2006 SUZUKI SX4 AIR
[x] Cancel search: AIRPage 100 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-50 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Improper engine idling or
engine fails to idleFaulty spark plug“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky or disconnected high-tension cord“High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil with ignitor“Ignition Coil Assembly (Including Ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Fuel pressure out of specification“Fuel Pressure Check”
Leaky manifold, throttle body, or cylinder
head gasket
Malfunctioning EGR valve“EGR Valve Inspection (If Equipped) in Section
1B”
Faulty evaporative emission control
system“EVAP Canister Purge Inspection in Section
1B”
Faulty EGR system“EGR System Inspection (If Equipped) in
Section 1B”
Faulty fuel injector(s)“Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Poor performance of ECT sensor or
MAF sensor“Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C”, or “Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor Inspection in
Section 1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly“Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly“Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty ECM
Loose connection or disconnection of
vacuum hoses
Malfunctioning PCV valve“PCV Valve Inspection in Section 1B”
Engine overheatingCondition “Engine overheating”
Low compression“Compression Check in Section 1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order (for engine with VVT
system)“Oil Control Valve Inspection (For Engine with
VVT) in Section 1D” Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 101 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-51
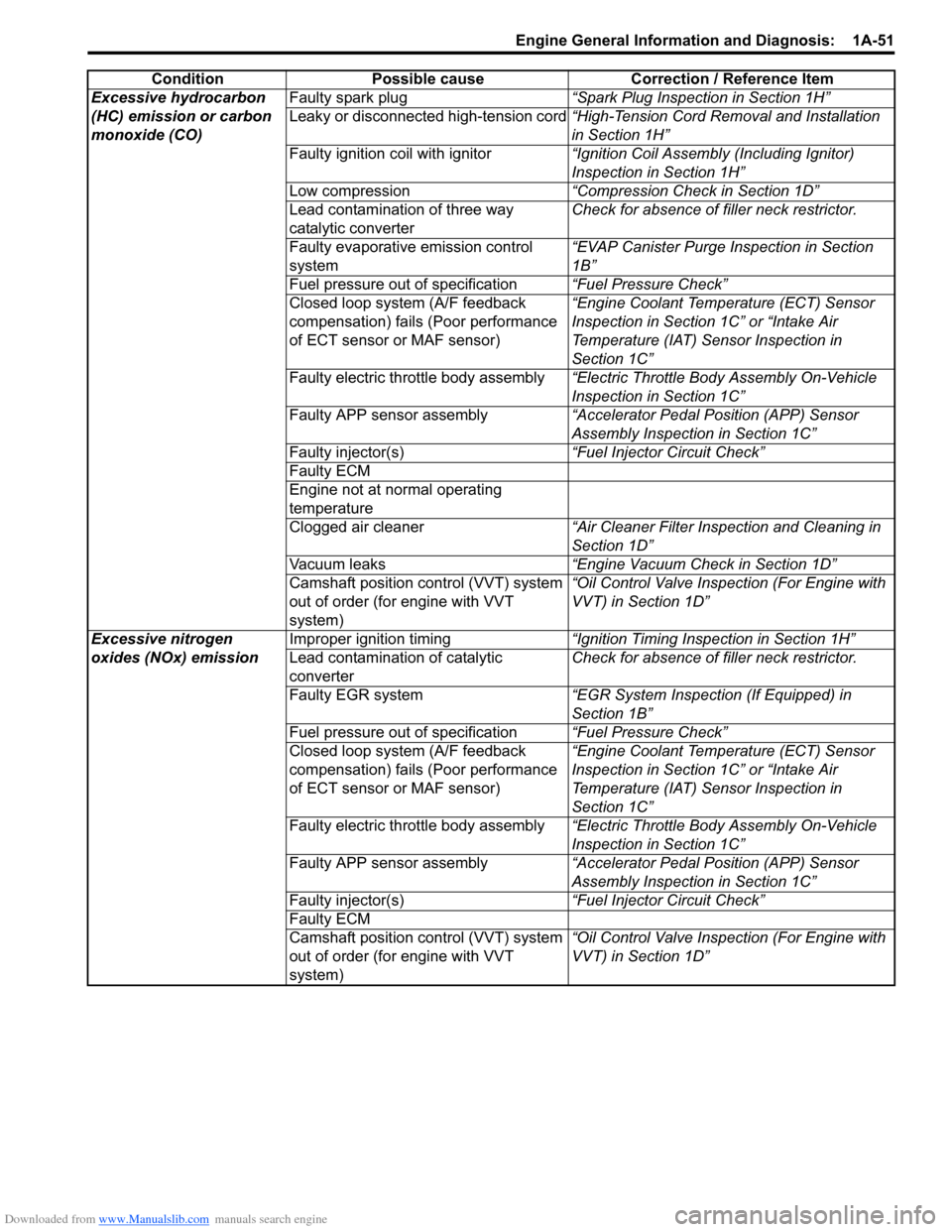
Excessive hydrocarbon
(HC) emission or carbon
monoxide (CO)Faulty spark plug“Spark Plug Inspection in Section 1H”
Leaky or disconnected high-tension cord“High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
in Section 1H”
Faulty ignition coil with ignitor“Ignition Coil Assembly (Including Ignitor)
Inspection in Section 1H”
Low compression“Compression Check in Section 1D”
Lead contamination of three way
catalytic converterCheck for absence of filler neck restrictor.
