinder head and engine
block for damage to the coolant passages
and/or a faulty head gasket.
b. Repair or replace as required.
Engine misfire with
excessive oil
consumption. Worn valves, guides and/or valve stem oil
seals.
Repair or replace as required.
Worn piston rings.
(Oil consumption may or may not cause the
engine to misfire) a.
Inspect the cylinder for a loss of
compression.
b. Repair or replace as required.
Engine noise on start -
up, but only lasting a
few seconds. Incorrect oil viscosity.
a.Drain the oil.
b. Install the correct viscosity oil.
Worn crankshaft thrust bearing. a.Inspect the thrust bearing and crankshaft.
b. Repair or replace as required.
Upper engine
noise,regardless of
engine speed. Low oil pressure.
Repair or replace as required.
Broken valve spring. Replace the valve spring.
Worn or dirty valve lifters. Replace the valve lifters.
Stretched or broken timing chain and/or
damaged sprocket teeth. Replace the timing chain and sprockets.
Worn timing chain tensioner, if applicable. Replace the timing chain tensioner as
required.
Worn camshaft lobes. a.Inspect the camshaft lobes.
b. Replace the timing camshaft and valve
lifters as required.
Worn valve guides or valve stems. Inspect the valves and valve guides,then
repair as required.
Stuck valves. Carbon on the valve stem or
valve seat may cause the valve to stay open. Inspect the valves and valve guides, then
repair as required.
Worn drive belt, idler, tensioner and bearing. Replace as required.
Lower engine
noise,regardless of Low oil pressure.
Repair as required.
Page 10 of 1575

noise,regardless of
engine speed.Loose or damaged drive plate.
Repair or replace the drive plate.
Damaged oil pan, contacting the oil pump
screen. a.
Inspect the oil pan.
b. Inspect the oil pump screen.
c. Repair or replace as required.
Oil pump screen loose, damaged or
restricted. a.
Inspect the oil pump screen.
b. Repair or replace as required.
Excessive piston- to- cylinder bore clearance. a.Inspect the piston, piston pin and cylinder
bore.
b. Repair as required.
Excessive piston pin- to- piston clearance. a.Inspect the piston, piston pin and the
connecting rod.
b. Repair or replace as required.
Excessive connecting rod bearing clearance Inspect the following components and repair
as required.
a. The connecting rod bearings.
b. The connecting rods.
c. The crankshaft pin journals.
Excessive crankshaft bearing clearance. Inspect the following components, and repair
as required.
a. The crankshaft bearings.
b. The crankshaft main journals.
c. The cylinder block.
Incorrect piston, piston pin and connecting rod
installation a.
Verify the piston pins and connecting rods
are installed correctly.
b. Repair as required.
Engine noise under
load. Low oil pressure
Repair or replace as required.
Excessive connecting rod bearing clearance . Inspect the following components and repair
as required :
a. The connecting rod bearings.
b. The connecting rods.
c. The crankshaft.
Excessive crankshaft bearing clearance. Inspect the following components, and repair
as required.
a. The crankshaft bearings.
b. The crankshaft main journals.
c. The cylinder block.
Engine will not crank-
crankshaft will not
rotate. Hydraulically locked cylinder.
a. Coolant/antifreeze in cylinder.
b. Oil in cylinder.
c. Fuel in cylinder. a.
Remove spark plugs and check for fluid.
b. Inspect for broken head gasket.
c. Inspect for cracked engine block or
cylinder head.
d. Inspect for a sticking fuel injector and/or
leaking fuel regulator.
Broken timing chain and/or timing chain
and/or timing chain gears. a.
Inspect timing chain and gears.
b. Repair as required.
Material in cylinder. a. Broken valve
b. Piston material
c. Foreign material a.
Inspect cylinder for damaged components
and/or foreign materials.
b. Repair or replace as required.
Page 12 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
Compression pressure inspection
If the there is lack of power, excessive oil consumption or poor fuel economy, measure the compression
pressure.
1. Warm up the engine until the normal operating temperature becoming 80~95°C(176~203°F).
2. Remove the surge tank.
3. Remove the ignition coil connectors(B) and ignition coils.
4.Using a 16mm plug wrench, remove the 6 spark plugs.
5. Check cylinder compression pressure.
(1) Insert a compression gauge into the spark plug hole.
(2) Open the throttle fully.
(3) With the fully - open throttle in cranking, measure the compression pressure.
Always use a fully charged battery to get the engine speed of 250 rpm or more.
Repeat steps 1) through 3) for each cylinder.
This measurement must be done in as short a time as possible.
Compression pressure: 1,176.79kPa (12.0kgf/cm², 170.68psi) - 200 ~ 250rpm
Minimum pressure: 1,029.69kPa (10.5kgf/cm², 149.34psi)
Difference between cylinders: 98.07kPa (1.0kgf/cm², 14.22psi)
(4) If the compression pressure in 1 or more cylinders is lower than the specification above, pour a small amount
of engine oil into the cylinder through the spark plug hole, repeat the steps (1) through (3) for the cylinder and
measure the pressure again.
a. If adding oil increases the pressure up, the piston rings or cylinder bores might be worn or damaged.
b. If the pressure doesn't increase, a valve may be sticking or seating may be improper, or there may be
leakage from the gasket.
