Page 4341 of 5135
A81479
Injection Control Diagram:
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Camshaft Position Sensor
Crankshaft Position Sensor
(NE Signal)
Other Sensors
Fuel TankFeed
Pump
Eccentric
CamPlungerCheck Valve Fuel Pressure SensorCommon Rail EDU
TWV
Orifice
Orifice
Nozzle
NeedleControl
Chamber
Piston
Injector ECM
Suction
Control
ValveSolenoid
Valve
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−263
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
4. INJECTION CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The ECM controls the fuel injection system by using the injectors and supply pump. The ECM determines
the fuel injection volume and timing by controlling both duration and timing of energization to the solenoid
valve in the injector, and determines the injection pressure by controlling the suction control valve located
on the supply pump.
The feed pump is used to pump fuel from the fuel tank into the supply pump.
Page 4342 of 5135
A81480
Plunger A: Pumping End
Plunger B: Suction EndPlunger A: Suction Start
Plunger B: Pumping Start Check Valve
Eccentric Cam
Ring Cam
Plunger B
Plunger A
Plunger A: Pumping Start
Plunger B: Suction StartPlunger A: Suction End
Plunger B: Pumping End Supply Pump Operation Diagram:
From
Feed Pump
To Common Rail Suction
Control
Valve
05−264
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
5. SUPPLY PUMP OPERATION SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The rotation of the eccentric cam causes the ring cam pushes plunger A upward as illustrated below. The
spring force pulls plunger B (located on the opposite of plunger A) upward. As a result, plunger B draws the
fuel in, and plunger A pumps the fuel at the same time.
Page 4343 of 5135
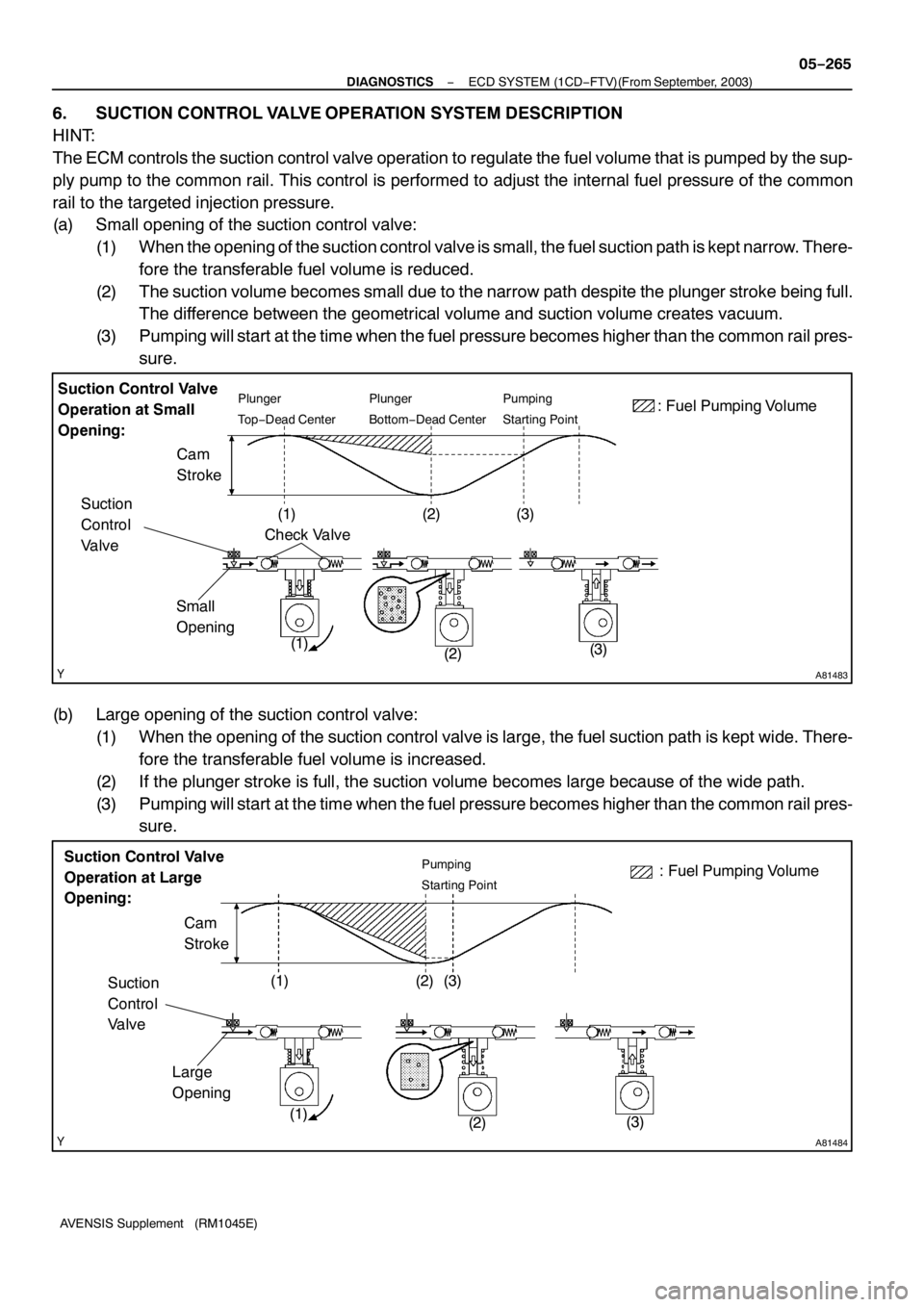
A81483
Suction Control Valve
Operation at Small
Opening:Plunger
To p−Dead CenterPlunger
Bottom−Dead CenterPumping
Starting Point
Cam
Stroke: Fuel Pumping Volume
Check Valve
Small
Opening
(1)
(2)(3)
(1) (2) (3) Suction
Control
Valve
A81484
Pumping
Starting Point
Large
Opening
(1)
(2)(3) Cam
Stroke
(1) (2) (3): Fuel Pumping Volume Suction Control Valve
Operation at Large
Opening:
Suction
Control
Valve
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−265
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
6. SUCTION CONTROL VALVE OPERATION SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
HINT:
The ECM controls the suction control valve operation to regulate the fuel volume that is pumped by the sup-
ply pump to the common rail. This control is performed to adjust the internal fuel pressure of the common
rail to the targeted injection pressure.
(a) Small opening of the suction control valve:
