2007 ISUZU KB P190 spark plugs replace
[x] Cancel search: spark plugs replacePage 2422 of 6020
6E–252 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
12 Monitor “B1S1 (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Status ” on the Tech
2.
Is the “ B1S1 (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Status ” in the rich
condition? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 Check items that can cause the engine to run rich. Refer to DTC P1167 “Fuel Supply System Rich During
Deceleration Fuel Cut Off”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 14
14 Check items that can cause the engine to run lean. Refer to DTC P1171 “Fuel Supply System Lean
During Power Enrichment”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 Check for proper ignition voltage output with a spark tester.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 1. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil fouling cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposits, or improper heat
range.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 Drain sample fuel, visual inspection. Any suspecion about the fuel, such as discoloration,
particle, contamination, water, unusual smell, then
drain the fuel from fuel tank.
Replace the fuel from know vehicle source.
If any suspencion of alcohol contamination,
completely drain the fuel, replace by fuel from known
vehicle source. — Verify repair Go to Step 18
18 Check the exhaust system for a possible restriction: • Damaged or collapsed pipes
• Internal muffler failure
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 19
19 Check for the following engine mechanical problems (refer to Engine Mechanical ):
• Low compression
• Leaking cylinder head gaskets
• Worn camshaft
• Loose timing belt
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 20
20 1. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table. 2. If all procedures have been completed and nomalfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
• Visual/physical inspection
• Tech 2 data
• All electrical connections within a suspected circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 21
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2425 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–255
12 Check spark plugs for proper heat range.Were incorrect spark plugs installed? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 1. Remove excessive carbon buildup with a top engine cleaner.
2. Re-evaluate vehicle performance.
Is detonation still present? — Verify repair Go to Step 14
14 Check for an engine mechanical problem. Perform a cylinder compression check. Refer to Engine
Mechanical .
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 1. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table. 2. If all procedures have been completed and nomalfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
• Visual/physical inspection
• Tech 2 data
• All electrical connections within a suspected circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify Repair —
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2427 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–257
