2006 INFINITI M35 Tail light
[x] Cancel search: Tail lightPage 2824 of 5621
![INFINITI M35 2006 Factory Service Manual DTC P1554 BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR
EC-1281
[VK45DE]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
DTC P1554 BATTERY CURRENT SENSORPFP:294G0
Component DescriptionNBS005M0
The power gener INFINITI M35 2006 Factory Service Manual DTC P1554 BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR
EC-1281
[VK45DE]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
DTC P1554 BATTERY CURRENT SENSORPFP:294G0
Component DescriptionNBS005M0
The power gener](/manual-img/42/57023/w960_57023-2823.png)
DTC P1554 BATTERY CURRENT SENSOR
EC-1281
[VK45DE]
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
DTC P1554 BATTERY CURRENT SENSORPFP:294G0
Component DescriptionNBS005M0
The power generation voltage variable control enables fuel con-
sumption to be decreased by reducing the engine load which is
caused by the power generation of the generator. The battery cur-
rent sensor (1) is installed to the battery cable at the negative termi-
nal. The sensor measures the charging/discharging current of the
battery. Based on the sensor signal, ECM judges whether or not the
power generation voltage variable control is performed. When per-
forming the power generation voltage variable control, ECM calcu-
lates the target power generation voltage based on the sensor
signal. And ECM sends the calculated value as the power genera-
tion command value to IPDM E/R. For the details of the power gen-
eration voltage variable control, refer to SC section.
CAUTION:
Do not connect the electrical component or the ground wire directly to the battery terminal. The con-
nection causes the malfunction of the power generation voltage variable control, and then the battery
discharge may occur.
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor ModeNBS005M1
Specification data are reference values.
*: Before measuring the terminal voltage, confirm that the battery is fully charged. Refer to SC-5, "SPECIFIC GRAVITY CHECK" .
On Board Diagnosis LogicNBS005M2
The MIL will not light up for this diagnosis.
NOTE:
If DTC P1554 is displayed with DTC P0643, first perform the trouble diagnosis for DTC P0643. Refer to
EC-1218, "
DTC P0643 SENSOR POWER SUPPLY" .
PBIB2685E
MONITOR ITEM CONDITION SPECIFICATION
BAT CUR SEN
Engine speed: Idle
Battery: Fully charged*
Selector lever: P or N
Air conditioner switch: OFF
No loadApprox. 2,600 - 3,500mV
DTC No. Trouble diagnosis name DTC detecting condition Possible cause
P1554
1554Battery current sensor perfor-
manceThe output voltage of the battery current