(1) When the opening of the suction control valve is small, the fuel suction path is kept narrow. There-
fore the transferable fuel volume is reduced.
(2) The suction volume becomes small due to the narrow path despite the plunger stroke being full.
The difference between the geometrical volume and suction volume creates vacuum.
(3) Pumping will start at the time when the fuel pressure becomes higher than the common rail pres-
sure.
(b) Large opening of the suction control valve:
(1) When the opening of the suction control valve is large, the fuel suction path is kept wide. There-
fore the transferable fuel volume is increased.
(2) If the plunger stroke is full, the suction volume becomes large because of the wide path.
(3) Pumping will start at the time when the fuel pressure becomes higher than the common rail pres-
sure.
Page 4366 of 5135

A80452
PCR1E
13
ECM Connector
E
12PCR2
E2VCS
E2S
VC
A80453
E2
PCR2
F
16
Wire Harness Side:
Fuel Pressure Sensor Connector
VC2
PCE2S
VC
Front View
05 −524
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
23 CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR(FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR − ECM)
(a) Disconnect the F 16 fuel pressure sensor connector.
(b) Disconnect the E 12 and E 13 ECM connectors.
(c) Check the resistance between the wire harness side con-
nectors.
Standard (Check for open):
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
PCR1 (E 13− 26) − PC (F 16− 5)
PCR2 (E 13− 33) − PCR2 (F 16− 2)
VCS (E 12− 2) − VC2 (F 16−1 )Below1�VC (E 13−1 8)− VC (F 16− 6)Below 1�
E2 (E 13− 28) − E2 (F 16− 4)
E2S (E 12−1 )− E2S (F 16− 3)
Standard (Check for short):
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
PCR 1 (E 13− 26) or PC (F 16− 5) − Body ground
PCR2 (E 13− 33) or PCR2 (F 16 − 2) − Body ground
VCS (E 12− 2) or VC2 (F 16 −1 )− Body ground10 k � or higherVC (E 13−1 8) or VC (F 16− 6) − Body ground10k � or higher
E2 (E 13− 28) or E2 (F 16− 4) − Body ground
E2S (E 12−1 ) or E2S (F 16− 3) − Body ground
(d) Reconnect the fuel pressure sensor connector.
(e) Reconnect the ECM connectors.
NG REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR
OK
24 REPLACE ECM (See page 10− 29)
NG REPLACE INJECTION OR SUPPLY PUMP ASSY
(See page 11− 58)
OK
END
Page 4377 of 5135

05−484
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
DTC P2237 OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR PUMPING
CURRENT CIRCUIT/OPEN (FOR A/F
SENSOR)(BANK1 SENSOR 1)
DTC P2238 OXYGEN (A/F)SENSOR PUMPING CURRENT CIRCUIT LOW (FOR A/F SENSOR)(BANK 1
SENSOR 1)
DTC P2239 OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR PUMPING CURRENT CIRCUIT HIGH (FOR A/F
SENSOR)(BANK1 SENSOR 1)
HINT:
S For more information on the A/F sensor and TOYOTA D −CAT (* 1) system, see page 05 −255.
