2006 SUZUKI SX4 engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 329 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-47
Cylinder Head InspectionS6RW0D1406029
• Remove all carbon deposits from combustion
chambers.
NOTE
Do not use any sharp-edged tool to scrape
off carbon deposits. Be careful not to scuff or
nick metal surfaces when decarbonizing. The
same applies to valves and valve seats, too.
• Check cylinder head for cracks on intake and exhaust
ports, combustion chambers, and head surface. Using
a straightedge and thickness gauge, check flatness of
gasketed surface at a total of 6 locations. If distortion
limit is exceeded, correct gasketed surface with a
surface plate and abrasive paper of about #400
(Waterproof silicon carbide abrasive paper): place
abrasive paper on and over surface plate, and rub
gasketed surface against paper to grind off high spots.
Should this fail to reduce thickness gauge readings to
within limit, replace cylinder head.
Leakage of combustion gases from this gasketed joint
is often due to warped gasketed surface: such
leakage results in reduced power output.Distortion for cylinder head surface on piston side
Limit: 0.03 mm (0.001 in.)
• Distortion of manifold seating faces:
Check seating faces of cylinder head for manifolds,
using a straightedge and thickness gauge, in order to
determine whether these faces should be corrected or
cylinder head replaced.
Distortion for cylinder head surface on intake and
exhaust manifold
Limit: 0.05 mm (0.002 in.)
I2RH0B140105-01
I2RH0B140106-01
I2RH0B140107-01
Page 330 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-48 Engine Mechanical:
Valve Spring InspectionS6RW0D1406030
Valve Spring Free Length and Preload
Referring to data, check to be sure that each spring is in
sound condition, free of any evidence of breakage or
weakening. Remember, weakened valve springs can
cause chatter, not to mention possibility of reducing
power output due to gas leakage caused by decreased
seating pressure.
Valve spring free length
Standard: 36.83 mm (1.450 in.)
Limit: 35.83 mm (1.411 in.)
Valve spring preload
Standard: 107 – 125 N (10.7 – 12.5 kgf) for 31.50 mm
(23.6 – 27.6 lb/1.240 in.)
Limit: 102 N (10.2 kgf) for 31.50 mm (22.5 lb/1.240 in.)Spring Squareness
Use a square and surface plate to check each spring for
squareness in terms of clearance between end of valve
spring and square. Valve springs found to exhibit a
larger clearance than limit must be replaced.
Valve spring squareness
Limit: 1.6 mm (0.063 in.)
I2RH01140143-01
I2RH01140144-01
Page 331 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-49
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and Cylinders ComponentsS6RW0D1406031
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation
S6RW0D1406032
Removal
1) Remove engine assembly from vehicle referring to
“Engine Assembly Removal and Installation”.
2) Remove cylinder head referring to “Valves and
Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
3) Mark cylinder number on all pistons, connecting rods
and connecting rod caps using silver pencil or quick
drying paint.
4) Remove rod bearing caps.
5) Install guide hose (1) over threads of rod bolts.
This prevents damage to crank pin and rod bolt
threads when removing connecting rod.6) Decarbonize top of cylinder bore before removing
piston from cylinder.
7) Push piston and connecting rod assembly out
through the top of cylinder bore.
1. Top ring 8. Piston pin
2. 2nd ring 9. Piston pin circlip
3. Oil ring 10. Bearing cap nut
4. Piston : Tighten 15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft), 45° and 45° by the specified procedure.
5. Connecting rod
: See “A”: Apply engine oil to sliding surface of each part.
6. Connecting rod bearing cap
: See “B”: Do not reuse.
7. Connecting rod bearing
: See “C”
“A”: Apply engine oil to sliding surface except inner surface of big end, and rod bolts. Make sure rod bolt diameter when reuse it due to plastic deformation
tightening. Refer to “Piston Pins and Connecting Rods Inspection”.
“B”: Point arrow mark on cap to crankshaft pulley side.
“C”: Do not apply oil between connecting rod and bearing or between bearing cap and bearing.
I5RW0C140045-01
I2RH0B140109-01
Page 332 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-50 Engine Mechanical:
Installation
1) Apply engine oil to pistons, rings, cylinder walls,
connecting rod bearings and crank pins.
NOTE
Do not apply oil between connecting rod and
bearing or between bearing cap and bearing.
