2007 ISUZU KB P190 oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 4406 of 6020

7A2-122 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Standard Value
Diagnosis 1. If the line pressure is lower than the standard value at idle in all ranges.
• Abraded oil pump.
• Faulty operation of each solenoid valve.
• Sticking of pressure regulator spool valve or pilot spool valve.
• Fatigued pressure regulator spool valve spring or pilot spool valve spring.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the oil strainer, oil pump, pressure regulator spool valve, torque
converter relief spool valve or pressure relief valve.
2. If the line pressure is lower than the standard value at idle in D, 3, 2 and L range.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the low clutch hydraulic circuit.
3. If the line pressure is lower than the standard value at idle in R range.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the reverse clutch hydraulic circuit.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the low & reverse brake hydraulic circuit.
4. If the line pressure is lower that the standard value at idle in L or R range.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the low & reverse brake hydraulic circuit.
5. If the line pressure is higher than the standard value at idle in all ranges.
• Faulty accelerator pedal position signal.
• Faulty transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor.
• Faulty operation of low clutch solenoid valve.
• Sticking pilot spool valve.
• Sticking pressure regulator spool valve or plug.
6. If the line pressure is lower than the standard value at stall speed in all ranges.
• Faulty accelerator pedal position signal.
• Faulty operation of pressure control (PC) solenoid valve.
• Faulty operation of low clutch solenoid valve.
• Sticking pilot spool valve.
• Sticking pressure regulator spool valve or plug.
Selector lever position Engine
speed Line pressure (kPa/ psi)
D, 3, 2 or D Idle 350 - 480 / 51 - 70
