2007 ISUZU KB P190 compression ratio
[x] Cancel search: compression ratioPage 3310 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–32
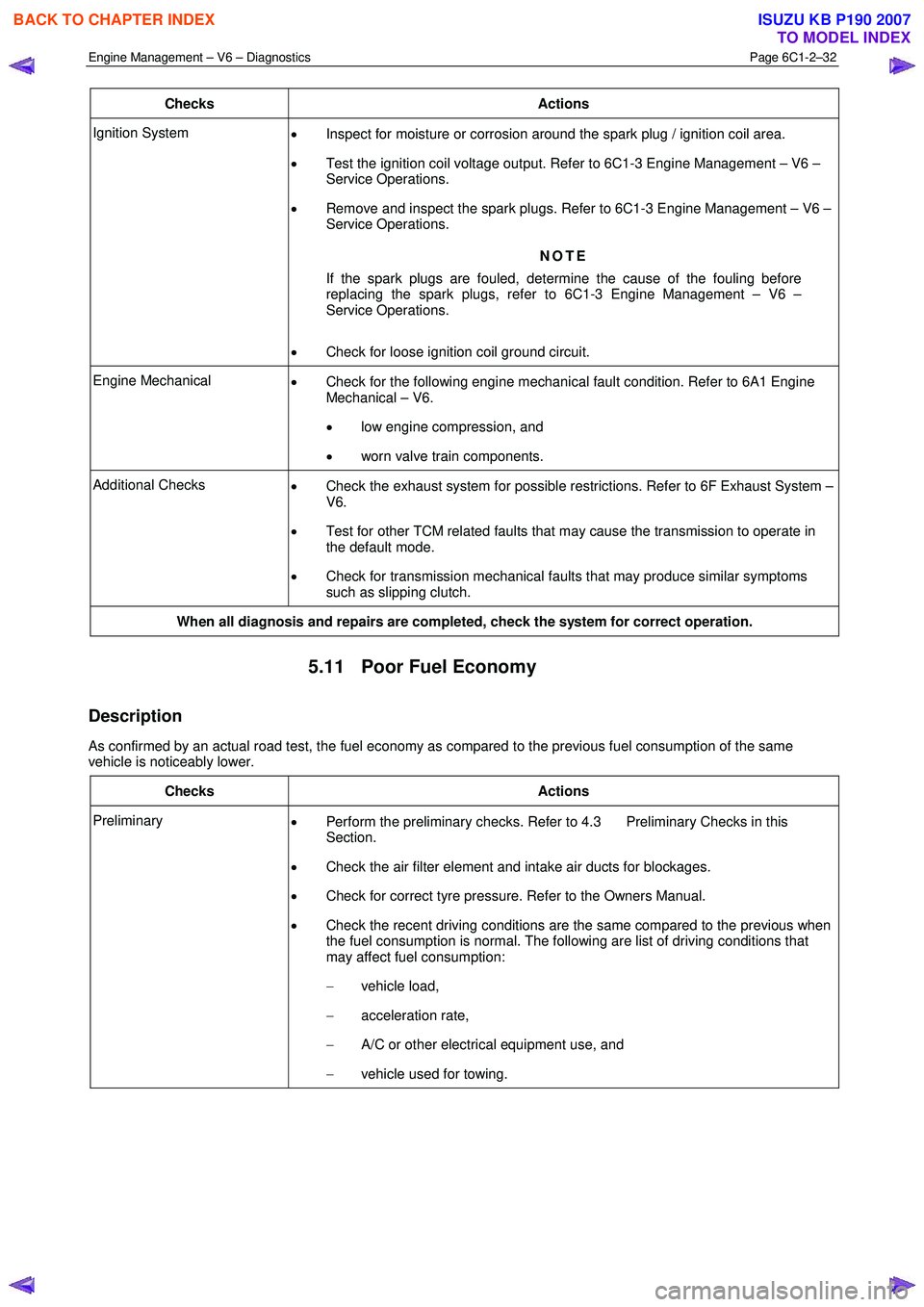
Checks Actions
Ignition System
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Mechanical
• Check for the following engine mechanical fault condition. Refer to 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• low engine compression, and
• worn valve train components.