sensor is lower than the specified value
while the battery voltage is high enough.
Harness or connectors
(The sensor circuit is open or shorted.)
Battery current sensor
Page 3010 of 5621
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
EI-5
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
EI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESPFP:00000
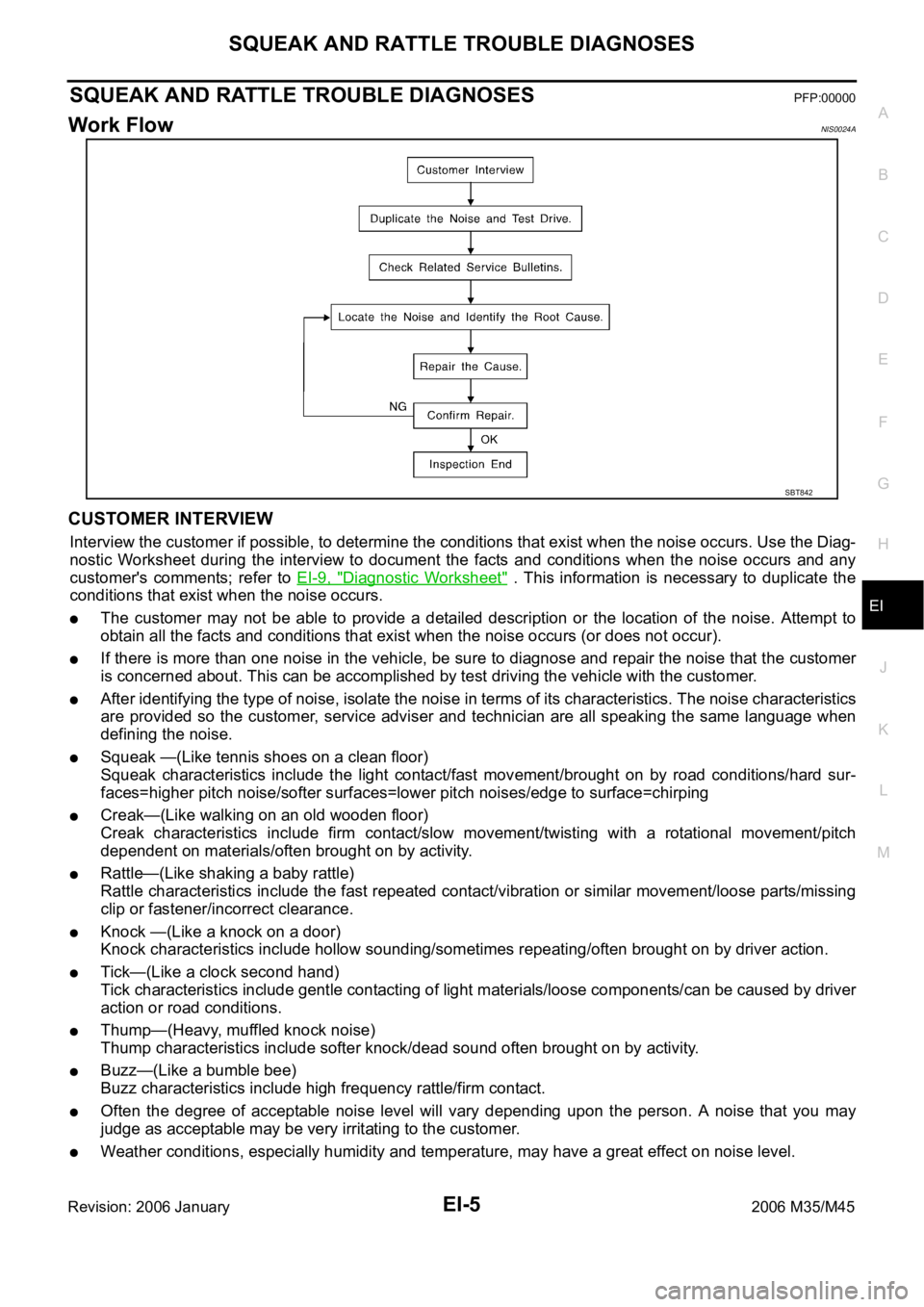
Work FlowNIS0024A
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to EI-9, "
Diagnostic Worksheet" . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces=higher pitch noise/softer surfaces=lower pitch noises/edge to surface=chirping
Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT842
Page 3482 of 5621

HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
GI-19
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
14 Wire color
This shows a code for the color of the wire.
B = Black
W = White
R = Red
G = Green
L = Blue
Y = Yellow
LG = Light GreenBR = Brown
OR or O = Orange
P = Pink
PU or V (Violet) = Purple
GY or GR = Gray
SB = Sky Blue
CH = Dark Brown
DG = Dark Green
When the wire color is striped, the base color is given first, followed by the stripe color as shown
below:
Example: L/W = Blue with White Stripe
15 Option description
This shows a description of the option abbreviation used on the page.
16 Switch
This shows that continuity exists between terminals 1 and 2 when the switch is in the A posi-
tion. Continuity exists between terminals 1 and 3 when the switch is in the B position.
17 Assembly parts
Connector terminal in component shows that it is a harness incorporated assembly.
18 Cell code
This identifies each page of the wiring diagram by section, system and wiring diagram page
number.
19 Current flow arrow
Arrow indicates electric current flow, especially where the direction of standard flow (vertically
downward or horizontally from left to right) is difficult to follow.
A double arrow “ ” shows that current can flow in either direction depending on cir-
cuit operation.
20 System branch
This shows that the system branches to another system identified by cell code (section and
system).
21 Page crossing
This arrow shows that the circuit continues to another page identified by cell code.
The C will match with the C on another page within the system other than the next or preced-
ing pages.
22 Shielded line
The line enclosed by broken line circle shows shield wire.
23Component box in
wave line
This shows that another part of the component is also shown on another page (indicated by
wave line) within the system.
24 Component name
This shows the name of a component.
