Page 22 of 2000
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
206EG40206EG41
206EG42
Stator Segment
ConductorStator
Joined
Joined Segment
Conductor SystemSegment
ConductorStator
StatorConductor
Wire
Conductor Wire
A
AA - A Cross
Section
Segment Conductor Type GeneratorB
BB - B Cross
Section
Conventional Type GeneratorWinding System
Stator
Segment
Conductor
Cross Section
Stator of Segment Conductor Type GeneratorEG-25
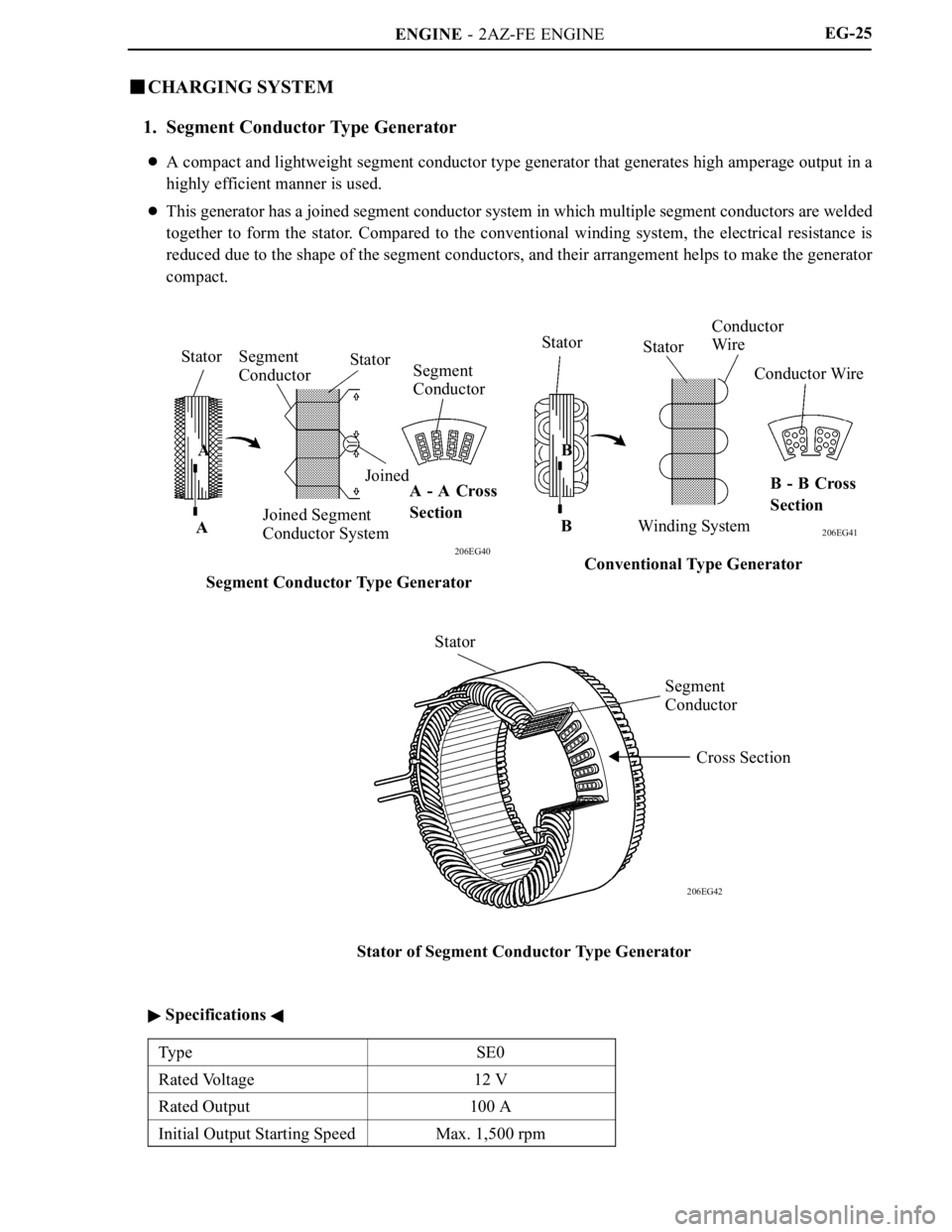
CHARGING SYSTEM
1. Segment Conductor Type Generator
A compact and lightweight segment conductor type generator that generates high amperage output in a
highly efficient manner is used.
