2007 ISUZU KB P190 ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 1968 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-351
Notice:If the ECM is replaced to new one, VIN does
not displayed. Input correct VIN reading from stamped
VIN or affixed VIN plate on the vehicle. If the ECM from
another vehicle is installed, input correct VIN by same
way.
g. Highlight Engine on the Select System Typescreen, then click "Next", if on-screen
instruction displayed.
h. Complete the following information based on the service ID plate on the Validate Vehicle
Data screen until "Next" is highlighted, then
click "Next".
• Model
• Model year
• Engine type
• Model designator
• Destination code
• Transmission type
i. Verify your selection on the Summary screen.
Notice: Refer to Service Bulletin and Description
column before service programming is performed if the
bulletins are listed along with the calibration files.
Notice: Select Cancel if you receive a message stating
that the calibration selected is already the current
calibration in the ECM and reprogramming with the
same download is not allowed.
j. Click "Reprog".
k. The Transfer Data screen will appear until the progress bar reaches 100%.
5. Close the application and return to the TIS application selection screen after the download is
completed.
6. Turn OFF the scan tool and disconnect from the terminal.
7. Transfer the data from the scan tool to the ECM using the following procedure:
a. Install a scan tool.
b. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
c. Select Service Programming System (SPS) > Program ECU.
d. Turn OFF all accessories and press "Continue".
e. Programming in Process will appear until the progress bar reaches 100%.
Notice: Some warning lamp may turn ON or blink while
programming the ECM since communication between
the ECM and other modules are interrupted. Clear DTC
in any module after programming.
f. Press "Continue" and exit the program after thescan tool displays "Programming Was
Successful".
8. Turn OFF the ignition.
9. Turn OFF the scan tool and disconnect from the vehicle.Service Programming System (SPS) (Pass-
Thru Procedure)
Pass-Thru programming allows the scan tool to remain
connected to the terminal and to the vehicle throughout
the programming process. The vehicle must be in close
proximity to the terminal while using Pass-Thru.
1. Launch the TIS application.
2. Select the Service Programming System at the main screen.
3. Highlight the following information on the Select Diagnostic Tool and Programming Process screen,
then click "Next":
• Select Diagnostic Tool-Select Pass - Thru
• Select Programming Process - Identify whether as existing ECM is being reprogrammed or an
ECM is being replaced with a new one.
• Select ECU Location - Vehicle
4. Complete all vehicle data on the Preparing for Communication/ Determine Vehicle screen until
"Next" is highlighted, then click "Next".
5. Follow the instruction on the Preparing for Communication screen, then click "Next".
Notice: In order to reduce the potential for signal loss,
the RS-232 cable should not be more than 25 feet long.
6. Verify the VIN on the Validate Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) screen, then click "Next".
Notice: If the ECM is replaced to new one, VIN does
not displayed. Input correct VIN reading from stamped
VIN or affixed VIN plate on the vehicle. If the ECM from
another vehicle is installed, input correct VIN by same
way.
7. Highlight Engine on the Select System Type screen, then click "Next", if on-screen instruction
displayed.
8. Complete the following information based on the service ID plate on the Validate Vehicle Data
screen until "Next" is highlighted, then click "Next".
• Model
• Model year
• Engine type
• Model designator
• Destination code
• Transmission type
9. Verify your selection on the Summary screen.
Notice: Refer to Service Bulletin and Description
column before service programming is performed if the
bulletins are listed along with the calibration files.
Notice: Select Cancel if you receive a message stating
that the calibration selected is already the current
calibration in the ECM and reprogramming with the
same download is not allowed.
10. Click "Reprog".
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1981 of 6020

6E-364 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Fuel Injection System Description
Fuel Injection Quantity Control
This control determines the fuel injection quantity by
adding coolant temperature, fuel temperature, intake
air temperature, barometric pressure, mass air flow and
some switch inputs information corrections to the basic
injection quantity is calculated by the ECM based on
the engine operating conditions (engine speed,
accelerator pedal pressing amount and boost pressure
sensor). More fuel rate indicates if the engine load is
increased as the accelerator pedal is stepped on at
constant engine speed.
Combined with high pressure injection of atomized fuel,
this control improves exhaust gas and ensures proper
fuel consumption. Compared with conventional
mechanical governors, an electronic control system
provides higher degree of freedom of fuel injection
quantity control, thereby presenting high accelerator
response (acceleration feeling and pressing feeling).
