2007 FORD FIESTA table
[x] Cancel search: tablePage 31 of 1226

General Information
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Two Pack
Can also contain harmful and toxic unreacted
resins and resin hardening agents. The
manufacturers instructions should be followed. See
also Resin-based Adhesives and
Isocyanate
Adhesives and Sealers under Adhesives and
Sealers.
Spraying should preferably be carried out in
exhausted ventilated booths removing vapor and
spray mists from the breathing zone. Individuals
working in booths should wear appropriate
respiratory protection. Those doing small-scale
repair work in the open workshop should wear
air-fed respirators.
Pressurized Equipment
See High Pressure Air, Lubrication and Oil Test
Equipment.
Solder
Solders are mixtures of metals such that the
melting point of the mixture is below that of the
constituent metals (normally lead and tin). Solder
application does not normally give rise to toxic lead
fumes, provided a
gaslair flame is used.
Oxy-acetylene flames should not be used, as they
are much hotter and will cause lead fumes to be
produced.
Some fumes may be produced by the application
of any flame to surfaces coated with grease, and
inhalation of these should be avoided.
Removal of excess solder should be undertaken
with care, to make sure that fine lead dust is not
produced, which can give toxic effects if inhaled.
Respiratory protection may be necessary.
Solder spillage and filings should be collected and
removed promptly to prevent general air
contamination by lead.
High standards of personal hygiene are necessary
in order to avoid ingestion of lead or inhalation of
solder dust from clothing.
Solvents
See also Chemical Materials, Fuels (Kerosene),
Fire.
For example acetone, white spirit, toluene, xylene,
trichloroethane.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006
Used in cleaning and dewaxing materials, paints,
plastics, resins and thinners.
Some may be highly flammable or flammable.
Skin contact will degrease the skin and may result
in irritation and dermatitis following repeated or
prolonged contact. Some can be absorbed through
the skin in toxic or harmful quantities.
Splashes in the eye may cause severe irritation
and could lead to loss of vision.
Brief exposure of high concentrations of vapors or
mists will cause eye and throat irritation,
drowsiness, dizziness, headaches and, in the worst
circumstances, unconsciousness.
Repeated or prolonged exposure to excessive but
lower concentrations of vapors or mists, for which
there might not be adequate warning indications,
can cause more serious toxic or harmful effects.
Aspiration into the lungs, for example through
vomiting, is the most serious consequence of
swallowing.
Avoid splashes to the skin, eyes and clothing. Wear
protective gloves, goggles and clothing if
necessary.
Make sure there is good ventilation when in use,
avoid breathing fumes, vapors and spray mists and
keep containers tightly sealed. Do not use in
confined spaces.
When spraying materials containing solvents, for
example paints, adhesive, coatings, use extraction
ventilation or personal respiratory protection in the
absence of adequate general ventilation.
Do not apply heat or flame except under specific
and detailed manufacturers instructions.
Sound Insulation
See Fibre Insulation, Foams.
Suspended Loads
A CAUTI0N:Never improvise lifting tackle.
There is always a danger when loads are lifted or
suspended. Never work under an unsupported,
suspended or raised load, for example a
suspended engine.
Always make sure that lifting equipment such as
jacks, hoists, axle stands and slings are adequate
and suitable for the job, in good condition and
regularly maintained.
procarmanuals.com
Page 35 of 1226

100-00-1 9 General Information 100-00-1 9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Standard Workshop Practices
Vehicle in Workshop
When working on a vehicle in the workshop always
make sure that:
- the parking brake is applied or the wheels are
securely chocked to prevent the vehicle moving
forwards or backwards.
- the key is removed from key operated hood
locks before any work is carried out around the
front of the vehicle.
- if the engine is to be run, there is adequate
ventilation, or an extraction hose to remove
exhaust fumes.
- there is adequate room to raise the vehicle and
remove the wheels, if necessary.
- fender covers are always fitted if any work is to
be carried out in the engine compartment.
- the battery is disconnected if working on the
engine, underneath the vehicle, or if the vehicle
is raised.
