2007 ISUZU KB P190 Electrical
[x] Cancel search: ElectricalPage 3460 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–182
• The APP sensor 1 signal voltage increases from 1 V at rest position to greater than 4 V when the accelerator
pedal is fully depressed.
• The APP sensor 2 signal voltage increases from 0.5 V at rest position to greater than 2 V when the accelerator
pedal is fully depressed.
The ECM monitors and evaluates the APP sensors signal voltage along with other sensor inputs to determine the
desired throttle opening. An APP sensor circuit DTC sets if the signal voltage of the APP sensor is outside the
predetermined range.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and P2138 runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is greater than 7 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2122
The ECM determines the APP sensor 1 signal voltage is less than 0.84 V.
DTC P2123
The ECM determines the APP sensor 1 signal voltage is greater than 4.82 V.
DTC P2127
The ECM determines the APP sensor 2 signal voltage is less than 0.66 V.
DTC P2128
The ECM determines the APP sensor 2 signal voltage is greater than 4.82 V.
DTC P2138
The ECM detects the difference between the APP sensor 1 and sensor 2 signal voltage is greater than the
predetermined value.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The APP sensor circuit DTCs are Type ‘A’ DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when a Type ‘A’ DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type ‘A’ DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the APP sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 Tests the APP sensor internal circuits throughout its range of motion. If the DTC fails while performing this test, there is an internal fault condition in the APP sensor internal circuitry.