R Stall 1050 - 1250 / 152 - 182
Idle 450 - 650 / 65 - 95
Stall 1400 - 1630 / 203 - 237
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4407 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-123
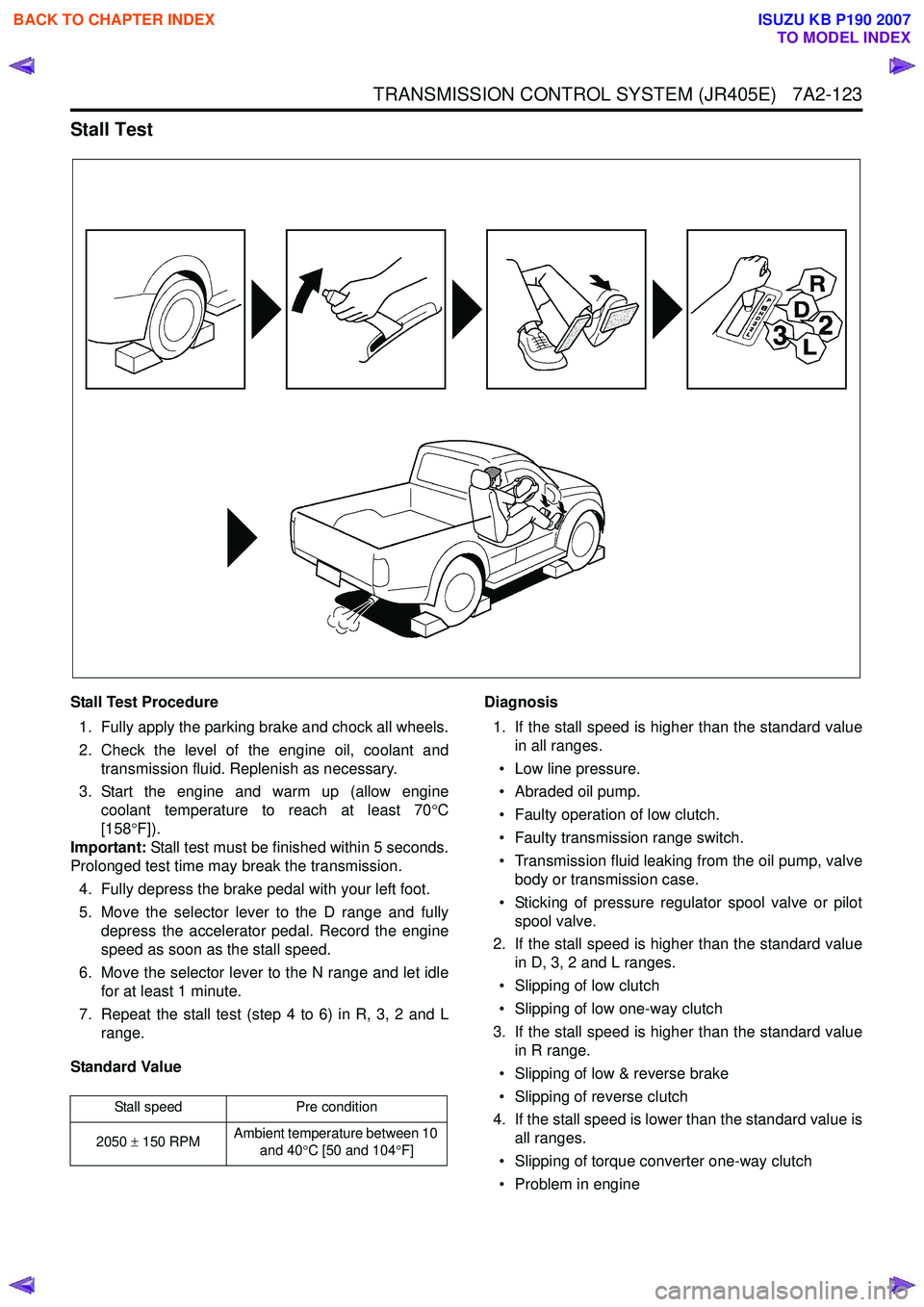
Stall Test
Stall Test Procedure1. Fully apply the parking brake and chock all wheels.
2. Check the level of the engine oil, coolant and transmission fluid. Replenish as necessary.
3. Start the engine and warm up (allow engine coolant temperature to reach at least 70 °C
[158 °F]).
Important: Stall test must be finished within 5 seconds.
Prolonged test time may break the transmission.
4. Fully depress the brake pedal with your left foot.
5. Move the selector lever to the D range and fully depress the accelerator pedal. Record the engine
speed as soon as the stall speed.
6. Move the selector lever to the N range and let idle for at least 1 minute.
7. Repeat the stall test (step 4 to 6) in R, 3, 2 and L range.
Standard Value Diagnosis
1. If the stall speed is higher than the standard value in all ranges.
• Low line pressure.
• Abraded oil pump.
• Faulty operation of low clutch.
• Faulty transmission range switch.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the oil pump, valve body or transmission case.
• Sticking of pressure regulator spool valve or pilot spool valve.
2. If the stall speed is higher than the standard value in D, 3, 2 and L ranges.
• Slipping of low clutch
• Slipping of low one-way clutch
3. If the stall speed is higher than the standard value in R range.
• Slipping of low & reverse brake
• Slipping of reverse clutch
4. If the stall speed is lower than the standard value is all ranges.
• Slipping of torque converter one-way clutch
• Problem in engine
Stall speed Pre condition
2050 ± 150 RPM Ambient temperature between 10
and 40 °C [50 and 104 °F]
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4408 of 6020
7A2-124 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
