2007 ISUZU KB P190 ECO mode
[x] Cancel search: ECO modePage 3499 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–221
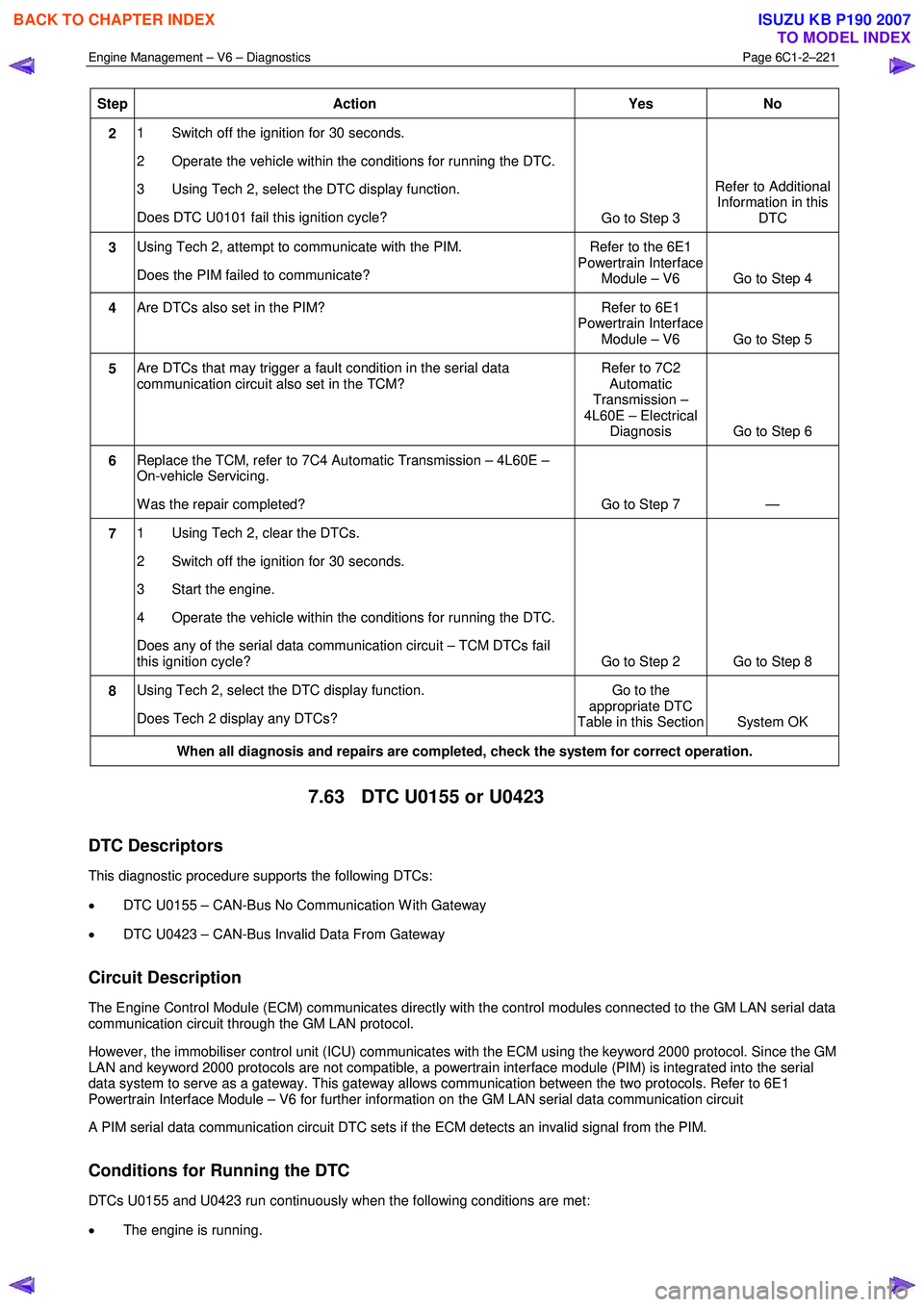
Step Action Yes No
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC U0101 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM.