5 Measures the integrity of the TP sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the ECM Fuse 29 enables the ECM to power down completely prior to the test procedure.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3461 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–183
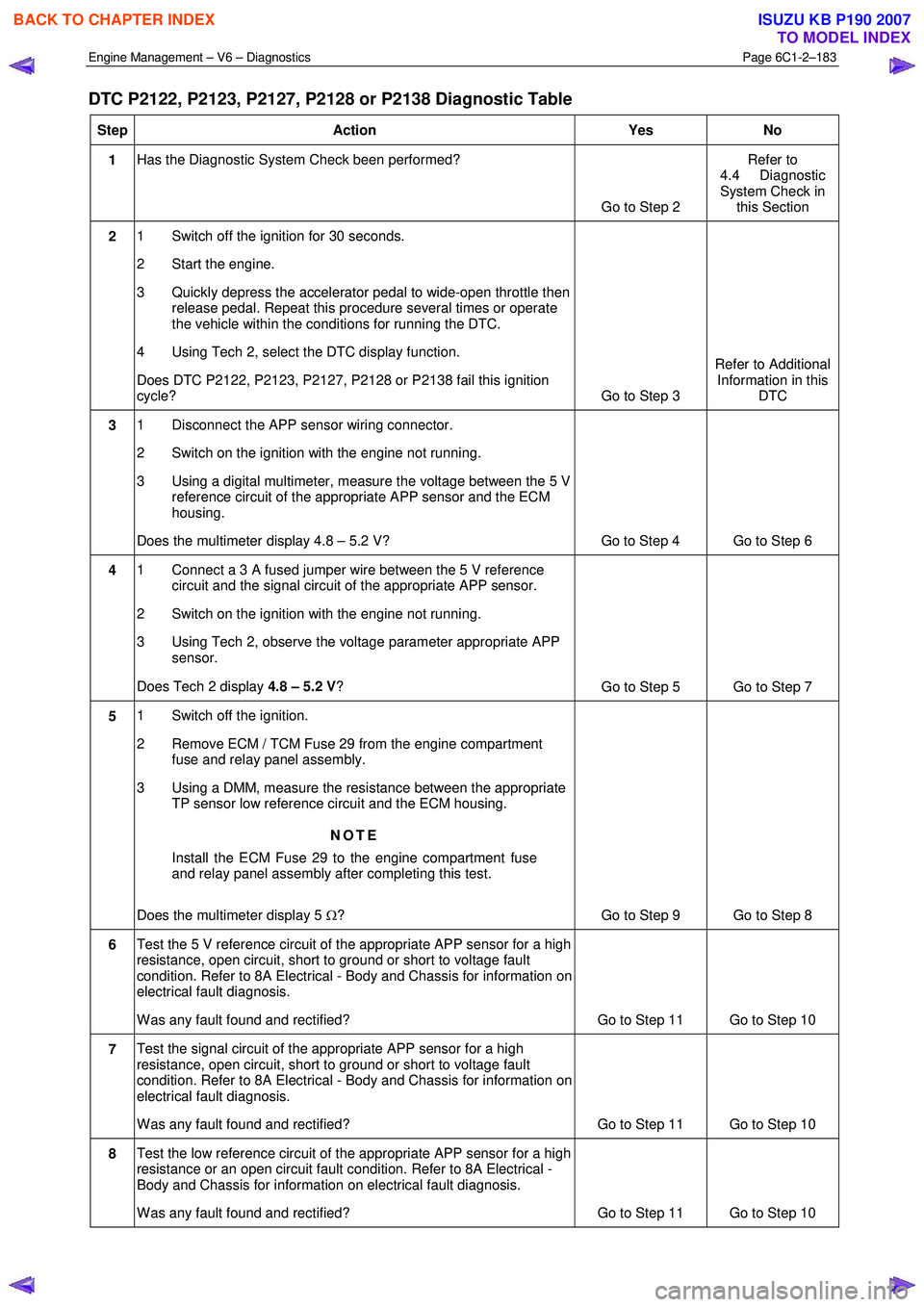
DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 or P2138 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Quickly depress the accelerator pedal to wide-open throttle then release pedal. Repeat this procedure several times or operate
the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
4 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 or P2138 fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 1 Disconnect the APP sensor wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the 5 V reference circuit of the appropriate APP sensor and the ECM
housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4 1 Connect a 3 A fused jumper wire between the 5 V reference
circuit and the signal circuit of the appropriate APP sensor.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using Tech 2, observe the voltage parameter appropriate APP sensor.
Does Tech 2 display 4.8 – 5.2 V ?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM / TCM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse and relay panel assembly.
3 Using a DMM, measure the resistance between the appropriate TP sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
6 Test the 5 V reference circuit of the appropriate APP sensor for a high
resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault
condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on
electrical fault diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
7 Test the signal circuit of the appropriate APP sensor for a high
resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault
condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on
electrical fault diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
8 Test the low reference circuit of the appropriate APP sensor for a high
resistance or an open circuit fault condition. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3465 of 6020
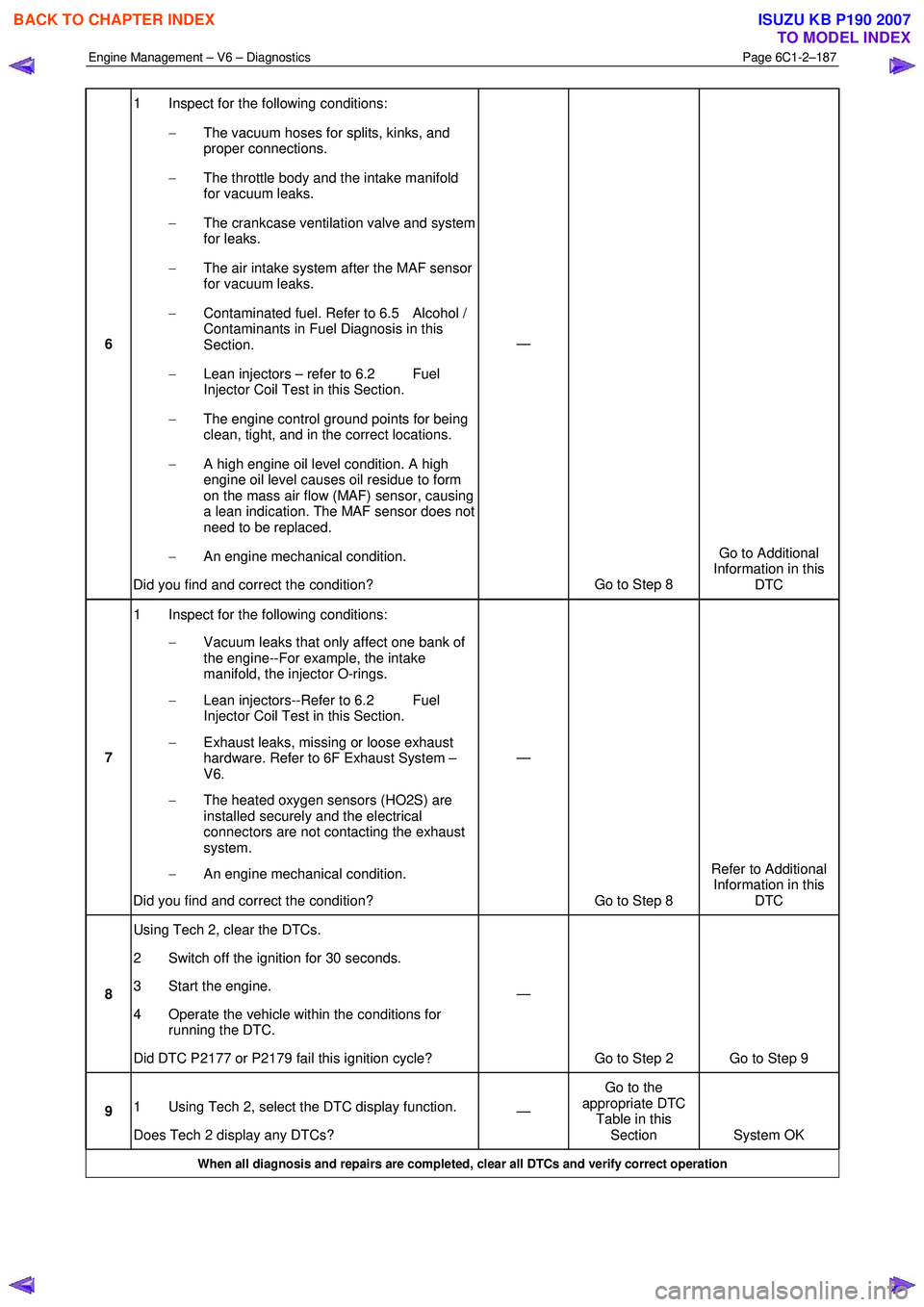
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–187
6 1 Inspect for the following conditions:
− The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and
proper connections.
− The throttle body and the intake manifold
for vacuum leaks.
− The crankcase ventilation valve and system
for leaks.
− The air intake system after the MAF sensor
for vacuum leaks.
− Contaminated fuel. Refer to 6.5 Alcohol /
Contaminants in Fuel Diagnosis in this
Section.
− Lean injectors – refer to 6.2 Fuel
Injector Coil Test in this Section.
− The engine control ground points for being
clean, tight, and in the correct locations.
− A high engine oil level condition. A high
engine oil level causes oil residue to form
on the mass air flow (MAF) sensor, causing
a lean indication. The MAF sensor does not
need to be replaced.
− An engine mechanical condition.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 8 Go to Additional
Information in this DTC
7 1 Inspect for the following conditions:
− Vacuum leaks that only affect one bank of
the engine--For example, the intake
manifold, the injector O-rings.
− Lean injectors--Refer to 6.2 Fuel
Injector Coil Test in this Section.
− Exhaust leaks, missing or loose exhaust
hardware. Refer to 6F Exhaust System –
V6.
− The heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) are
installed securely and the electrical
connectors are not contacting the exhaust
system.
