2007 FORD FIESTA change wheel
[x] Cancel search: change wheelPage 66 of 1226

100-04-1 0 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Power Steering Whine Noise 2. Engine speed at 1800 +/- 50 rpm with slow 90
degrees turning of the steering wheel.
Test Condition 3. Engine speed at 3000 +I- 50 rpm with no
Listen for steering whine noise with the vehicle steering action.
parked, transmission in neutral and all windows
4. Engine speed at 3000
+I- 50 rpm with slow 90
closed in the following test conditions. degrees turning of the steering wheel.
1. Engine speed at 1800
+I- 50 rpm with no
steering action. Symptom
Power steering system moan
noise
- A continuous low pitched
humming noise occurs when the
steering wheel is turned and the
steering system is loaded. Noise
frequency changes with engine
rpm changes. Particularly
annoying at lower engine speed.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
Possible Sources
Power steering lines.
Incorrect power steering fluid.
Power steering pump. Action
CHECK
the routing of the
power steering lines.
CHECK the power steering line
clamps are secure.
CHECK the power steering
lines for clearance from the
vehicle body, front axle cross-
member and steering gear.
FLUSH the power steering
system. REFER to: (21 1-00
)
Power Steering System
Flushing
- I .8L Duratec-HE
(M14)/1.8L Duratec-SCi
(M14)/2.OL Duratec-HE (M14)
(General Procedures),
Power Steering System
Flushing
- 3.OL Duratec-SE
(VE6)/2.5L Duratec-VE
(VE6)/3.OL Duratec-ST (VE6)
(General Procedures),
Power Steering System
Flushing
- 2.OL Duratorq-
DirrDDi (Puma) Diesel12.0L
Duratorq-TDCi (Puma)
Diesell2.2L Duratorq-TDCi
(Puma) Diesel (General
Procedures).
Pressure pulses from the power
steering pump. Certain amount of
noise level acceptable, not a
safety critical item.
procarmanuals.com
Page 68 of 1226

I 00-04-1 2 Noise, Vibration and Harshness I 00=04m12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Power Steering Hiss Noise
Test Condition
Listen for steering hiss noise with the vehicle
parked, transmission in neutral and all windows
-
closed in the following test conditions.
Power Steering Lock Stop Impact Knock 1. Turn the steering wheel to the left-hand and
Noise right-hand steering locks and listen for the
impact noise.
Test Condition
Listen for steering knock noise with the engine
speed at idle in the following test conditions (noise
also apparent with engine off).
Action
CHECK the installation and
potential damage of the floor seal.
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Symptom
N0TE:Engine speed at idle
turning the steering wheel slowly
lock to lock.
Power steering system hiss noise
- a high frequency, continuous
rush or swish noise like escaping
air from a balloon. Hiss occurs
while turning between the steering
lock stops, all steering angles.
Noise does not change with
engine rpm and is worse at high
operating temperatures.
N0TE:Engine speed at idle
holding the steering wheel against
a steering lock for three seconds.
Do not hold for more than five
seconds.
Power steering system hiss noise
- a continuous noise like escaping
air occurs while holding the
steering against a steering lock
stop.
Possible Sources
Floor seal.
Power steering gear valve design.
Power steering system hydraulic
design.
Power pump pressure
relief valve.
Power Steering Mechanical Knock Noise 1. Turn the steering wheel 90 degrees to the right,
(PAS off) hold and then quickly release.
2. Turn the steering wheel 90 degrees to the left, Test Condition hold and then quickly release.
Listen for steering knock noise with the engine off
in the following test conditions (no power assist).
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
Action
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Symptom
Power steering system knock
noise
- a heavy loud sound like a
knock on a door that occurs in
parking condition when hitting the
lock stop.