S If P2237, P2238 and/or P2239 is present, refer to the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) table for TOYO-
TA D −CAT system on page 05 −255.
S These DTCs are recorded when A/F sensor has malfunction, although the caption is the oxygen sen-
sor.
* 1 : Diesel Clean Advanced Technology.
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P003 1 on page 05 −305.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P2237ECM internal error ( 10 seconds)
( 1 trip detection logic)S ECM
P2238
S A/F sensor circuit low (bank 1 sensor 1)
AF+ is less than 04 V for 50 seconds or more
Main trouble area: Open in A/F sensor circuit
S Open or short in A/F sensor circuit
S A/F sensor
S A/F sensor heaterP2238AF+ is less than 0.4 V for 5.0 seconds or more
( 1 trip detection logic)S A/F sensor heater
S A/F sensor heater relay
S A/F sensor heater and relay circuit
S ECM
P2239
S A/F sensor circuit high (bank 1 sensor 1)
AF+ is more than 44 V for 50 seconds or more
Main trouble area: Short in A/F sensor circuit
S Open or short in A/F sensor circuit
S A/F sensor
S A/F sensor heaterP2239AF+ is more than 4.4 V for 5.0 seconds or more
( 1 trip detection logic)S A/F sensor heater
S A/F sensor heater relay
S A/F sensor heater and relay circuit
S ECM
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The A/F sensor has a characteristic that it varies its voltage output in proportion to the air −fuel ratio. If imped-
ance (alternating current resistance) or voltage output of the sensor extraordinarily deviates from the stan-
dard range, the ECM interprets this as an open or short malfunction of the A/F sensor circuit.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P003 1 on page 05 −305.
05I7U −01
Page 4403 of 5135
A85355
Exhaust Fuel
Addition Injector
Injector Spray Supply PumpExhaust Gas
Temperature
Sensor (on up stream)
ECM Exhaust
Gas
Exhaust Gas Temperature
Sensor (on down stream)
Exhaust Fuel Addition InjectorA/F Sensor DPNR Catalytic
Converter
Turbocharger
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−445
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The exhaust fuel addition injector is mounted on the exhaust port of the cylinder head, and low pressure is