Starting Injection Quantity Control
At the engine starting (after the key switch is turned to
the START position to start the engine, up to return of
key switch to the ON position), optimum fuel injection
quantity is controlled based on the information on the
engine speed and coolant temperature. At low
temperature, the fuel injection quantity increases.
When the engine started completely, this boosted
quantity mode at the starting is cancelled and normal
running mode is restored.
Idle Speed Control
A control is made so as to achieve stable idling speed
at all time regardless of engine secular changes or
engine condition variations. The ECM sets target idling
speed and controls the fuel injection quantity according
to the engine conditions (actual engine speed, coolant
temperature and engine load) to follow actual engine
speed to the target idling speed so as to ensure stable
idling speed.
Idle Vibration Control
A control is made so as to reduce the engine vibration
caused by torque variations between cylinders due to
variations in fuel injection quantity of each cylinder or
injector performance. The ECM corrects the injection
quantity between cylinders based on the revolution
signals from the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
Normal range of correction quantity between cylinders
is within ±5 mm
3.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1984 of 6020
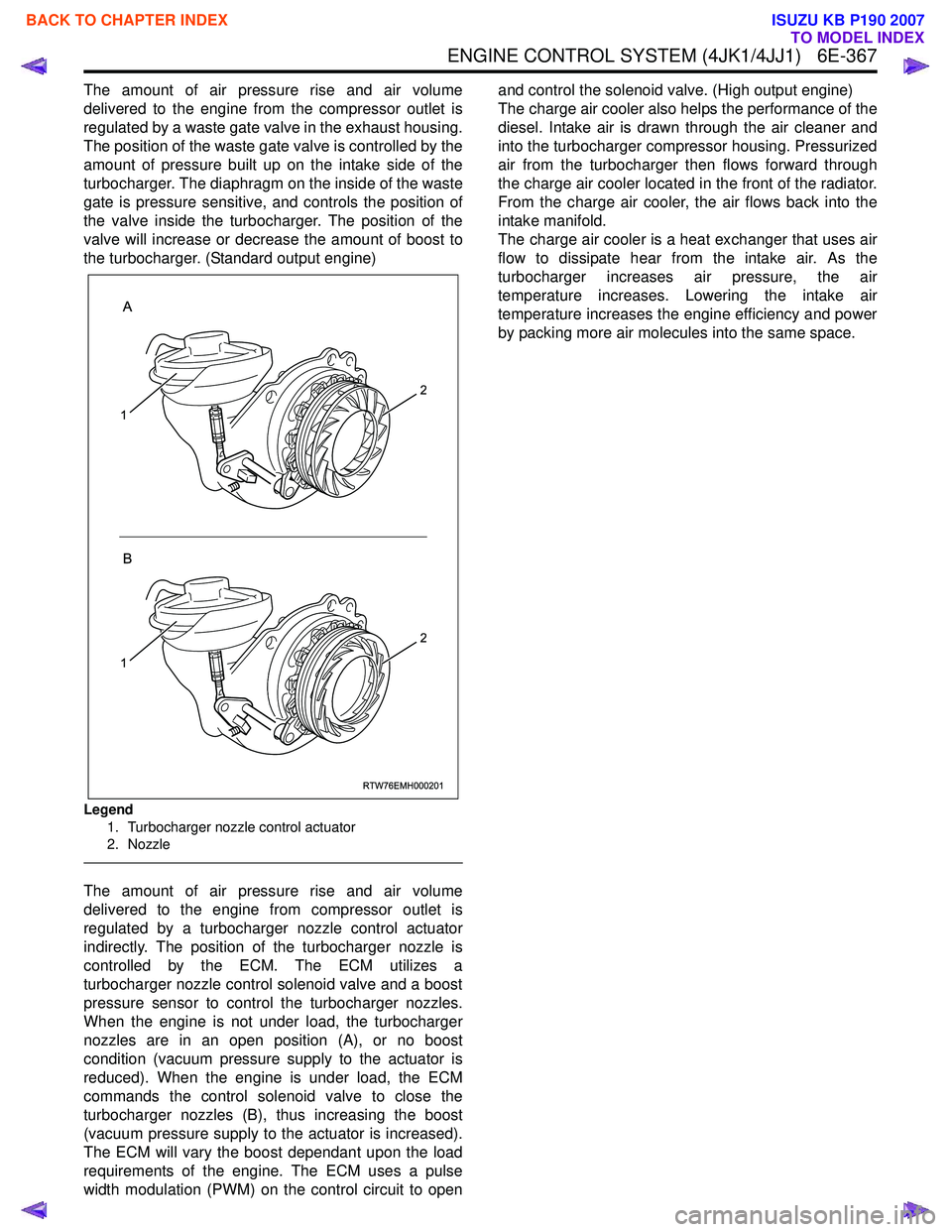
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-367
The amount of air pressure rise and air volume
delivered to the engine from the compressor outlet is
regulated by a waste gate valve in the exhaust housing.
