2006 MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER stop start
[x] Cancel search: stop startPage 670 of 2305

NO START VERIFICATION - VER-1 APPLICABILITY
1. NOTE: IMPORTANT! If the Engine Control Module or Sentry Key Immobilizer
Module has been replaced, ensure the programming procedure for the module has
been performed in accordance with the Service Information.
2. Inspect the vehicle to ensure that all engine components are properly installed and
connected. Reassemble and reconnect components as necessary.
3. Inspect the engine oil for contamination. If it is contaminated, change the oil and filter.
4. With the DRB, erase all diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
5. Turn the ignition off for at least 10 seconds.
6. Attempt to start the engine.
7. If the engine is unable to start, look for any Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) that may
relate to this condition. Return to the Symptom List if necessary.
8. If the engine starts and continues to run, the repair is now complete.
Are any DTCs or symptoms remaining?All
Ye s!Repair is not complete, refer to appropriate symptom.
No!Repair is complete.
ROAD TEST VERIFICATION - VER-2 APPLICABILITY
1. Inspect the vehicle to ensure that all engine components are properly installed and
connected. Reassemble and reconnect components as necessary.
2. If this verification procedure is being performed after a non-DTC test, perform steps 3 and
4. If not, proceed to step 5.
3. Check to see if the initial symptom still exists. If there are no trouble codes and the symptom
no longer exists, the repair was successful and testing is now complete.
4. If the initial or another symptom exists, the repair is not complete. Check all pertinent
Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) and return to the Symptom List if necessary.
5. For previously read DTCs that have not been dealt with, return to the Symptom List and
follow the diagnostic path for that DTC; otherwise, continue.
6. If the Engine Control Module (ECM) has not been changed, perform steps 7 and 8, otherwise,
continue with step 9.
7. With the DRB IIIt, erase all diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), then disconnect the DRB IIIt.
8. Turn the ignition off for at least 10 seconds.
9. If equipped with a Transfer Case Position Switch, perform step 10, otherwise, continue with
step 11.
10. With the ignition switch on, place the Transfer Case Shift Lever in each gear position,
stopping for 15 seconds in each position.
11. Ensure no DTCs remain by performing steps 12 through 15.
12. Road test the vehicle. For some of the road test, go at least 64 km/h (40 MPH). If this test
is for an A/C Relay Control Circuit, drive the vehicle for at least 5 minutes with the A/C on.
13. At some point, stop the vehicle and turn the engine off for at least 10 seconds, then restart
the engine and continue.
14. Upon completion of the road test, turn the engine off and check for DTCs with the DRB IIIt.
15. If the repaired DTC has set again, the repair is not complete. Check for any pertinent
Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) and return to the Symptom List. If there are no DTCs, the
repair was successful and is now complete.
Are any DTCs or symptoms remaining?All
Ye s!Repair is not complete, refer to appropriate symptom.
No!Repair is complete.
247
VERIFICATION TESTS
Verification Tests ÐContinued
Page 722 of 2305

(6) Start the engine in the vehicle which has the
booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes,
then start the engine in the vehicle with the dis-
charged battery.
CAUTION: Do not crank starter motor on disabled
vehicle for more than 15 seconds, starter will over-
heat and could fail.
(7) Allow battery in disabled vehicle to charge to
at least 12.4 volts (75% charge) before attempting to
start engine. If engine does not start within 15 sec-
onds, stop cranking engine and allow starter to cool
(15 min.), before cranking again.
DISCONNECT CABLE CLAMPS AS FOLLOWS:
²Disconnect BLACK cable clamp from engine
ground on disabled vehicle.
²When using a Booster vehicle, disconnect
BLACK cable clamp from battery negative terminal.
Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery positive
terminal.
²Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery posi-
tive terminal on disabled vehicle.