− An engine mechanical condition.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 8 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
8 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Did DTC P2177 or P2179 fail this ignition cycle? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Step 9
9 1 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? —
Go to the
appropriate DTC Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and verify correct operation
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3467 of 6020
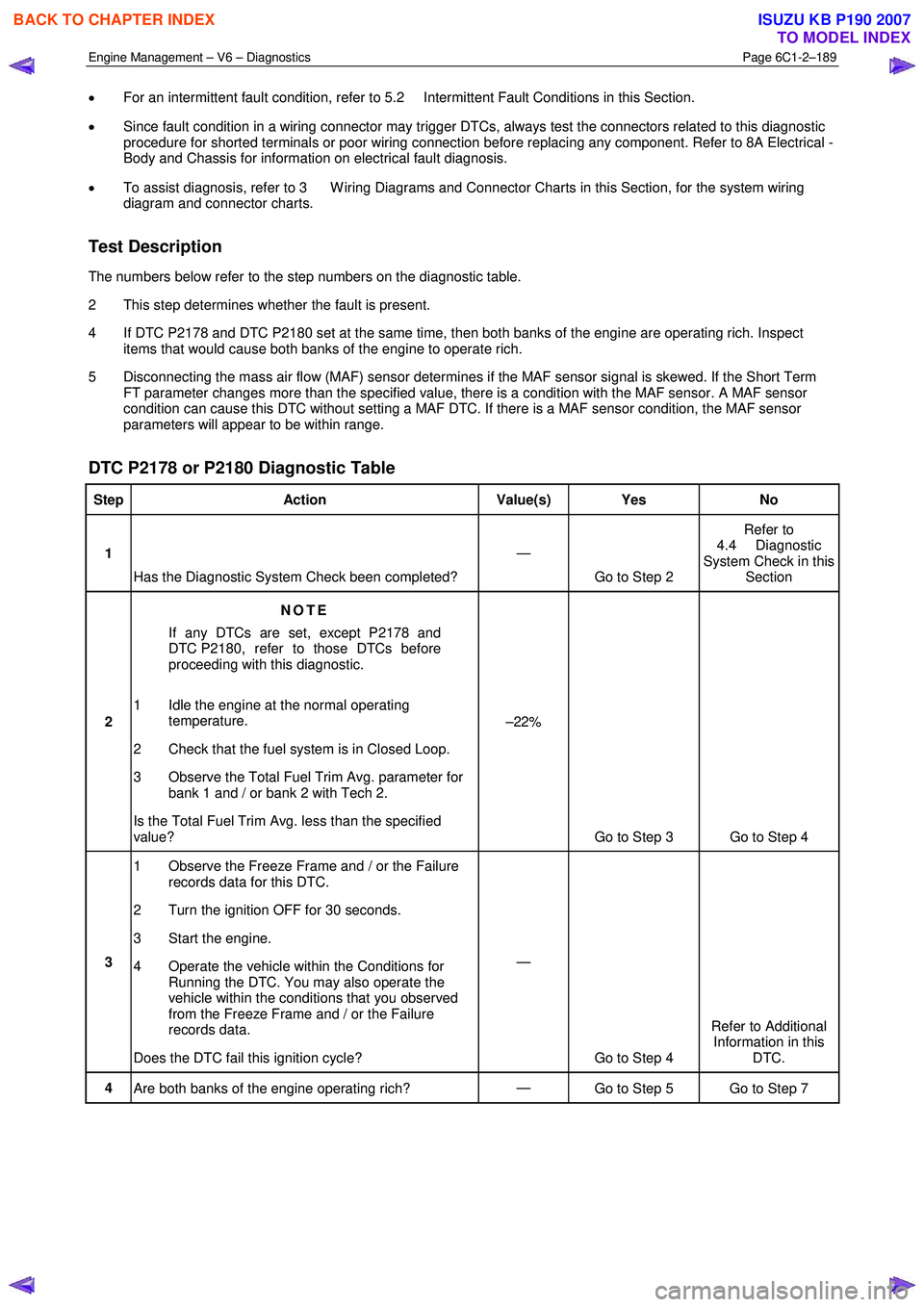
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–189
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
2 This step determines whether the fault is present.
4 If DTC P2178 and DTC P2180 set at the same time, then both banks of the engine are operating rich. Inspect items that would cause both banks of the engine to operate rich.