The position of the waste gate valve is controlled by the
amount of pressure built up on the intake side of the
turbocharger. The diaphragm on the inside of the waste
gate is pressure sensitive, and controls the position of
the valve inside the turbocharger. The position of the
valve will increase or decrease the amount of boost to
the turbocharger. (Standard output engine)
Legend
1. Turbocharger nozzle control actuator
2. Nozzle
The amount of air pressure rise and air volume
delivered to the engine from compressor outlet is
regulated by a turbocharger nozzle control actuator
indirectly. The position of the turbocharger nozzle is
controlled by the ECM. The ECM utilizes a
turbocharger nozzle control solenoid valve and a boost
pressure sensor to control the turbocharger nozzles.
When the engine is not under load, the turbocharger
nozzles are in an open position (A), or no boost
condition (vacuum pressure supply to the actuator is
reduced). When the engine is under load, the ECM
commands the control solenoid valve to close the
turbocharger nozzles (B), thus increasing the boost
(vacuum pressure supply to the actuator is increased).
The ECM will vary the boost dependant upon the load
requirements of the engine. The ECM uses a pulse
width modulation (PWM) on the control circuit to open and control the solenoid valve. (High output engine)
The charge air cooler also helps the performance of the
diesel. Intake air is drawn through the air cleaner and
into the turbocharger compressor housing. Pressurized
air from the turbocharger then flows forward through
the charge air cooler located in the front of the radiator.
From the charge air cooler, the air flows back into the
intake manifold.
The charge air cooler is a heat exchanger that uses air
flow to dissipate hear from the intake air. As the
turbocharger increases air pressure, the air
temperature increases. Lowering the intake air
temperature increases the engine efficiency and power
by packing more air molecules into the same space.
RTW76EMH000201
A
B
1
2
1
2
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2084 of 6020