TOWING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TOWING
WARNING: Do not tow the vehicle if the key cannot
be turned in the ignition lock. If the key cannot be
turned, the ignition lock remains locked and the
vehicle cannot be steered. With the engine not run-
ning there is no power assistance for the braking
and steering systems. In this case, it is important to
keep in mind that a considerably higher degree of
effort is necessary to brake and steer the vehicle.
The vehicle must not be towed with the front axle
raised and the key in position 2 in the ignition lock
as the drive wheels could then lock due to the
acceleration skid control (ASR)
If the Engine is Damaged
For towing distances up to 30 miles (about 50
km)
²Shift selector lever in ªNº position.
²Do not exceed a towing speed of 30 m.p.h. (50
km/h).
For towing distances greater than 30 mile
(about 50 km)
²Remove the propeller shafts leading to the drive
axles. The vehicle can be towed without restriction.
If the Transmission is Damaged
²Remove the propeller shafts leading to the drive
axles. The vehicle can be towed without restriction.
If the Front Axle is Damaged
²Raise the front axle.
²Observe the same towing restrictions as for
engine damage.
If the Rear Axle is Damaged
²Raise the rear axle.
NOTE: Comply with local legal regulations regard-
ing towing vehicles.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
NOTE: The following safety precautions must be
observed when towing a vehicle.
²Secure loose and protruding parts.
²Always use a safety chain system that is inde-
pendent of the lifting and towing equipment.
²Do not allow towing equipment to contact the
disabled vehicle's fuel tank.
²Do not allow anyone under the disabled vehicle
while it is lifted by the towing device.
²Do not allow passengers to ride in a vehicle
being towed.
²Always observe state and local laws regarding
towing regulations.
²Do not tow a vehicle in a manner that could
jeopardize the safety of the operator, pedestrians or
other motorists.
²Do not attach tow chains, T-hooks, J-hooks, or a
tow sling to a bumper, steering linkage, drive shafts
or a non-reinforced frame hole.
²Remove exhaust pipe tips that interfere with the
tow sling and crossbar
²Padding should be placed between the tow sling/
crossbar and any painted surfaces
²When placing tow hooks on the rear axle, posi-
tion them so they do not damage the brake tubing or
hoses
²Do not tow the vehicle by connecting to the front
or rear shock absorbers
²Do not tow a heavily loaded vehicle. Damage to
the vehicle may result. Use a flatbed device to trans-
port a loaded vehicle.
GROUND CLEARANCE
CAUTION: If vehicle is towed with wheels removed,
install lug nuts to retain brake drums.
A towed vehicle should be raised until lifted wheels
are a minimum 100 mm (4 in) from the ground. Be
sure there is adequate ground clearance at the oppo-
site end of the vehicle, especially when towing over
rough terrain, steep rises in the road or if the vehicle
is equipped with air dams, spoilers, and/or ground
VALUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 7
Page 793 of 2305

As the dragging brake overheats, efficiency is so
reduced that fade occurs. Since the opposite brake
unit is still functioning normally, its braking effect is
magnified. This causes pull to switch direction in
favor of the normally functioning brake unit.
An additional point when diagnosing a change in
pull condition concerns brake cool down. Remember
that pull will return to the original direction, if the
dragging brake unit is allowed to cool down (and is
not seriously damaged).
REAR BRAKE GRAB OR PULL
Rear grab or pull is usually caused by improperly
adjusted or seized parking brake cables, contami-
nated lining, bent or binding shoes and support
plates, or improperly assembled components. This is
particularly true when only one rear wheel is
involved. However, when both rear wheels are
affected, the master cylinder or proportioning valve
could be at fault.
BRAKES DO NOT HOLD AFTER DRIVING THROUGH DEEP
WATER PUDDLES
This condition is generally caused by water soaked
lining. If the lining is only wet, it can be dried by
driving with the brakes very lightly applied for a
mile or two. However, if the lining is both soaked and
dirt contaminated, cleaning and/or replacement will
be necessary.
