2007 ISUZU KB P190 compression ratio
[x] Cancel search: compression ratioPage 2822 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–45
Page 6A1–45
2.15 Engine Compression Test
A compression pressure test of the engine cylinders determines the condition of the rings, the valves and the head
gasket.
Preliminary Steps
1 Ensure the battery is fully charged.
2 Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
DTCs will set when the fuel system or the ignition
system is disabled and the engine is cranked.
Disregard DTCs that set under this condition.
3 Disable the fuel system by removi ng the fuel pump relay, refer to Section 8A Electrical Body & Chassis .
4 Start the engine to use any resi dual fuel from the fuel lines.
4 Disable the ignition coils by removing fuses 34 and 35, refer to Section 8A Electrical Body & Chassis .
5 Using Tech 2, command the throttle plate to wide open throttle.
Engine Cylinder Compression Test
1 Install the compression tester to cylinder number 1.
2 While observing the compression tester reading, turn t he ignition to the START position for several seconds and
then allow the ignition to return to the ON position.
3 Record the highest compression reading obtained.
4 Repeat the engine compression test for each cylinder.
Test Result Evaluation
Normal engine compression pressure builds quickly and evenly to over 965 kPa. In addition, the lowest reading of an
engine cylinder should not be less than 70 per cent of the highest reading. If any cylinder fails the compression test,
adding 15 ml of engine oil to the suspected cylinder may help isolate the following fault condition.
1 A fault condition in the piston rings will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression tends to build-up with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression improves with the addition of engine oil.
2 A fault condition in an intake or exhaus t valve will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression does not build with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression does not improve with the addition of engine oil.
3 A fault condition in the cylinder head gasket will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression does not build with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression does not improve with the addition of engine oil.
• The suspected cylinders are pos itioned adjacent to each other.
• The engine oil may be contaminated with engine coolant.
• The engine coolant may be cont aminated with engine oil.
Once the fault has been identified, refe r to the relevant service procedure and reinstall the removed components.
Using Tech 2, clear DTCs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2823 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–46
Page 6A1–46
2.16 Cylinder Leakage Test
A leakage test may be performed to measure cylinder/combustion chamber leakage. High cylinder leakage may indicate
one or more of the following:
• worn or burnt valves,
• broken valve springs,
• stuck valve lifters,
• incorrect valve lash/adjustment,
• damaged piston,
• worn piston rings,
• worn or scored cylinder bore,
• damaged cylinder head gasket,
• cracked or damaged cylinder head, or
• cracked or damaged engine block.
1 Disconnect the battery ground negative cable.
2 Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
3 Rotate the crankshaft to place the piston in the cyli nder being tested at top dead centre (TDC) of the compression
stroke.
4 Install a commercially available cylinder head leak down tester into the spark plug hole.
NOTE
If required, hold the crankshaft balancer bolt to
prevent the engine from rotating.
5 Apply shop air pressure to the cylinder head leak dow n tester and adjust according to the manufacturers
instructions.
6 Record the cylinder leakage value. Cylinder leakage t hat exceeds 25 percent is considered excessive and may
require component service. In excessive leakage situations, inspect for the following conditions:
• air leakage sounds at the throttle body or air inlet duct that may indicate a worn or burnt intake valve or a
broken valve spring,
• air leakage sounds at the exhaust system tailpipe that may indicate a worn or burnt exhaust valve or a broken
valve spring,
• air leakage sounds from the crankcase, oil level indicator tube, or oil fill tube that may indicate worn piston
rings, a damaged piston, a worn or scored cylinder bore, a damaged engine block or a damaged cylinder
head, or
• air bubbles in the cooling system may indicate a damaged cylinder head or a damaged cylinder head gasket.