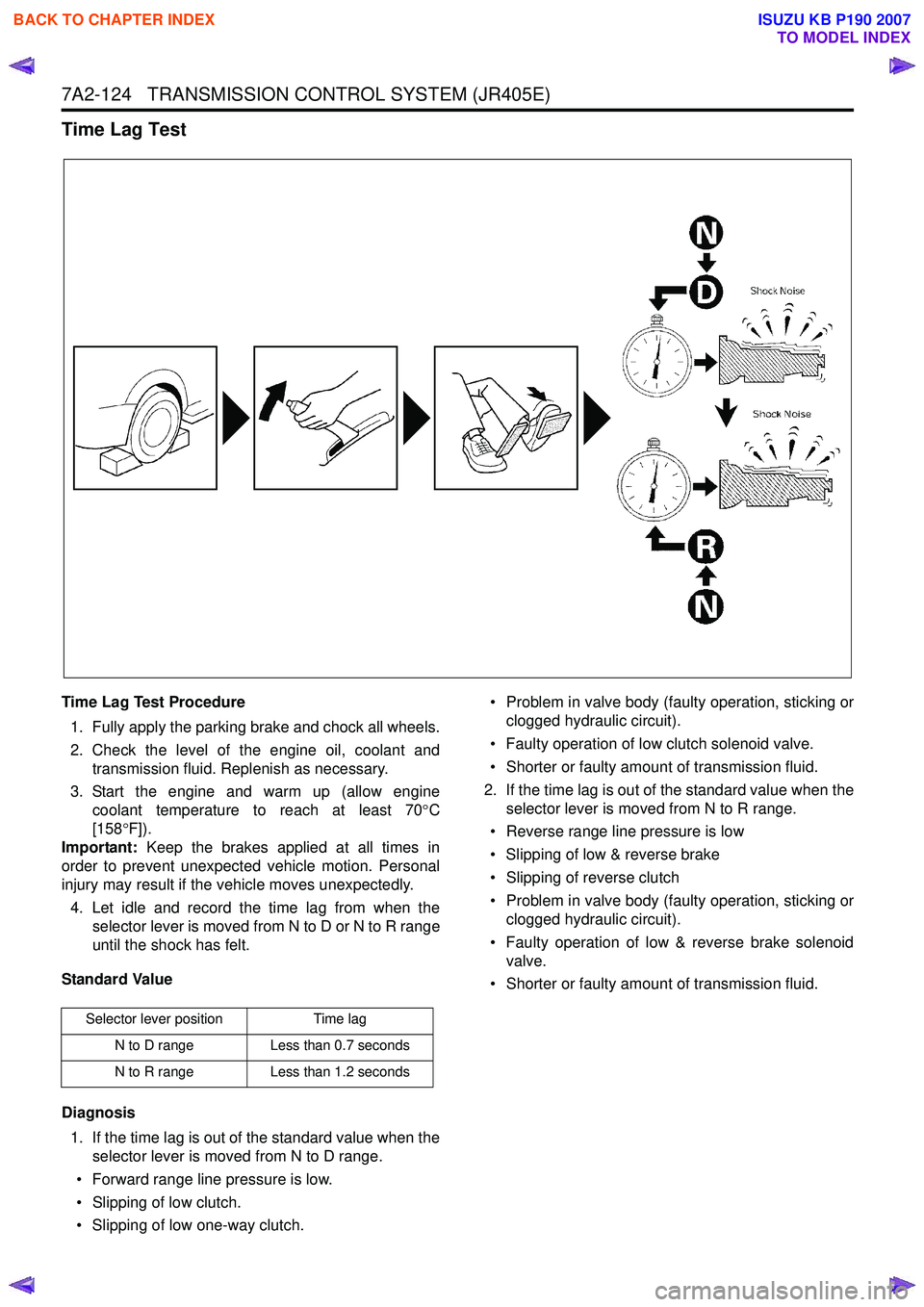
Time Lag Test
Time Lag Test Procedure1. Fully apply the parking brake and chock all wheels.
2. Check the level of the engine oil, coolant and transmission fluid. Replenish as necessary.
3. Start the engine and warm up (allow engine coolant temperature to reach at least 70 °C
[158 °F]).
Important: Keep the brakes applied at all times in
order to prevent unexpected vehicle motion. Personal
injury may result if the vehicle moves unexpectedly.
4. Let idle and record the time lag from when the selector lever is moved from N to D or N to R range
until the shock has felt.
Standard Value
Diagnosis 1. If the time lag is out of the standard value when the selector lever is moved from N to D range.
• Forward range line pressure is low.
• Slipping of low clutch.
• Slipping of low one-way clutch. • Problem in valve body (faulty operation, sticking or
clogged hydraulic circuit).
• Faulty operation of low clutch solenoid valve.
• Shorter or faulty amount of transmission fluid.
2. If the time lag is out of the standard value when the selector lever is moved from N to R range.
• Reverse range line pressure is low
• Slipping of low & reverse brake
• Slipping of reverse clutch
• Problem in valve body (faulty operation, sticking or clogged hydraulic circuit).
• Faulty operation of low & reverse brake solenoid valve.
• Shorter or faulty amount of transmission fluid.
Selector lever position Time lag
N to D range Less than 0.7 seconds
N to R range Less than 1.2 seconds
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4418 of 6020
7A2-134 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
TCM Signal Test
Inspection Tool
Use a DMM to measure voltage and circuit continuity.
Also use an oscilloscope to measure waveform. Refer
to the following table for the specified ranges or
reference waveform. Since the TCM terminals are extremely small, use
appropriate test adapter from the test adapter kit. This
will make measurement easier.