BRAKE LINING CONTAMINATION
Brake lining contamination is mostly a product of
leaking calipers or worn seals, driving through deep
water puddles, or lining that has become covered
with grease and grit during repair. Contaminated lin-
ing should be replaced to avoid further brake prob-
lems.
WHEEL AND TIRE PROBLEMS
Some conditions attributed to brake components
may actually be caused by a wheel or tire problem.
A damaged wheel can cause shudder, vibration and
pull. A worn or damaged tire can also cause pull.
Severely worn tires with very little tread left can
produce a grab-like condition as the tire loses and
recovers traction. Flat-spotted tires can cause vibra-
tion and generate shudder during brake operation. A
tire with internal damage such as a severe bruise,
cut, or ply separation can cause pull and vibration.
BRAKE NOISES
Some brake noise is common with rear drum
brakes and on some disc brakes during the first few
stops after a vehicle has been parked overnight or
stored. This is primarily due to the formation of trace
corrosion (light rust) on metal surfaces. This light
corrosion is typically cleared from the metal surfacesafter a few brake applications causing the noise to
subside.
BRAKE SQUEAK / SQUEAL
Brake squeak or squeal may be due to linings that
are wet or contaminated with brake fluid, grease, or
oil. Glazed linings and rotors with hard spots can
also contribute to squeak. Dirt and foreign material
embedded in the brake lining will also cause squeak/
squeal.
A very loud squeak or squeal is frequently a sign of
severely worn brake lining. If the lining has worn
through to the brake pads in spots, metal-to-metal
contact occurs. If the condition is allowed to continue,
rotors can become so scored that replacement is nec-
essary.
BRAKE CHATTER
Brake chatter is usually caused by loose or worn
components, or glazed/burnt lining. Rotors with hard
spots can also contribute to chatter. Additional causes
of chatter are out-of-tolerance rotors, brake lining not
securely attached to the shoes, loose wheel bearings
and contaminated brake lining.
THUMP / CLUNK NOISE
Thumping or clunk noises during braking are fre-
quentlynotcaused by brake components. In many
cases, such noises are caused by loose or damaged
steering, suspension, or engine components. However,
calipers that bind on the slide surfaces can generate
a thump or clunk noise.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANUAL BLEEDING
Use approved brake fluid (Refer to LUBRICATION
& MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES - DESCRIP-
TION). Use fresh, clean fluid from a sealed container
at all times.
(1) Remove reservoir filler caps and fill reservoir.
(2) If calipers, or wheel cylinders were overhauled,
open all caliper and wheel cylinder bleed screws.
Then close each bleed screw as fluid starts to drip
from it. Top off master cylinder reservoir once more
before proceeding.
(3) Attach one end of bleed hose to bleed screw
and insert opposite end in glass container partially
filled with brake fluid (Fig. 1). Be sure end of bleed
hose is immersed in fluid.
5 - 4 BRAKES - BASEVA
Page 806 of 2305

NOTE: The pressure gauge, connected at the ALB
controller must indicate the outlet pressure which
is assigned on the ALB plate to the rear axle load
determined.
NOTE: If the rear axle load determined is between
two figures indicated on the ALB plate, the outlet
pressure should be determined accordingly.
(8) If the pressure measured differs from the spec-
ification, adjust the ALB controller (Fig. 16).
(9) Loosen the brake pedal winch.
(10) Adjust the outlet pressure by turning the
adjusting nut (Fig. 16)To increase pressure -
tighten the adjusting nut. To reduce pressure -
loosen the adjusting nut.
(11) After adjustment reinstall the brake pedal
winch and recheck the pressures and readjust if
needed.
(12) Tighten the lock adjusting nut.
MASTER CYLINDER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MASTER CYLIN-
DER / POWER BOOSTER
(1) Start engine and check booster vacuum hose
connections. A hissing noise indicates vacuum leak.
Correct any vacuum leak before proceeding.
(2) Stop engine and shift transmission into Neu-
tral.
(3) Pump brake pedal until all vacuum reserve in
booster is depleted.