Faulty evaporative emission control
system“EVAP Canister Purge Inspection in Section
1B”
Fuel pressure out of specification“Fuel Pressure Check”
Closed loop system (A/F feedback
compensation) fails (Poor performance
of ECT sensor or MAF sensor)“Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C” or “Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor Inspection in
Section 1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly“Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly“Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty injector(s)“Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Engine not at normal operating
temperature
Clogged air cleaner“Air Cleaner Filter Inspection and Cleaning in
Section 1D”
Vacuum leaks“Engine Vacuum Check in Section 1D”
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order (for engine with VVT
system)“Oil Control Valve Inspection (For Engine with
VVT) in Section 1D”
Excessive nitrogen
oxides (NOx) emissionImproper ignition timing“Ignition Timing Inspection in Section 1H”
Lead contamination of catalytic
converterCheck for absence of filler neck restrictor.
Faulty EGR system“EGR System Inspection (If Equipped) in
Section 1B”
Fuel pressure out of specification“Fuel Pressure Check”
Closed loop system (A/F feedback
compensation) fails (Poor performance
of ECT sensor or MAF sensor)“Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Inspection in Section 1C” or “Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor Inspection in
Section 1C”
Faulty electric throttle body assembly“Electric Throttle Body Assembly On-Vehicle
Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty APP sensor assembly“Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly Inspection in Section 1C”
Faulty injector(s)“Fuel Injector Circuit Check”
Faulty ECM
Camshaft position control (VVT) system
out of order (for engine with VVT
system)“Oil Control Valve Inspection (For Engine with
VVT) in Section 1D” Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 103 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-53
Troubleshooting
NOTE
• Before performed trouble shooting, be sure to read the “Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection”.
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
Step Action Yes No
1MIL power supply check
1) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
Do other warning lights come ON?Go to Step 2. Go to Step 3.
2DTC check
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and check DTC in ECM.
Is there DTC(s) U0073 and/or U0121?Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.Go to Step 3.
3Combination meter power supply and ground circuit
check
1) Turn ignition switch OFF position.
2) Disconnect connector from combination meter.
3) Check for proper connection to power supply and
ground terminals of combination meter connector.
4) If connections are OK, check that combination meter
circuit is as follows.
• Circuit voltage between combination meter power
supply terminal and vehicle body ground is 10 –14 V.
• Wiring harness resistance of combination meter
ground terminal and vehicle body ground is less than
3 Ω.
Are they in good condition?Go to Step 4. Repair or replace.
4CAN communication line circuit check
1) Check CAN communication line circuit between control
modules for open, short, high resistance and
connections referring to Step 5 to 10 under
“Troubleshooting for Communication Error with Scan
Tool Using CAN”.
Is circuit in good condition?Substitute a known-
good combination meter
and recheck. If MIL still
remains OFF, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.Repair or replace.
Page 104 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-54 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON after Engine StartsS6RW0D1104012
Wiring Diagram
Refer to “Malfunction Indicator Lamp Does Not Come ON with Ignition Switch ON and Engine Stop (but Engine Can
Be Started)”.
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is turned ON, ECM causes the main relay to turn ON (close the contact point). Then, ECM
being supplied with the main power, transmits indication ON signal of malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) to combination
meter in order to turn MIL ON. And then, combination meter turns MIL ON. When the engine starts to run and no
malfunction is detected in the system, ECM transmits MIL indication OFF signal to combination meter in order to turn
MIL OFF. And then, combination meter turns MIL OFF, but if a malfunction was or is detected, MIL remains ON even
when the engine is running.