14 Monitor “B1S1 (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Status ” on the Tech
2.
Is the “ B1S1 (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Status ” in the rich
condition? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 Check items that can cause the engine to run rich. Refer to DTC P1167 “Fuel Supply System Rich During
Deceleration Fuel Cut Off”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 1. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil fouling cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposits, or improper heat
range.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 Check for proper calibration of the speedometer. Does the speed indicated on the speed meter closely
match the vehicle speed displayed on the Tech 2? — Go to Step 19Go to Step 18
18 Diagnose and repair the inaccurate speedometer condition as necessary. Refer to Vehicle Speed
Sensor in Electrical Diagnosis . — Verify Repair —
19 Check for proper calibration of the fuel gauge. Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 20
20 Check for the following engine mechanical problems (refer to Engine Mechanical ):
• Low compression
• Worn camshaft
• Sticking or leaking valves
• Valve timing
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 21
21 1. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table. 2. If all procedures have been completed and nomalfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
• Visual/physical inspection
• Tech 2 data
• All electrical connections within a suspected circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 22
22 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 23
23 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify Repair —
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2445 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–275
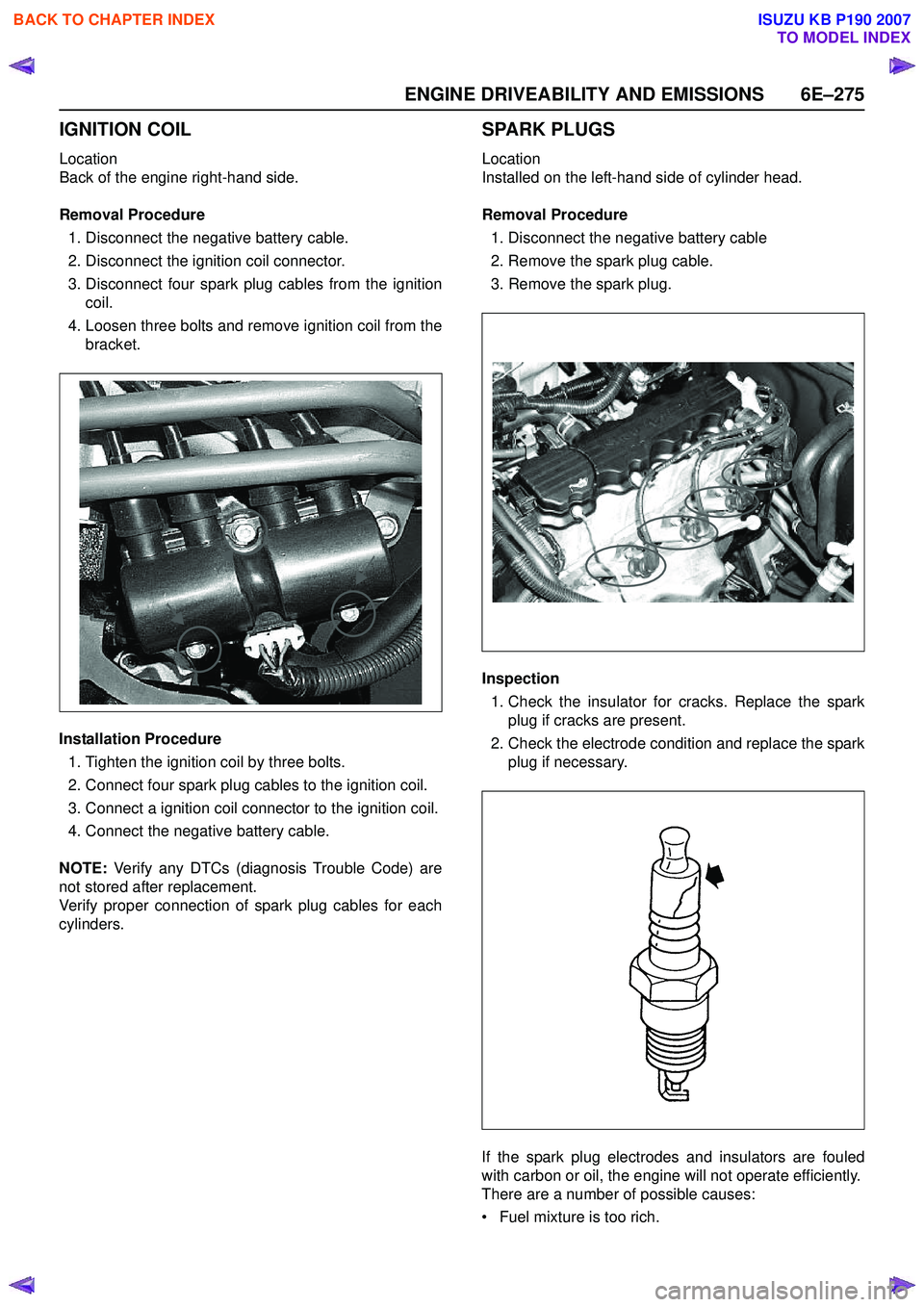
IGNITION COIL
Location
Back of the engine right-hand side.
Removal Procedure 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the ignition coil connector.
3. Disconnect four spark plug cables from the ignition coil.
4. Loosen three bolts and remove ignition coil from the bracket.
Installation Procedure 1. Tighten the ignition coil by three bolts.
2. Connect four spark plug cables to the ignition coil.
3. Connect a ignition coil connector to the ignition coil.
4. Connect the negative battery cable.
NOTE: Verify any DTCs (diagnosis Trouble Code) are
not stored after replacement.
Verify proper connection of spark plug cables for each
cylinders.
SPARK PLUGS
Location
Installed on the left-hand side of cylinder head.
Removal Procedure 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable
2. Remove the spark plug cable.
3. Remove the spark plug.
Inspection 1. Check the insulator for cracks. Replace the spark plug if cracks are present.
2. Check the electrode condition and replace the spark plug if necessary.
If the spark plug electrodes and insulators are fouled
with carbon or oil, the engine will not operate efficiently.
There are a number of possible causes:
• Fuel mixture is too rich.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2446 of 6020

6E–276 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
• Oil in the combustion chamber.