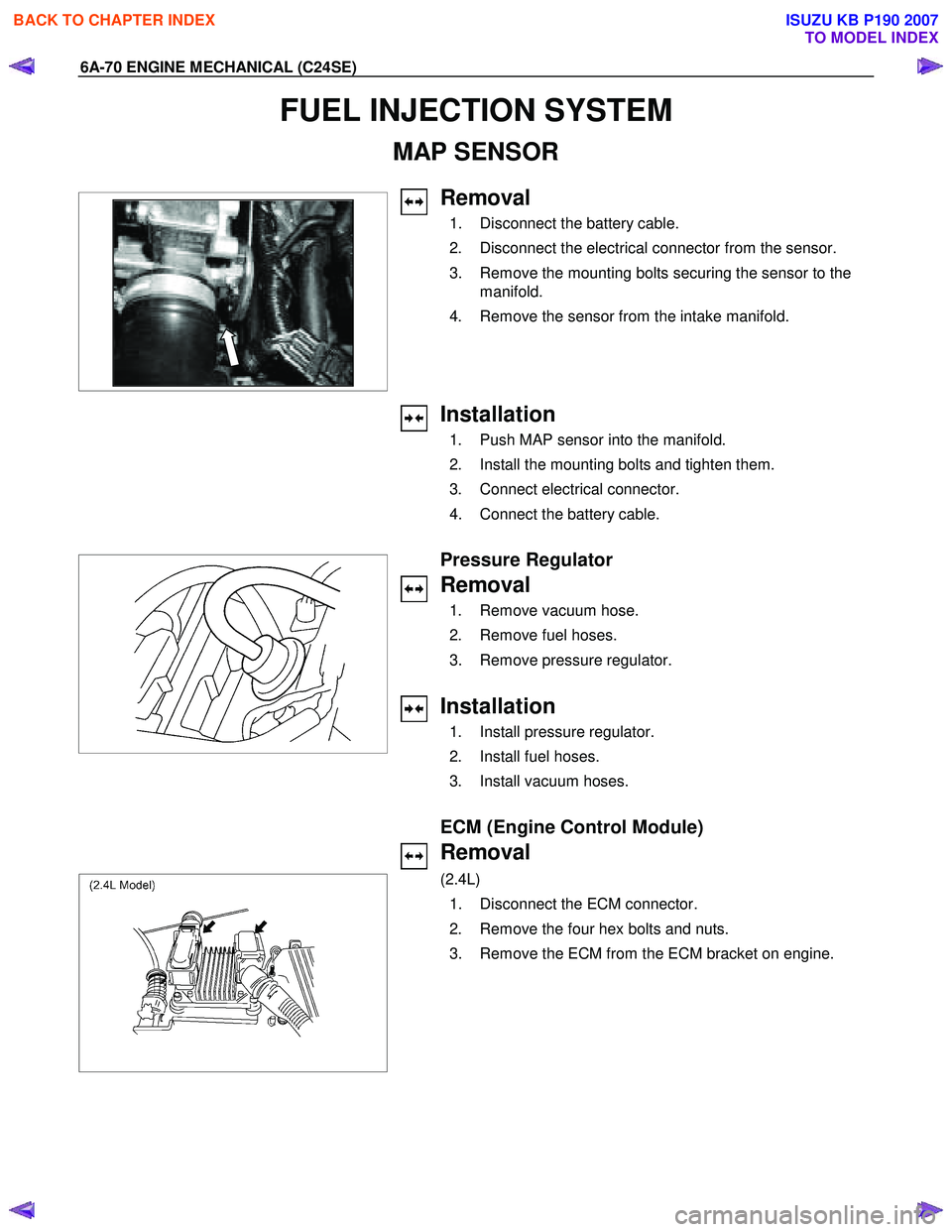
6A-70 ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE)
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
MAP SENSOR
Removal
1. Disconnect the battery cable.
2. Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
3. Remove the mounting bolts securing the sensor to the manifold.
4. Remove the sensor from the intake manifold.
Installation
1. Push MAP sensor into the manifold.
2. Install the mounting bolts and tighten them.
3. Connect electrical connector.
4. Connect the battery cable.
Pressure Regulator
Removal
1. Remove vacuum hose.
2. Remove fuel hoses.
3. Remove pressure regulator.
Installation
1. Install pressure regulator.
2. Install fuel hoses.
3. Install vacuum hoses.
ECM (Engine Control Module)
Removal
(2.4L)
1. Disconnect the ECM connector.
2. Remove the four hex bolts and nuts.
3. Remove the ECM from the ECM bracket on engine.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2090 of 6020

6A-76 ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE)
Spark Plug Thread
Recondition
Ream thread and recut using commercially available spark
plug thread drill (observe manufacturer's instructions).
Removal
Remove thread bush on spark plug. (dimensions (A) =
17mm/0.67in.)
Tighten (Torque)
Spark plug with thread bush into cylinder head - 25N ⋅m (2.5
kgf ⋅m) - use.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2129 of 6020
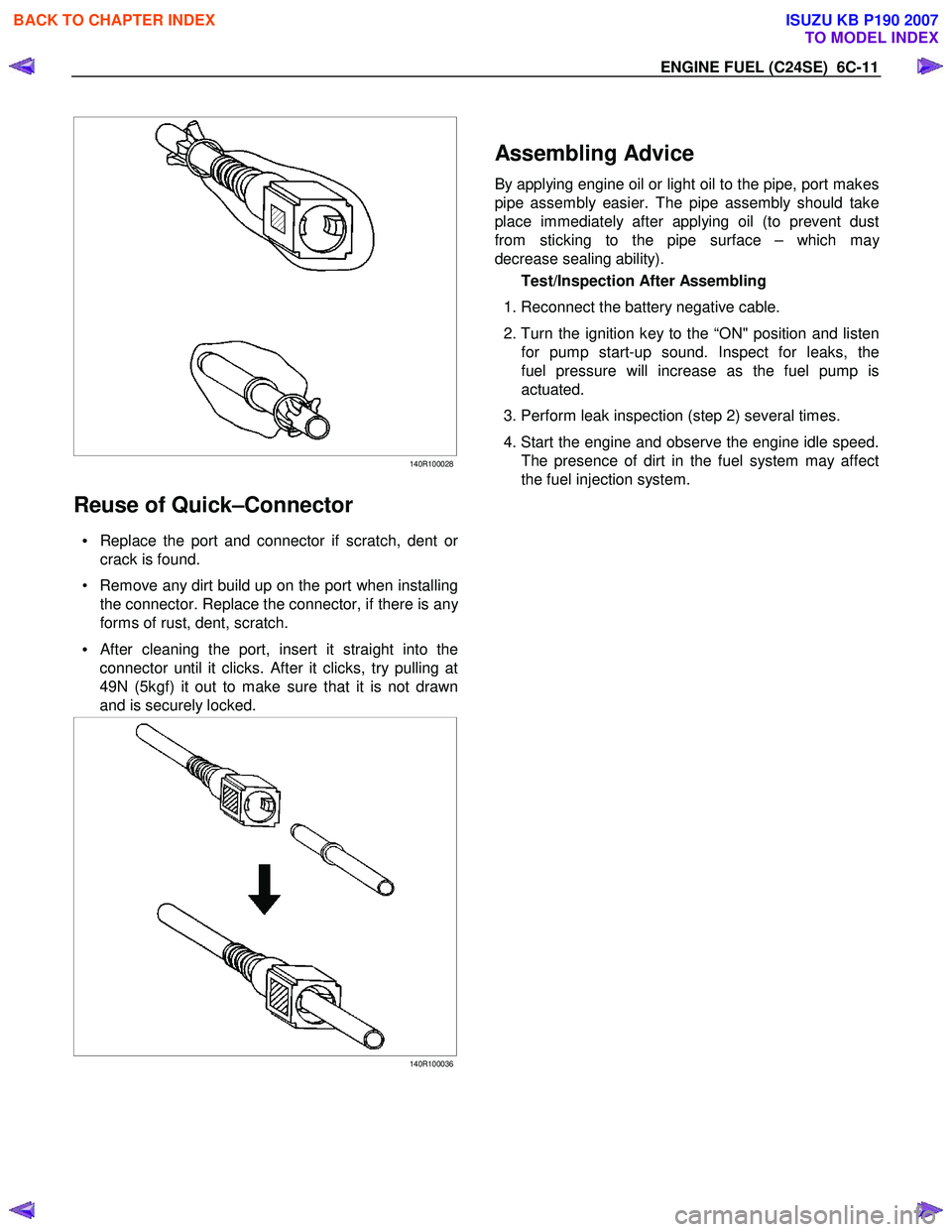
ENGINE FUEL (C24SE) 6C-11
140R100028
Reuse of Quick–Connector
• Replace the port and connector if scratch, dent or
crack is found.
• Remove any dirt build up on the port when installing the connector. Replace the connector, if there is an
y
forms of rust, dent, scratch.
•
After cleaning the port, insert it straight into the
connector until it clicks. After it clicks, try pulling at
49N (5kgf) it out to make sure that it is not drawn
and is securely locked.
140R100036
Assembling Advice
By applying engine oil or light oil to the pipe, port makes
pipe assembly easier. The pipe assembly should take