(4) Press and hold brake pedal under light foot
pressure. The pedal should hold firm, if the pedal
falls away master cylinder is faulty (internal leak-
age).
(5) Start engine and note pedal action. It should
fall away slightly under light foot pressure then holdfirm. If no pedal action is discernible, power booster,
vacuum supply, or vacuum check valve is faulty. Pro-
ceed to the POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST.
(6) If the POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST
passes, rebuild booster vacuum reserve as follows:
Release brake pedal. Increase engine speed to 1500
rpm, close the throttle and immediately turn off igni-
tion to stop engine.
(7) Wait a minimum of 90 seconds and try brake
action again. Booster should provide two or more vac-
uum assisted pedal applications. If vacuum assist is
not provided, booster is faulty.
POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST
(1) Connect vacuum gauge to booster check valve
with short length of hose and T-fitting (Fig. 17).
(2) Start and run engine at curb idle speed for one
minute.
(3) Observe the vacuum supply. If vacuum supply
is not adequate, repair vacuum supply.
(4) Clamp hose shut between vacuum source and
check valve.
(5) Stop engine and observe vacuum gauge.
(6) If vacuum drops more than one inch HG (33
millibars) within 15 seconds, booster diaphragm or
check valve is faulty.
POWER BOOSTER CHECK VALVE TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose from check valve.
(2) Remove check valve and valve seal from
booster.
Fig. 16 ALB CONTROLLER ADJUSTER NUT
1 - ALB ADJUSTER NUT
2 - SPRING
Fig. 17 Typical Booster Vacuum Test Connections
1 - TEE FITTING
2 - SHORT CONNECTING HOSE
3 - CHECK VALVE
4 - CHECK VALVE HOSE
5 - CLAMP TOOL
6 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
7 - VACUUM GAUGE
VABRAKES - BASE 5 - 17
Page 837 of 2305

Propylene - glycol / Ethylene - glycol Mixtures - Should Not
Be Used in Chrysler Vehicles
Propylene-glycol/ethylene-glycol Mixtures can
cause the destabilization of various corrosion inhibi-
tors, causing damage to the various cooling system
components. Also, once ethylene-glycol and propy-
lene-glycol based coolants are mixed in the vehicle,
conventional methods of determining freeze point will
not be accurate. Both the refractive index and spe-
cific gravity differ between ethylene glycol and propy-
lene glycol.
CAUTION: Richer antifreeze mixtures cannot be
measured with normal field equipment and can
cause problems associated with 100 percent ethyl-
ene-glycol.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
COOLING SYSTEM LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT METHOD
A leak detection additive is available through the
parts department that can be added to cooling sys-
tem. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
light (black light). Pour one ounce of additive into
cooling system. Place heater control unit in HEAT
position. Start and operate engine until radiator
upper hose is warm to touch. Aim the commercially
available black light tool at components to be
checked. If leaks are present, black light will cause
additive to glow a bright green color.
The black light can be used in conjunction with a
pressure tester to determine if any external leaks
exist (Fig. 1).
PRESSURE TESTER METHOD
The engine should be at normal operating temper-
ature. Recheck the system cold if cause of coolant
loss is not located during the warm engine examina-
tion.
WARNING: Hot, pressurized coolant can cause
injury by scalding.
Carefully remove coolant recovery pressure con-
tainer cap and check coolant level. Push down on cap
to disengage it from stop tabs. Wipe inside of con-
tainer and examine lower inside sealing seat for
nicks, cracks, paint, dirt and solder residue. Inspect
radiator-to- pressure container hose for internal
obstructions. Insert a wire through the hose to be
sure it is not obstructed.
Inspect cams on outside of pressure container. If
cams are damaged, seating of pressure cap valve and
tester seal will be affected.
Attach pressure tester (7700 or an equivalent) to
coolant pressure container (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 Leak Detection Using Black Light - Typical
1 - TYPICAL BLACK LIGHT TOOL
7 - 10 ENGINEVA
Page 952 of 2305

electrical package have a heavy duty 7-way trailer
tow connector installed in a bracket on the trailer
hitch receiver. This package includes a 7-way to
4-way connector adapter unit.