Does the PIM failed to communicate? Refer to the 6E1
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Go to Step 4
4 Are DTCs also set in the PIM? Refer to 6E1
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Go to Step 5
5 Are DTCs that may trigger a fault condition in the serial data
communication circuit also set in the TCM? Refer to 7C2
Automatic
Transmission –
4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Go to Step 6
6 Replace the TCM, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Servicing.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 7 —
7 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the serial data communication circuit – TCM DTCs fail
this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 8
8 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.63 DTC U0155 or U0423
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC U0155 – CAN-Bus No Communication W ith Gateway
• DTC U0423 – CAN-Bus Invalid Data From Gateway
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) communicates directly with the control modules connected to the GM LAN serial data
communication circuit through the GM LAN protocol.
However, the immobiliser control unit (ICU) communicates with the ECM using the keyword 2000 protocol. Since the GM
LAN and keyword 2000 protocols are not compatible, a powertrain interface module (PIM) is integrated into the serial
data system to serve as a gateway. This gateway allows communication between the two protocols. Refer to 6E1
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 for further information on the GM LAN serial data communication circuit
A PIM serial data communication circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects an invalid signal from the PIM.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTCs U0155 and U0423 run continuously when the following conditions are met:
• The engine is running.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3500 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–222
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM did not receive a valid signal from the PIM within the specified time frame.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The PIM serial data communication circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this
Section, for action taken when a Type C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 The following tests are included in the Diagnostic System Check.