Alternative Fuel - Dons
- Do work on the vehicle in a designated area,
that is well ventilated and with access restricted
to qualified personnel only.
- Install new warning labels to their original
locations.
- If possible always isolate the alternative fuel
tank, and run the vehicle on the alternative fuel
until it automatically switches to its normal fuel
prior to taking the vehicle into the workshop
service area.
- Only use tested and approved components and
pipes when repairing or servicing
LPG and CNG
systems.
Alternative Fuel - Do Nots
- Do not vent off LPG fuel.
- Do not use shop air pressure to force LPG fuel
from the fuel tank.
( A CAUTION:When electric arc welding on a - Do not use paint drying ovens above 40°C for vehicle, always disconnect the generator any alternative fuel vehicle. LPG and CNG fuel wiring to prevent the possibility of a surge tanks must be removed from the vehicle prior of current causing damage to the internal to being put into paint drying ovens above 40°C. components of the generator. - Do not modify the system or install new - if using welding equipment on the vehicle, a
components that are not designed for gas
suitable fire extinguisher is readily available.
vehicles.
Alternative Fuel
A WARNING:When servicing the fuel system
always follow the recommended
procedures. Failure to follow these
instructions may result in personal injury.
If the odor of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) or
compressed natural gas
(CNG) is present in the
air in the workshop, warn all persons in the area
to:
- extinguish all flames and lighted tobacco.
- shut off electrical and air powered equipment.
- evacuate the area.
- ventilate the area.
- contact the fire control authorities.
- remove the vehicle to a dedicated, ventilated
area.
- Do not evacuate fuel tanks unless there is repair
that requires the removal of the fuel tank.
- Do not work on the fuel lines or system
components unless the alternative fuel has been
evacuated and the pressure in the system
reduced to atmospheric or less.
- Do not use anything other than the specified
leak detector fluid to trace fuel leaks.
Be aware of situations that may cause the
LPG or I
CNG fuel system to vent off fuel, such as: I
- extremely hot days.
- parking by a space heater.
- hoisting a vehicle up near a ceiling heater.
Only fully trained personnel, who are conversant
with local standards, are to work on alternative fuel
vehicles.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 GI 7373en
procarmanuals.com
Page 37 of 1226

I 00-00-21 General Information 1 00-00-21
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Always disconnect the jumper cables in the reverse
order to the connecting sequence and do not short
i the ends of the cables.
Do not rely on the generator to restore a
discharged battery. For a generator to recharge a
battery, it would take in excess of eight hours
continuous driving with no additional loads placed
on the battery.
Component Cleaning
To prevent the ingress of dirt, accumulations of
loose dirt and greasy deposits should be removed
before disconnecting or dismantling components
or assemblies.
Components should be thoroughly cleaned before inspection prior to reassembly.
Cleaning Methods:
- Dry cleaning.
- Removal of loose dirt with soft or cable brushes.
- Scraping dirt off with a piece of metal or wood.
( ,- Wiping off with a rag.
A WARN1NG:Wear eye protection when
cleaning vehicle components with
compressed air, a steam cleaner or a
power washer. Failure to follow this
instruction may result in personal injury.
CAUTIONS:
A Compressed air is sometimes 'wet' so use
with caution, especially on hydraulic
systems.
A To prevent damage to the electrical
connectors in the engine compartment, do
not use a steam cleaner or a power washer
to clean the engine compartment.
- Blowing dirt off with compressed air.
- Removal of dry dust using vacuum equipment.
This method must always be used to remove
friction lining material dust (asbestos particles).
- Steam cleaning.
A WARN1NG:Most solvents require careful
handling and some are harmful. Refer to
Health and Safety Precautions and to the
manufacturers literature for the relevant
safety precautions. Failure to follow these
instructions may result in personal injury.
Various solvents are available which are suitable
for component cleaning. Some components, such
as brake hydraulic parts and electrical assemblies
should be cleaned only with recommended solvents
- refer to Solvents, Sealers and Adhesives or to
the section of the manual relevant to the
component.