Possible Sources
Power steering gear mechanical
noise, metal to metal at end of
steering travel.
procarmanuals.com
Page 95 of 1226

204-00-1 5 Suspension System - General Information 204-00-1 5 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
2. If there is any free movement install a new lower 4. Compress and pull the piston rod in the vertical
arm. position. Feel if the resistance force at the point
REFER to: Lower Arm (204-01 Front
Suspension, Removal and Installation).
3. If a new lower arm is installed it will be
necessary to check and adjust the front wheel
alignment.
REFER to: Specifications (204-00 Suspension
System
- General Information, Specifications). of direction change-over
is perceptible without
a lag. If a lag is perceptible it is an indication of
damper valve damage and new struts or shock
absorbers must be installed. REFER to:
Front Strut and Spring Assembly (204-01 Front
Suspension, Disassembly and Assembly),
Front Strut and Spring Assembly (204-01 Front
Suspension, Removal and Installation),
Rear Shock Absorber (204-02 Rear Suspension,
Removal and Installation).
Strut or Shock Absorber Inspection
N0TE:lnspect the struts or shock absorber for
signs of oil
weepage or leaks. Make sure that the
oil is not from another source.
Weepage:
deposits a thin film of oil on the strut and spring
assembly or shock absorber.
is normally noticed due to a collection of dust
on the strut and spring assembly or shock
absorber.
occurs during the normal running-in period of
4800
- 8050 km. After this period no new signs
of oil should be visible.
does not require new struts or shock absorbers
to be installed.
Leakage:
covers the entire strut and spring assembly or
shock absorber with oil.
will drip oil onto the surrounding suspension
components.
requires new struts or shock absorbers to be
installed.
Strut or Shock Absorber Testing
N0TE:Struts or shock absorbers must be tested
in the vertical position.
I. Remove both strut and spring assemblies or
shock absorbers. The piston rods should extend.
Disassemble the strut and spring assemblies.
REFER to: Front Strut and Spring Assembly
(204-01 Front Suspension, Disassembly
and Assembly).
2. Compress the piston rods. Both piston rods
should offer the same resistance when
compressing.
3. Compress and release the piston rods. The
piston rods should extent equally.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 Gl49885en
procarmanuals.com
Page 147 of 1226

204-04-3 Wheels and Tires 204-04-3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Wheels and Tires
lnspection and Verification
Visual Inspection Chart
I Mechanical I
I Tire pressure(s) * I
I Wheel nuts I
I Wheel studs I
* Vehicles equipped with a tire pressure monitoring system must be inspected for correct operation
using the diagnostic tool.
To maximize tire performance, inspect the tires for
signs of incorrect inflation and uneven wear which
may indicate a need for balancing, rotation or
suspension alignment. Tires should also be
checked frequently for cuts, stone bruises,
abrasions, blisters and for objects that may have
become embedded in the tread. More frequent
inspections are recommended when rapid or ( extreme temperature changes occur or when road
surfaces are rough or occasionally littered with
foreign material.
As a further visible check of tire condition, tread
wear indicators are molded into the bottom of the
tread grooves. When these indicator bands become
visible, new tires must be installed.
Tire Wear Diagnosis
Uneven wear is usually caused by either excessive
camber or excessive toe on tires.
Sometimes incorrect toe settings or worn struts will
cause severe 'cupping' or 'scalloped' tire wear on
non-driven wheels.
Severely incorrect toe settings will also cause other unusual wear patterns.
Tire Vibration Diagnosis
A tire vibration diagnostic procedure always begins
with a road test. The road test and customer
interview (if available) will provide much of the
information needed to find the source of a vibration. During
the road test, drive the vehicle on a road
that is smooth and free of undulations. If vibration
is apparent, note and record the following:
- the speed at which the vibration occurs.
- what type of vibration occurs in each speed
range.
- mechanical or audible
- how the vibration is affected by changes in the
following:
- engine torque
- vehicle speed
- engine speed
- type of vibration - sensitivity:
- torque sensitive
- vehicle speed sensitive
- engine speed sensitive
The following explanations help isolate the source
of the vibration.