provided to the injector by the feed pump in the supply pump. This injector adds fuel by a control signal from
the ECM.
This injector is used for two different controls: DPNR catalyst regeneration and nitrogen oxides (NOx) reduc-
tion.
Under the DPNR catalyst regeneration control, the injector adds fuel to raise a catalyst temperature.
In the other control, the injector helps the air−fuel ratio become RICH. As a result, NOx in the exhaust gas
will be reduced in response to the RICH air−fuel ratio.
Page 4404 of 5135
05−446
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
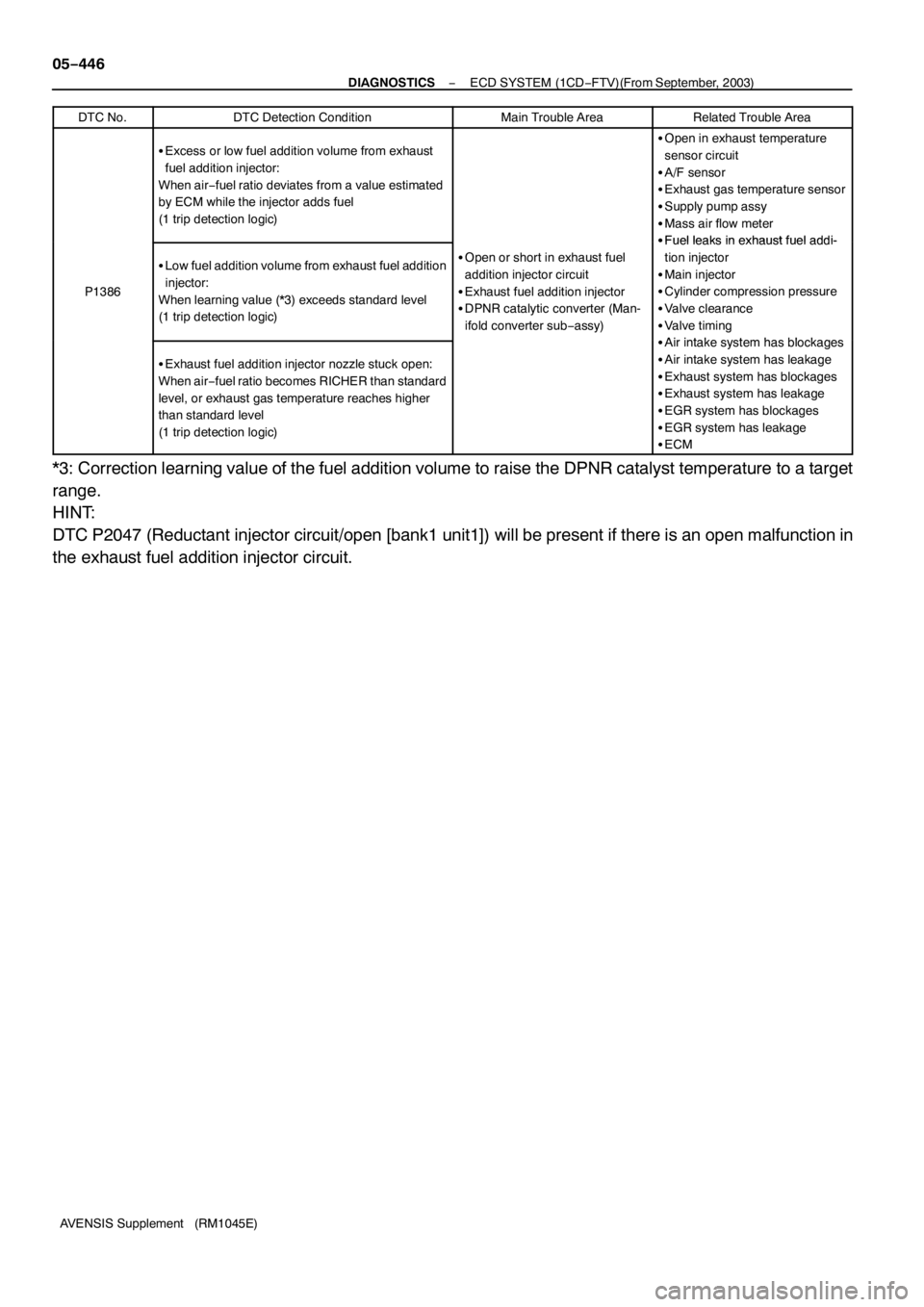
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E) DTC No.
DTC Detection ConditionMain Trouble AreaRelated Trouble Area
SExcess or low fuel addition volume from exhaust
fuel addition injector:
When air−fuel ratio deviates from a value estimated
by ECM while the injector adds fuel
(1trip detection logic)SOpen in exhaust temperature
sensor circuit
SA/F sensor
SExhaust gas temperature sensor
SSupply pump assy
SMass air flow meter
SFuelleaksinexhaustfueladdi-
P1386
SLow fuel addition volume from exhaust fuel addition
injector:
When learning value (*3) exceeds standard level
(1trip detection logic)SOpen or short in exhaust fuel
addition injector circuit
SExhaust fuel addition injector
SDPNR catalytic converter (Man-
ifold converter sub−assy)
SFuelleaksinexhaustfueladdi-
tion injector
SMain injector
SCylinder compression pressure
SValve clearance
SValve timing
Airintakesystemhasblockages
SExhaust fuel addition injector nozzle stuck open:
When air−fuel ratio becomes RICHER than standard
level, or exhaust gas temperature reaches higher
than standard level
(1trip detection logic)
SAir intake system has blockages
SAir intake system has leakage
SExhaust system has blockages
SExhaust system has leakage
SEGR system has blockages
SEGR system has leakage
SECM
*3: Correction learning value of the fuel addition volume to raise the DPNR catalyst temperature to a target
range.
HINT:
DTC P2047 (Reductant injector circuit/open [bank1unit1]) will be present if there is an open malfunction in
the exhaust fuel addition injector circuit.