Pin No. Wire color Pin function DMM (+) DMM (-) Test condition Standard value
1 of C-94 RED/ WHT Battery voltage 1 of C-94 Ground Any time Nearly 12 volts
2 of C-94 YEL/ VIO P range switch signal 2 of C-94 Ground P range
Nearly 12 volts
Other than P range Less than 2 volts
3 of C-94 RED Brake pedal switch
signal 3 of C-94 Ground Pedal is released Less than 2 volts
Pedal is applied Nearly 12 volts
4 of C-94 PNK/ WHT 3rd start lamp control 4 of C-94
(back probe) Ground Lamp OFF Nearly 12 volts
Lamp ON Less than 2 volts
5 of C-94 VIO/ GRN Keyword serial data
communication 5 of C-94 7 of B-58 Ignition OFF
Continuity
6 of C-94 — Not used— — ——
7 of C-94 BLK/ RED Engine speed signal
input 7 of C-94
(back probe) 5 of C-95
(back
probe) Engine run at 2000
RPM Nearly 6.2 volts by
AC range or
waveform
8 of C-94 — Not used— — ——
9 of C-94 — Not used— — ——
10 of C-94 BLK/ YEL Vehicle speed signal
output (2WD) 10 of C-94
(back probe) 5 of C-95
(back
probe) Vehicle run at 20 km/h
(12 MPH) Nearly 6.5 volts by
AC range or waveform
11 of C-94 GRN/ WHT 3rd start switch signal 11 of C-94
(back probe) GroundSwitch is released Nearly 12 volts
Switch is pressed Less than 2 volts
12 of C-94 BLU/ WHT 4WD low signal output 12 of C-94
(back probe) Ground 4L mode Less than 2 volts
Other than 4L Nearly 12 volts
13 of C-94 — Not used— — ——
14 of C-94 — Not used— — ——
15 of C-94 — Not used— — ——
16 of C-94 RED/ WHT Accelerator pedal
position (APP) signal
input 16 of C-94
(back probe) 5 of C-95Pedal is released (0%) Off duty ratio 10%
Pedal is fully applied (100%) Off duty ratio 90%
17 of C-94 BLK/GRN 3 range switch signal 17 of C-94 Ground 3 range
Nearly 12 volts
Other than 3 range Less than 2 volts
18 of C-94 YEL/ BLK Diagnostic request
switch 5 of C-9411 o f B -
58 Ignition OFF
Continuity
19 of C-94 ORN/ BLU Transmission oil
temperature lamp control 19 of C-94
(back probe) Ground Lamp OFF Nearly 12 volts
Lamp ON Less than 2 volts
20 of C-94 GRY/ YEL Check trans lamp
control 20 of C-94
(back probe) Ground Lamp OFF Nearly 12 volts
Lamp ON Less than 2 volts
21 of C-94 PNK Power drive lamp
control 21 of C-94
(back probe) Ground Lamp OFF Nearly 12 volts
Lamp ON Less than 2 volts
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4428 of 6020
7A2-144 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
The JR405E automatic transmission is electrically
controlled by a transmission control module (TCM).
There are four forward speeds and one reverse speed.
This JR405E automatic transmission employs a clutch
pressure direct control system (Direct Electronic Shift
Control: DESC) using duty cycle type solenoid valves,
which ensure high shift quality. This transmission also
has a learning function and constantly checks the time
of each clutch and brake required for the shift in order
to match this time with the target value for the optimum
shift. The TCM will automatically select the most
appropriate shift points and lock-up points depending
on the accelerator pedal opening, the vehicle speed
and the vehicle load. If any trouble arises in the speed
sensor, solenoid valve, etc., the fail-safe control
function is activated to keep the running performance.
The JR405E automatic transmission consists of the
torque converter, oil pump, input shaft, out put shaft,
planetary gears and valve body. The gear train consists
of two planetary gear sets and three multiple plate
clutches in combination with two multiple plate brakes
and a one-way clutch.
Transmission Component Description
Torque Converter
Legend
1. Pump impeller
2. Turbine runner
3. Stator
4. Converter front cover
5. One-way clutch
6. Torque converter clutch (TCC) piston
7. Torsion damper
The torque converter is a device for transmitting the
engine torque to the transmission. It transmits power by
means of oil when the lock up clutch is disengaged,
and by means of a lock up clutch when it is engaged. The torque converter is of the symmetrical, three-
element, single-stage, two-phase type. As shown in the
picture, the symmetrical three-elements refer to three
elements (components) consisting of impeller (1),
turbine (2) and stator (3) that are arranged
symmetrically. Single-stage means that there is only
one turbine as an output element; two-phase means
that the pump impeller acts as a torque converter when
the turbine speed is comparatively low, and as a fluid
coupling when the speed is high. Lock up refers to a
fixed state of the lock up clutch (=torque converter
clutch (TCC) inside the torque converter and thus
connects the engine directly to the transmission.