• The spark plug gap is not set correctly.
If spark plug fouling is excessive, check the fuel and al
system for possible causes of trouble. If fuel and al
system are normal, install spark plugs of a higher heat
range which have the same physical dimensions as the
original equipment spark plugs.
The following symptoms are characteristics of spark
plugs that are running too hot:
• Fuel mixture is too lean.
• Heat range is incorrect.
If vehicle usage does not conform to normal driving
conditions, a more suitable spark plug may be
substituted.
If fuel and al system are normal, in most cases of this
sort, the problem can be corrected by using a colder
type spark plug with the same physical dimensions as
the original equipment spark plug.
3. Check the gaskets for damage and replace if necessary.
4. Measure the spark plug gap. The specification is 1.0 to 1.1mm (0.039 to 0.043").
5. Adjust the spark gap by bending the grounded electrode. Installation
1. Tighten the spark plug to the 25N·m (2.5kgf·m).
2. Push the spark plug cable in until it snaps in.
Installation Procedure 1. Install the spark plug to the cylinder head.
2. Tighten the spark plug with specified tightening torque.
Tightening Torque
• Bolt: 25N·m (2.5kgf·m) 3. Connect the spark plug cable to the spark plug.
4. Connect the negative battery cable.
NOTE: Verify any DTCs (diagnosis Trouble Code) are
not stored after replacement.
Verify proper connection of spark plug cables for each
cylinders.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2509 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–30
Cause Correction
Faulty cylinder head gasket and/or cracking or other
damage to the cylinder head and cylinder block coolant
passages.
Coolant consumption may or may not cause the engine to
overheat. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for coolant saturation, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect the cylinder heads, cylinder block and/or head gaskets, refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly and/or
4.7 Cylinder Block.
3 Repair or replace components as required.
W orn piston rings.
Oil consumption may or may not cause the engine to
misfire. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for oil deposits, refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Check the cylinders for a loss of compression, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
3 Perform compression testing to identify the cause of low compression.
4 Repair or replace components as required.
A damaged crankshaft reluctor wheel.
A damaged crankshaft reluctor wheel can result in different
symptoms depending on the severity and location of the
damage.
Systems with severe reluctor ring damage may exhibit
periodic loss of crankshaft position, stop delivering a signal,
and then re-sync the crankshaft position.
Systems with slight reluctor ring damage may exhibit no
loss of crankshaft position and no misfire may occur,
however, a DTC may set. Replace the crankshaft as required, refer to 4.6
Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
2.4 Engine Misfire with Abnormal Internal Lower Engine Noises
Cause Correction
Abnormalities, severe cracking, bumps or missing areas in
the accessory drive belt.
Abnormalities in the accessory drive system and/or
components may cause engine speed variations that result
in a misfire diagnostic trouble code (DTC). A misfire code
may be present without an actual misfire condition. Replace the accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5
Accessory
Drive Belt.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
W orn, damaged or misaligned accessory drive components
and excessive pulley run-out may lead to a misfire DTC.
A misfire code may be present without an actual misfire
condition. Inspect the components and repair or replace as required.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
Loose or Incorrectly fitted flexplate or crankshaft balancer
assembly.
A misfire code may be present without an actual misfire
condition. Repair or replace the flexplate or crankshaft balancer as
required, refer to 3.13 Crankshaft Balancer Assembly
or 4.3 Flexplate Assembly.
W orn or broken piston rings.
Oil consumption may or may not cause an actual misfire. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for oil deposits, refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Check the cylinders for a loss of compression, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
3 Perform compression testing to identify the cause of low compression.
4 Repair or replace components as required.
W orn crankshaft thrust bearing.
Severely worn thrust surfaces on the crankshaft and/or
thrust bearing may permit fore and aft movement of the
crankshaft and create a DTC without an actual misfire
condition being present. Replace the crankshaft and/or bearings as required, refer to
4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2510 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–31
2.5 Engine Misfire with Abnormal Valve
Train Noise
Cause Correction
W orn or loose stationary hydraulic lash adjusters (SHLA)
and/or valve rocker arms.