Calibration of Essential Measuring
Equipment
A WARNING:Equipment, which requires
regular calibration, must be calibrated in
accordance with the manufacturers
instructions. Failure to follow this
instruction may result in personal injury
or damage to components.
It is of fundamental importance that certain
essential equipment, for example torque wrenches,
multimeters, exhaust gas analyzers or rolling roads,
are regularly calibrated in accordance with the
manufacturers instructions.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 GI 7373en
procarmanuals.com
Page 52 of 1226
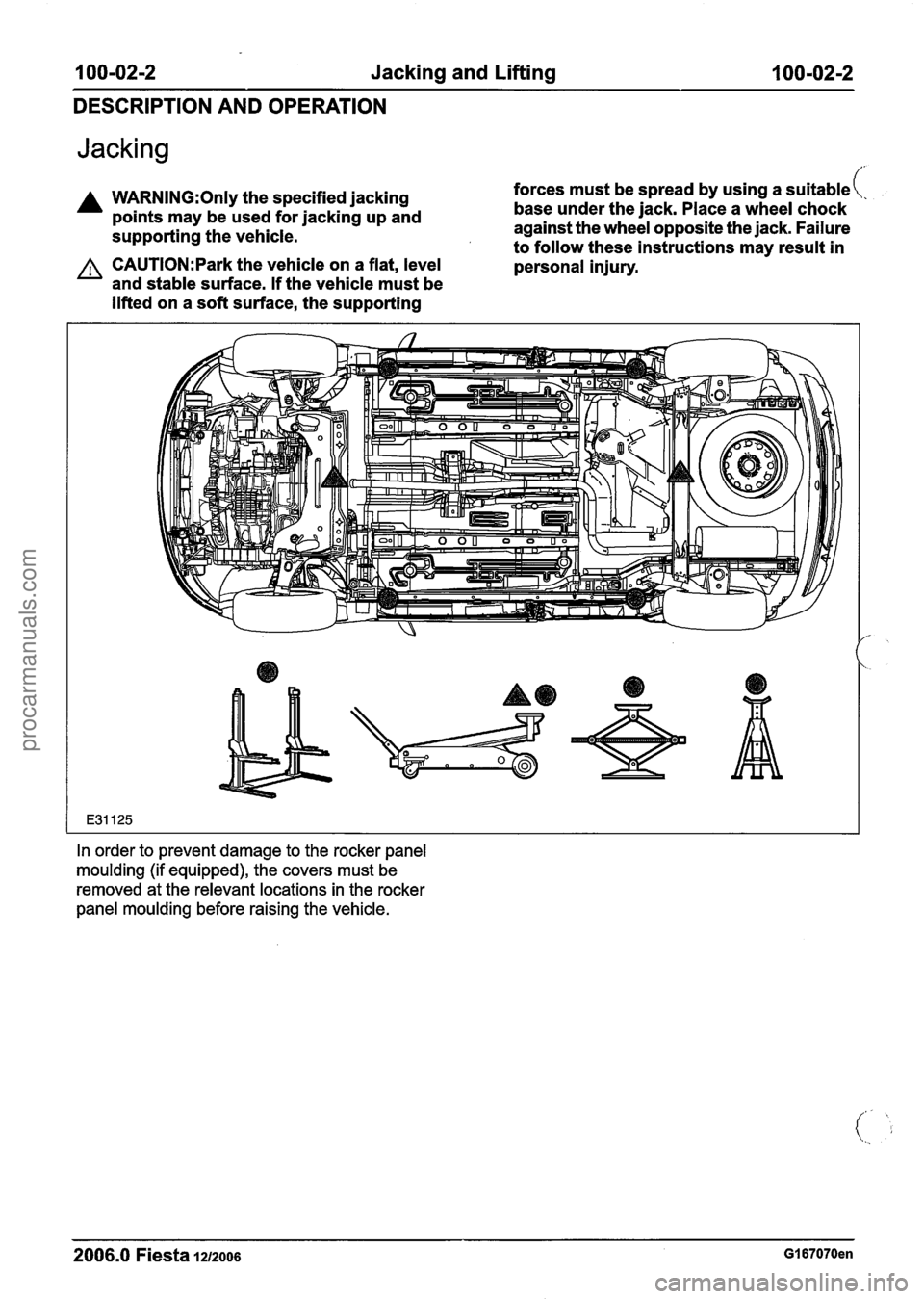
100-02-2 Jacking and Lifting 100-02-2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Jacking
A WARN1NG:Only the specified jacking
points may be used for jacking up and
supporting the vehicle.