²Trailer Tow Control Module- Vehicles
equipped with a factory-approved, field-installed
trailer towing electrical package have a trailer tow
brake/turn control module located within the driver
side front seat riser that controls the brake lamp and
turn signal lamp outputs to the trailer lighting cir-
cuits.
²Turn Signal Relay- A turn signal relay is
installed in the fuse block located on the underside of
the steering column behind a fuse access panel in the
steering column opening cover on the instrument
panel. The electronic circuitry of the wipers, turn sig-
nals and engine start control module within the fuse
block controls the turn signal relay.
²Wipers, Turn Signals, Engine Start Control
Module- The wipers, turn signals and engine start
control module is integral to the fuse block located on
the underside of the steering column behind a fuse
access panel in the steering column opening cover on
the instrument panel. This module includes active
electronic elements that control the operation of the
turn signal relay based upon inputs from the multi-
function switch and feedback from the turn signal
circuits. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRI-
BUTION/FUSE BLOCK - DESCRIPTION).
Hard wired circuitry connects the exterior lighting
system components to the electrical system of the
vehicle. These hard wired circuits are integral to sev-
eral wire harnesses, which are routed throughout the
vehicle and retained by many different methods.
These circuits may be connected to each other, to the
vehicle electrical system and to the exterior lighting
system components through the use of a combination
of soldered splices, splice block connectors, and many
different types of wire harness terminal connectors
and insulators. Refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring dia-
grams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
further details on wire harness routing and reten-
tion, as well as pin-out and location views for the
various wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
OPERATION
Following are paragraphs that briefly describe the
operation of each of the major exterior lighting sys-
tems. The hard wired circuits and components of the
exterior lighting systems may be diagnosed and
tested using conventional diagnostic tools and proce-
dures. However, conventional diagnostic methods
may not prove conclusive in the diagnosis of the wip-
ers, turn signals and engine start control module
located within the fuse block underneath the steering
column, the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster
(EMIC), the Engine Control Module (ECM), or theController Area Network (CAN) data bus network.
The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means to
diagnose the electronic module within the fuse block,
the EMIC, the ECM, and the CAN data bus network
inputs and outputs related to the various exterior
lighting systems requires the use of a diagnostic scan
tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
BACKUP LAMPS
The backup (or reverse) lamps have a path to
ground received at all times through the vehicle wire
harness from a ground point located on the frame
near the left end of the tailgate sill. The backup
lamps receive battery current on the backup lamp
supply circuit only when the backup lamp switch cir-
cuit of the Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) integral
to the gear shifter assembly is closed by the gear
shifter mechanism.
BRAKE LAMPS
The brake (or stop) lamps have a path to ground at
all times through the vehicle wire harness from a
ground point located on the frame near the left end
of the tailgate sill. The Center High Mounted Stop
Lamp (CHMSL) has a path to ground at all times
through the vehicle wire harness from a ground point
on the left side of the dash panel. The brake lamps
and CHMSL receive battery current on the brake
lamp switch output circuit when the brake lamp
switch is closed by the brake pedal arm.
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMPS
Vehicles manufactured for sale in Canada illumi-
nate the low beam headlamp bulb when the engine is
running and the exterior lamps are turned off. This
feature is enabled by the right and left Daytime Run-
ning Lamps (DRL) relays. When the DRL relays are
de-energized, they provide fused battery current from
the circuit K26 relay to the headlamp low beams.
When the headlamps are turned On using the left
(lighting) control stalk of the multi-function switch
the DRL relays are energized, which returns control
of the headlamps to the headlamp switch circuitry of
the multi-function switch. The circuit K26 relay is
energized by the ElectroMechanical Instrument Clus-
ter (EMIC) whenever it receives an electronic mes-
sage from the Engine Control Module (ECM) over the
Controller Area Network (CAN) data bus indicating
that the engine is running. The DRL and circuit K26
relays are installed in a relay bracket located below
the forward edge of the driver side front seat cushion
within the driver side front seat riser.