7 Perform the leakage test on the rema ining cylinders and record the values.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3124 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–347
Page 6A1–347
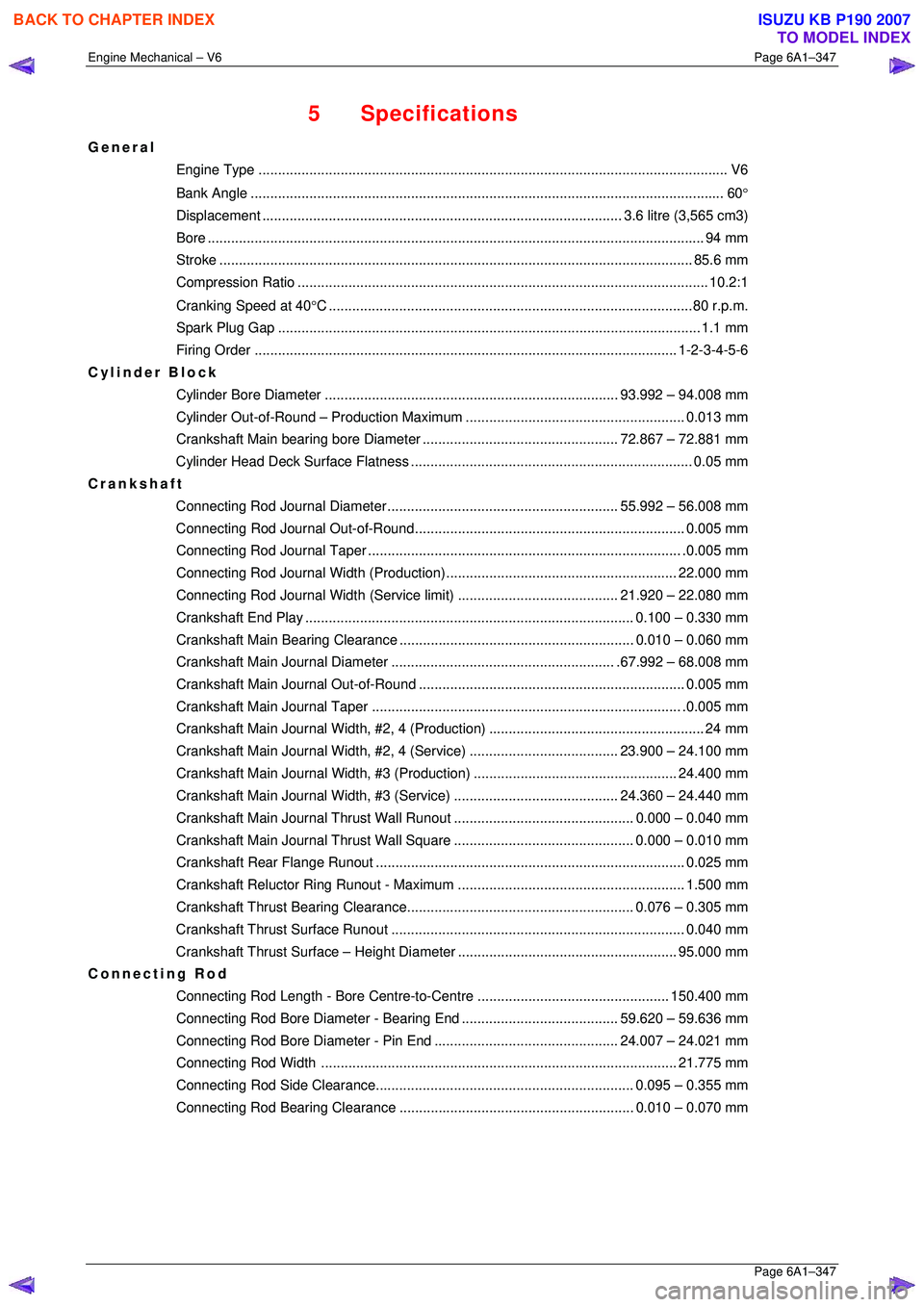
5 Specifications
General
Engine Type .................................................................................................................... .... V6
Bank An gle ..................................................................................................................... .... 60°
Displacement ............................................................................................ 3.6 litre (3,565 cm3)
Bore ........................................................................................................................... .... 94 mm
Stroke ......................................................................................................................... 85.6 mm
Compression Ratio......................................................................................................... 10. 2:1
Cranking Speed at 40 °C .............................................................................................80 r.p.m.