This generator has a joined segment conductor system in which multiple segment conductors are welded
together to form the stator. Compared to the conventional winding system, the electrical resistance is
reduced due to the shape of the segment conductors, and their arrangement helps to make the generator
compact.
Specifications
Ty p eSE0
Rated Voltage12 V
Rated Output100 A
Initial Output Starting SpeedMax. 1,500 rpm
Page 39 of 2000

ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
00SEG39Y
228TU25 228TU24
A
AInternal Construction
A - A Cross SectionAccelerator
Pedal Arm
Hall IC
Magnetic Yoke
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Magnetic Yoke
Hall
IC
Hall
IC
VPA
EPA
VCPA
VPA2
EPA2ECM
Output
Voltage(V)
5
0VPA2
VPA
Fully Close Fully Open90
Accelerator Pedal Depressed Angle VCP2
Service Tip
The inspection method differs from the conventional contact type accelerator pedal position sensor
because this non-contact type sensor uses a Hall IC.
For details, refer to the 2006 RAV4 Repair Manual (Pab. No. RM01M0U).
EG-42
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
The non-contact type accelerator pedal position sensor uses a Hall IC.
The magnetic yoke that is mounted at the accelerator pedal arm rotates around the Hall IC in accordance
with the amount of effort that is applied to the accelerator pedal. The Hall IC converts the changes in the
magnetic flux at that time into electrical signals, and outputs them as accelerator pedal effort to the ECM.
The Hall IC contains circuits for the main and sub signals. It converts the accelerator pedal depressed
angles into electric signals with two differing characteristics and outputs them to the ECM.
Page 62 of 2000

ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
01NEG13Y
Generator
RegulatorB
DF
RLOECM
Various Electrical
Loads
Battery Current Sensor
Battery Temperature Sensor
Battery Voltage
Battery
Various Sensors and Switches
Throttle Position Sensor
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Accelerator Pedal Position
SensorEG-65
11. Charging Control
General
This system lowers the generated voltage when the vehicle is idling or is being driven at a constant speed,
and raises the generated voltage when the vehicle is decelerating. This reduces the load on the engine as
a result of the electric generation of the generator, thus contributing to the fuel economy of the engine.
During acceleration, this system regulates the generated voltage in order to place the amperage estimation
value close to the target value.
This control consists of the ECM, battery current sensor with a built-in battery temperature sensor,
generator, and various sensors and switches.
The ECM detects driving condition based on signals from various sensors and switches, and detects
charging condition based on signals from the generator, battery current sensor and battery temperature
sensor. Then the ECM outputs signals to the IC regulator to control the genetated voltage of the generator.
The ECM stops the charging control and the generator switches to normal power generation mode under
the following conditions:
Low battery capacity
Low or high battery temparature
Wipers operating or blower motor operating with tail lamp relay ON
System Diagram
Page 110 of 2000
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
01MEG37Y
Throttle Body
Throttle Position
Sensor Portion
Magnetic Yoke
Hall IC
(For Throttle Position Sensor)
Magnetic Yoke A
Cross SectionView from A EG-114
Throttle Position Sensor
The non-contact type throttle position sensor uses a Hall IC, which is mounted on the throttle body.
The Hall IC is surrounded by a magnetic yoke. The Hall IC converts the changes that occur in the
magnetic flux at that time into electrical signals and outputs them in the form of a throttle valve effort
to the ECM.
The Hall IC contains circuits for the main and sub signals. It converts the throttle valve opening angles
into electric signals with two differing characteristics and outputs them to the ECM.