• Tests the integrity of the GM LAN serial data communication circuit.
• Tests for fault conditions on the vehicle immobiliser system stored in the ICU.
DTC U0155 or U0423 Diagnostic Table
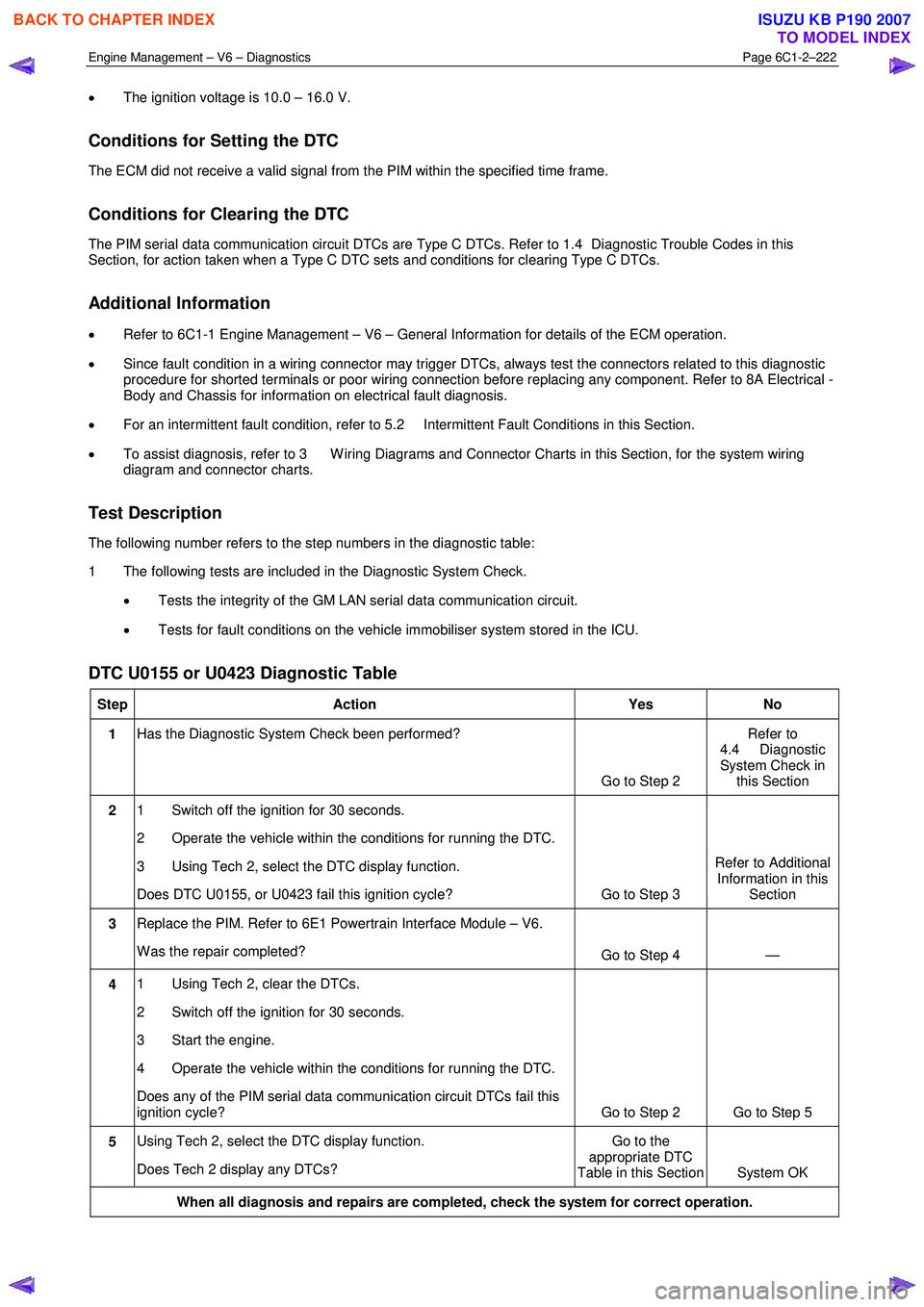
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC U0155, or U0423 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this Section
3 Replace the PIM. Refer to 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 4 —
4 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the PIM serial data communication circuit DTCs fail this
ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 5
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3501 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–223
8 HFV6 Engine – Tech 2 Functions
8.1 Introduction
Do not use a Tech 2 that displays faulty data;
have the Tech 2 repaired. The use of a faulty
Tech 2 can result in misdiagnosis and the
unnecessary replacement of parts.
From the Main Menu, having selected Diagnostics / 2006 / RA Rodeo / Engine , the Tech 2 functions for the HFV6
engine, include:
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Codes
F1: Data Display
F2: OBD Data
F3: Snapshot
F4: Actuator Test
F5: Additional Functions
F6: Programming
8.2 Tech 2 Functions
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Codes
W hen this test mode is initiated, DTCs stored by the ECM can be displayed or cleared. W hen entered, there are three
additional modes for selection:
F0: Read DTC Information: All DTCs stored in the ECM will be displayed.
F1: Clear Engine & Transmission DTCs: Clears all current DTCs in the ECM and TCM memories.
F2: Freeze Frame/Failure Records: Shows the Freeze Frame information. Freeze Frames are types of snapshots stored in the ECM memory.
F1: Data Display
• Use the Tech 2 Data List under the following conditions:
• The Diagnostic System Check – HFV6 Engine has been completed.
• The On-Board Diagnostics are functioning correctly.
• No DTCs are present.
NOTE
• Tech 2 values from an engine that is
operating correctly may be used for
comparison with the engine you are
diagnosing. The Tech 2 engine data lists
represent typical values that would be seen
on a normal operating engine.
• The Tech 2 Data Definitions list that follows
the Data Lists, is arranged in alphabetical
order and contains a brief description of all of
the engine related parameters that are
available.
