2007 ISUZU KB P190 compression ratio
[x] Cancel search: compression ratioPage 1956 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-339
Fuel System ChecksInspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to Fuel System Check Chart
and appropriate procedure in the Fuel System section.
• Air in the fuel system.
• Water contamination in the fuel.
• Fuel waxing or icing.
• Fuel filter indicator lamp is continuously or frequently turned ON with engine run.
• External fuel leaks or high engine oil level.
• In-tank fuel pump operation. Refer to In-tank Fuel Pump System Check in this section.
• Fuel leak off from the fuel pressure limiter valve and fuel injectors.
• Fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel supply pump for being crushed, kinked, tightness, cracks and plugged.
• A plugged fuel tank vent valve and hose.
• Inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition.
• Fuel supply pump operation.
Notice: The fuel supply pump must be timed to the engine and adjustment value must
be learned to the ECM.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Injector Force Drive with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• Perform the Swirl Control Solenoid Test with a scan tool. Inspect the diaphragm valve operation when it commanded ON/ OFF.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
• Turbocharger wastegate valve operation. Refer to wastegate valve inspection in the Engine Mechanical section. (Standard output)
• Turbocharger nozzle control actuator operation. Refer to Turbocharger Control System Check in this section. (High output)
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Improper valve gap.
• Broken or weak valve springs.
• Worn camshaft lobes.
Additional Checks • Inspect the EGR system operating correctly. Refer to EGR Control System Check in
this section.
• Inspect for an engine overheat condition. Refer to Engine Cooling section.
• Inspect the A/C operation.
• Inspect the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. (A/T only)
Checks
Action
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1957 of 6020
6E-340 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Abnormal Combustion Noise
ChecksAction
Definition:
A mild to severe ping, usually worse under acceleration. The engine makes sharp metallic knocks that change with the throttle
opening.
Preliminary Checks • Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls.
• Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Inspect for smoke associated with the combustion noise.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the programmed fuel injector ID code for each cylinder.
• Inspect the Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletin.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the Scan Tool
Data List in this section.
• Compare the Coolant Temperature with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) parameters on a cold engine condition. If the difference among
temperature reading is more than 5 °C (9 °F) on a cold engine, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT may indicate
a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor parameter with the engine OFF. The FRP Sensor should read 0.9 to 1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1 minute. If not, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure and Desired Fuel Rail Pressure parameter between idle and W.O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) in Neutral. Fuel Rail Pressure
parameter should follow within ± 5 MPa ( ± 725 psi) quick enough.
• Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is tight and the sensor rotor is not damaged.
Fuel System Checks • If excessive smoke is present, check for a stuck open fuel injector. Inspect for fuel
leakage into the combustion chamber.
• Inspect the fuel injectors. Remove the injectors and visually inspect.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Injector Force Drive with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Incorrect basic engine parts such as camshaft, cylinder head, pistons, etc..
• Inspect for any excessive oil entering combustion chamber.
Additional Checks • Inspect other possible causes that can make similar noise such as loose component
parts, bracket, mount and weak clutch damper spring.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1959 of 6020
6E-342 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Air Intake System ChecksInspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• Perform the Swirl Control Solenoid Test with a scan tool. Inspect the diaphragm valve operation when it commanded ON/ OFF.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
• Turbocharger wastegate valve operation. Refer to wastegate valve inspection in the Engine Mechanical section. (Standard output)
• Turbocharger nozzle control actuator operation. Refer to Turbocharger Control System Check in this section. (High output)
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Improper valve gap.
• Broken or weak valve springs.
• Worn camshaft lobes.
Checks
Action
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1963 of 6020

6E-346 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Engine Mechanical ChecksInspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Improper mechanical timing (timing gear and timing chain).
• Improper valve gap.
• Broken or weak valve springs.
• Worn camshaft lobes.
• Thermostat working (open stuck).
• Any excessive oil entering combustion chamber.
Electrical System Checks • Glow plug control (preheating) system operation. Refer to Glow Control System
Check in this section.