5 Disconnecting the mass air flow (MAF) sensor determines if the MAF sensor signal is skewed. If the Short Term FT parameter changes more than the specified value, there is a condition with the MAF sensor. A MAF sensor
condition can cause this DTC without setting a MAF DTC. If there is a MAF sensor condition, the MAF sensor
parameters will appear to be within range.
DTC P2178 or P2180 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been completed? —
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 NOTE
If any DTCs are set, except P2178 and
DTC P2180, refer to those DTCs before
proceeding with this diagnostic.
1 Idle the engine at the normal operating temperature.
2 Check that the fuel system is in Closed Loop.
3 Observe the Total Fuel Trim Avg. parameter for bank 1 and / or bank 2 with Tech 2.
Is the Total Fuel Trim Avg. less than the specified
value? –22%
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 1 Observe the Freeze Frame and / or the Failure
records data for this DTC.
2 Turn the ignition OFF for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for Running the DTC. You may also operate the
vehicle within the conditions that you observed
from the Freeze Frame and / or the Failure
records data.
Does the DTC fail this ignition cycle? —
Go to Step 4 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC.
4 Are both banks of the engine operating rich? —
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3470 of 6020
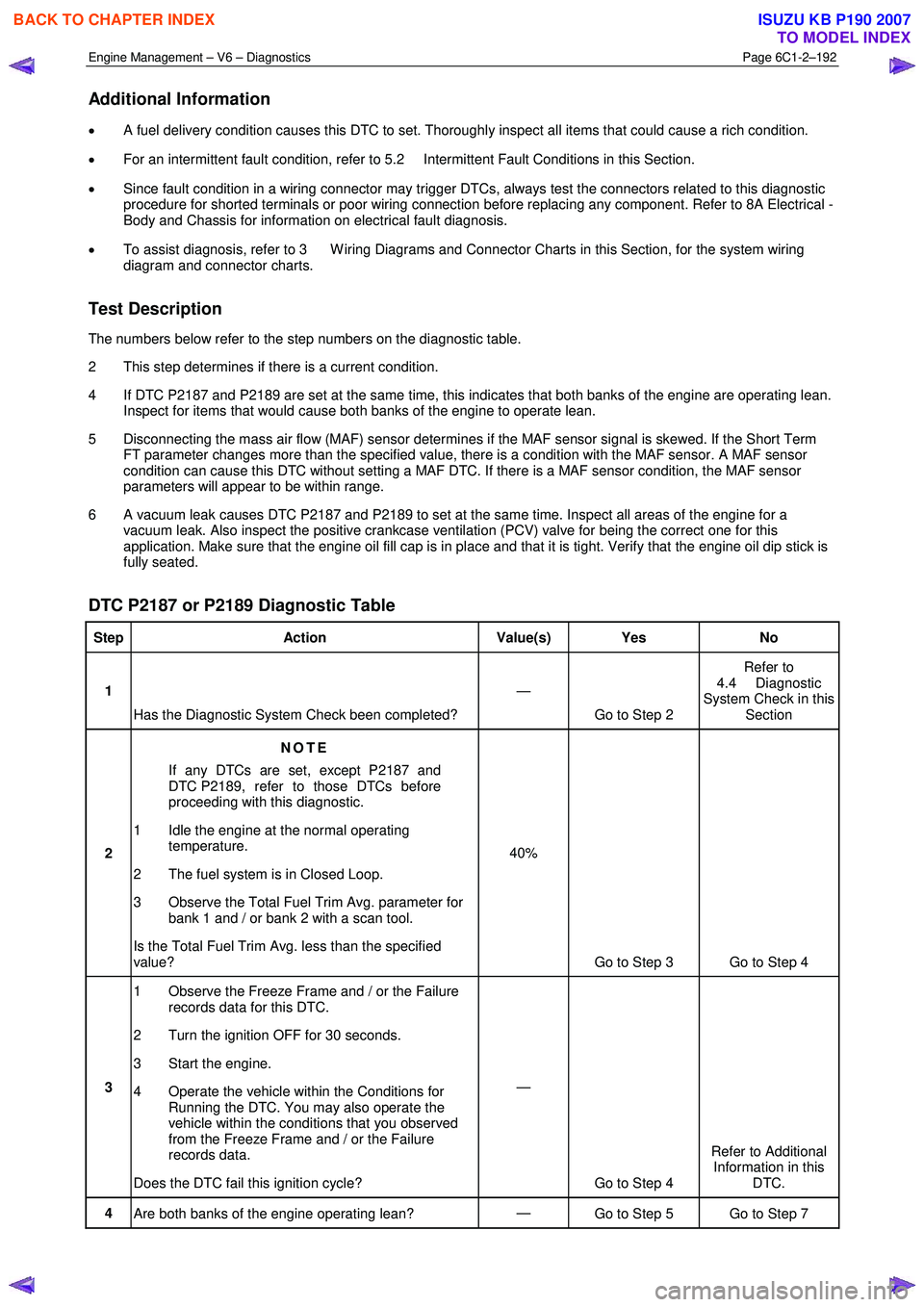
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–192
Additional Information
• A fuel delivery condition causes this DTC to set. Thoroughly inspect all items that could cause a rich condition.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
2 This step determines if there is a current condition.
4 If DTC P2187 and P2189 are set at the same time, this indicates that both banks of the engine are operating lean. Inspect for items that would cause both banks of the engine to operate lean.
5 Disconnecting the mass air flow (MAF) sensor determines if the MAF sensor signal is skewed. If the Short Term FT parameter changes more than the specified value, there is a condition with the MAF sensor. A MAF sensor
condition can cause this DTC without setting a MAF DTC. If there is a MAF sensor condition, the MAF sensor
parameters will appear to be within range.