A CAUTI0N:Park the vehicle on a flat, level
and stable surface. If the vehicle must be
lifted on a soft surface, the supporting forces
must be spread by using a suitable(:
base under the jack. Place a wheel chock
against the wheel opposite the jack. Failure
to follow these instructions may result in
personal injury.
In order to prevent damage to the rocker panel
moulding (if equipped), the covers must be
removed at the relevant locations in the rocker
panel moulding before raising the vehicle.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 GI 67070en
procarmanuals.com
Page 60 of 1226

100-04-4 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-0414
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH)
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern. Identify the Condition
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical NVH usually occur in four areas:
or electrical damage.
tires
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported
concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) engine accessories
before proceeding to the next step.
suspension
4. If the concern is not visually evident, verify the
symptom and REFER to the Symptom Chart.
How to Use this Diagnostic Procedure
Section
Noise, vibration and harshness (NVH) concerns
have become more important as
vehjcles have
become more sensitive to these vibrations. This
section is designed to aid in identifying these
concerns.
The section provides diagnostic procedures based on symptom. If the condition occurs at
high speed, for instance, the most likely place
to start is under Shake and Vibration While
Driving.
The road test procedure will tell how to sort the
conditions into categories and how to tell a
vibration from a shake.
A series of Road Test Quick Checks are
provided to make sure that a cause is either
pinpointed or eliminated.
Name the condition, proceed to the appropriate
section and locate the correct diagnosis. When
the condition is identified, the job is partly done.
Follow the diagnostic procedure as outlined.
Quick Checks are described within the step,
while more involved tests and adjustments are
outlined in General Procedures.
Always follow each step exactly and make notes
to recall important findings later.
driveline
It is important, therefore, that an NVH concern be
isolated into its specific
area(s) as soon as
possible. The easiest and quickest way to do this
is to carry out the Road Test as outlined. To assist
in the diagnosis and testing
procedure(s), use a
suitable approved NVH diagnosis tester.
Noise Diagnostic Procedure
Non-Axle Noise
The five most common sources of non-axle noise
are exhaust, tires, roof racks, trim panels and
( transmission.
Therefore, make sure that none of the following
conditions are the cause of the noise before
proceeding with a driveline
teardown and
diagnosis.
In certain conditions, the pitch of the exhaust
may sound very much like gear noise. At other
times, it can be mistaken for a wheel bearing
rumble.
Tires, especially snow tires, can have a high
pitched tread whine or roar, similar to gear
noise. Radial tires may have this characteristic.
Also, any non-standard tire with an unusual
tread construction may emit a roar or whine
noise.
Trim panels can also cause whistling or whining
noise.
Clunk may be a metallic noise heard when the
Customer Interview automatic transaxle is engaged in "R
(REVERSE) or "D" (DRIVE) or it may occur
The road test and customer interview (if available) when
the throttle is applied or released. It is
provide information that will help identify the caused
by backlash somewhere in the driveline.
,
concern and will provide direction to the correct Bearing rumble sounds like marbles being
starting point for diagnosis. (
tumbled. This condition is usually caused by a
damaged wheel bearing.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
procarmanuals.com
Page 61 of 1226

100-04-5 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Noise Conditions
Gear noise is typically a howling or whining due
to gear damage or incorrect bearing preload. It
can occur at various speeds and driving
conditions, or it can be continuous.
Chuckle is a particular rattling noise that sounds
like a stick against the spokes of a spinning
bicycle wheel. It occurs while decelerating from
64
kmlh (40 mph) and can usually be heard all
the way to a stop. The frequency varies with
vehicle speed.