Torque Sensitive
This means that the condition can be improved or
made worse by accelerating, decelerating,
coasting, maintaining a steady vehicle speed or
applying engine torque.
Vehicle Speed Sensitive
This means that the vibration always occurs at the
same vehicle speed and is not affected by engine
torque, engine speed or the transmission gear
selected.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006
procarmanuals.com
Page 202 of 1226

Brake System - General Information
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
evidence of a brake concern. Check for the brake
warning indicator illumination and the fluid level in
the master cylinder reservoir.
Normal Conditions
The following conditions are considered normal
and are not indications that the brake master
cylinder is in need of service.
- Modern brake systems are not designed to
produce as hard a pedal effort as in the past.
Complaints of light pedal efforts should be
compared to pedal efforts of another vehicle, of
the same model and year.
- During normal operation of the brake the fluid
level in the reservoir will rise during brake
application and fall during release. The net fluid
level
(i.e., after brake application and release)
will remain unchanged.
- A trace of brake fluid will exists on the brake
booster shell below the master cylinder
mounting flange. This results from the normal
lubricating action of the master cylinder bore
end seal.
- The fluid level will fall with brake shoe and lining
wear.
Abnormal Conditions
N0TE:Prior to performing any diagnosis, make
sure the brake system warning indicator is
functional.
Changes in brake pedal feel or travel are indicators
that something could be wrong with the braking system. The diagnostic procedure and techniques
use brake pedal feel, warning indicator illumination
and low brake fluid level as indicators in diagnosing
braking system concerns. The following conditions
are considered abnormal and indicate that the
brake master cylinder is in need of service.
- The brake pedal effort is excessive. This may
be caused by a bind or obstruction in the pedal
.
or linkage, clogged fluid control valve or ( ' insufficient booster vacuum.
- The rear brakes lock up during light pedal force.
This may be caused by incorrect tire pressures,
grease or fluid on the brake shoes and linings,
damaged brake shoes and linings, incorrectly
adjusted parking brake, or damaged or
contaminated brake pressure control valves.
- The brake pedal effort is erratic. This condition
could be caused by a brake booster malfunction,
extreme caliper piston knock back or incorrectly
installed brake shoes and linings.
- The brake warning indicator is ON. This may
be caused by low fluid level, ignition wire routing
too close to the fluid level indicator assembly,
or float assembly damage.
Bypass Condition Test
1. Check the fluid in brake master cylinder. Fill the
brake master cylinder reservoir if low or empty.
2. Observe the fluid level in the brake master
cylinder reservoir. If after several brake
applications, the fluid level remains the same,
measure the wheel turning torque required to
rotate the wheels with the brakes applied as
follows:
Place the transaxle in NEUTRAL and raise and
support the vehicle. REFER to: (1 00-02 Jacking
and Lifting)
Jacking (Description and Operation),
Lifting (Description and Operation).
Apply the brakes with a minimum of 445 N (100
Ib) and hold for approximately 15 seconds. With
the brakes still applied, exert a torque on the front
wheels of 10.1 Nm (75
1b.R). If either wheel rotates,
install a new brake master cylinder. REFER to:
(206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation)
- The brake pedal goes down fast. This could be Brake Master Cylinder - RHD (Removal and
caused by an external or internal leak. Installation),
- The brake
pedal eases down slowly. This could Brake Master Cylinder - LHD
(Removal and
be caused by an external or internal leak. Installation).
- The
brake pedal is low and or feels spongy. This
condition may be caused by no fluid in the brake
Non-Pressure Leaks master cylinder reservoir, reservoir cap vent
holes clogged or air in the hydraulic system.
Any empty brake master cylinder reservoir
condition may be caused by two types of
non-pressure external leaks.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006
procarmanuals.com
Page 631 of 1226

303101 B-9 Engine - 2.OL Duratec-HE (M14) 303-01 B-9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The complete engine is made of cast aluminum
which, when combined with the plastic intake
manifold, gives a very light unit.