6 A vacuum leak causes DTC P2187 and P2189 to set at the same time. Inspect all areas of the engine for a vacuum leak. Also inspect the positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve for being the correct one for this
application. Make sure that the engine oil fill cap is in place and that it is tight. Verify that the engine oil dip stick is
fully seated.
DTC P2187 or P2189 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been completed? —
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 NOTE
If any DTCs are set, except P2187 and
DTC P2189, refer to those DTCs before
proceeding with this diagnostic.
1 Idle the engine at the normal operating temperature.
2 The fuel system is in Closed Loop.
3 Observe the Total Fuel Trim Avg. parameter for bank 1 and / or bank 2 with a scan tool.
Is the Total Fuel Trim Avg. less than the specified
value? 40%
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 1 Observe the Freeze Frame and / or the Failure
records data for this DTC.
2 Turn the ignition OFF for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for Running the DTC. You may also operate the
vehicle within the conditions that you observed
from the Freeze Frame and / or the Failure
records data.
Does the DTC fail this ignition cycle? —
Go to Step 4 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC.
4 Are both banks of the engine operating lean? —
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3471 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–193
5 1 Start the engine.
NOTE
Additional DTCs will set when the MAF
sensor is disconnected.
2 Disconnect the mass air flow (MAF) sensor harness connector while the engine is operating.
3 Observe the Short Term FT parameter for bank 1 and bank 2 with Tech 2.
4 Reconnect the MAF sensor after completing this step.
Does the Short Term FT parameter for both banks of
the engine change more than the specified value with
the MAF sensor disconnected? 20%
Go to 7.6
DTC
P0101, P0102 or P0103 in this Section Go to Step 6
6 1 Inspect for the following conditions:
− Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections.
− The throttle body and the intake manifold
for vacuum leaks.
− The crankcase ventilation valve and system
for leaks.
− Air intake system after the MAF sensor for
vacuum leaks.
− Contaminated fuel – Refer to 6.5 Alcohol /
Contaminants in Fuel Diagnosis in this
Section.