Checks
Action
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2026 of 6020
6A-12 ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE)
Engine - General C24SE
Fuel system Electronically controlled Multi Port Fuel Injection System
Fuel pump type Electric
Fuel pressure kg/cm2 (psi/Pa) 3.4 (48.4/334)
Fuel filter type Cartridge paper element
Air cleaner type Dry paper element
Battery Type/V-Ax No. of units 34B19L/50D20L
Alternator
Capacity V-A(W ) 12-90 (1080), 12-100 (1200)
Starter
Output V-kW 1.4
Exhaust system CO Adjustment (1) Applicable to Open Loop System (Not equipped H2OS)
(2) Not applicable to Closed Loop System (Equipped H2OS)
Compression Ratio (with Tolerance) 9.6:1±0.25
Cylinder Head Material Aluminum Alloy (gravity cast)
Cylinder Block Material Cast Iron
No. of Mounting Points (including trans.) 3
Engine Installation Angles
-Longitudinal 4
° 60'
-Lateral 7° 50' (towards exhaust side)
Overall Dimensions (L ×
××
×
W ×
××
×
H):
- TF (2.4Litre/2W D)610×564 ×708mm
- TF (2.4Litre/4W D) 610×564 ×746mm
Engine Weight
Engine W eight
- TF (2.4Liter/Man) 140kg
Camshaft Type
SOHC
No. of Valves per Cylinder
- Inlet1
- Exhaust
1
Spark Plug Location Side
Port Arrangement Cross Flow
W orking Principle Spark Ignition 4-stroke
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2029 of 6020
ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE) 6A-15
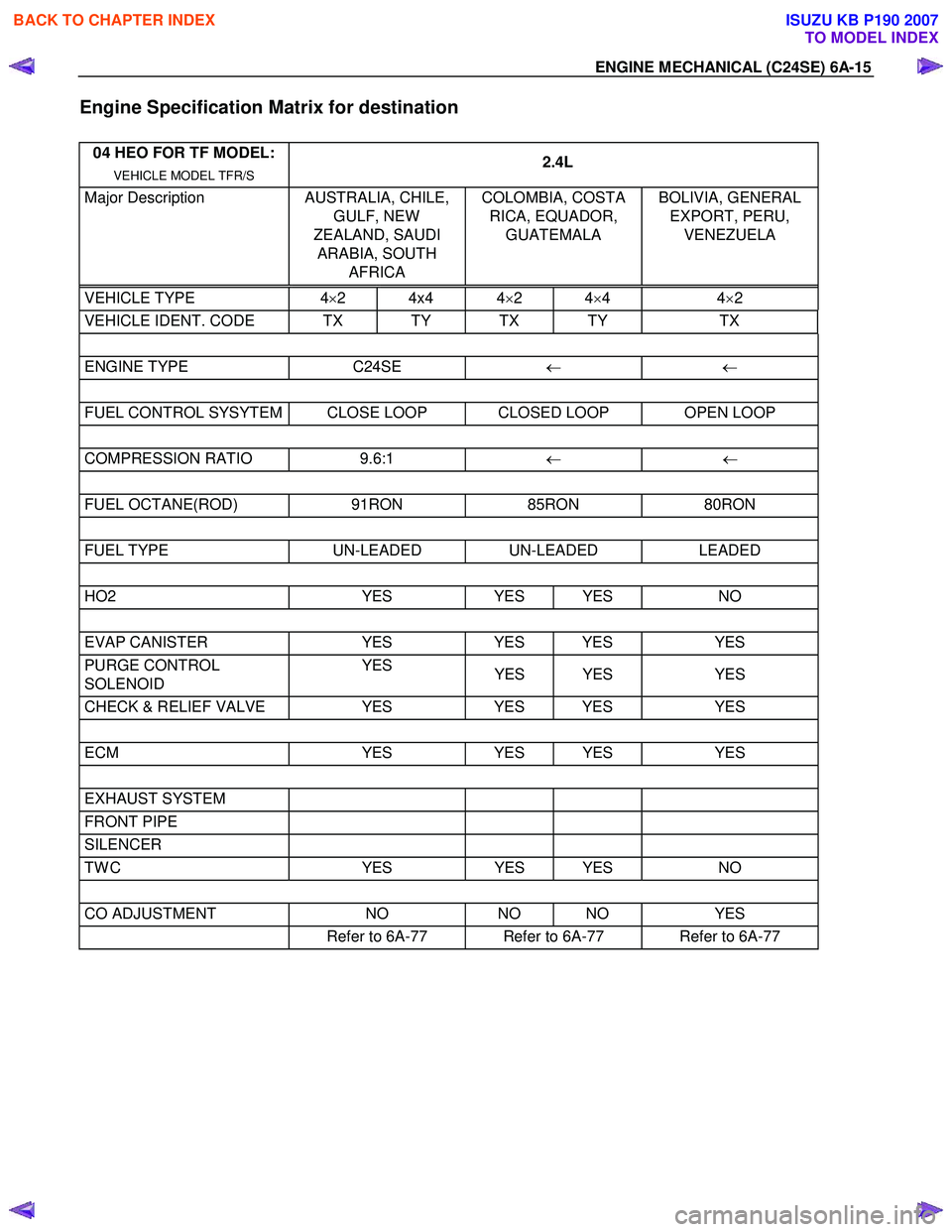
Engine Specification Matrix for destination
04 HEO FOR TF MODEL:
VEHICLE MODEL TFR/S 2.4L