Page 4410 of 5135
2
1
A80992
E 16
Front View
Wire Harness Side:
Exhaust Fuel Addition
Injector Connector
FIV
A80456
E13
ECM Connector FIV
05
−452
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
NG REPLACE EXHAUST FUEL ADDITION
INJECTOR ASSY (See page 14−1 66)
OK
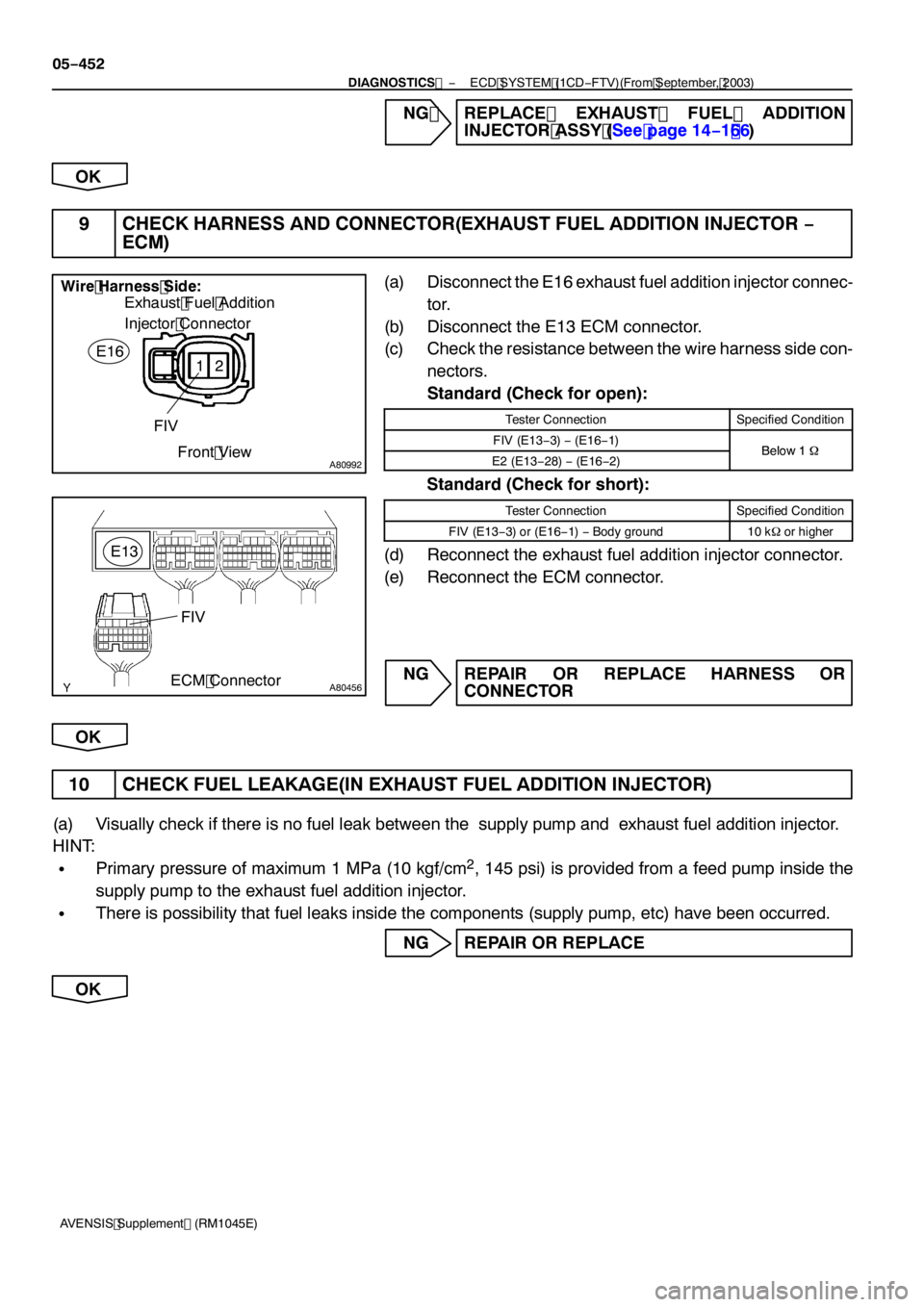
9 CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR(EXHAUST FUEL ADDITION INJECTOR −
ECM)
(a) Disconnect the E 16 exhaust fuel addition injector connec-
tor.
(b) Disconnect the E 13 ECM connector.
(c) Check the resistance between the wire harness side con-
nectors.
Standard (Check for open):
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
FIV (E 13− 3) −(E 16−1 )Below1�E2 (E 13− 28) −(E 16− 2)Below 1�
Standard (Check for short):
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
FIV (E 13− 3) or (E 16−1 )− Body ground10k �or higher
(d) Reconnect the exhaust fuel addition injector connector.
(e) Reconnect the ECM connector.
NG REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR
OK
1 0 CHECK FUEL LEAKAGE(IN EXHAUST FUEL ADDITION INJECTOR)
(a) Visually check if there is no fuel leak between the supply pump and exhaust fuel addition injector.
HINT:
SPrimary pressure of maximum 1MPa ( 10 kgf/cm2, 145 psi) is provided from a feed pump inside the
supply pump to the exhaust fuel addition injector.
SThere is possibility that fuel leaks inside the components (supply pump, etc) have been occurred.
NG REPAIR OR REPLACE
OK