Page 174 of 2000
PREPARATION – 2AZ-FE CHARGINGPP–31
PP
RECOMMENDED TOOLS
09082-00040 TOYOTA Electrical Tester -
(09083-00150) Test Lead Set -
Page 215 of 2000
IN–38INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT INSPECTION
PROCEDURE
1. BASIC INSPECTION
(a) WHEN MEASURING RESISTANCE OF
ELECTRONIC PARTS
(1) Unless otherwise stated, all resistance
measurements should be made at an ambient
temperature of 20
C (68F). Resistance
measurements may be inaccurate if measured
at high temperatures, i.e. immediately after the
vehicle has been running. Measurements should
be made after the engine has cooled down.
(b) HANDLING CONNECTORS
(1) When disconnecting a connector, first squeeze
the mating halves tightly together to release the
lock, and then press the lock claw and separate
the connector.
(2) When disconnecting a connector, do not pull on
the harnesses. Grasp the connector directly and
separate it.
(3) Before connecting a connector, check that there
are no deformed, damaged, loose or missing
terminals.
(4) When connecting a connector, press firmly until
it locks with a "click" sound.
(5) If checking a connector with a TOYOTA
electrical tester, check the connector from the
backside (harness side) using a mini test lead.
NOTICE:
• As a waterproof connector cannot be
checked from the backside, check it by
connecting a sub-harness.
• Do not damage the terminals by moving
the inserted tester needle.
(c) CHECKING CONNECTORS
(1) Checking when a connector is connected:
Squeeze the connector together to confirm that
they are fully connected and locked.
(2) Checking when a connector is disconnected:
Pull the wire harness lightly from the backside of
the connector. Visually check for the following: 1)
unlatched terminals, missing terminals, loose
crimps and broken conductor wires; 2)
corrosion, metallic matter, foreign matter and
water; and 3) bent, rusted, overheated,
contaminated and deformed terminals.
D100803E01
D100734E01
Page 220 of 2000

IN–48INTRODUCTION – TERMS
IN
GLOSSARY OF SAE AND TOYOTA
TERMS
This glossary lists all SAE-J1930 terms and abbreviations
used in this manual in compliance with SAE
recommendations, as well as their TOYOTA equivalents.
SAE
ABBREVIATIONSSAE TERMS TOYOTA TERMS ( )-ABBREVIATIONS
3GR Third Gear -
4GR Fourth Gear -
A/C Air Conditioning Air Conditioner
ACL Air Cleaner Air Cleaner, A/CL
AIR Secondary Air Injection Air Injection (AI)
AP Accelerator Pedal -
B+ Battery Positive Voltage +B, Battery Voltage
BARO Barometric Pressure HAC
CAC Charge Air Cooler Intercooler
CARB Carburetor Carburetor
CFI Continuous Fuel Injection -
CKP Crankshaft Position Crank Angle
CL Closed Loop Closed Loop
CMP Camshaft Position Cam Angle
CPP Clutch Pedal Position -
CTOX Continuous Trap Oxidizer -
CTP Closed Throttle Position LL ON, Idle ON
DFI Direct Fuel Injection Direct Injection (DI/INJ)
DI Distributor Ignition -
DLC3 Data Link Connector 3 OBD II Diagnostic Connector
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code Diagnostic Trouble Code
DTM Diagnostic Test Mode -
ECL Engine Coolant Level -
ECM Engine Control Module Engine Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
ECT Engine Coolant Temperature Coolant Temperature, Water Temperature (THW)
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only MemoryElectrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
(EEPROM)
EFE Early Fuel Evaporation Cold Mixture Heater (CMH), Heat Control Valve (HCV)
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
EI Electronic Ignition Distributorless Ignition (DLI)
EM Engine Modification Engine Modification (EM)
EPROM Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM)
EVAP Evaporative Emission Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP)
FC Fan Control -
FEEPROMFlash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory-
FEPROM Flash Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory -
FF Flexible Fuel -
FP Fuel Pump Fuel Pump
GEN Generator Alternator
GND Ground Ground (GND)
HO2S Heated Oxygen Sensor Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
IAC Idle Air Control Idle Speed Control (ISC)
Page 259 of 2000
PREPARATION – 2AZ-FE FUELPP–13
PP
RECOMMENDED TOOLS
09082-00040 TOYOTA Electrical Tester -
(09083-00150) Test Lead Set -