− Lean injectors – Refer to 6.2 Fuel
Injector Coil Test in this Section.
− The ECM grounds for being clean, tight,
and in the correct locations
− A high engine oil level condition. A high
engine oil level causes oil residue to form
on the MAF sensor, causing a lean
indication. The MAF sensor does not need
to be replaced.
− An engine mechanical condition – refer to
6A1 – Engine Mechanical V6.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 8 Refer to Additional
Information and Test Descriptionin this DTC
7 1 Inspect for the following conditions:
− Vacuum leaks that only affect one bank of
the engine – For example, the intake
manifold, the injector O-rings.
− Lean injectors – refer to 6.2 Fuel
Injector Coil Test in this Section
− Exhaust leaks, missing or loose exhaust
hardware.
− The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) is
installed securely and the electrical
connector is not contacting the exhaust
system.
− An engine mechanical condition – 6A1 –
Engine Mechanical V6.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 8 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3476 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–198
• The rear fuel trim, long and short term, is more than a threshold.
• This DTC sets after the air flow coming into the engine accumulates to more than 200 grams and the above
conditions are met for more than 4 seconds.
Condition 2
• The ECM detects that the rear HO2S is operating too rich while the ECM is commanding a lean air / fuel mixture.
• This DTC sets after the air flow coming into the engine accumulates to more than 800 grams and the above
condition is met for more than 4 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM activates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the
diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the
control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second
consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The
control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after four consecutive ignition cycles that the
diagnostic runs and does not fail.
• A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission
related diagnostic.
• Use Tech 2 to clear the MIL and the DTC.
Additional Information
• A HO2S fault condition may cause this DTC to set. Thoroughly inspect all items that could cause a lean condition.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since a fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this
diagnostic procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
2 This step determines if a condition exists.
5 This step is testing for a rear HO2S sensor circuit condition. A circuit condition sets this DTC.
8 This step is testing for an intermittent circuit condition. Thoroughly inspect the HO2S circuits for an intermittent circuit condition.
9 This step is testing for an intermittent circuit condition. Thoroughly inspect the HO2S circuits for an intermittent circuit condition.
DTC P2195 or P2197 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been completed? —
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3477 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–199
2 1 Allow the engine to reach operating temperature.
2 Operate the vehicle within the parameters specified in Conditions for Running the DTC.
3 Observe the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) information, using Tech 2.
Did DTC P2195 or DTC P2197 fail this ignition? —
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
3 1 Observe the Freeze Frame and/or the Failure
records data for this DTC.
2 Turn the ignition OFF for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for Running the DTC. You may also operate the
vehicle within the conditions that you observed
from the Freeze Frame and / or the Failure
records data.
Does the DTC fail this ignition cycle? —
Go to Step 4 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC.
4 Is DTC P0041, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0157, P0158,
or P0160 also set? —
Go to the
appropriate DTC Table in this Section Go to Step 5
5 1 Operate the engine above 1,200 RPM for
30 seconds.
2 Observe the appropriate rear HO2S voltage, using Tech 2.
Is the voltage more than the specified value? 60 mV
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 6
6 1 Ignition OFF.
2 Disconnect the appropriate rear heated oxygen sensor (HO2S).
3 Ignition ON, engine OFF.
4 Observe the appropriate rear HO2S voltage parameter with Tech 2.
Is the voltage within the specified range? 350 – 550 mV
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 7
7 1 Test the appropriate rear HO2S signal circuit for
a short to ground. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body
and Chassis.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 19 Go to Step 14
8 1 Shake the related HO2S harnesses for the front
sensor between the HO2S harness connector
and the engine control module (ECM) while
monitoring the appropriate HO2S lambda
parameter.
Does the HO2S parameter change abruptly while
moving the related harnesses? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 9
9 1 Shake the related HO2S harnesses for the rear
sensor between the HO2S harness connector
and the ECM while monitoring the appropriate
HO2S voltage parameter.
Does the HO2S parameter change abruptly while
moving the related harnesses? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 10
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007