Additional Checks
• Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to 6F Exhaust System –
V6.
• Test for other TCM related faults that may cause the transmission to operate in
the default mode.
• Check for transmission mechanical faults that may produce similar symptoms
such as slipping clutch.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.11 Poor Fuel Economy
Description
As confirmed by an actual road test, the fuel economy as compared to the previous fuel consumption of the same
vehicle is noticeably lower.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
• Check for correct tyre pressure. Refer to the Owners Manual.
• Check the recent driving conditions are the same compared to the previous when
the fuel consumption is normal. The following are list of driving conditions that
may affect fuel consumption:
− vehicle load,
− acceleration rate,
− A/C or other electrical equipment use, and
− vehicle used for towing.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3311 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–33
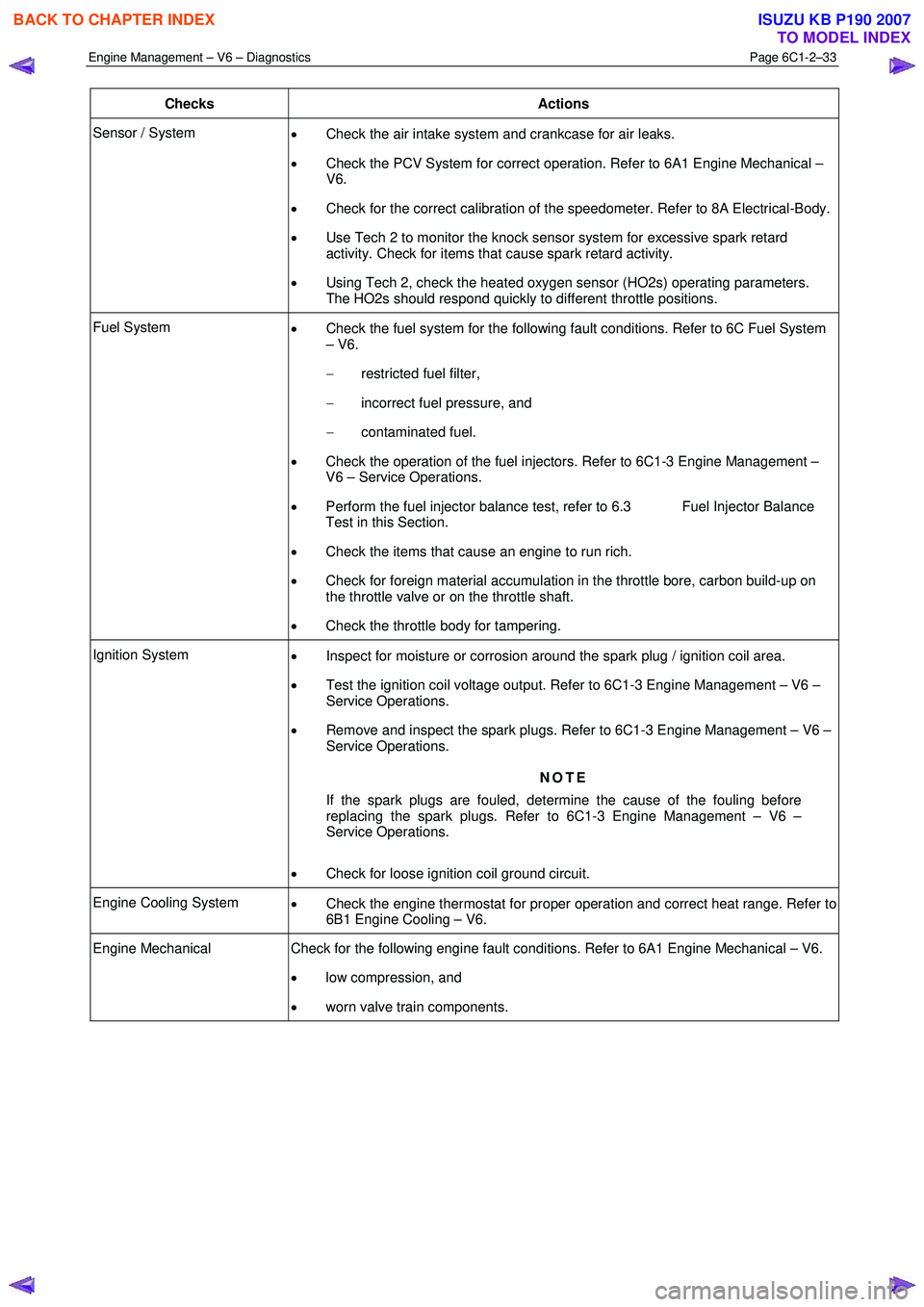
Checks Actions
Sensor / System
• Check the air intake system and crankcase for air leaks.