6. Reinstall the spark plugs.
7. Install the ignition coils and connect ignition coil connectors.
8. Install the surge tank.
VALVE CLEARANCE INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT
Inspect and adjust the valve clearance when the engine is cold (Engine coolant temperature : 20°C
±5°C(59~77°F)) and cylinder head is installed on the cylinder block.
Page 13 of 1575
1.Remove the engine cover.
2. Remove air cleaner assembly.
3. Remove the surge tank.
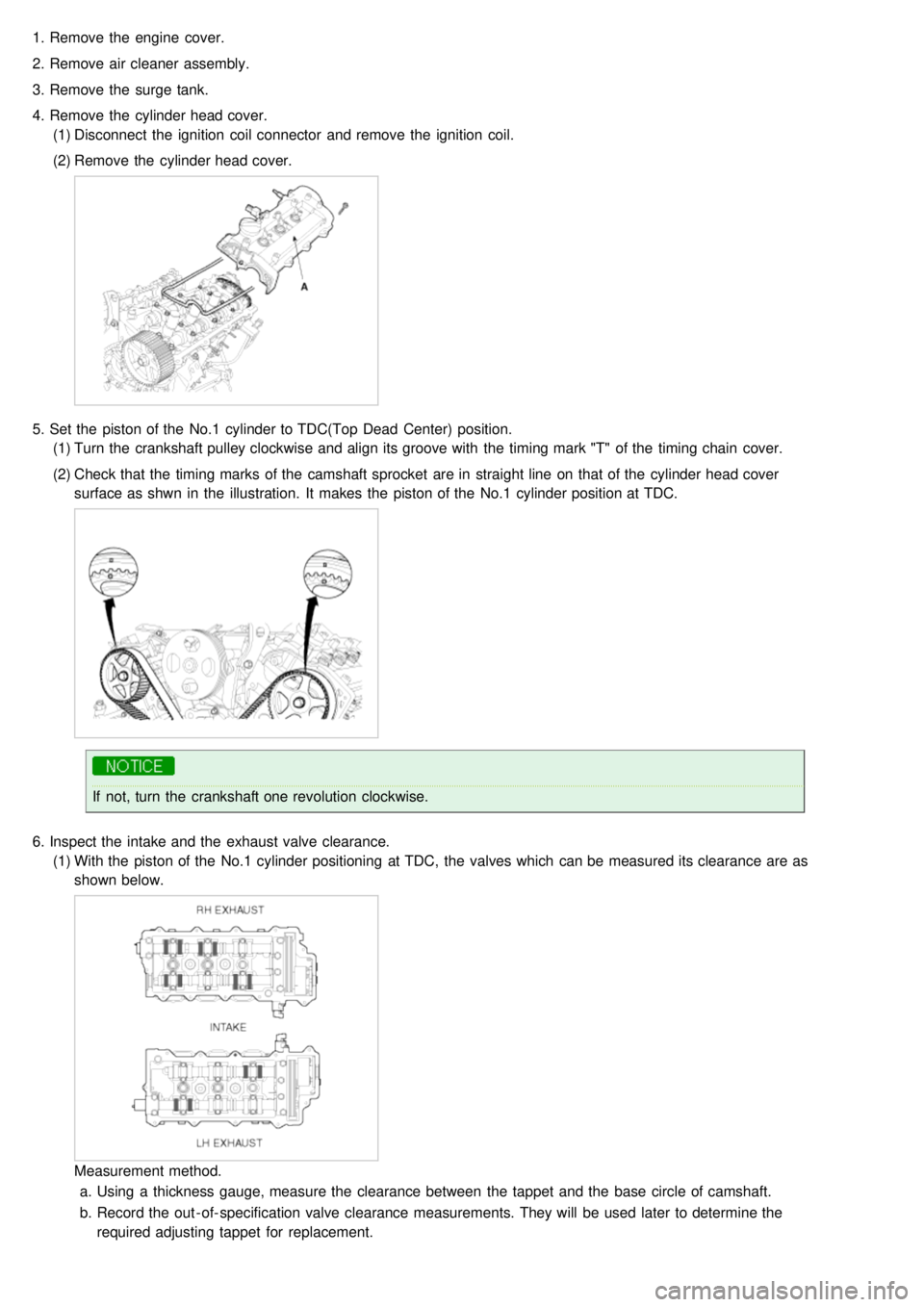
4. Remove the cylinder head cover.
(1) Disconnect the ignition coil connector and remove the ignition coil.
(2) Remove the cylinder head cover.
5.Set the piston of the No.1 cylinder to TDC(Top Dead Center) position.
(1) Turn the crankshaft pulley clockwise and align its groove with the timing mark "T" of the timing chain cover.
(2) Check that the timing marks of the camshaft sprocket are in straight line on that of the cylinder head cover
surface as shwn in the illustration. It makes the piston of the No.1 cylinder position at TDC.
If not, turn the crankshaft one revolution clockwise.
6. Inspect the intake and the exhaust valve clearance.
(1) With the piston of the No.1 cylinder positioning at TDC, the valves which can be measured its clearance are as
shown below.
Measurement method.
a. Using a thickness gauge, measure the clearance between the tappet and the base circle of camshaft.
b. Record the out - of- specification valve clearance measurements. They will be used later to determine the
required adjusting tappet for replacement.