The following ‘typical’ Tech 2 values were recorded under the following conditions:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3516 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–238
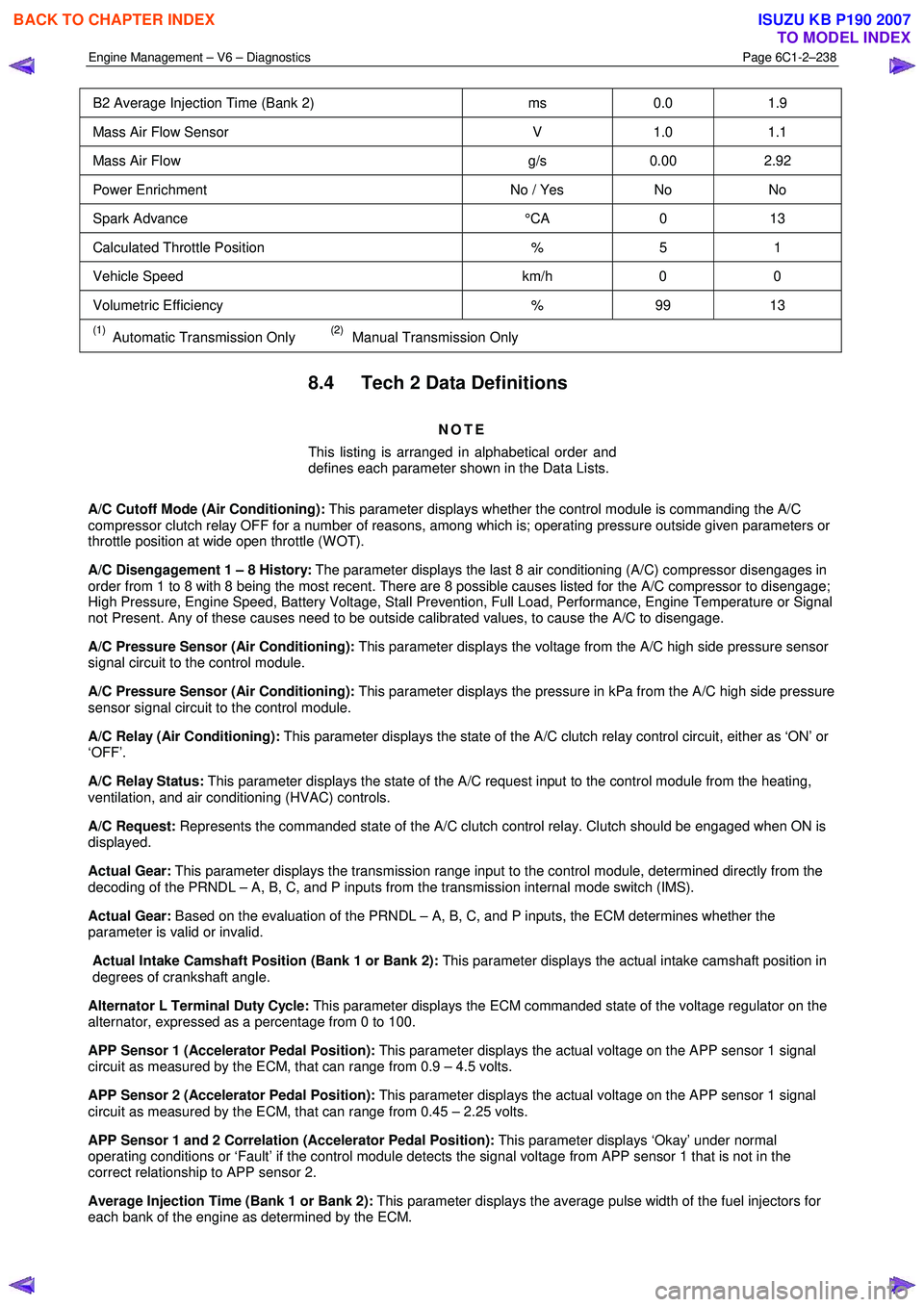
B2 Average Injection Time (Bank 2) ms 0.0 1.9
Mass Air Flow Sensor V 1.0 1.1
Mass Air Flow g/s 0.00 2.92
Power Enrichment No / Yes No No
Spark Advance °CA 0 13
Calculated Throttle Position % 5 1
Vehicle Speed km/h 0 0
Volumetric Efficiency % 99 13
(1) Automatic Transmission Only (2) Manual Transmission Only
8.4 Tech 2 Data Definitions
NOTE
This listing is arranged in alphabetical order and
defines each parameter shown in the Data Lists.
A/C Cutoff Mode (Air Conditioning): This parameter displays whether the control module is commanding the A/C
compressor clutch relay OFF for a number of reasons, among which is; operating pressure outside given parameters or
throttle position at wide open throttle (W OT).
A/C Disengagement 1 – 8 History: The parameter displays the last 8 air conditioning (A/C) compressor disengages in
order from 1 to 8 with 8 being the most recent. There are 8 possible causes listed for the A/C compressor to disengage;
High Pressure, Engine Speed, Battery Voltage, Stall Prevention, Full Load, Performance, Engine Temperature or Signal
not Present. Any of these causes need to be outside calibrated values, to cause the A/C to disengage.
A/C Pressure Sensor (Air Conditioning): This parameter displays the voltage from the A/C high side pressure sensor
signal circuit to the control module.
A/C Pressure Sensor (Air Conditioning): This parameter displays the pressure in kPa from the A/C high side pressure
sensor signal circuit to the control module.