FRONT FOG LAMPS
Vehicles equipped with optional front fog lamps
have a front fog lamp relay installed in a relay
bracket located below the forward edge of the driver
side front seat cushion within the driver side front
VALAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 3
Page 954 of 2305

TURN SIGNAL LAMPS
When the left (lighting) control stalk of the multi-
function switch is activated (Fig. 1), the turn signal
system illuminates the selected right or left turn sig-
nal indicator and the turn signal lamps begin to
flash. The turn signal lamps include a bulb integral
to each front lamp unit and each tail lamp unit, as
well as a repeater lamp bulb located on each front
fender above the front wheels. When the turn signal
system is activated, the turn signal switch circuitry
within the multi-function switch and the electronic
circuitry of the wipers, turn signals and engine start
control module within the fuse block will repeatedly
energize and de-energize the turn signal relay
located in the fuse block. The turn signal relay
switches battery current from a fused ignition switch
output fuse in the fuse block to the appropriate turn
signal indicator and turn signal lamps.
The ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC)
contactless relay will generate repetitive, audible
turn signal ªclickº sounds to emulate the sounds of a
conventional electro-mechanical turn signal flasher
at one of two rates to coincide with the flashing of
the turn signals. The slow rate emulates normal turn
signal operation, while the fast rate emulates ªbulb
outº turn signal operation.
SPECIFICATIONS - LAMPS / LIGHTING - EXTE-
RIOR
BULB SPECIFICATIONS
LAMP BULB
Backup P21W - 12V 21W
Brake & Rear Park P21/5W - 12V 21/5W
Center High Mounted
StopP21W - 12V 21W
Clearance W3W - 12V 3W
Front Fog H1 - 12V 55W
Front Position W5W - 12V 5W
Front Turn, Park & Side
Marker3457 NA - 12V 28/7.5W
Amber Glass
Low Beam Headlamp H7 - 12V 55W
High Beam Headlamp H1 - 12V 55W
License Plate C5W - 12V 5W
Rear Side Marker R5W - 12V 5W
Rear Turn P21W - 12V 21W
Side Repeater W5W - 12V 3W
BACKUP LAMP BULB
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) If the vehicle is so equipped, remove the trim
from the inside of the right or left rear corner pillar.
(3) From inside the vehicle, use hand pressure to
push the two latch tabs toward the center of the tail
lamp unit socket plate and pull the socket plate
straight out from the inner rear pillar (Fig. 2).
(4) Pull the socket plate away from the inner rear
pillar far enough to access the backup lamp bulb
(Fig. 3).