Troubleshooting
NOTE
• Before performed trouble shooting, be sure to read the “Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection”.
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
Step Action Yes No
1DTC check
1) Start engine and recheck DTC of ECM and TCM (for A/T
model) while engine running.
Is there any DTC(s)?Go to Step 2 of “Engine
and Emission Control
System Check”, Step 2
of “A/T System Check in
Section 5A”.Go to Step 2.
2CAN communication line circuit check
1) Check CAN communication line circuit between control
modules for open, short, high resistance and
connections referring to Step 5 to 10 under
“Troubleshooting for Communication Error with Scan
Tool Using CAN”.
Is circuit in good condition?Substitute a known-
good combination meter
and recheck. If MIL still
remains ON, substitute
a known-good ECM and
recheck.Repair or replace CAN
communication circuit.
Page 108 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-58 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
Before this troubleshooting is performed, read the precautions for DTC troubleshooting referring to
“Precautions for DTC Troubleshooting”.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed?Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2Do you have SUZUKI scan tool?Go to Step 3. Go to Step 5.
3Camshaft position control check
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect SUZUKI scan
tool.
2) Start engine and warm up to normal operating
temperature.
3) Select menu to “Data List”.
4) Check that “VVT GAP” displayed on SUZUKI scan tool is
0 – 3°.
Is it OK?Go to Step 4. Check valve timing
referring to “Timing
Chain and Chain
Tensioner Removal and
Installation in Section
1D”. If OK, go to Step 5.
4Camshaft position control check
1) Drive vehicle under following conditions.
• Vehicle speed at 80 km/h (50 mile/h).
• Gear position at 5th or D range.
2) Check that “VVT GAP” displayed on SUZUKI scan tool is
0 – 5°.
Is it OK?Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.Go to Step 5.
5Oil control circuit visual inspection
1) Remove cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder Head
Cover Removal and Installation in Section 1D”.
2) Check oil pressure leakage from oil control circuit.
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 6. Repair or replace.
6Oil control valve and oil gallery pipe check
1) Remove oil control valve referring to “Oil Control Valve
Removal and Installation (For Engine with VVT) in
Section 1D”.
2) Remove oil gallery pipe referring to “Timing Chain Cover
Removal and Installation in Section 1D”.
3) Check oil gallery pipe and oil control valve for clog or
sludge.
Are they in good condition?Go to Step 7. Clean oil control valve
and oil gallery pipe.
Replace oil control valve
if a problem is not
solved after cleaning oil
control valve and oil
gallery pipe.
7Oil control valve electrical circuit check
1) Check that oil control valve circuit is in good condition
referring to “DTC P0010: Camshaft Position Actuator
Circuit (for engine with VVT system)”.
Is circuit in good condition?Repair circuit. Go to Step 8.
8Oil control valve check
1) Check oil control valve referring to “Oil Control Valve
Inspection (For Engine with VVT) in Section 1D”.
Is it in good condition?Replace camshaft
timing sprocket.Replace oil control
valve.
Page 113 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-63
DTC P0101: Mass Air Flow Circuit Range / PerformanceS6RW0D1104017
Wiring Diagram
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
E01C01
3 4
18 19 5 6 7 10 11
17 20
47 46 49 50 51 21 22
5216 259
24 14
29
55 57 54 53 59
60 582
26 27 28 15
30
56 4832 31 34 35 36 37 40 42 39 38 44
45 43 41 331 12 13
238 3 4
18 19 5 6 7 10 11
17 20
47 46 49 50 51 21 22
5216 259
24 14
29
55 57 54 53 59
60 582
26 27 28 15
30
56 4832 31 34 35 36 37 40 42 39 38 44
45 43 41 331 12 13
238
BLK/WHT
BLK/RED
BLK/RED
WHTBLK/YELBLK/YEL
BLK/YEL
GRN
BRN/WHT
12V5V
5V
2
34E01-29
E01-1
E01-60
C01-58
C01-15 C01-30
BLK/ORN
BLKBLK
BLK/REDE01-16
BLK/YEL
GRY/BLU
1BLK/RED
C01-25
C01-55 5
E01-31 BLK
GRY/BLU
GRY
GRN/BLKC01-26
C01-27
I6RW0D110022-02
1. MAF and IAT sensor 3. Main relay 5. To other sensors
2. Ignition switch 4. ECM
DTC detecting condition Trouble area
• MAF volume is greater than specified value after warming up engine with
idling condition.