2) Install guide hoses (1) over connecting rod bolts.
These guide hoses protect crank pin and threads of
rod bolt from damage during installation of
connecting rod and piston assembly.
3) When installing piston and connecting rod assembly
into cylinder bore, point front mark (1) on piston head
to crankshaft pulley side.4) Install piston and connecting rod assembly into
cylinder bore. Use special tool (Piston ring
compressor) to compress rings. Guide connecting
rod into place on crankshaft.
Using a hammer handle, tap piston head to install
piston into bore. Hold ring compressor firmly against
cylinder block until all piston rings have entered
cylinder bore.
Special tool
(A): 09916–77310
5) Install bearing cap (1):
Point arrow mark (2) on cap to crankshaft pulley
side.
After applying engine oil to rod bolts and tighten cap
nuts (3) gradually as follows.
a) Tighten all cap nuts to 15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-
ft).
b) Retighten them to 45°.
c) Repeat Step b) once again.
NOTE
Before installing bearing cap, make sure that
checking for connecting rod bolt
deformation. Refer to “Piston Pins and
Connecting Rods Inspection”.
Tightening torque
Connecting rod bearing cap nut (a): Tighten
15 N⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft), 45° and 45° by
the specified procedure
6) Install cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder
Head Removal and Installation”.A: Crankshaft pulley side B: Flywheel side
I2RH01140147-01
I2RH0B140110-01
I2RH0B140111-01
I2RH0B140112-01
Page 333 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-51
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Disassembly and Assembly
S6RW0D1406033
Disassembly
1) Using piston ring expander, remove two
compression rings (Top and 2nd) and oil ring from
piston.
2) Remove piston pin from connecting rod as follows.
a) Ease out piston pin circlips (1), as shown.
b) Force piston pin out.
Assembly
1) Decarbonize piston head and ring grooves using a
suitable tool.
2) Install piston pin to piston (1) and connecting rod (2):
a) After applying engine oil to piston pin and piston
pin holes in piston and connecting rod.
b) Installing connecting rod to piston.
NOTE
Be sure to position front mark (4) on piston
and oil hall (5) of connecting rod at specified
position as shown in figure.
c) Insert piston pin to piston and connecting rod.
d) Install piston pin circlips (3).
NOTE
Circlip should be installed with its cut part
facing as shown in figure. Install so that
circlip end gap comes within such range as
indicated by arrow.
3) Install piston rings to piston:
• As indicated in figure, 1st and 2nd rings have “T”
mark (4) respectively. When installing these piston
rings to piston, direct marked side of each ring
toward top of piston.
• 1st ring (1) differs from 2nd ring (2) in thickness,
shape and color of surface contacting cylinder
wall.
Distinguish 1st ring from 2nd ring by referring to
the figure.
• When installing oil ring (3), install spacer first and
then two rails.
4) After installing three rings (1st, 2nd and oil rings),
distribute their end gaps as shown in figure.
I2RH0B140113-01
I2RH0B140114-01
1. Front mark 4. Oil ring upper rail gap
2. 1st ring end gap 5. Oil ring lower rail gap
3. 2nd ring end gap and oil ring spacer gap
I5RW0C140026-01
I6RW0B140011-01
I5RW0C140046-01
Page 334 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-52 Engine Mechanical:
Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings InspectionS6RW0D1406034
Cylinder
Visual inspection
Inspect cylinder walls for scratches, roughness or ridges
which indicate excessive wear. If cylinder bore is very
rough or deeply scratched, or ridged, rebore cylinder and
use over size piston.
Cylinder bore diameter, taper and out-of-round
Using a cylinder gauge (1), measure cylinder bore in
thrust and axial directions at two positions (“a” and “b”)
as shown in figure.
If any of the following conditions is noted, rebore
cylinder.
1) Cylinder bore dia. exceeds limit.
2) Difference of measurements at two positions
exceeds taper limit.
3) Difference between thrust and axial measurements
exceeds out-of-round limit.
Cylinder bore diameter
Standard: 78.000 – 78.014 mm (3.0709 – 3.0714
in.)
Limit: 78.050 mm (3.073 in.)
Cylinder taper and out-of-round
Limit: 0.10 mm (0.004 in.)
NOTE
If any one of four cylinders has to be rebored,
rebore all four to the same next oversize.
This is necessary for the sake of uniformity
and balance.