Fig. 2 Tail Lamp Socket Plate Remove/Install
1 - SOCKET PLATE
2 - INNER REAR PILLAR
3 - LATCH TAB (2)
VALAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 5
Page 1092 of 2305
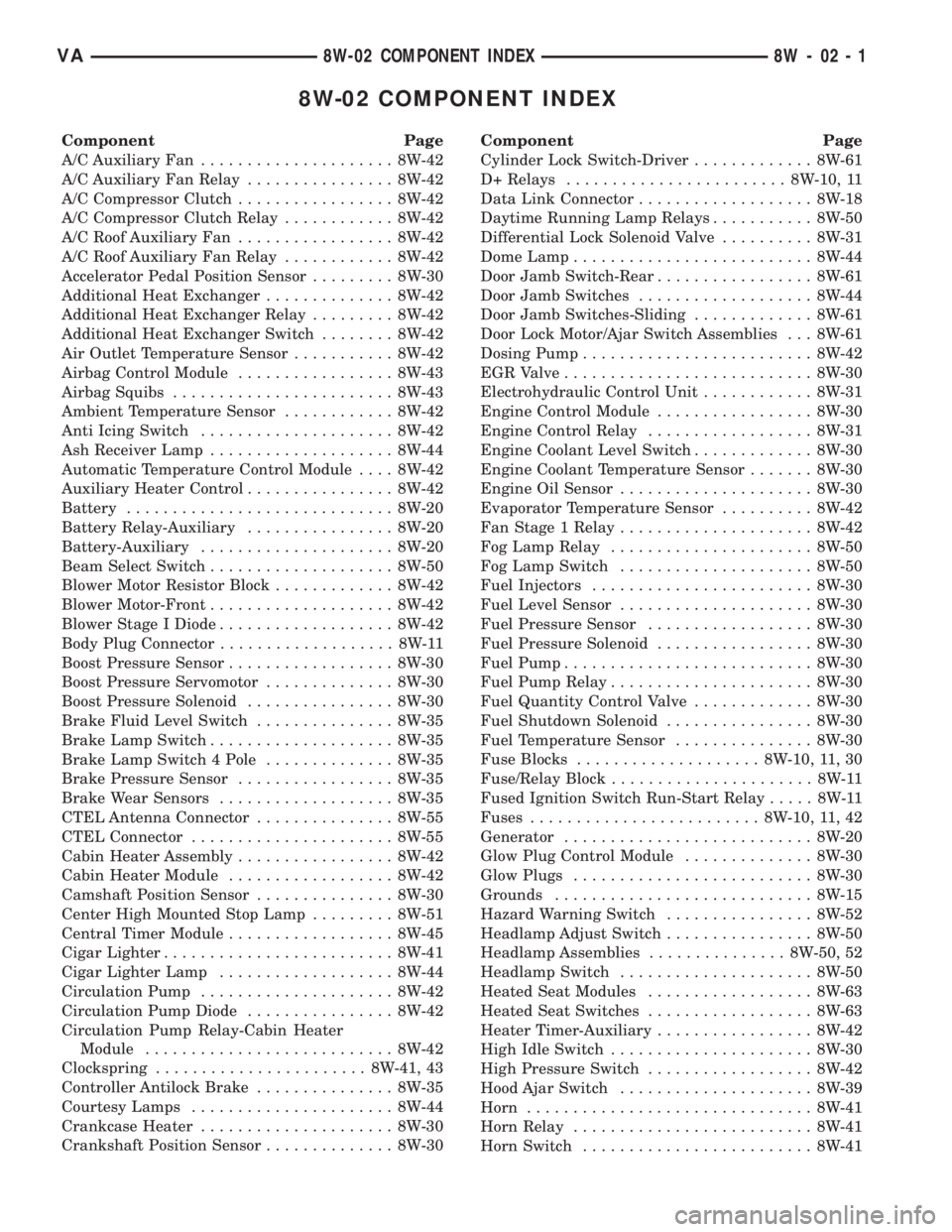
8W-02 COMPONENT INDEX
Component Page
A/C Auxiliary Fan..................... 8W-42
A/C Auxiliary Fan Relay................ 8W-42
A/C Compressor Clutch................. 8W-42
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay............ 8W-42
A/C Roof Auxiliary Fan................. 8W-42
A/C Roof Auxiliary Fan Relay............ 8W-42
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor......... 8W-30
Additional Heat Exchanger.............. 8W-42
Additional Heat Exchanger Relay......... 8W-42
Additional Heat Exchanger Switch........ 8W-42
Air Outlet Temperature Sensor........... 8W-42
Airbag Control Module................. 8W-43
Airbag Squibs........................ 8W-43
Ambient Temperature Sensor............ 8W-42
Anti Icing Switch..................... 8W-42
Ash Receiver Lamp.................... 8W-44
Automatic Temperature Control Module.... 8W-42
Auxiliary Heater Control................ 8W-42
Battery............................. 8W-20
Battery Relay-Auxiliary................ 8W-20
Battery-Auxiliary..................... 8W-20
Beam Select Switch.................... 8W-50
Blower Motor Resistor Block............. 8W-42
Blower Motor-Front.................... 8W-42
Blower Stage I Diode................... 8W-42
Body Plug Connector................... 8W-11
Boost Pressure Sensor.................. 8W-30
Boost Pressure Servomotor.............. 8W-30
Boost Pressure Solenoid................ 8W-30
Brake Fluid Level Switch............... 8W-35
Brake Lamp Switch.................... 8W-35
Brake Lamp Switch 4 Pole.............. 8W-35
Brake Pressure Sensor................. 8W-35
Brake Wear Sensors................... 8W-35
CTEL Antenna Connector............... 8W-55
CTEL Connector...................... 8W-55
Cabin Heater Assembly................. 8W-42
Cabin Heater Module.................. 8W-42
Camshaft Position Sensor............... 8W-30
Center High Mounted Stop Lamp......... 8W-51
Central Timer Module.................. 8W-45
Cigar Lighter......................... 8W-41
Cigar Lighter Lamp................... 8W-44
Circulation Pump..................... 8W-42
Circulation Pump Diode................ 8W-42
Circulation Pump Relay-Cabin Heater
Module........................... 8W-42
Clockspring....................... 8W-41, 43
Controller Antilock Brake............... 8W-35