25 Connector number
This shows the connector number.
The letter shows which harness the connector is located in.
Example: M : main harness. For detail and to locate the connector, refer to PG section "Main
Harness", “Harness Layout”. A coordinate grid is included for complex harnesses to aid in
locating connectors.
26 Ground (GND)
The line spliced and grounded under wire color shows that ground line is spliced at the
grounded connector.
27 Ground (GND)
This shows the ground connection. For detailed ground distribution information, refer to
"Ground Distribution" in PG section.
28 Connector views
This area shows the connector faces of the components in the wiring diagram on the page.
29 Common component
Connectors enclosed in broken line show that these connectors belong to the same compo-
nent.
30 Connector color
This shows a code for the color of the connector. For code meaning, refer to wire color codes,
Number 14 of this chart.
31Fusible link and fuse
box
This shows the arrangement of fusible link(s) and fuse(s), used for connector views of
"POWER SUPPLY ROUTING" in PG section.
The open square shows current flow in, and the shaded square shows current flow out.
32 Reference area
This shows that more information on the Super Multiple Junction (SMJ) and Joint Connectors
(J/C) exists on the PG section. Refer to "Reference Area" for details. Num-
berItem Description
Page 3496 of 5621
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-33
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check
for voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
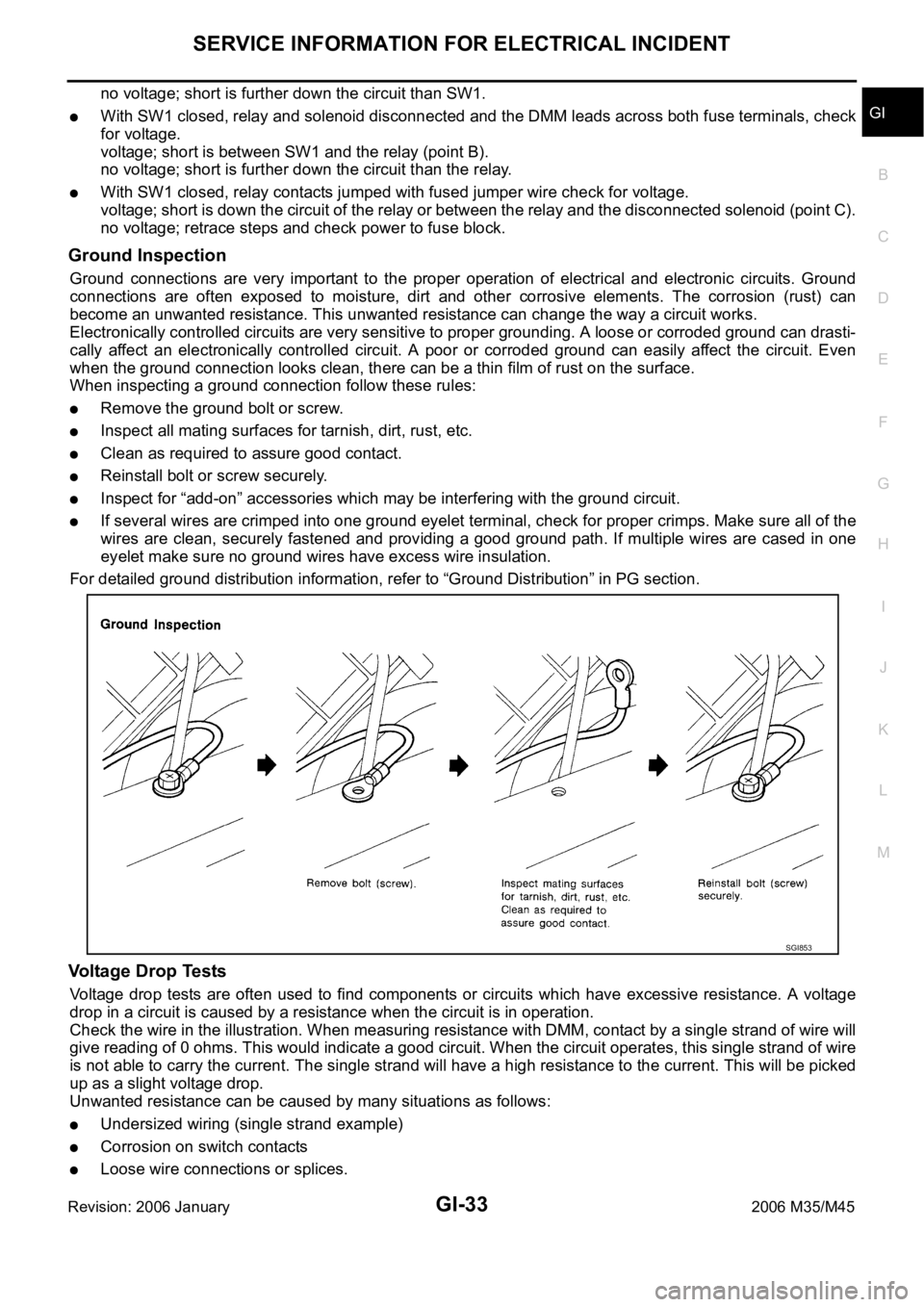
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
Remove the ground bolt or screw.
Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
Clean as required to assure good contact.
Reinstall bolt or screw securely.
Inspect for “add-on” accessories which may be interfering with the ground circuit.
If several wires are crimped into one ground eyelet terminal, check for proper crimps. Make sure all of the
wires are clean, securely fastened and providing a good ground path. If multiple wires are cased in one
eyelet make sure no ground wires have excess wire insulation.
For detailed ground distribution information, refer to “Ground Distribution” in PG section.
Voltage Drop Tests
Voltage drop tests are often used to find components or circuits which have excessive resistance. A voltage
drop in a circuit is caused by a resistance when the circuit is in operation.
Check the wire in the illustration. When measuring resistance with DMM, contact by a single strand of wire will
give reading of 0 ohms. This would indicate a good circuit. When the circuit operates, this single strand of wire
is not able to carry the current. The single strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will be picked
up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
Undersized wiring (single strand example)
Corrosion on switch contacts
Loose wire connections or splices.
SGI853
Page 3502 of 5621
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-39
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
Nickel Metal Hydride Battery Replacement NAS0007U
CONSULT-II contains a nickel metal hydride battery. When replacing the battery obey the following:
WAR NING :
Replace the nickel metal hydride battery with Genuine CONSULT-II battery only. Use of another bat-
tery may present a risk of fire or explosion. The battery may present a fire or chemical burn hazard if
mistreated. Do not recharge, disassemble or dispose of in fire.
Keep the battery out of reach of children and discard used battery conforming to the local regulations.
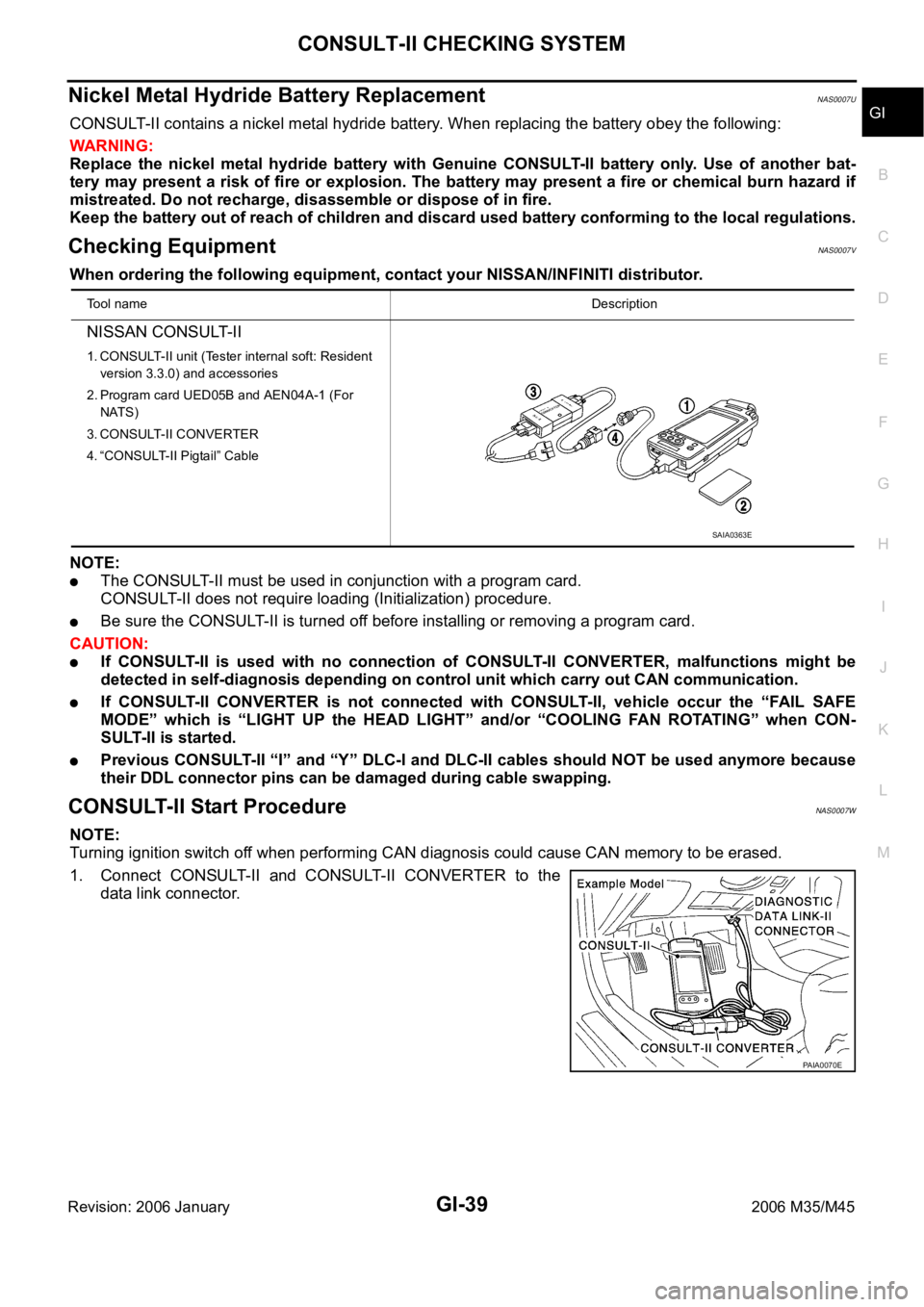
Checking Equipment NAS0007V
When ordering the following equipment, contact your NISSAN/INFINITI distributor.
NOTE:
The CONSULT-II must be used in conjunction with a program card.
CONSULT-II does not require loading (Initialization) procedure.
Be sure the CONSULT-II is turned off before installing or removing a program card.
CAUTION:
If CONSULT-II is used with no connection of CONSULT-II CONVERTER, malfunctions might be
detected in self-diagnosis depending on control unit which carry out CAN communication.
If CONSULT-II CONVERTER is not connected with CONSULT-II, vehicle occur the “FAIL SAFE
MODE” which is “LIGHT UP the HEAD LIGHT” and/or “COOLING FAN ROTAT I N G ” w h e n C O N -
SULT-II is started.
Previous CONSULT-II “I” and “Y” DLC-I and DLC-II cables should NOT be used anymore because
their DDL connector pins can be damaged during cable swapping.
CONSULT-II Start ProcedureNAS0007W
NOTE:
Turning ignition switch off when performing CAN diagnosis could cause CAN memory to be erased.
1. Connect CONSULT-II and CONSULT-II CONVERTER to the
data link connector.