• MAF volume is lower than specified value at high speed condition.
(2 driving cycle detection logic)• Air intake system (clog or leakage)
• MAF sensor circuit
• MAF sensor
• TP sensor and/or its circuit
• MAP sensor and/or its circuit
•ECM
Page 114 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-64 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
DTC Confirmation Procedure
WARNING!
• When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic
accident and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
• Road test should be carried out by 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
NOTE
Check to make sure that the following conditions are satisfied when using this “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”.
• Intake air temperature at engine start: –10 °C (14°F) to 80 °C (176 °F)
• Intake air temperature: –10 °C (14 °F) to 70 °C (158 °F)
• Engine coolant temperature: 70 °C (158 °F) or more
• Altitude (barometric pressure): 2500 m, 8200 ft or less (560 mmHg, 74.4 kPa or more)
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, connect scan tool.
2) Turn ON ignition switch and clear DTC using scan tool.
3) Start engine and warm up to normal operating temperature. (ECT approx. 90 – 95 °C, 194 – 203 °F)
4) Drive vehicle with engine speed: more than 2500 rpm for 1 min.
5) Increase vehicle speed to 100 km/h (62 mile/h) at 5th gear or D range.
6) Release accelerator pedal to decrease vehicle speed to 40 km/h (25 mile/h).
7) Stop vehicle and run it idle for 1 min.
8) Check DTC and pending DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting
NOTE
Before this troubleshooting is performed, read the precautions for DTC troubleshooting referring to
“Precautions for DTC Troubleshooting”.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine and Emission Control System Check”
performed?Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine and
Emission Control
System Check”.
2Visual inspection
Check MAF sensor and air intake system for:
• Objects which block measuring duct and resistor of MAF
sensor.
• Other air flow which does not pass the MAF sensor.
Are they in good condition?Go to Step 3. Repair or replace.
3MAF sensor and its circuit check
1) With ignition switch turned OFF, install scan tool.
2) Start engine and warm up to normal operation
temperature.
3) Check MAF value using scan tool. (Refer to “Scan Tool
Data” for normal value.)
Is each value within specified range?Go to Step 11. Go to Step 4.
Page 115 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-65
4MAF sensor output voltage check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch.
2) Remove ECM from its bracket with ECM connectors
connected.
3) Measure voltage between “C01-26” and “C01-27”
terminals of ECM connector referring to “Mass Air Flow
(MAF) and Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor On-
Vehicle Inspection in Section 1C”.
Is each value within specified range?Poor “C01-26” and/or
“C01-27” terminal
connection.
If OK, substitute a
known-good ECM and
recheck.Go to Step 5.
5MAF sensor power supply voltage check
1) Disconnect connector from MAF and IAT sensor with
ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch, measure voltage between
engine ground and “BLK/RED” wire terminal (2) of MAF
and IAT sensor connector (1).
Is voltage 10 – 14 V?Go to Step 6. “BLK/RED” wire is open
circuit.
6MAF sensor ground circuit check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch, measure resistance between
“GRY” wire terminal of MAF and IAT sensor connector
and engine ground.
Is resistance below 5
Ω?Go to Step 8. Go to Step 7.
7Ground circuit check
1) Measure resistance between “C01-27” terminal of ECM
connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance below 5
Ω?“GRY” wire is open or
high resistance circuit.ECM grounds “C01-58”,
“C01-15”, “C01-30” and/
or “E01-31” circuit is
open or high resistance.
If wires are OK,
substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
8MAF sensor signal circuit check
1) Disconnect connectors from ECM with ignition switch
turned OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch, measure voltage between
“GRN/BLK” wire terminal of MAF and IAT sensor
connector and engine ground.
Is voltage 0 V?Go to Step 9. “GRN/BLK” wire is
shorted to others circuit.
9MAF sensor signal circuit check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch, measure resistance between
“GRN/BLK” wire terminal of MAF and IAT sensor
connector and engine ground.
Is resistance infinity?Go to Step 10. “GRN/BLK” wire is
shorted to ground
circuit. Step Action Yes No
I4RS0A110020-01