• Check the PCV System for correct operation. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• Check for the correct calibration of the speedometer. Refer to 8A Electrical-Body.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard
activity. Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
• Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters.
The HO2s should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
− restricted fuel filter,
− incorrect fuel pressure, and
− contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
• Check for foreign material accumulation in the throttle bore, carbon build-up on
the throttle valve or on the throttle shaft.
• Check the throttle body for tampering.
Ignition System
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Cooling System
• Check the engine thermostat for proper operation and correct heat range. Refer to
6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3313 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–35
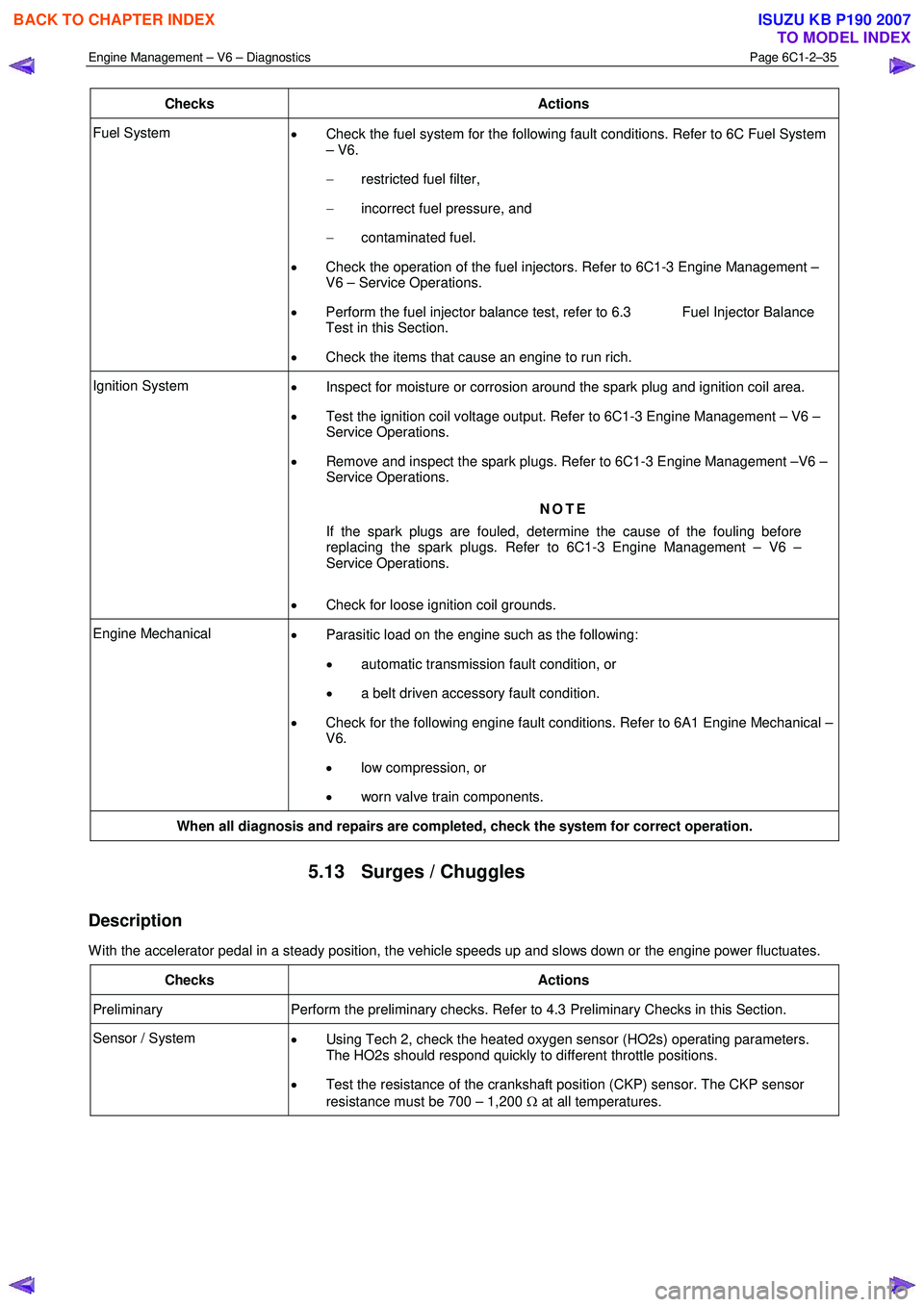
Checks Actions
Fuel System
• Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
− restricted fuel filter,
− incorrect fuel pressure, and
− contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
Ignition System
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug and ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil grounds.
Engine Mechanical
• Parasitic load on the engine such as the following:
• automatic transmission fault condition, or
• a belt driven accessory fault condition.
• Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• low compression, or
• worn valve train components.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.13 Surges / Chuggles
Description
W ith the accelerator pedal in a steady position, the vehicle speeds up and slows down or the engine power fluctuates.
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this Section.
Sensor / System
• Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters.
The HO2s should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
• Test the resistance of the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor. The CKP sensor
resistance must be 700 – 1,200 Ω at all temperatures.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3390 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–112