A/C Relay (Air Conditioning): This parameter displays the state of the A/C clutch relay control circuit, either as ‘ON’ or
‘OFF’.
A/C Relay Status: This parameter displays the state of the A/C request input to the control module from the heating,
ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) controls.
A/C Request: Represents the commanded state of the A/C clutch control relay. Clutch should be engaged when ON is
displayed.
Actual Gear: This parameter displays the transmission range input to the control module, determined directly from the
decoding of the PRNDL – A, B, C, and P inputs from the transmission internal mode switch (IMS).
Actual Gear: Based on the evaluation of the PRNDL – A, B, C, and P inputs, the ECM determines whether the
parameter is valid or invalid.
Actual Intake Camshaft Position (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the actual intake camshaft position in
degrees of crankshaft angle.
Alternator L Terminal Duty Cycle: This parameter displays the ECM commanded state of the voltage regulator on the
alternator, expressed as a percentage from 0 to 100.
APP Sensor 1 (Accelerator Pedal Position): This parameter displays the actual voltage on the APP sensor 1 signal
circuit as measured by the ECM, that can range from 0.9 – 4.5 volts.
APP Sensor 2 (Accelerator Pedal Position): This parameter displays the actual voltage on the APP sensor 1 signal
circuit as measured by the ECM, that can range from 0.45 – 2.25 volts.
APP Sensor 1 and 2 Correlation (Accelerator Pedal Position): This parameter displays ‘Okay’ under normal
operating conditions or ‘Fault’ if the control module detects the signal voltage from APP sensor 1 that is not in the
correct relationship to APP sensor 2.
Average Injection Time (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the average pulse width of the fuel injectors for
each bank of the engine as determined by the ECM.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3519 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–241
Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fan relay control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the fan relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter displays
‘Undefined’ until the relay control circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Fuel Level: This parameter displays the amount of fuel in the fuel tank in litres, as calculated by the ECM from data
received from the fuel level sensor.
Fuel Level Sensor: This parameter displays the voltage received from the fuel level sensor in the fuel tank, by the ECM.
Fuel Pump Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fuel pump relay control circuit. The
parameter displays ‘Fault’ if the fuel pump relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The
parameter displays ‘Undefined’ until the relay control circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Fuel Pump Relay: This parameter displays the ECM commanded state of the fuel pump relay control circuit.
Fuel Trim Learn: This parameter displays ‘Enabled’ when conditions are appropriate for enabling long term fuel trim
corrections. This indicates that the long term fuel trim is adapting continuing amounts of short term fuel trim. If Tech 2
displays ‘Disabled’, then long term fuel trim will not respond to changes in short term fuel trim.
Ignition Accessory Signal: This parameter displays ‘On’ when the control module detects a voltage at the
ignition ‘ACC’ terminal, X1-4 of the ignition switch.
Ignition On Signal: This parameter displays ‘On’ when the control module detects a voltage at the ignition ‘IGN’
terminal X1-3 of the ignition switch.
Initial Brake Apply Signal: This parameter displays the status of the brake lamp switch. Before the cruise control can
be activated, this switch contact must be open circuit when the brake pedal is pressed.
Injection Time Cylinder 1 – 6: This parameter displays the amount of fuel injector On-time or pulse width as
commanded by the ECM.
Intake Air Temperature: This parameter displays the temperature of the air entering the air induction system based on
input to the ECM from the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor.
Knock Sensor Signal (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameters displays the voltage input to the control module from the
knock sensor (KS).
Knock Retard: This parameter indicates the amount of spark advance in crankshaft degrees, that the ECM removes
from the ignition control (IC) spark advance in response to the signal from the knock sensors.
Knock Retard Cylinder 1 – 6: This parameter displays the knock retard as commanded by the ECM for cylinders 1-6.
Each cylinder is controlled individually based on both knock sensor signal inputs.
Loop Status B1S1 / B2S1 (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 1): This parameter displays the state of the fuel control system
as commanded by the ECM. ‘Closed’ Loop operation indicates that the ECM is controlling the fuel delivery based on the
oxygen sensors input signal. In ‘Open’ Loop operation the ECM ignores the oxygen sensor input signal and bases the
amount of fuel to be delivered on other sensor inputs.