Piston
Visual inspection
Inspect piston for faults, cracks or other damages.
Damaged or faulty piston should be replaced.
Piston diameter
As indicated in figure, piston diameter should be
measured at a position 19.5 mm (0.77 in.) (“a”) from
piston skirt end in the direction perpendicular to piston
pin.
Piston diameter specification
Standard size (used piston): 77.953 – 77.968 mm
(3.0690 – 3.0696 in.)
Standard size (new piston with coating): 77.963 –
77.990 mm (3.0694 – 3.0704 in.)
Oversize (0.50 mm (0.0196 in.)) (used piston): 78.453
– 78.468 mm (3.0887 – 3.0893 in.)
Oversize (0.50 mm (0.0196 in)) (new piston with
coating): 78.463 – 78.490 mm (3.0891 – 3.0901 in.)
“a”: 50 mm (1.96 in.)
“b”: 100 mm (3.94 in.)
I2RH0B140117-01
I2RH01140157-01
Page 335 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-53
Piston clearance
Measure cylinder bore diameter and piston diameter to
find their difference which is piston clearance. Piston
clearance should be within specification as follows. If it is
out of specification, rebore cylinder and use oversize
piston.
NOTE
Cylinder bore diameters used here are
measured in thrust direction at two positions.
Piston clearance
Standard (used piston): 0.032 – 0.061 mm (0.0013 –
0.0024 in.)
Standard (new piston with coating): 0.010 – 0.051
mm (0.0004 – 0.0020 in.)
Limit: 0.161 mm (0.0065 in.)
Ring groove clearance
Before checking, piston grooves must be clean, dry and
free of carbon deposits.
Fit new piston ring (1) into piston groove, and measure
clearance between ring and ring land by using thickness
gauge (2). If clearance is out of specification, replace
piston.
Ring groove clearance
Piston Ring
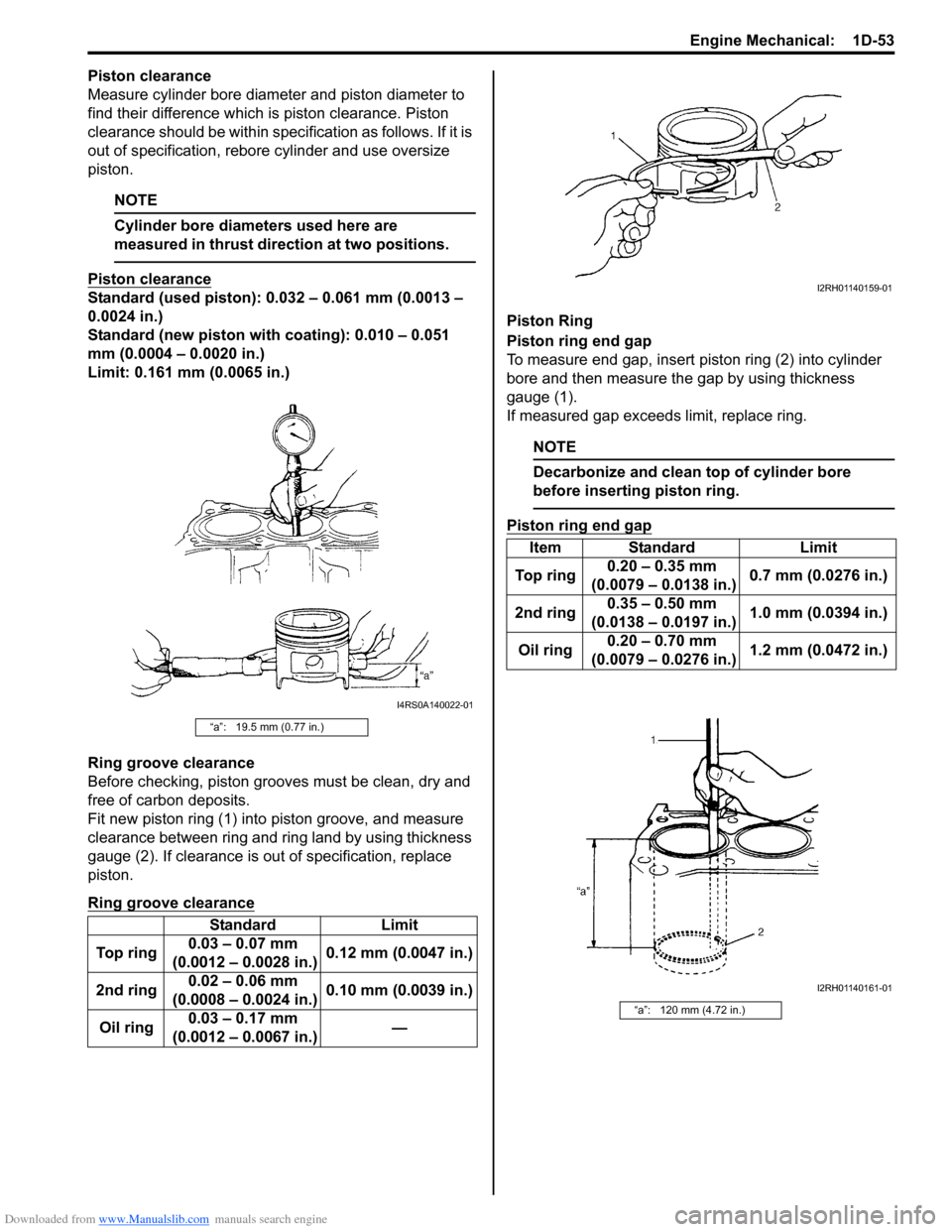
Piston ring end gap
To measure end gap, insert piston ring (2) into cylinder
bore and then measure the gap by using thickness
gauge (1).
If measured gap exceeds limit, replace ring.
NOTE
Decarbonize and clean top of cylinder bore
before inserting piston ring.
Piston ring end gap
“a”: 19.5 mm (0.77 in.)
Standard Limit
To p r i n g0.03 – 0.07 mm
(0.0012 – 0.0028 in.)0.12 mm (0.0047 in.)
2nd ring0.02 – 0.06 mm