Step Action Yes No
5 Test the appropriate KS signal circuit and low reference circuit for a
high resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage or
shorted together fault condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and
Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
6 Replace the faulty KS. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 7 —
7 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the knock sensor circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 8
8 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.20 DTC P0335, P0336, P0337 or P0338
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0335 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0336 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Signal Range / Performance
• DTC P0337 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low Duty Cycle
• DTC P0338 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit High Duty Cycle
Circuit Description
The ECM applies the ground to the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor low reference circuit.
The CKP sensor in conjunction with the 58X reluctor wheel generates an AC signal voltage. The amplitude and
frequency of the signal generated is proportional to the engine speed. The ECM uses this signal from the CKP sensor
signal circuit to determine the engine rpm
In addition, the CKP sensor sends a signal to the ECM when piston No. 1 and piston No. 4 are at the top dead centre
position. The ECM monitors both the CKP signal and the camshaft position (CMP) sensor signal to determine the
compression stroke of piston No. 1.
A CKP sensor DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the CKP sensor signal circuit.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0335
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine is cranking or running.
• The ECM detects greater than 8 CMP sensor pulses.
DTC P0336
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3753 of 6020

Exhaust System – V6 Page 6F – 5
Service Notes
1. Vehicles fitted with catalytic converters should not be operated with leaded petrol. Lead will contaminate
the ceramic monolith.