LTFT Idle/Deceleration (Bank 1 or Bank 2) (Long Term Fuel Trim): This parameter displays the commanded Long
Term Fuel Trim correction by the ECM for bank 1 or bank 2 for idle and deceleration conditions.
LTFT Cruise/Acceleration (Bank 1 or Bank 2) (Long Term Fuel Trim): This parameter displays the commanded Long
Term Fuel Trim correction by the ECM for bank 1 or bank 2 for cruise and acceleration conditions.
Malfunction Indicator (MI): This parameter displays the commanded (‘On, ‘Off’ or ‘Flashing’) state of the malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) control circuit by the ECM.
Malfunction Indicator (MI) Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the MIL control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the MIL control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. This parameter displays
‘Undefined Status’ until the circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Mass Air Flow: This parameter displays the measured quantity (g/s) of air flowing into the engine during all operating
conditions.
Mass Air Flow Sensor: This parameter displays the signal voltage from the mass air flow (MAF) sensor to the ECM.
Misfire Current Cyl. #1 – #6: Tech 2 displays a range of 0 – 200 counts. This parameter displays the number of
misfires that have been detected during the last 200 cylinder firing events. The counters may normally display some
activity, but the activity should be nearly equal for all of the cylinders, and in low numbers.
Misfire History Cyl. #1 – #6: Tech 2 displays a range of 0 – 65,535 counts. The misfire history counters display the total
level of misfire that has been detected on each cylinder. The misfire history counters will not update or show any activity
until a misfire DTC P0300 has become active. The misfire history counters will update every 200 cylinder firing events.
Oil Level: W hen the ECM receives information from the engine oil level switch, where the engine oil level is within
preset parameters, Tech 2 will display ‘Normal’. If not within preset parameters, the display will show ‘Low’.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3520 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–242
Oil Temperature Sensor: This parameter displays the engine oil temperature in degrees C.
Power Enrichment: This parameter displays the status of the operating mode of the ECM used to increase fuel delivery
during certain acceleration conditions.
Reduced Engine Power: This parameter displays when the ECM is commanding reduced engine power due to a
throttle actuator control (TAC) system condition.
Requested Torque: This parameter displays the calculated amount torque requested of the ECM by the Transmission
Control Module (TCM).
Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the short-term correction to the fuel delivery by the
ECM in response to oxygen sensor 1 or 2. If the oxygen sensor indicates a lean air/fuel mixture, the control module will
add fuel, increasing the short term fuel trim above 0. If the oxygen sensor indicates a rich air/fuel mixture, the control
module will reduce fuel decreasing the short term fuel trim below 0.
Spark Advance: This parameter displays the amount of spark advance the ECM is commanding on the ignition control
circuits. The ECM determines the desired advance.
Starter Relay: This parameter displays the Em’s commanded state of the starter motor relay control circuit.
Starter Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the starter relay control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the starter relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter
displays Undefined Status’ until the circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’. This parameter may not change if Tech 2
is used to command the relay control circuit ON.
Start Up ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature): This parameter displays the temperature of the engine coolant on start
up based on input to the ECM from the ECT sensor.
Start Up IAT (Intake Air Temperature): This parameter displays the temperature of the intake air at start in the air
induction system based on input to the ECM from the IAT sensor.
Time Since Engine Off: This parameter displays the amount of time (hours:minutes:seconds) that has elapsed since
the engine was last cycled OFF.
Total Fuel Trim (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the overall fuel trim from the idle/decel cell and the
cruise/accel cell.
Total Misfire: This parameter displays the total number of cylinder firing events that the control module detected as
misfires for the last 200 crankshaft revolution sample period.
TP Sensor 1 (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the actual voltage on the TP sensor 1 signal circuit as
measured by the ECM.
TP Sensor 1 Learned Lower Position (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the learned minimum value of TP
sensor 1 as recorded by the ECM during the last learn procedure.
TP Sensor 2 (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the actual voltage on the TP sensor 2 signal circuit as
measured by the ECM.
TP Sensor 2 Learned Lower Position (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the learned minimum value of TP
sensor 2 as recorded by the ECM during the last learn procedure.