Major Description
AUSTRALIA, CHILE,
GULF, NEW
ZEALAND, SAUDI ARABIA, SOUTH AFRICA COLOMBIA, COSTA
RICA, EQUADOR, GUATEMALA BOLIVIA, GENERAL
EXPORT, PERU, VENEZUELA
VEHICLE TYPE 4× 2 4x4 4 ×2 4 ×4 4 ×2
VEHICLE IDENT. CODE TX TY TX TY TX
ENGINE TYPE C24SE ← ←
FUEL CONTROL SYSYTEM CLOSE LOOP CLOSED LOOP OPEN LOOP
COMPRESSION RATIO 9.6:1 ← ←
FUEL OCTANE(ROD) 91RON 85RON 80RON
FUEL TYPE UN-LEADED UN-LEADED LEADED
HO2 YES YES YES NO
EVAP CANISTER YES YES YES YES
PURGE CONTROL
SOLENOID YES
YES YES YES
CHECK & RELIEF VALVE YES YES YES YES
ECM YES YES YES YES
EXHAUST SYSTEM
FRONT PIPE
SILENCER
TW C YES YES YES NO
CO ADJUSTMENT NO NO NO YES
Refer to 6A-77 Refer to 6A-77 Refer to 6A-77
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2408 of 6020
6E–238 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
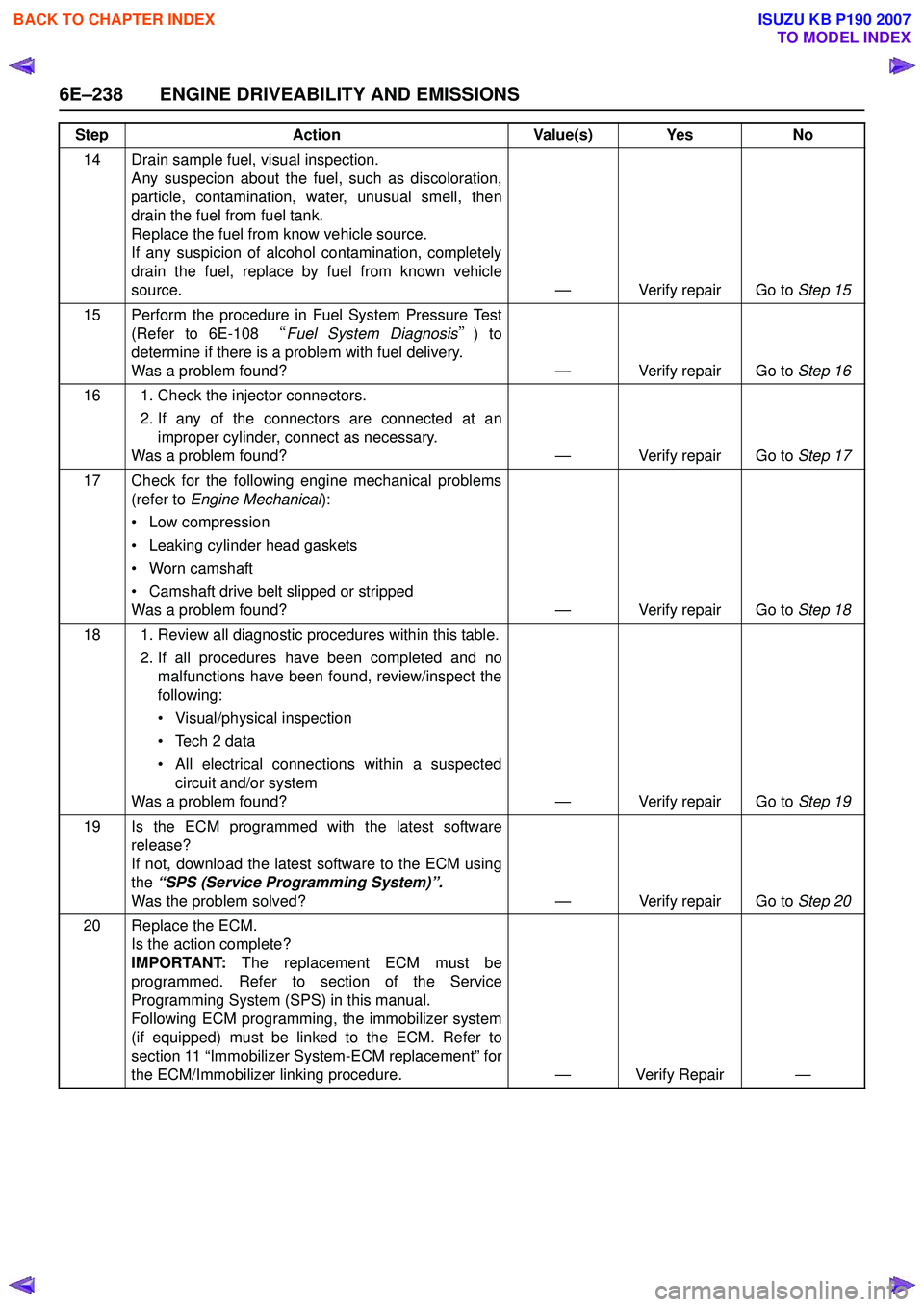
14 Drain sample fuel, visual inspection.Any suspecion about the fuel, such as discoloration,
particle, contamination, water, unusual smell, then
drain the fuel from fuel tank.
Replace the fuel from know vehicle source.
If any suspicion of alcohol contamination, completely
drain the fuel, replace by fuel from known vehicle
source. — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 Perform the procedure in Fuel System Pressure Test (Refer to 6E-108 “Fuel System Diagnosis ”) to
determine if there is a problem with fuel delivery.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 1. Check the injector connectors. 2. If any of the connectors are connected at animproper cylinder, connect as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 Check for the following engine mechanical problems (refer to Engine Mechanical ):