Spark Plug Gap ............................................................................................................ 1.1 mm
Firing Order ............................................................................................................ 1- 2-3-4-5-6
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore Diame ter ........................................................................... 93.992 – 94.008 mm
Cylinder Out-of-Round – Pr oduction Maximum ........................................................ 0.013 mm
Crankshaft Main bearing bor e Diameter .................................................. 72. 867 – 72.881 mm
Cylinder Head Deck Surf ace Flatness ........................................................................ 0. 05 mm
Crankshaft
Connecting Rod Journal Diameter........................................................... 55. 992 – 56.008 mm
Connecting Rod Journa l Out-of-Round..................................................................... 0.005 mm
Connecting Rod Jour nal Taper................................................................................ .0. 005 mm
Connecting Rod Journal Width (Production)........................................................... 22.000 mm
Connecting Rod Journal Width (Service limit)......................................... 21. 920 – 22.080 mm
Crankshaft End Pl ay .................................................................................... 0.100 – 0.330 mm
Crankshaft Main Bearing Clearance ............................................................ 0.010 – 0.060 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Diameter......................................................... .67. 992 – 68.008 mm
Crankshaft Main Journa l Out-of-Round .................................................................... 0.005 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Taper ............................................................................... .0. 005 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Width, #2, 4 (Pr oduction)....................................................... 24 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Width, #2, 4 (Service)...................................... 23. 900 – 24.100 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Wi dth, #3 (Production) .................................................... 24.400 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Width, #3 (Service).......................................... 24. 360 – 24.440 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Thru st Wall Runout.............................................. 0.
000 – 0.040 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Thru st Wall Square.............................................. 0. 000 – 0.010 mm