Knock is very similar to chuckle, though it may
be louder and occurs on acceleration or
deceleration. The
teardown will disclose what
has to be corrected.
Clicking, popping or grinding noises may be caused
by the following:
worn, damaged or incorrectly installed wheel
bearing, suspension or brake component.
Check and rule out tires, exhaust and trim items
before disassembling the transmission to diagnose
and correct gear noise.
The noises described under Road Test usually
( have specific causes that can be diagnosed by
observation as the unit is disassembled. The initial
clues are the type of noise heard on the road test
and driving conditions.
Vibration Conditions
Vibration at highway speeds may be caused by
the following:
out-of-balance front or rear wheels.
out-of-round tires.
Shudder or vibration during acceleration may be
caused by the following:
damaged powertrainldrivetrain mounts.
excessively high constant velocity (CV) joint
operating angles caused by incorrect ride height.
Check ride height, verify correct spring rate and
check items under inoperative conditions.
Road Test
I A gear-driven unit will produce a certain amount
of noise. Some noise is acceptable and may be
audible at certain speeds or under various driving conditions,
as on a newly paved asphalt road. The
slight noise is in no way detrimental and must be
considered normal.
The road test and customer interview (if available)
provide information needed to identify the condition
-
and give direction to the correct starting point for
diagnosis.
1. Make notes throughout the diagnosis routine.
Make sure to write down even the smallest bit
of information, because it may turn out to be the
most important.
2. Do not touch anything until a road test and a
thorough visual inspection of the vehicle have been carried out. Leave the tire pressures and
vehicle load just where they were when the
condition was first observed. Adjusting tire
pressures, vehicle load or making other
adjustments may reduce the
condition(s)
intensity to a point where it cannot be identified
clearly. It may also inject something new into
the system, preventing correct diagnosis.
3. Make a visual inspection as part of the
preliminary diagnosis routine, writing down
anything that does not look right. Note tire
pressures, but do not adjust them yet. Note
leaking fluids, loose nuts and bolts, or bright
spots where components may be rubbing
against each other. Check the load space for
unusual loads.
4. Road test the vehicle and define the condition
by reproducing it several times during the road
test.
5. Carry out the Road Test Quick Checks as soon
as the condition is reproduced. This will identify
the correct diagnostic procedure. Carry out the
Road Test Quick Checks more than once to
verify they are providing a valid result.
Remember, the Road Test Quick Checks may
not tell where the concern is, but they will tell
where it is not.
Road Test Quick Checks
1. 24-80 kmlh (1 5-50 mph): with light acceleration,
a moaning noise is heard and possibly a
vibration felt in the front floor panel. It is usually
worse at a particular engine speed and at a
particular throttle setting during acceleration at
that speed. It may also produce a moaning
sound, depending on what component is
causing it. REFER to Tip-in Moan in the
Driveline Noise and Vibration Symptom Chart.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
procarmanuals.com
Page 62 of 1226

100-04-6 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
2. AccelerationIDeceleration: With slow
acceleration and deceleration, a shake is
sometimes noticed in the steering
wheellcolumn,
seats, front floor panel, front door trim panel or
front end sheet metal. It is a low frequency
vibration (around
9-1 5 cycles per second). It
may or may not be increased by applying the
brakes lightly. REFER to
Idle
BoomIShakeNibration in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
High Speed: A vibration is felt in the front floor
panel or seats with no visible shake, but with
an accompanying sound or rumble, buzz, hum,
drone or booming noise. Coast with the clutch
pedal depressed (manual transmission) or shift
control selector lever in "N" (NEUTRAL)
(automatic transmission) and engine idling. If
vibration is still evident, it may be related to
wheels, tires, front brake discs, wheel hubs or
front wheel bearings. REFER to Shake and
Vibration While Driving in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
4. Engine rpm Sensitive: A vibration is felt
whenever the engine reaches a particular rpm.