Oil Pump
Legend 1. Torque converter
2. Oil pump
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4429 of 6020

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-145
Legend1. Oil pump cover
2. Inner rotor
3. Outer rotor
4. Oil pump housing
The oil pump generating oil pressure is a small sized
trochoid gear type oil pump. It feeds oil to the torque
converter, lubricates the power train mechanism, and
feeds the oil pressure to the oil pressure control unit
under pressure. The oil pump is located behind the
torque converter. Since the inner rotor in the oil pump is
fitted with the drive sleeve of the torque converter, it
works using power from the engine.
Legend
1. Pressure regulator valve
2. Outlet
3. Inlet
When the inner rotor in the oil pump rotates,
transmission fluid is sucked in from the oil pan, passed
between the inner rotor, outer rotor and crescent, and
then discharged. This discharged pressure is sent to
the pressure regulator valve in the valve body, and
adjusted as required for operating the transmission.
The flow rate under pressure increases or decreases in
proportion to the number of rotations.
Input Shaft
The input shaft has some oil holes, through which
lubricating transmission fluid is supplied to the torque
converter, the bearings, etc. The input shaft is fitted to
the turbine runner in the torque converter, the reverse &
high clutch drum and the rear sun gear by means of the
spline. Therefore, the engine driving force received by
the torque converter is transmitted to the reverse &
high clutch drum and rear sun gear.
Output Shaft
The output shaft has some oil holes, through which the
lubricating transmission fluid is supplied to the
bearings, the planetary gear unit, etc. The output shaft
transmits the engine driving force from the planetary
gear to the propeller shaft. The front internal gear is
fitted with the rear carrier assembly by spline. The
parking gear is also fitted by spline. By fixing this gear
mechanically, the output shaft is fixed as required when
parking the vehicle.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4430 of 6020