Crankshaft Rear Fl ange Runout............................................................................... 0. 025 mm
Crankshaft Reluctor Ring Ru nout - Maximum .......................................................... 1.500 mm
Crankshaft Thrust Bearin g Clearance.......................................................... 0. 076 – 0.305 mm
Crankshaft Thrust Su rface Runout........................................................................... 0. 040 mm
Crankshaft Thrust Surface – Height Diameter ........................................................ 95.000 mm
Connecting Rod
Connecting Rod Length - Bore Centre-to-Centre ................................................. 150.400 mm
Connecting Rod Bore Diameter - Bearing End........................................ 59. 620 – 59.636 mm
Connecting Rod Bore Diamet er - Pin End............................................... 24. 007 – 24.021 mm
Connecting Rod Width ........................................................................................... 21.775 mm
Connecting Rod Side Cl earance.................................................................. 0.095 – 0.355 mm
Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance ............................................................ 0.010 – 0.070 mm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3303 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–25
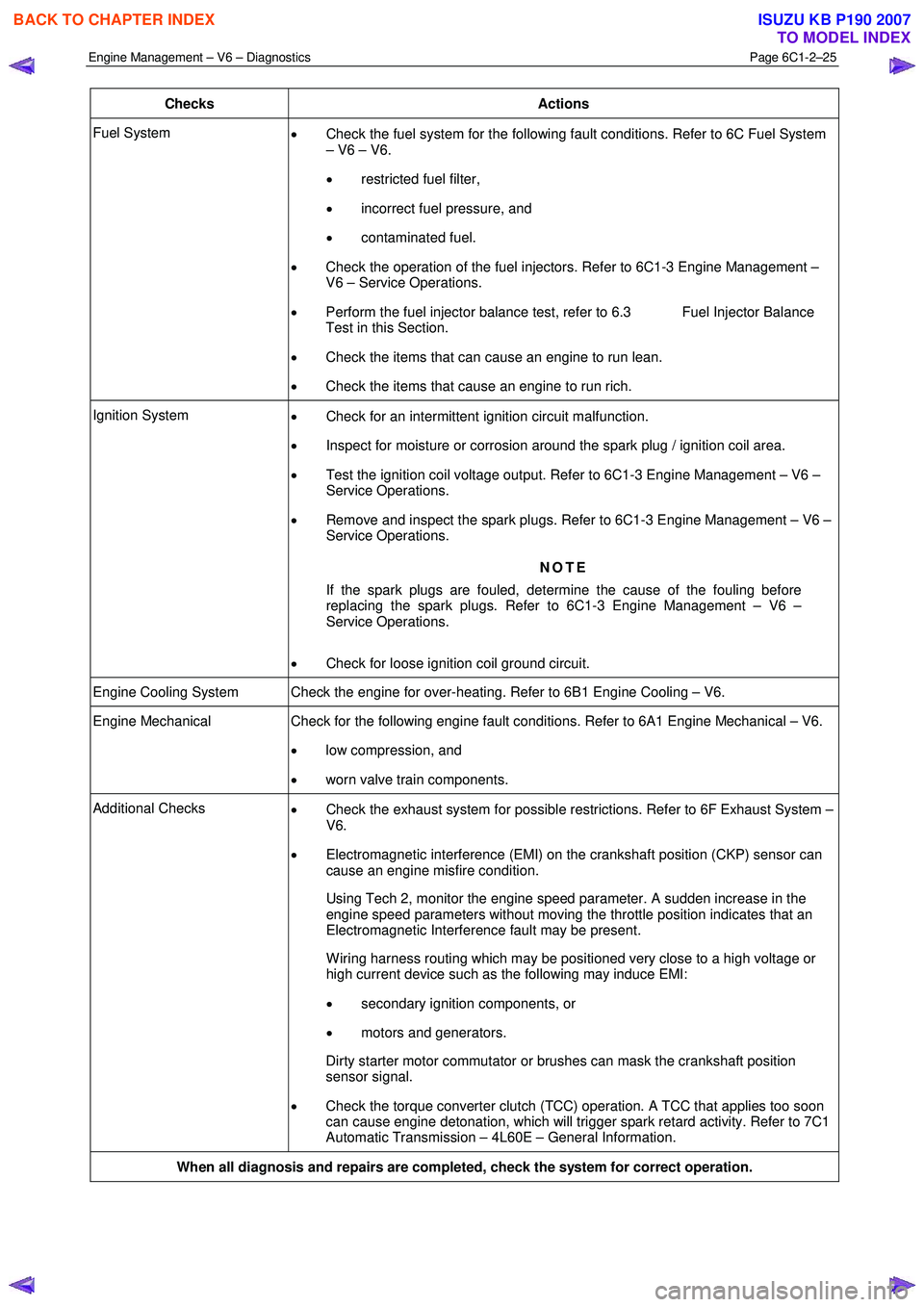
Checks Actions
Fuel System
• Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6 – V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check the items that can cause an engine to run lean.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
Ignition System
• Check for an intermittent ignition circuit malfunction.
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Cooling System Check the engine for over-heating. Refer to 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
Additional Checks
• Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to 6F Exhaust System –
V6.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
Electromagnetic Interference fault may be present.
W iring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, or
• motors and generators.
Dirty starter motor commutator or brushes can mask the crankshaft position sensor signal.
• Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. A TCC that applies too soon
can cause engine detonation, which will trigger spark retard activity. Refer to 7C1
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3304 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–26
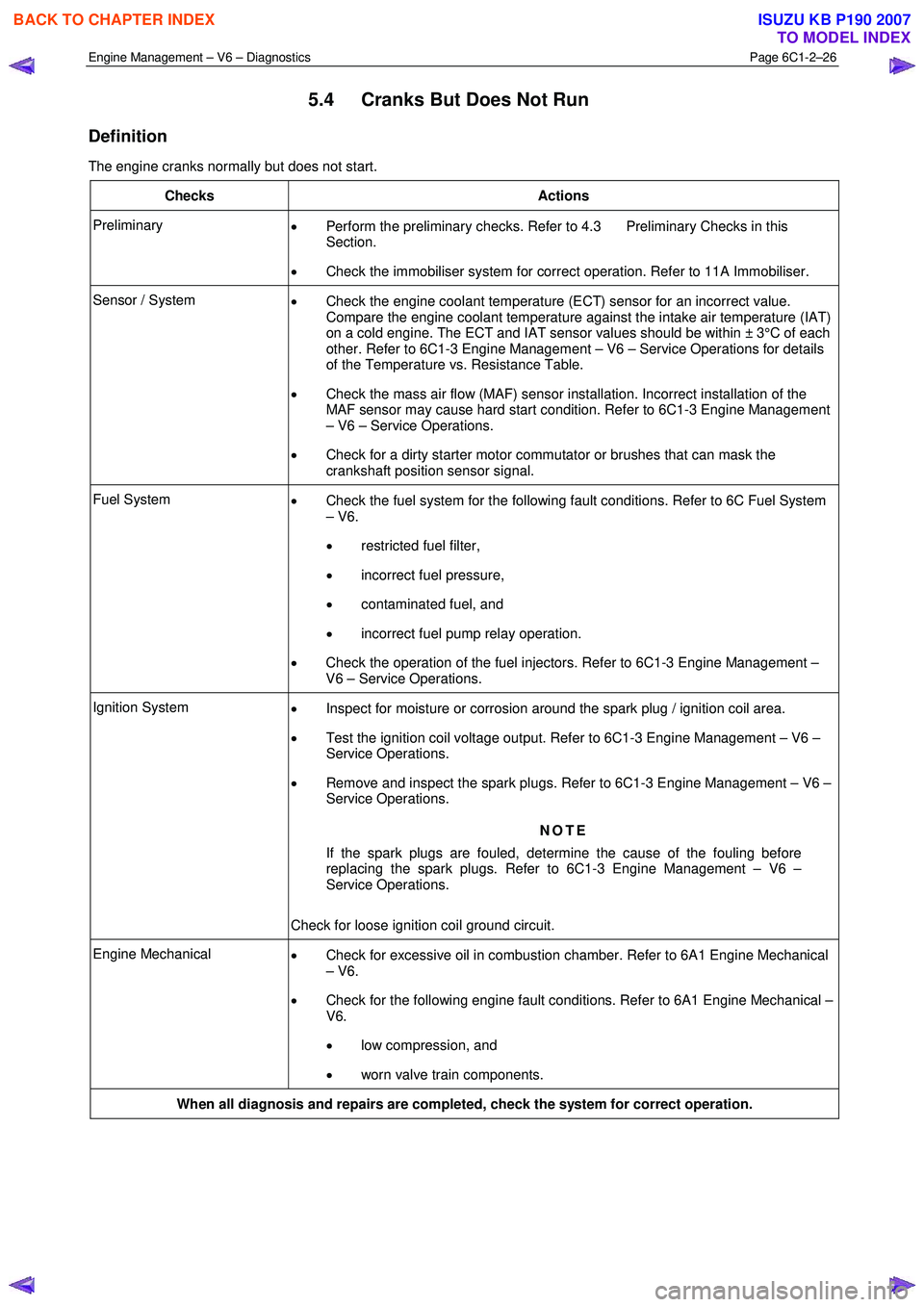
5.4 Cranks But Does Not Run
Definition
The engine cranks normally but does not start.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the immobiliser system for correct operation. Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