It will disappear in neutral coasts. The vibration
can be duplicated by operating the engine at
the problem rpm while the vehicle is stationary.
It can be caused by any component, from the
accessory drive belt to the clutch or torque
converter which turns at engine speed when the
vehicle is stopped. REFER to Shake and
Vibration While Driving in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
5. Noise and Vibration While Turning: Clicking,
popping or grinding noises may be due to the
following:
worn, damaged or incorrectly installed front
wheel bearing.
damaged
powertrainldrivetrain mounts.
Road Conditions
An experienced technician will always establish a
route that will be used for all NVH diagnosis road
tests. The road selected should be reasonably
smooth, level and free of undulations (unless a
particular condition needs to be identified). A
smooth asphalt road that allows driving over a
range of speeds is best. Gravel or bumpy roads
are unsuitable because of the additional road noise produced.
Once the route is established and
consistently used, the road noise variable is
eliminated from the test results.
N0TE:Some concerns may be apparent only on
smooth asphalt roads.
If a customer complains of a noise or vibration on
a particular road and only on a particular road, the
source of the concern may be the road surface. If
possible, try to test the vehicle on the same type
of road.
Vehicle Preparation
Carry out a thorough visual inspection of the
vehicle before carrying out the road test. Note
anything which is unusual. Do not repair or adjust
any condition until the road test is carried out,
unless the vehicle is inoperative or the condition
could pose a hazard to the technician. After
verifying that the condition has been corrected,
make sure all components removed have been
installed.
Power Steering Conditions
c !
Check for the noise in the following conditions to
verify the customer concern.
Check for the noise in several temperature
conditions.
Is the noise from when the vehicle was new?
Can the noise be repeated constantly or is it
random?
Check the condition of the vehicle age, mileage
and service record.
Interview the customer to find the operating
condition in which the noise will occur. Test the
vehicle based on the
detail(s) from the customer
interview.
Follow the power steering operation noise
condition tables below, to find which condition
the noise will occur.
Power Steering Operation Noise Check
Step 1 : Check for NVH concerns from non-steering
components, which may sound like noises coming
from the steering system.
I:. ':
2006.0 Fiesta 121zoo6 G37349en
procarmanuals.com
Page 66 of 1226

100-04-1 0 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Power Steering Whine Noise 2. Engine speed at 1800 +/- 50 rpm with slow 90
degrees turning of the steering wheel.
Test Condition 3. Engine speed at 3000 +I- 50 rpm with no
Listen for steering whine noise with the vehicle steering action.
parked, transmission in neutral and all windows
4. Engine speed at 3000
+I- 50 rpm with slow 90
closed in the following test conditions. degrees turning of the steering wheel.
1. Engine speed at 1800
+I- 50 rpm with no
steering action. Symptom
Power steering system moan
noise
- A continuous low pitched
humming noise occurs when the
steering wheel is turned and the
steering system is loaded. Noise
frequency changes with engine
rpm changes. Particularly
annoying at lower engine speed.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
Possible Sources
Power steering lines.
Incorrect power steering fluid.
Power steering pump. Action
CHECK
the routing of the
power steering lines.
CHECK the power steering line
clamps are secure.
CHECK the power steering
lines for clearance from the
vehicle body, front axle cross-
member and steering gear.
FLUSH the power steering
system. REFER to: (21 1-00
)
Power Steering System
Flushing
- I .8L Duratec-HE
(M14)/1.8L Duratec-SCi
(M14)/2.OL Duratec-HE (M14)
(General Procedures),
Power Steering System
Flushing
- 3.OL Duratec-SE
(VE6)/2.5L Duratec-VE
(VE6)/3.OL Duratec-ST (VE6)
(General Procedures),
Power Steering System
Flushing
- 2.OL Duratorq-
DirrDDi (Puma) Diesel12.0L
Duratorq-TDCi (Puma)
Diesell2.2L Duratorq-TDCi
(Puma) Diesel (General
Procedures).
Pressure pulses from the power
steering pump. Certain amount of
noise level acceptable, not a
safety critical item.
procarmanuals.com