Tool nameDescription
NISSAN CONSULT-II
1. CONSULT-II unit (Tester internal soft: Resident
version 3.3.0) and accessories
2. Program card UED05B and AEN04A-1 (For
NATS)
3. CONSULT-II CONVERTER
4. “CONSULT-II Pigtail” Cable
SAIA0363E
PAIA0070E
Page 3524 of 5621
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
GW-5
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESPFP:00000
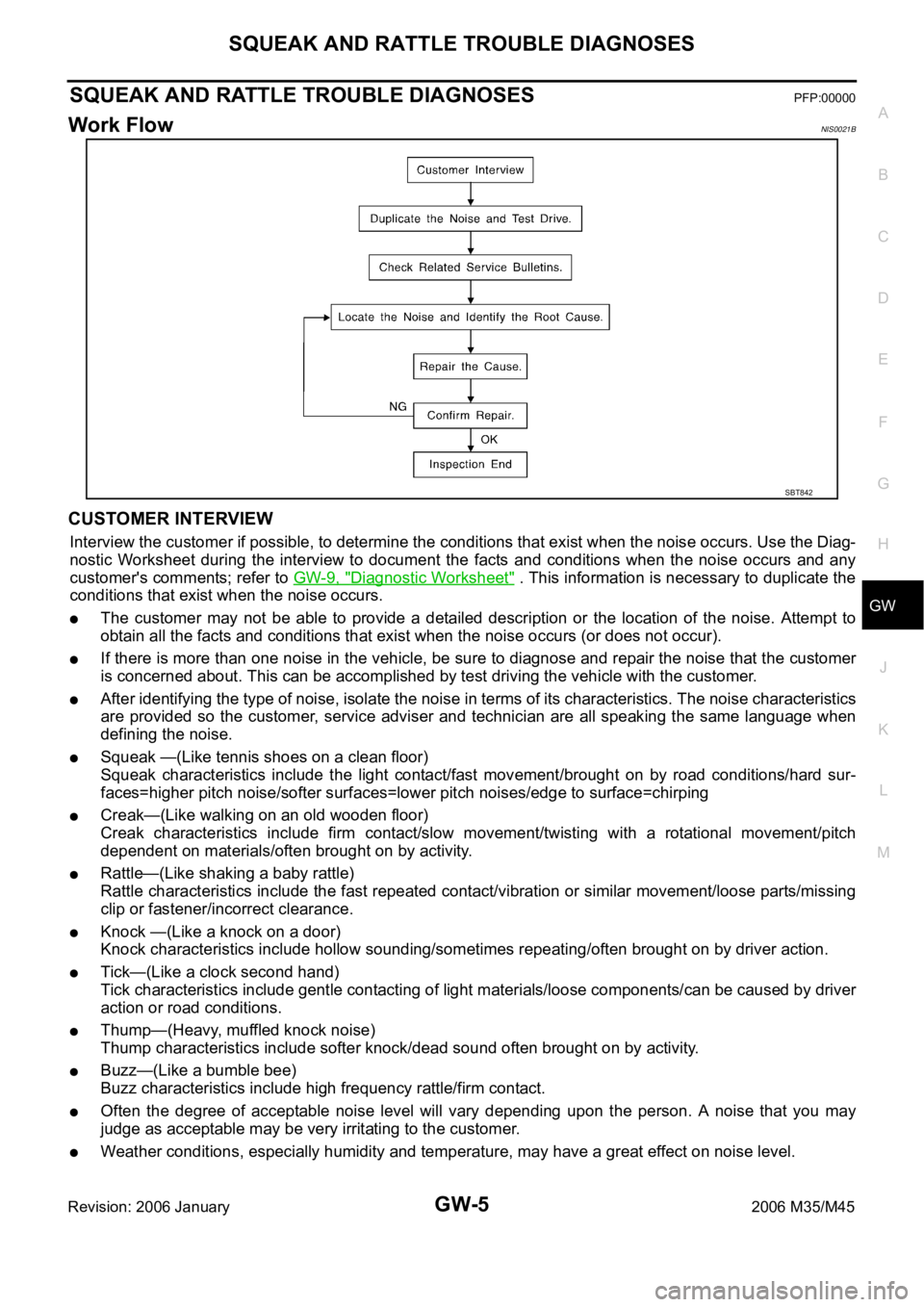
Work FlowNIS0021B
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to GW-9, "
Diagnostic Worksheet" . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces=higher pitch noise/softer surfaces=lower pitch noises/edge to surface=chirping
Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT842
Page 3653 of 5621
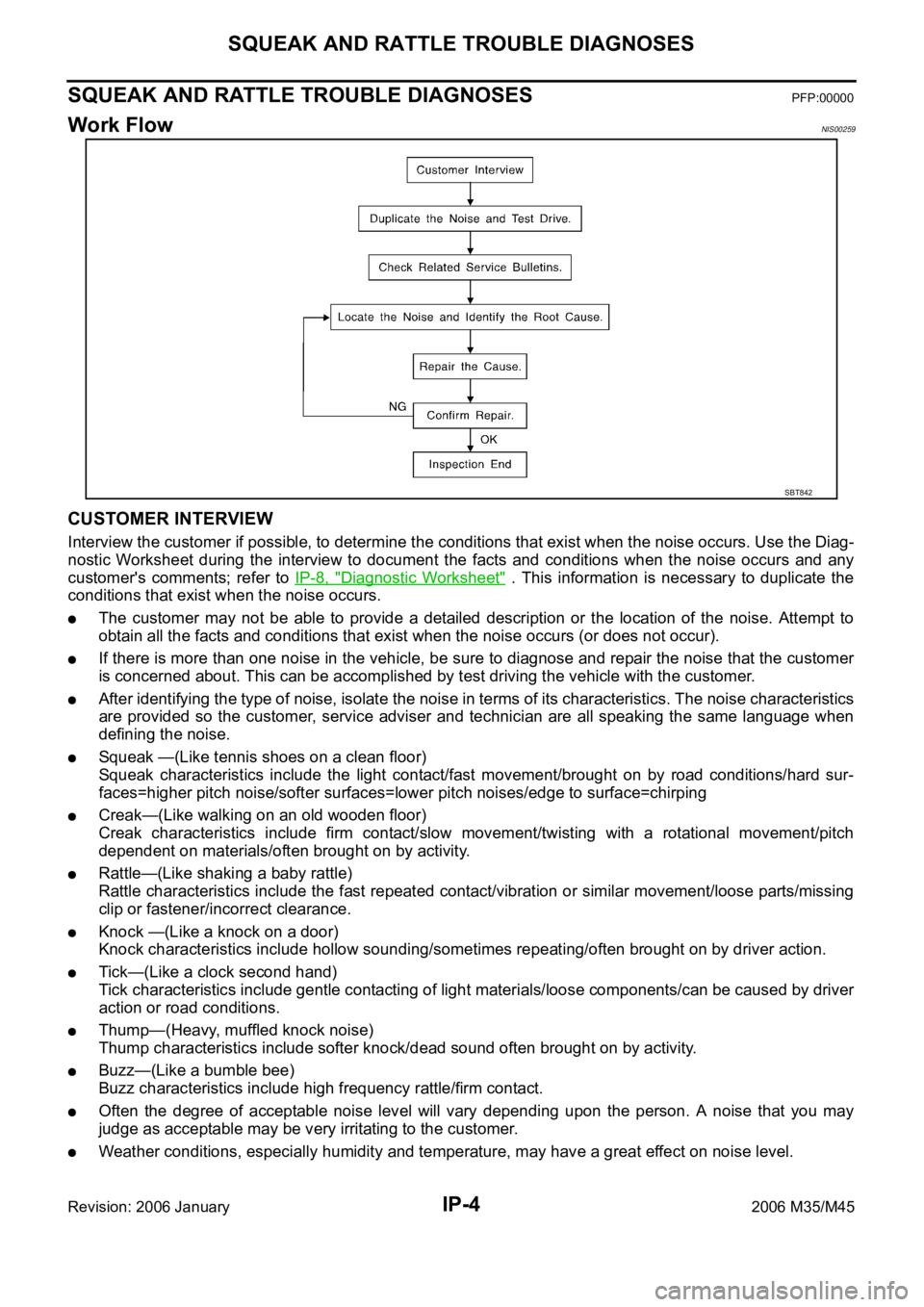
IP-4
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESPFP:00000
Work FlowNIS00259
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to IP-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet" . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces=higher pitch noise/softer surfaces=lower pitch noises/edge to surface=chirping
Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT842
Page 4431 of 5621

LT-4Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45 HAZARD SWITCH ..................................................231
Removal and Installation ......................................231
REMOVAL ........................................................
.231
COMBINATION SWITCH ........................................232
Wiring Diagram — COMBSW — ..........................232
Combination Switch Reading Function .................233
Terminals and Reference Values for BCM ............233
CONSULT-II Functions (BCM) ..............................238
CONSULT-II BASIC OPERATION .....................238
DATA MONITOR ................................................239
Combination Switch Inspection ............................240
Removal and Installation ......................................242
STOP LAMP ............................................................243
Wiring Diagram — STOP LAMP — ......................243
High-Mounted Stop Lamp .....................................245
BULB REPLACEMENT, REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION ..................................................245
Stop Lamp ............................................................245
BULB REPLACEMENT .....................................245
BULB REPLACEMENT .....................................245
BACK-UP LAMP .....................................................246
Wiring Diagram — B/LAMP — .............................246
Bulb Replacement ...............................................