Sensor / System
• Check the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor for an incorrect value.
Compare the engine coolant temperature against the intake air temperature (IAT)
on a cold engine. The ECT and IAT sensor values should be within ± 3°C of each
other. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations for details
of the Temperature vs. Resistance Table.
• Check the mass air flow (MAF) sensor installation. Incorrect installation of the
MAF sensor may cause hard start condition. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Check for a dirty starter motor commutator or brushes that can mask the
crankshaft position sensor signal.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure,
• contaminated fuel, and
• incorrect fuel pump relay operation.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
Ignition System • Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Mechanical • Check for excessive oil in combustion chamber. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical
– V6.
• Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3305 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–27
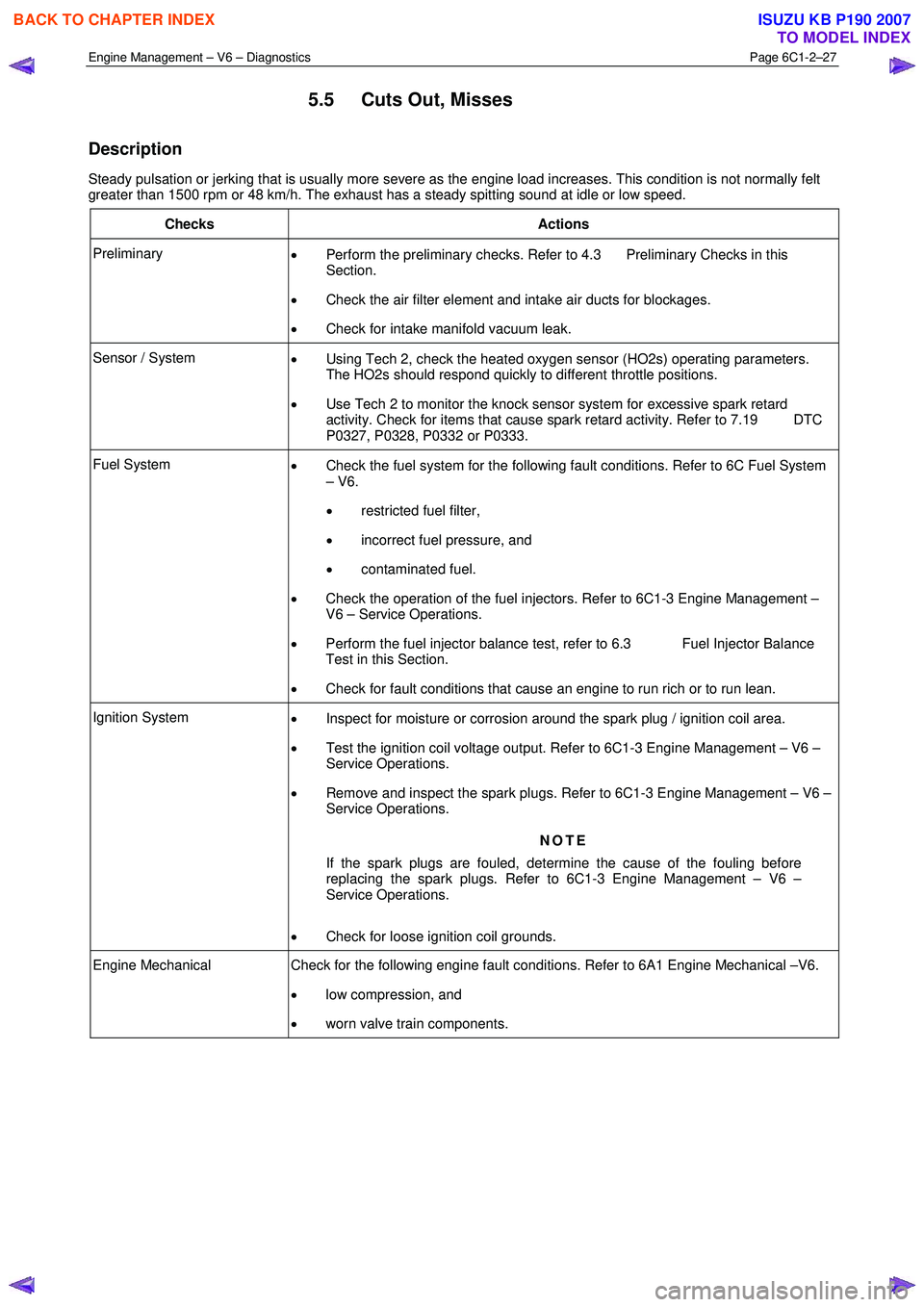
5.5 Cuts Out, Misses
Description
Steady pulsation or jerking that is usually more severe as the engine load increases. This condition is not normally felt
greater than 1500 rpm or 48 km/h. The exhaust has a steady spitting sound at idle or low speed.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
• Check for intake manifold vacuum leak.
Sensor / System
• Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters.
The HO2s should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard
activity. Check for items that cause spark retard activity. Refer to 7.19 DTC
P0327, P0328, P0332 or P0333.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check for fault conditions that cause an engine to run rich or to run lean.
Ignition System
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil grounds.
Engine Mechanical Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3307 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–29
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this Section.
Fuel System Inspect the injectors for leaking condition. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Engine Cooling System • Check for engine overheating. Refer to 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
• Check the engine thermostat for proper operation and correct heat range. Refer to
6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical • Check for build up of carbon deposit in the combustion chamber, which may