2. Do not drop the catalytic converter as it will damage the ceramic monolith.
3. Replace the catalytic converter if it is damaged.
4. Do not allow water, oil or fuel to enter the converter as the ceramic monolith will be contaminated.
5. Do not use engine and/or fuel additives unless approved by General Motors. Many additives contain phosphorous that will contaminate the ceramic monolith.
6. The vehicle must not be started by pushing or towing, as unburned fuel could reach the catalytic converter and destroy the ceramic monolith. Always use jumper leads to start a vehicle that has a flat or
defective battery.
7. W hen carrying out a compression test, for V6 engines use Tech 2 to ensure the output control Engine Compression Test is set to enable, refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical. This prevents fuel injection and
ignition during engine cranking.
8. Do not drive the vehicle with the engine misfiring or with any of the spark plug leads disconnected, as the catalytic converter will overheat.
9. Do not coast downhill with the engine misfiring or with any of the spark plug leads disconnected.
10. The catalytic converter is serviceable as part of the front exhaust assembly only. Refer to the service operations in this section for details of front exhaust pipe assembly removal and reinstallation.
11. The exhaust flange gaskets must be replaced whenever a new exhaust pipe, muffler or catalytic converter is installed.
1.3 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
1.1 Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is
ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3772 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–12
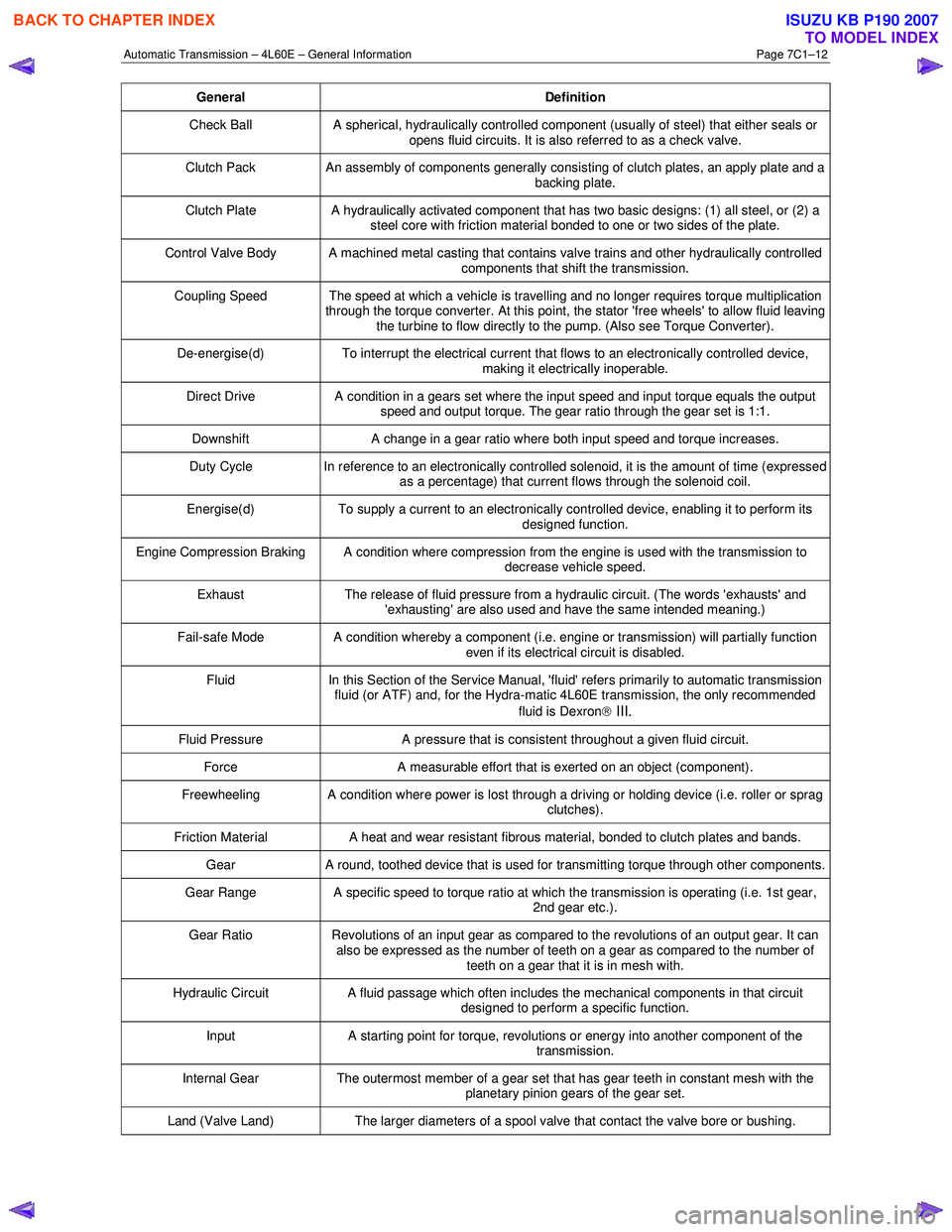
General Definition
Check Ball A spherical, hydraulically controlled component (usually of steel) that either seals or
opens fluid circuits. It is also referred to as a check valve.