Courtesy Lamps...................... 8W-44
Crankcase Heater..................... 8W-30
Crankshaft Position Sensor.............. 8W-30Component Page
Cylinder Lock Switch-Driver............. 8W-61
D+ Relays........................ 8W-10, 11
Data Link Connector................... 8W-18
Daytime Running Lamp Relays........... 8W-50
Differential Lock Solenoid Valve.......... 8W-31
Dome Lamp.......................... 8W-44
Door Jamb Switch-Rear................. 8W-61
Door Jamb Switches................... 8W-44
Door Jamb Switches-Sliding............. 8W-61
Door Lock Motor/Ajar Switch Assemblies . . . 8W-61
Dosing Pump......................... 8W-42
EGR Valve........................... 8W-30
Electrohydraulic Control Unit............ 8W-31
Engine Control Module................. 8W-30
Engine Control Relay.................. 8W-31
Engine Coolant Level Switch............. 8W-30
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor....... 8W-30
Engine Oil Sensor..................... 8W-30
Evaporator Temperature Sensor.......... 8W-42
Fan Stage 1 Relay..................... 8W-42
Fog Lamp Relay...................... 8W-50
Fog Lamp Switch..................... 8W-50
Fuel Injectors........................ 8W-30
Fuel Level Sensor..................... 8W-30
Fuel Pressure Sensor.................. 8W-30
Fuel Pressure Solenoid................. 8W-30
Fuel Pump........................... 8W-30
Fuel Pump Relay...................... 8W-30
Fuel Quantity Control Valve............. 8W-30
Fuel Shutdown Solenoid................ 8W-30
Fuel Temperature Sensor............... 8W-30
Fuse Blocks.................... 8W-10, 11, 30
Fuse/Relay Block...................... 8W-11
Fused Ignition Switch Run-Start Relay..... 8W-11
Fuses......................... 8W-10, 11, 42
Generator........................... 8W-20
Glow Plug Control Module.............. 8W-30
Glow Plugs.......................... 8W-30
Grounds............................ 8W-15
Hazard Warning Switch................ 8W-52
Headlamp Adjust Switch................ 8W-50
Headlamp Assemblies............... 8W-50, 52
Headlamp Switch..................... 8W-50
Heated Seat Modules.................. 8W-63
Heated Seat Switches.................. 8W-63
Heater Timer-Auxiliary................. 8W-42
High Idle Switch...................... 8W-30
High Pressure Switch.................. 8W-42
Hood Ajar Switch..................... 8W-39
Horn............................... 8W-41
Horn Relay.......................... 8W-41
Horn Switch......................... 8W-41
VA8W-02 COMPONENT INDEX 8W - 02 - 1