place immediately after applying oil (to prevent dust
from sticking to the pipe surface – which ma
y
decrease sealing ability).
Test/Inspection After Assembling
1. Reconnect the battery negative cable.
2. Turn the ignition key to the “ON" position and listen
for pump start-up sound. Inspect for leaks, the
fuel pressure will increase as the fuel pump is
actuated.
3. Perform leak inspection (step 2) several times.
4. Start the engine and observe the engine idle speed.
The presence of dirt in the fuel system may affect
the fuel injection system.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2161 of 6020

STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM 6D3-13
5. During current output tests please make sure that the
ammeter is securely connceted into the charge circuit.
6. Some battery powered timing lights can produce high transient voltages when connected or disconnected. Onl
y
disconnect or connect timing lights when the engine is
switched off.
7. Make sure the warning lamp circuit is functioning normall
y
before commencing tests.
8. Battery isolation switches must only be operated when the engine is stopped.
9. To protect the charging system when using 240 volt chargers it is recommeneded that the battery is
disconnected whilst charging.
10. Due to the very low resistance value of the stator winding it may not be possible to obtain accurate readings without
special equipment.
11. 12 volts must never be connected to the "L" terminal of the regulator as this will damage the lamp driver circuit.
12. No loads apart from the warning lamp can be connected to the "L" termainal. The "W " terminal is provided for this
purpose.
Disassembly
1. Mark the relative positions of the end housings in relation to the stator assembly to aid reassembly. Use a permanent
marking pen do not use centre punched as this can cause
misalignmnet of the housings.
2. Remove the EP regulator from the slipring end housing b
y
removing the two screws. Tilt the regulator slightly from the
plug connection until the regulator clears the housing, then
lift clear.