TP Sensor 1-2 Correlation (Throttle Position): This parameter displays ‘Fault’ when the ECM detects that TP sensor 1
voltage signal is not within the correct relationship to TP sensor 2. Tech 2 displays ‘Okay’ under normal operating
conditions.
Transmission Gear: This parameter displays the position of the transmission gear selector that is transmitted over the
serial data circuit from the TCM.
Transmission Gear Selector Signal: This parameter displays the position of the transmission gear selector that is
transmitted over the serial data circuit from the TCM.
Vehicle Speed: This parameter displays the speed of the vehicle as calculated by the TCM from information received
from the vehicle speed sensor (VSS).
Volumetric Efficiency: This parameter displays the volumetric efficiency of the engine as calculated by the control
module.
8.5 OBD Data
Typical Values Tech 2 Display Units Displayed
Ignition On Engine Running
B1S1 O2 Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 1) mA 0.008 0
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3521 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–243
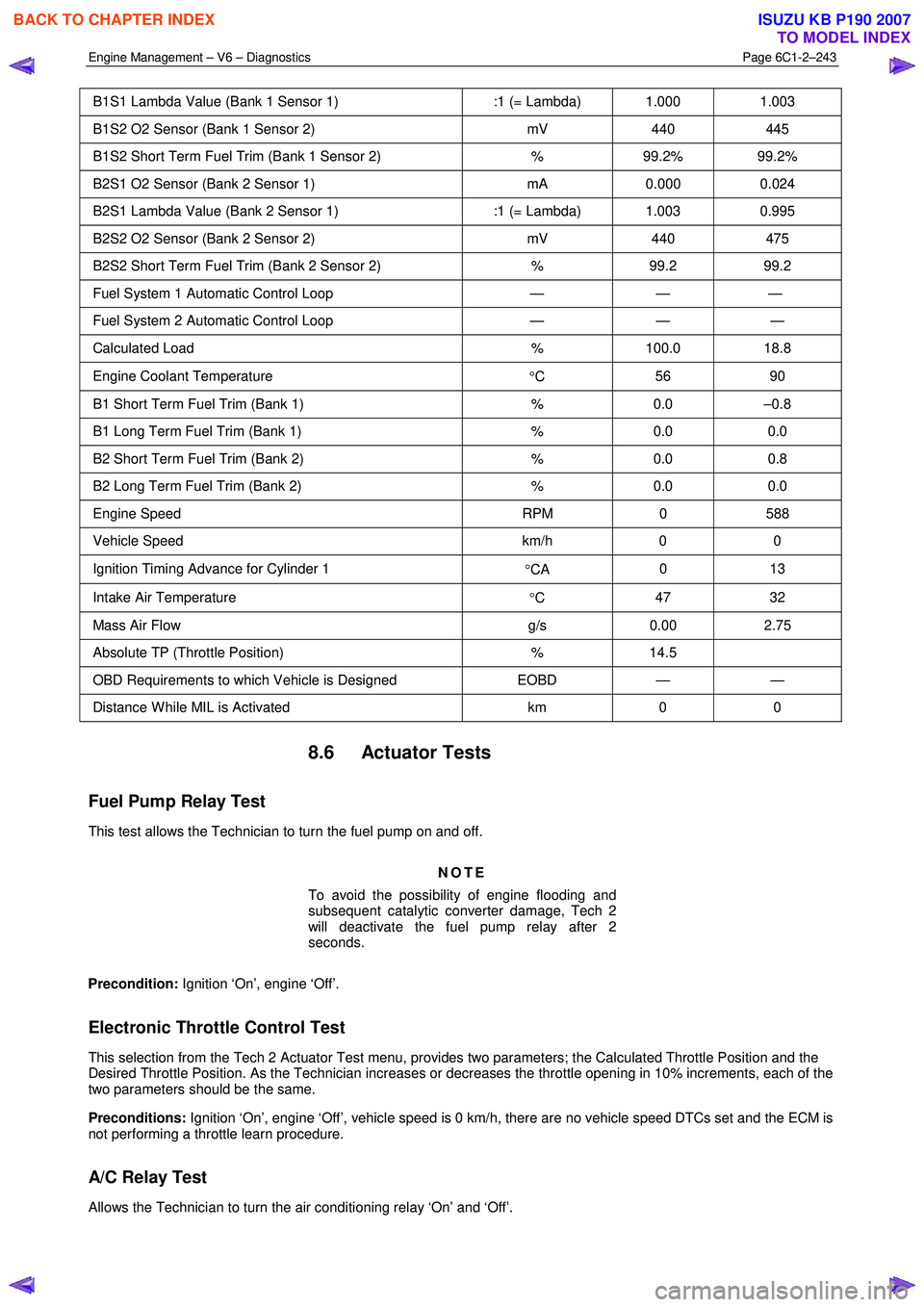
B1S1 Lambda Value (Bank 1 Sensor 1) :1 (= Lambda) 1.000 1.003
B1S2 O2 Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 2) mV 440 445
B1S2 Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1 Sensor 2) % 99.2% 99.2%
B2S1 O2 Sensor (Bank 2 Sensor 1) mA 0.000 0.024
B2S1 Lambda Value (Bank 2 Sensor 1) :1 (= Lambda) 1.003 0.995
B2S2 O2 Sensor (Bank 2 Sensor 2) mV 440 475
B2S2 Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 2 Sensor 2) % 99.2 99.2
Fuel System 1 Automatic Control Loop — — —
Fuel System 2 Automatic Control Loop — — —
Calculated Load % 100.0 18.8
Engine Coolant Temperature
°C 56 90
B1 Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1)
% 0.0 –0.8
B1 Long Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1) % 0.0 0.0
B2 Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 2) % 0.0 0.8
B2 Long Term Fuel Trim (Bank 2) % 0.0 0.0
Engine Speed RPM 0 588
Vehicle Speed km/h 0 0
Ignition Timing Advance for Cylinder 1
°CA 0 13
Intake Air Temperature
°C 47 32
Mass Air Flow
g/s 0.00 2.75
Absolute TP (Throttle Position) % 14.5
OBD Requirements to which Vehicle is Designed EOBD — —
Distance W hile MIL is Activated km 0 0
8.6 Actuator Tests
Fuel Pump Relay Test
This test allows the Technician to turn the fuel pump on and off.
NOTE
To avoid the possibility of engine flooding and