Clutch Pack An assembly of components generally consisting of clutch plates, an apply plate and a
backing plate.
Clutch Plate A hydraulically activated component that has two basic designs: (1) all steel, or (2) a
steel core with friction material bonded to one or two sides of the plate.
Control Valve Body A machined metal casting that contains valve trains and other hydraulically controlled components that shift the transmission.
Coupling Speed The speed at which a vehicle is travelling and no longer requires torque multiplication through the torque converter. At this point, the stator 'free wheels' to allow fluid leaving
the turbine to flow directly to the pump. (Also see Torque Converter).
De-energise(d) To interrupt the electrical current that flows to an electronically controlled device,
making it electrically inoperable.
Direct Drive A condition in a gears set where the input speed and input torque equals the output
speed and output torque. The gear ratio through the gear set is 1:1.
Downshift A change in a gear ratio where both input speed and torque increases.
Duty Cycle In reference to an electronically controlled solenoid, it is the amount of time (expressed
as a percentage) that current flows through the solenoid coil.
Energise(d) To supply a current to an electronically controlled device, enabling it to perform its
designed function.
Engine Compression Braking A condition where compression from the engine is used with the transmission to decrease vehicle speed.
Exhaust The release of fluid pressure from a hydraulic circuit. (The words 'exhausts' and
'exhausting' are also used and have the same intended meaning.)
Fail-safe Mode A condition whereby a component (i.e. engine or transmission) will partially function even if its electrical circuit is disabled.
Fluid In this Section of the Service Manual, 'fluid' refers primarily to automatic transmission
fluid (or ATF) and, for the Hydra-matic 4L60E transmission, the only recommended
fluid is Dexron
III.
Fluid Pressure A pressure that is consistent throughout a given fluid circuit.
Force A measurable effort that is exerted on an object (component).
Freewheeling A condition where power is lost through a driving or holding device (i.e. roller or sprag
clutches).
Friction Material A heat and wear resistant fibrous material, bonded to clutch plates and bands.
Gear A round, toothed device that is used for transmitting torque through other components.
Gear Range A specific speed to torque ratio at which the transmission is operating (i.e. 1st gear,
2nd gear etc.).
Gear Ratio Revolutions of an input gear as compared to the revolutions of an output gear. It can
also be expressed as the number of teeth on a gear as compared to the number of
teeth on a gear that it is in mesh with.
Hydraulic Circuit A fluid passage which often includes the mechanical components in that circuit
designed to perform a specific function.
Input A starting point for torque, revolutions or energy into another component of the
transmission.
Internal Gear The outermost member of a gear set that has gear teeth in constant mesh with the
planetary pinion gears of the gear set.
Land (Valve Land) The larger diameters of a spool valve that contact the valve bore or bushing.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007