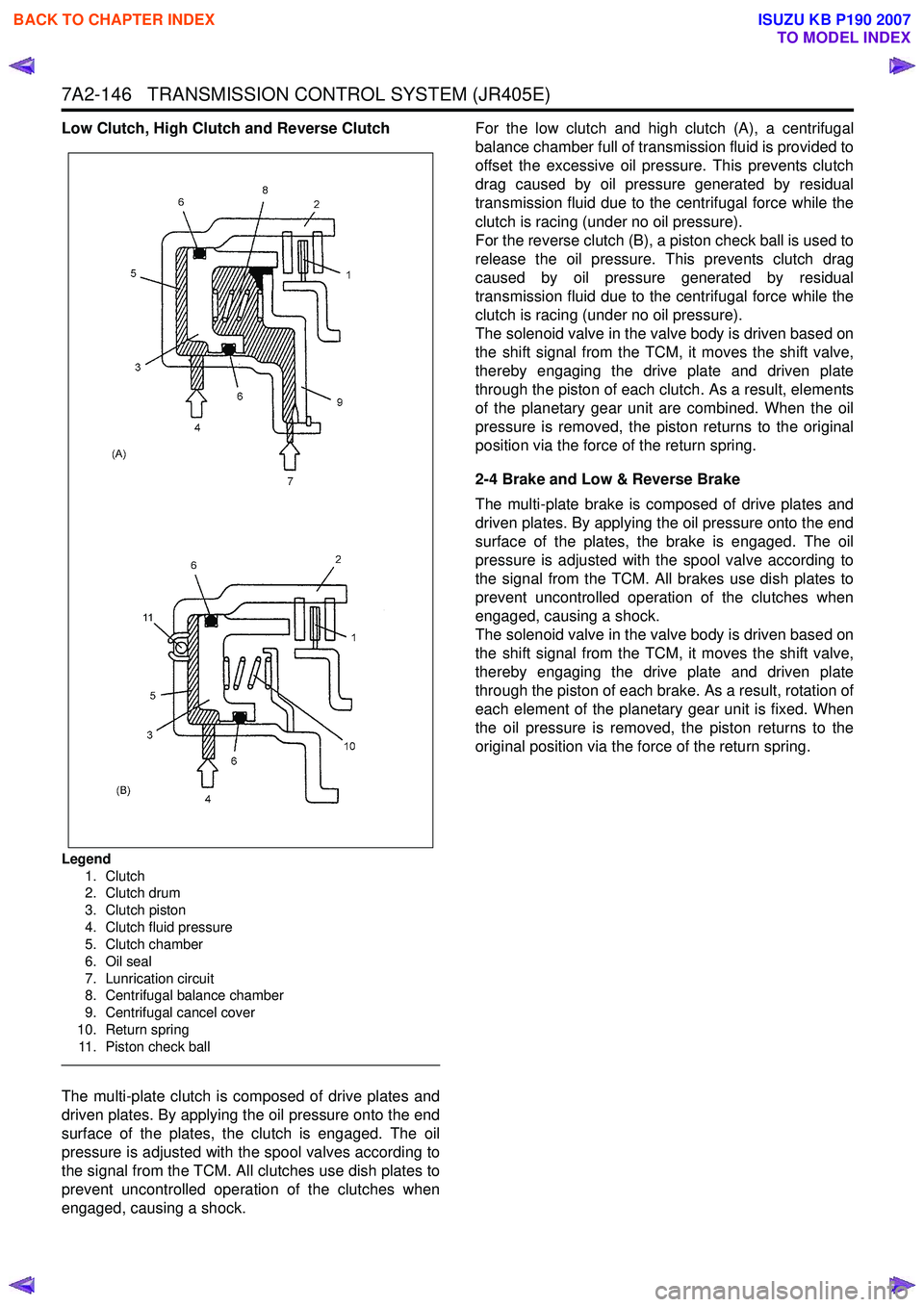
7A2-146 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Low Clutch, High Clutch and Reverse Clutch
Legend1. Clutch
2. Clutch drum
3. Clutch piston
4. Clutch fluid pressure
5. Clutch chamber
6. Oil seal
7. Lunrication circuit
8. Centrifugal balance chamber
9. Centrifugal cancel cover
10. Return spring 11. Piston check ball
The multi-plate clutch is composed of drive plates and
driven plates. By applying the oil pressure onto the end
surface of the plates, the clutch is engaged. The oil
pressure is adjusted with the spool valves according to
the signal from the TCM. All clutches use dish plates to
prevent uncontrolled operation of the clutches when
engaged, causing a shock. For the low clutch and high clutch (A), a centrifugal
balance chamber full of transmission fluid is provided to
offset the excessive oil pressure. This prevents clutch
drag caused by oil pressure generated by residual
transmission fluid due to the centrifugal force while the
clutch is racing (under no oil pressure).
For the reverse clutch (B), a piston check ball is used to
release the oil pressure. This prevents clutch drag
caused by oil pressure generated by residual
transmission fluid due to the centrifugal force while the
clutch is racing (under no oil pressure).
The solenoid valve in the valve body is driven based on
the shift signal from the TCM, it moves the shift valve,
thereby engaging the drive plate and driven plate
through the piston of each clutch. As a result, elements
of the planetary gear unit are combined. When the oil
pressure is removed, the piston returns to the original
position via the force of the return spring.
2-4 Brake and Low & Reverse Brake
The multi-plate brake is composed of drive plates and
driven plates. By applying the oil pressure onto the end
surface of the plates, the brake is engaged. The oil
pressure is adjusted with the spool valve according to
the signal from the TCM. All brakes use dish plates to
prevent uncontrolled operation of the clutches when
engaged, causing a shock.