(0.0008 – 0.0024 in.)0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
Oil ring0.03 – 0.17 mm
(0.0012 – 0.0067 in.)—
I4RS0A140022-01
Item Standard Limit
To p r i n g0.20 – 0.35 mm
(0.0079 – 0.0138 in.)0.7 mm (0.0276 in.)
2nd ring0.35 – 0.50 mm
(0.0138 – 0.0197 in.)1.0 mm (0.0394 in.)
Oil ring0.20 – 0.70 mm
(0.0079 – 0.0276 in.)1.2 mm (0.0472 in.)
“a”: 120 mm (4.72 in.)
I2RH01140159-01
I2RH01140161-01
Page 336 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-54 Engine Mechanical:
Piston Pins and Connecting Rods InspectionS6RW0D1406035
Piston Pin
Visual inspection
Check piston pin, connecting rod small end bore and
piston bore for wear or damage, paying particular
attention to condition of small end bore bush. If pin,
connecting rod small end bore or piston bore is badly
worn or damaged, replace pin, connecting rod and/or
piston.
Piston pin clearance
Check piston pin clearance in small end and piston.
Replace connecting rod and/or piston if its small end is
badly worn or damaged or if measured clearance
exceeds limit.
Piston pin clearance in connecting rod small end
Standard: 0.003 – 0.014 mm (0.0001 – 0.0006 in.)
Limit: 0.05 mm (0.00020 in.)
Piston pin clearance in piston
Standard: 0.006 – 0.017 mm (0.00024 – 0.00067 in.)
Limit: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.)
Small-end bore
20.003 – 20.011 mm (0.7875 – 0.7878 in.)
Piston pin dia.
19.997 – 20.000 mm (0.7873 – 0.7874 in.)
Piston bore
20.006 – 20.014 mm (0.7876 – 0.7880 in.)Connecting Rod
Big-end side clearance
Check big-end of connecting rod for side clearance, with
rod fitted and connected to its crank pin in the normal
manner. If measured clearance is found to exceed its
limit, replace connecting rod.
Big-end side clearance
Standard: 0.25 – 0.40 mm (0.0098 – 0.0157 in.)
Limit: 0.55 mm (0.0217 in.)
Connecting rod alignment
Mount connecting rod on aligner to check it for bow and
twist. If measured value exceeds the limit, replace it.
Connecting rod alignment
Limit on bow: 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.)
Limit on twist: 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
I4RS0A140023-01
I2RH0B140148-01
I4RH01140053-01