2.OL Duratec-HE (M14) engine
Emission standard
N0TE:Due to the fine tolerance in the bearing
clearances and bearing shells, no service
operations whatsoever are permitted on the crank
assembly. In the event of damage, the complete
cylinder block and crank assembly must be
changed. European
Emissions Standard Stage
IV (Stage II I, depending
on country)
Further design features include a ladder frame
incorporating the main bearing caps which support
the crankshaft in the cylinder block, and the
deep-drawn side walls of the cylinder block which
reduce engine vibration.
The camshafts are driven by a pinned link chain
which runs very quietly and is also
maintenance-free.
Cvlinder head
Item Description
1
2
The engine management for the 2.OL Duratec-HE
(M14) is provided by a Visteon system.
Item Description
Exhaust camshaft
Camshaft bearing cap
', This engine management systems controls the ' , sequential multipoint fuel injection (SFI) and the
I 1 (Enngine code I
3
4
wl~n~ine serial number I
Cam to identify cylinder No. 1
Intake camshaft
ele~tronically controlled coolant-cooled exhaust The design and the valve arrangement in the gas recirculation (EGR) valve.
cylinder head is similar to the head of the Zetec-SE
engines.
Enaine codes
5
The engine code and the engine serial number are
stamped on the right-hand side of the cylinder block
on the flywheel side of the engine. Camshaft sprockets
Cvlinder
head gasket
Item Description
I 1 I Cylinder head gasket I
1 2 1 Locating dowels 1
A four-layer laminated steel cylinder head gasket
is used.
The cylinder head gasket and cylinder head are
located with two locating dowels.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G461395en
procarmanuals.com
Page 1084 of 1226

Clutch Controls
DESCRIPTION
AND OPERATION
Because of this separate chamber, the braking
system remains operational if a leak occurs in the
hydraulic clutch system.
Function
Pressure is created in the master cylinder when
the clutch pedal is operated.
The hydraulic fluid in the master cylinder is put
under pressure and fed through the pressure pipe
to the slave cylinder.
The displaced hydraulic fluid moves the piston in
the slave cylinder and this in turn slides the release
bearing axially.
The release bearing pushes the bearing inner ring
against the tongues of the diaphragm spring.
The spring induced grip between the clutch disc
and the flywheel is broken.
When the clutch pedal is released the diaphragm
spring presses the piston in the slave cylinder back
to its starting position. The spring induced grip
between the clutch disc and the flywheel is created
again.
A spring in the slave cylinder ensures preload on
the release bearing.
The release bearing is always touching the
pressure plate because of this preload. The extra
travel caused by clutch lining wear is compensated
for by the preload.
There is a choke assembly in the slave cylinder
which helps to increase smoothness when pulling
away.
Because of the choke assembly, the pressure drop
of the fluid leaving the slave cylinder and returning
to the reservoir is delayed.
Because of this, the clutch closing time is delayed
when the clutch pedal is released suddenly, and
a soft and comfortable clutch engagement is
achieved.
Choking does not occur during clutch
disengagement.
A CAUTI0N:Vehicles with an automated shift
manual (ASM) transmission have
a slave
cylinder without
a choke assembly. The
slave cylinders must not be exchanged for
one another.
N0TE:The clutch pedal travel cannot be adjusted.