.247
Removal and Installation ......................................248
REMOVAL ........................................................
.248
INSTALLATION ..................................................248
PARKING, LICENSE PLATE AND TAIL LAMPS ....249
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location .249
System Description ...............................................249
OUTLINE ...........................................................249
OPERATION BY LIGHTING SWITCH ...............250
COMBINATION SWITCH READING FUNCTION .250
EXTERIOR LAMP BATTERY SAVER CONTROL .250
CAN Communication System Description ............250
CAN Communication Unit .....................................250
Schematic .............................................................251
Wiring Diagram — TAIL/L — ................................252
Terminals and Reference Values for BCM ............257
Terminals and Reference Values for IPDM E/R ....258
How to Perform Trouble Diagnoses ......................258
Preliminary Check ................................................258
CHECK POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND CIR-
CUIT ..................................................................258
CONSULT-II Functions (BCM) ..............................259
CONSULT-II Functions (IPDM E/R) ......................259
Parking, License Plate and Tail Lamps Do Not Illu-
minate ...................................................................260
Parking, License Plate and Tail Lamps Do Not Turn
OFF (After Approx. 10 Minutes) ...........................264
License Plate Lamp ..............................................265
BULB REPLACEMENT .....................................265
Removal and Installation ......................................265
REMOVAL ........................................................
.265
INSTALLATION ..................................................265
Front Parking (Clearance) Lamp ..........................265
BULB REPLACEMENT .....................................265
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION .......................265
REAR COMBINATION LAMP .................................266
Bulb Replacement ...............................................
.266REAR TURN SIGNAL LAMP BULB, STOP/TAIL
LAMP BULB ...................................................... .266
Removal and Installation .......................................266
REMOVAL ..........................................................266
INSTALLATION ..................................................266
INTERIOR ROOM LAMP ........................................267
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location .267
System Description ...............................................267
ROOM LAMP TIMER BASIC OPERATION .......267
POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND .....................268
SWITCH OPERATION .......................................269
ROOM LAMP TIMER OPERATION ...................270
CONDITIONS FOR CANCELING TIMER ..........271
ROOM LAMP TIMER INAPPLICABLE LAMPS
OPERATION ......................................................271
INTERIOR ROOM LAMP BATTERY SAVER
FUNCTION .......................................................
.271
Schematic .............................................................272
Wiring Diagram — ROOM/L — .............................274
Terminals and Reference Values for BCM ............281
How to Perform Trouble Diagnoses ......................282
Preliminary Check .................................................283
CHECK POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND CIR-
CUIT ...................................................................283
CONSULT-II Functions (BCM) ..............................284
CONSULT-II BASIC OPERATION .....................284
WORK SUPPORT (INT LAMP) .........................285
DATA MONITOR (INT LAMP) ............................286
ACTIVE TEST (INT LAMP) ................................287
WORK SUPPORT (BATTERY SAVER) .............287
DATA MONITOR (BATTERY SAVER) ...............287
ACTIVE TEST (BATTERY SAVER) ...................288
Interior Room Lamp Control Does Not Operate ....289
Map Lamp .............................................................291
BULB REPLACEMENT ......................................291
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION .......................291
Personal Lamp ......................................................291
BULB REPLACEMENT ......................................291
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION .......................291
Foot Lamp (Driver Side) .......................................
.292
BULB REPLACEMENT ......................................292
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION .......................292
Foot Lamp (Passenger Side) ................................293
BULB REPLACEMENT ......................................293
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION .......................293
Vanity Mirror Lamp ................................................293
BULB REPLACEMENT ......................................293
Step Lamp .............................................................294
BULB REPLACEMENT ......................................294
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION .......................294
Kicking Plate Illumination .....................................
.294
BULB REPLACEMENT ......................................294
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION .......................294
Trunk Room Lamp (Upper/Lower) ........................294
BULB REPLACEMENT ......................................294
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION .......................294
ILLUMINATION ........................................................295
System Description ...............................................295
OUTLINE ...........................................................295