The SHLAs, rocker arm and roller bearings should be intact
and in the correct position. Replace the SHLAs and/or rocker arms as required, refer to
3.21 Stationary Hydraulic Lash Adjuster or 3.20
Rocker Arm.
Stuck valves.
Carbon build up on the valve stems can result in the valves
not closing correctly. Repair or replace as required, refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head
Assembly.
Excessively worn or misaligned timing chain/s. Replace the timing chain/s and components as required,
refer to 3.16 Timing Chains, Tensioners, Shoes and
Guides.
W orn camshaft lobes. Replace the camshaft/s and SHLAs as required, refer to
3.19 Camshaft or 3.21 Stationary Hydraulic Lash
Adjuster.
Sticking camshaft lash adjusters. Replace the lash adjusters as required, refer to 3.21
Stationary Hydraulic Lash Adjuster.
2.6 Engine Misfire with Coolant
Consumption
Cause Correction
Faulty cylinder head gasket and/or cracking or other
damage to the cylinder heads and cylinder block coolant
passages.
Coolant consumption may or may not cause the engine to
overheat. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for coolant saturation, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect the cylinder heads, cylinder block and/or head gaskets, refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly and/or
4.7 Cylinder Block.
3 Repair or replace components as required.
2.7 Engine Misfire with Excessive Oil Consumption
Cause Correction
W orn valves, valve guides and/or valve stem oil seals. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for coolant saturation, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Repair or replace components as required, refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly.
W orn or broken piston rings.
Oil consumption may or may not cause an actual misfire. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for oil deposits, refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Check the cylinders for a loss of compression, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
3 Perform compression testing to identify the cause of low compression.
4 Repair or replace components as required.
2.8 Engine Noise on Start-up, but only Lasting a Few Seconds
NOTE
A cold piston knock, which disappears in
approximately 1.5 minutes from start up, should
be considered acceptable. A cold engine knock
usually disappears when the specific cylinder’s
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2514 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–35
2.11 Engine Noise Under Load
NOTE
A cold piston knock which disappears in
approximately 1.5 minutes from start up, should
be considered acceptable. A cold engine knock
usually disappears when the specific cylinder’s
secondary ignition circuit is grounded out during
diagnosis.
A light rattle/tapping noise may indicate a valve train/upper engine concern, while a low rumble/knocking may indicate a
crankshaft, piston or lower engine concern.
Cause Correction
Low oil pressure. 1 Perform an oil pressure test, refer to 2.19
Engine Oil Pressure Diagnosis.
2 Repair or replace the engine oil pump as required, refer to 3.17 Oil Pump Assembly.
Detonation or spark knock. Confirm the correct operation of the ignition system, refer to
6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics.
Loose torque converter bolts. Inspect and tighten the torque converter bolts to the correct
torque specification, refer to 7C1 Automatic – 4L60E –
General Information – 4L60E – General Information.
Cracked flexplate. Replace the flywheel/flex-plate as required, refer to 4.3
Flexplate Assembly.
Excessive connecting rod bearing clearance. Inspect the connecting rod, crankshaft and bearings and
repair/replace components as required, refer to 4.5
Pistons, Pins, Rings, Connecting Rods and Big-
end Bearings and 4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Excessive crankshaft bearing clearance Inspect the crankshaft, cylinder block journals, main
bearings and main bearing caps and repair/replace
components as required, refer to 4.6 Crankshaft
and Main Bearings and 4.7Cylinder Block.
2.12 Engine Will Not Crank – Crankshaft Will Not Rotate
Cause Correction
Seized accessory drive system component. 1 Remove the accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5
Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace accessory drive system components as required.
Hydraulically locked cylinder caused by:
• coolant in cylinder,
• oil in cylinder, or
• fuel in cylinder. 1 Remove the spark plugs and check for fluid, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect for broken head gasket/s.
3 Inspect for cracked engine block or cylinder head.
4 Inspect for sticking fuel injector.
5 Repair or replace components as required.
Seized torque converter. 1 Remove the torque converter bolts, refer to 7C1
Automatic – 4L60E – General Information – 4L60E –
General Information.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace torque converter as required.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007