The release bearing is an interference fit in the
slave cylinder and cannot be renewed separately.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G281360en
procarmanuals.com
Page 1095 of 1226
308-03-5 Manual Transmission/Transaxle 308-0315
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Manual Transaxle
i
General
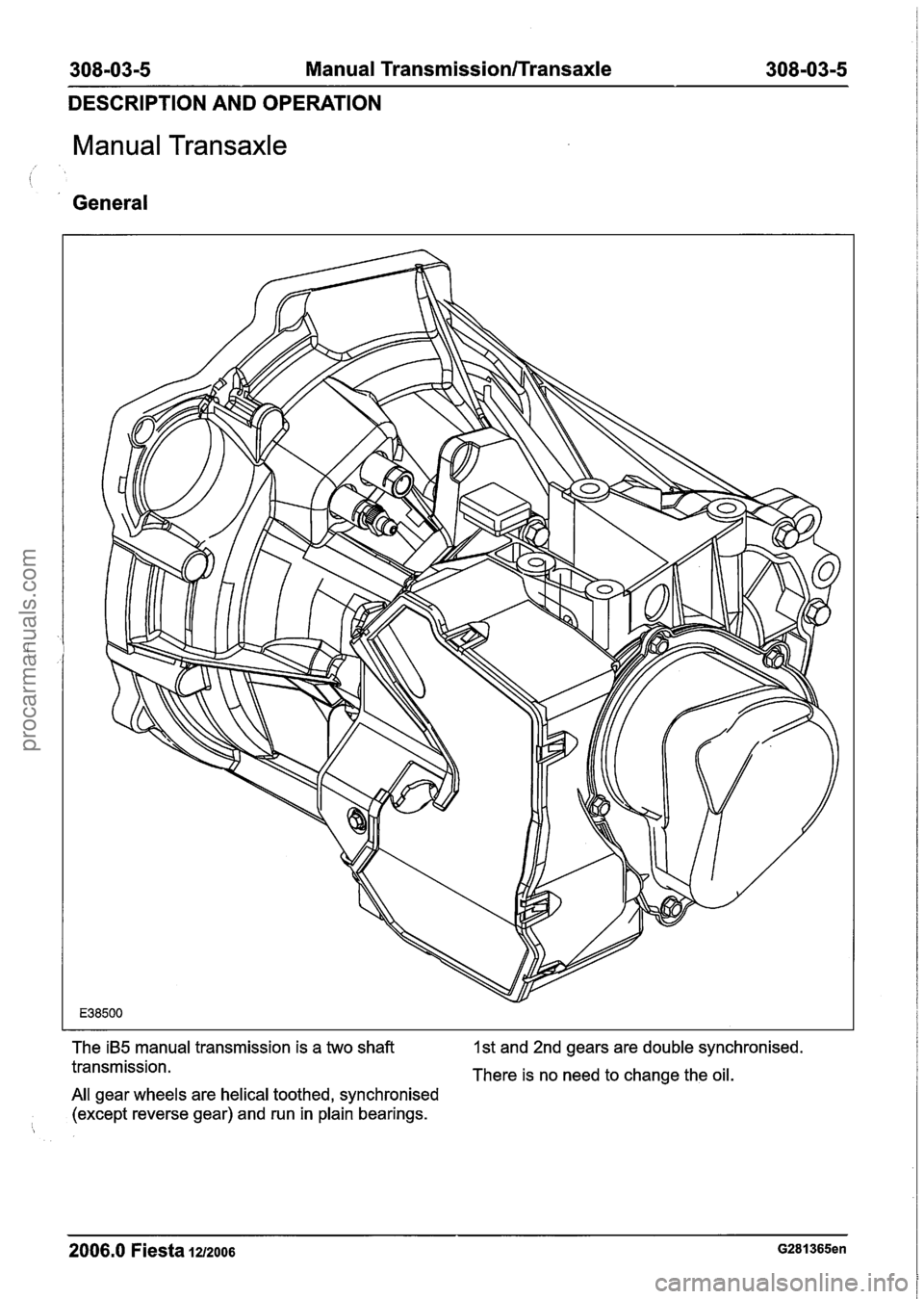
The iB5 manual transmission is a two shaft 1st and 2nd gears are double synchronised.
transmission. There is no need to change the oil.
All gear wheels are helical toothed, synchronised
(except reverse gear) and run in plain bearings.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G281365en
procarmanuals.com