subsequent catalytic converter damage, Tech 2
will deactivate the fuel pump relay after 2
seconds.
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’, engine ‘Off’.
Electronic Throttle Control Test
This selection from the Tech 2 Actuator Test menu, provides two parameters; the Calculated Throttle Position and the
Desired Throttle Position. As the Technician increases or decreases the throttle opening in 10% increments, each of the
two parameters should be the same.
Preconditions: Ignition ‘On’, engine ‘Off’, vehicle speed is 0 km/h, there are no vehicle speed DTCs set and the ECM is
not performing a throttle learn procedure.
A/C Relay Test
Allows the Technician to turn the air conditioning relay ‘On’ and ‘Off’.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3522 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–244
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’.
Cooling Fan (PWM)
Take care that no-one can access the engine
compartment during these tests!
This test allows the Technician to turn the cooling fan on in increments to its maximum speed.
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’ Air conditioning is ‘Off’..
Alternator L Terminal
This test allows the Technician to turn ‘On’ and ‘Off’, the commanded state of the voltage regulator in the alternator. ‘On’
displays a commanded state of 99%, while ‘Off’ displays a commanded state of 0%.
Precondition: Engine running.
EVAP Purge Solenoid
This test allows the Technician to control the EVAP purge solenoid valve. The normal commanded state is ‘0%’. The
system will increase or decrease the amount of purge by changing the duty cycle of the purge valve in 10% increments
within a range of 0 – 100%. The system will remain in the commanded state until cancelled by Tech 2.
NOTE
The EVAP Purge Solenoid Command parameter
may not change states when using this output
control.
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’, engine ‘Off’.
Engine Speed Control
Other DTCs may set when the Engine Speed
Control function is used. Disregard those
DTCs that set under this condition.
Allows the increase / decrease of the engine speed in 20 – 30 rpm increments from the base idle speed, up to 1,600
rpm.
NOTE
If the engine coolant temperature is below the
prescribed minimum, a message to that effect is
displayed and access to engine speed control is
blocked.
Preconditions: Engine running, engine temperature above 80 °C, transmission in Park or Neutral.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007