cause hot spots and increased compression ratio. Refer to 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• Using Tech 2, check for incorrect engine idle speed.
Additional
• If the engine continues to run after the ignition is switched off but the engine runs
normally, check the following:
• ignition switch operation,
• voltage feedback from alternator L terminal to ignition switch, and
• sticking ignition control relay.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.8 Hard Start
Definition
The engine cranks normally but takes longer to start than usual. As soon as the engine runs, the engine may stall
immediately.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the immobiliser system for correct operation. Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
Sensor / System
• Check the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor for an incorrect value.
Compare the engine coolant temperature against the intake air temperature (IAT)
on a cold engine. The ECT and IAT sensor values should be within ± 3°C of each
other. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations for details
of the Temperature vs. Resistance Table.
• Check the mass air flow (MAF) sensor installation. Incorrect installation of the
MAF sensor may cause hard start condition. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Test the resistance of the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor. The CKP sensor
resistance must be within 700 – 1,200 Ω at all temperatures.
• Check for dirty starter motor commutator or brushes that can mask the crankshaft
position sensor signal.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3308 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–30
Checks Actions
Ignition System
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Mechanical
• Check for excessive oil in combustion chamber. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical
– V6.
• Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.9 Hesitation, Sag and Stumble
Description
Momentary lack of response or hesitation as the accelerator is depressed. This condition is usually more severe when
first trying to make the vehicle move from a standing start but can occur at any vehicle speed.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
Sensor / System
• Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters.
The HO2s should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
• Inspect the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor harness connector for correct
connection. Poor connection of this connector will not set a DTC.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C Fuel System – V6.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check for fault conditions that cause an engine to run rich or to run lean.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007