• Low compression
• Leaking cylinder head gaskets
• Worn camshaft
• Camshaft drive belt slipped or stripped
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 18
18 1. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table. 2. If all procedures have been completed and nomalfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
• Visual/physical inspection
• Tech 2 data
• All electrical connections within a suspected circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 19
19 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 20
20 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify Repair —
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2422 of 6020
6E–252 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
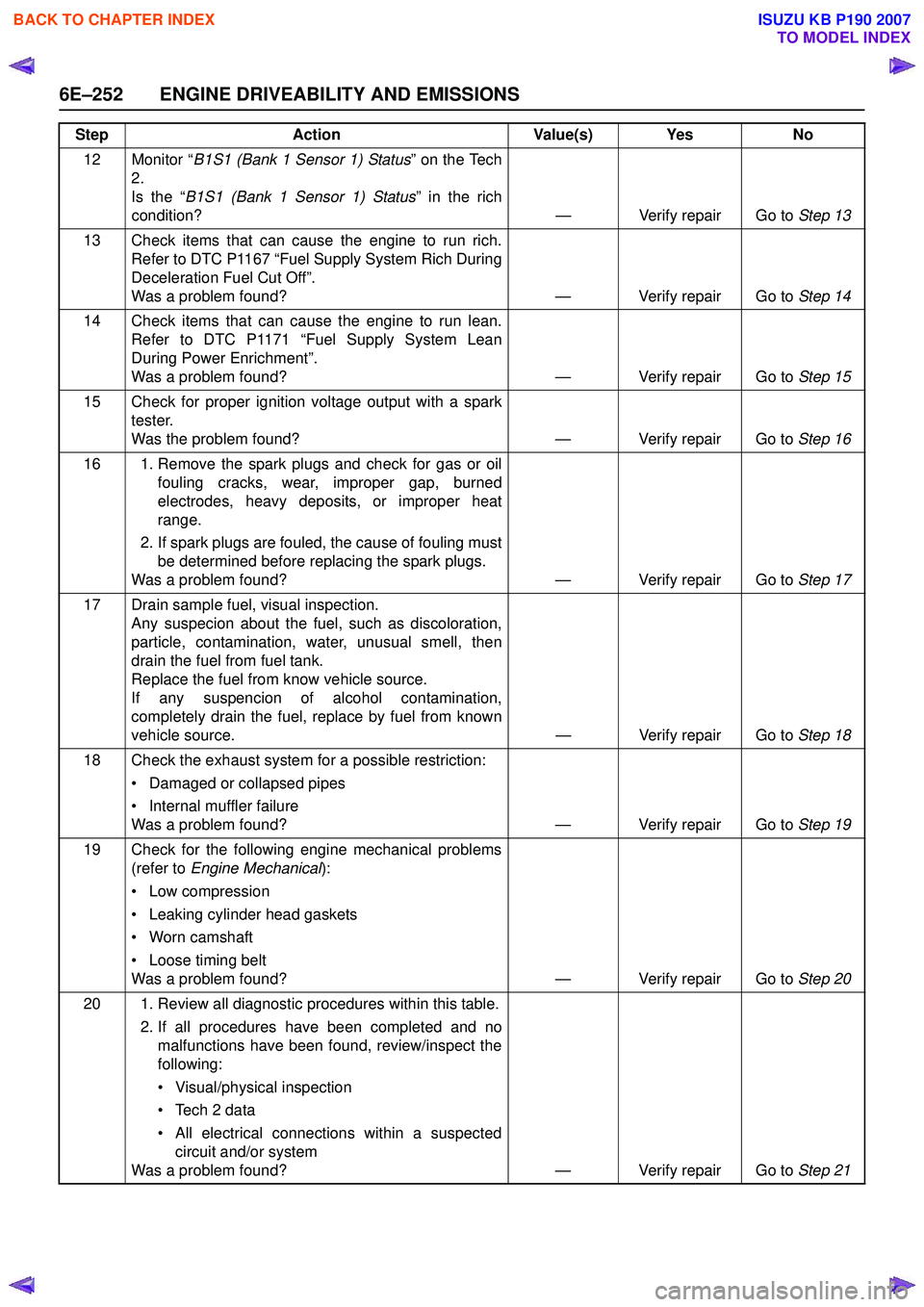
12 Monitor “B1S1 (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Status ” on the Tech
2.
Is the “ B1S1 (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Status ” in the rich
condition? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 Check items that can cause the engine to run rich. Refer to DTC P1167 “Fuel Supply System Rich During
Deceleration Fuel Cut Off”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 14
14 Check items that can cause the engine to run lean. Refer to DTC P1171 “Fuel Supply System Lean
During Power Enrichment”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 Check for proper ignition voltage output with a spark tester.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 1. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil fouling cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposits, or improper heat
range.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 Drain sample fuel, visual inspection. Any suspecion about the fuel, such as discoloration,
particle, contamination, water, unusual smell, then
drain the fuel from fuel tank.
Replace the fuel from know vehicle source.
If any suspencion of alcohol contamination,
completely drain the fuel, replace by fuel from known
vehicle source. — Verify repair Go to Step 18
18 Check the exhaust system for a possible restriction: • Damaged or collapsed pipes
• Internal muffler failure
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 19
19 Check for the following engine mechanical problems (refer to Engine Mechanical ):
• Low compression
• Leaking cylinder head gaskets
• Worn camshaft
• Loose timing belt
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 20
20 1. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table. 2. If all procedures have been completed and nomalfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
• Visual/physical inspection
• Tech 2 data
• All electrical connections within a suspected circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 21
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007