The solenoid valve in the valve body is driven based on
the shift signal from the TCM, it moves the shift valve,
thereby engaging the drive plate and driven plate
through the piston of each brake. As a result, rotation of
each element of the planetary gear unit is fixed. When
the oil pressure is removed, the piston returns to the
original position via the force of the return spring.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4432 of 6020
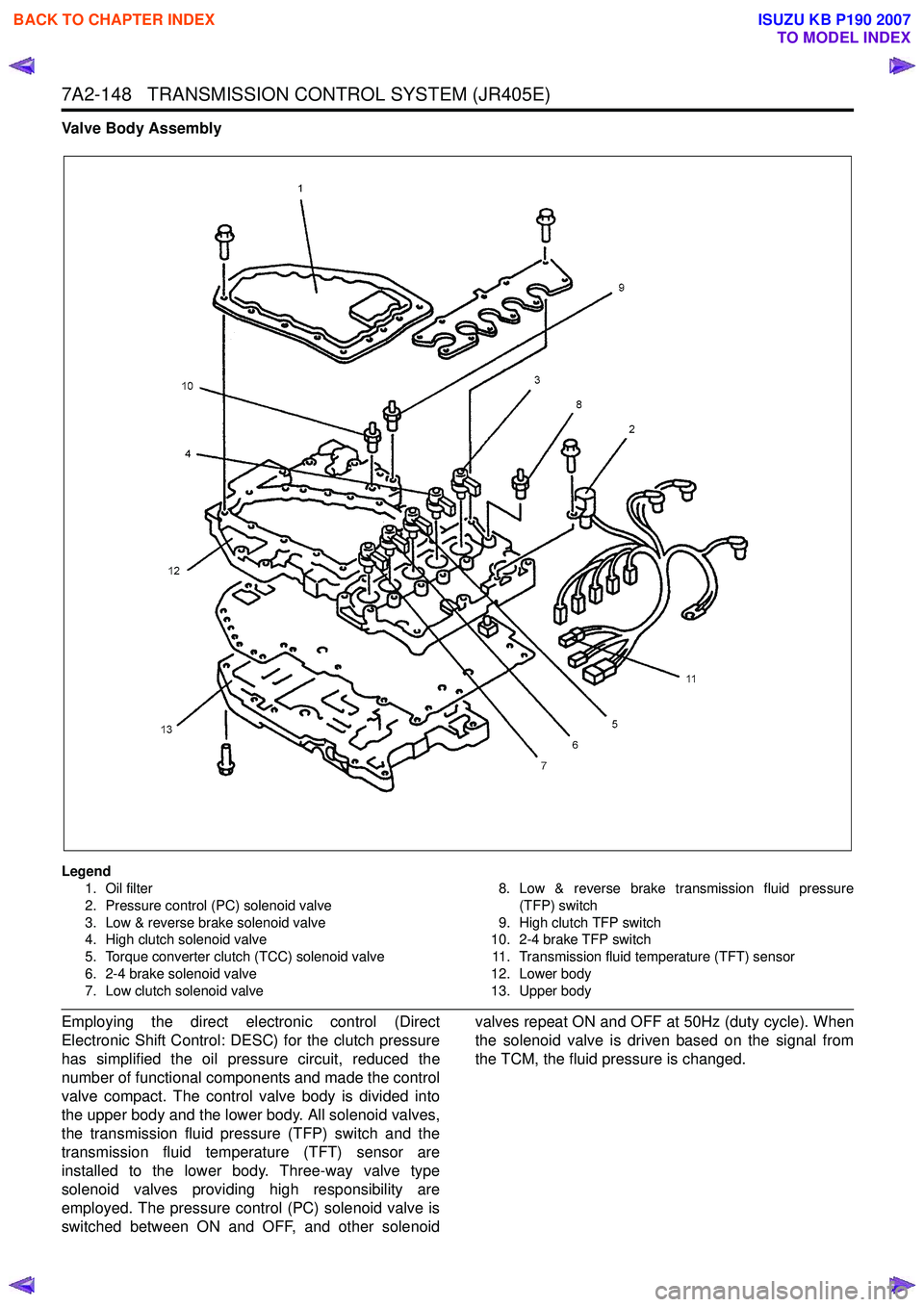
7A2-148 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Valve Body Assembly
Legend1. Oil filter
2. Pressure control (PC) solenoid valve
3. Low & reverse brake solenoid valve
4. High clutch solenoid valve
5. Torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve
6. 2-4 brake solenoid valve
7. Low clutch solenoid valve 8. Low & reverse brake transmission fluid pressure
(TFP) switch
9. High clutch TFP switch
10. 2-4 brake TFP switch
11. Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
12. Lower body
13. Upper body
Employing the direct electronic control (Direct
Electronic Shift Control: DESC) for the clutch pressure
has simplified the oil pressure circuit, reduced the
number of functional components and made the control
valve compact. The control valve body is divided into
the upper body and the lower body. All solenoid valves,
the transmission fluid pressure (TFP) switch and the
transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor are
installed to the lower body. Three-way valve type
solenoid valves providing high responsibility are
employed. The pressure control (PC) solenoid valve is
switched between ON and OFF, and other solenoid valves repeat ON and OFF at 50Hz (duty cycle). When
the solenoid valve is driven based on the signal from
the TCM, the fluid pressure is changed.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007