3. Remove the four through bolts.
4. Carefully remove the stator assembly along with the slipring end housing taking care not to put strain on the stator wires.
5. To disconnect the stator from the rectifier assembly, grasp the stator wires close to the wire loop with a pair of long
nosed pliers, heat the joint with a soldering iron, when the
point becomes plastic apply a slight twisting motion to the
wires, then pull upwards to release the wires. Remove the
stator.
This procedure opens the wire loop to release the stato
r
connections easily.
6. To remove the rectifier remove the three retaining scre
w
and the B+ terminal nut and washers.
Note: the B+ bolt and the positive heatsink retaining screw are
fitted with mica insulating washers.
These must be discarded and replaced with new washers and
heatsink compound.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2172 of 6020

6E–2 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
5e. Vehicle Operates as Designed ............ 6E-65
6. Re-examine the complaint ..................... 6E-66
7. Repair and Verify Fix ............................. 6E-66
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION .......... 6E-67 On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) ...................... 6E-68
On-Board Diagnostic Tests ....................... 6E-68
The Diagnostic Executive .......................... 6E-68
Diagnostic Information ............................... 6E-68
Check Engine Lamp .................................. 6E-68
Data Link Connector (DLC) ....................... 6E-68
Tech 2 Operating Flow Cart (Start Up) ...... 6E-70
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS (ENGINE DATA) ......................................... 6E-72
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS (O2 SENSOR DATA) .................................. 6E-74
MISCELLANEOUS TEST ............................. 6E-76
PLOTTING SNAPSHOT GRAPH ................. 6E-78 Plotting Graph Flow Chart (Plotting graph after obtaining vehicle information) .................. 6E-79
Flow Chart for Snapshot Replay (Plotting Graph) ....................................... 6E-80
SNAPSHOT DISPLAY WITH TIS2000 ......... 6E-81
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM CHECK 6E-98
Circuit Description ......................................... 6E-90
Diagnostic Aids ............................................. 6E-90
Test Description ............................................ 6E-90
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM CHECK .................................................... 6E-91
NO CHECK ENGINE LAMP (MIL) ................ 6E-94 Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-94
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-94
No Check Engine Lamp (MIL) ................... 6E-94
CHECK ENGINE LAMP (MIL) “ON” STEADY 6E-96 Circuit description ...................................... 6E-96
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-96
Check Engine Lamp (MIL) “ON” Steady .... 6E-96
FUEL METERING SYSTEM CHECK ........... 6E-98
FUEL INJECTOR COIL TEST PROCEDURE AND FUEL INJECTOR BALANCE TEST
PROCEDURE ............................................. 6E-98
Test Description ......................................... 6E-98
Injector Coil Test Procedure (Steps 1-6) and Injector Balance Test Procedure
(Steps 7-11) ............................................. 6E-99
Injector Coil Test Procedure (Steps 1-6) and Injector Balance Test Procedure
(Steps 7-11) ............................................. 6E-100
FUEL SYSTEM ELECTRICAL TEST ........... 6E-103 Circuit Description ..................................... 6E-103
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-104 Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure ................. 6E-104
Fuel Pressure Gauge Installation .............. 6E-104
Fuel System Electrical Test ....................... 6E-104
FUEL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS ........................ 6E-108 Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-108
Test Description ......................................... 6E-108
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure ................. 6E-109
Fuel Pressure Gauge Installation .............. 6E-109
Fuel System Diagnosis .............................. 6E-110
ECM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC) 6E-113
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0107 MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE
CIRCUIT LOW INPUT ................................ 6E-119
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-119
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-119
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107 Manifold Absolute Pressure Circuit Low
Input ......................................................... 6E-120
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0108 MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE
CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT ............................... 6E-123
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-123
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-124
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0108 Manifold Absolute Pressure Circuit High
Input ......................................................... 6E-124
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0112 INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR LOW
INPUT ......................................................... 6E-127
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-127
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-127
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0112 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Low Input 6E-128
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0113 INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR HIGH
INPUT ......................................................... 6E-131
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-131
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-131
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0113 Intake Air Temperature Sensor High Input 6E-132
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0117 ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR LOW INPUT ................................ 6E-136
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-136
Diagnostic Aids .......................................... 6E-136
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0117 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Low
Input ......................................................... 6E-137
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0118 ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR HIGH INPUT ............................... 6E-139
Circuit Description ...................................... 6E-139
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007