Page 39 of 364

ENGINE – ENGINE ASSY
11-33
� �
B� �
Fitting the engine mount bracket & stopper ASSY
1. Support the engine oil pan component with the garage jack
through the engine block, and fit the engine mount bracket &
stopper ASSY whilst checking the position of the engine. Fix the
engine mount stopper so that the arrow points in the direction
shown in the diagram.
2. Support the engine ASSY with a garage jack.
3. Remove the chain block.
4. In the same way as when it was removed, hold the engine
ASSY with the special tool.
(1)
(MZ203830 or MZ203831)>
Install the special mechanical engine hanger (MZ203830
or MZ203831).
(2)
Fit the following parts to the base hanger.
• Slide bracket (HI)
• Foot (standard) (MB991932)
• Joint (90) (MB991930)
Install the special engine hanger (MB991928)
� �
C� �
Fitting the transfer ASSY and the transmission ASSY
1. Fit the transfer ASSY and the transmission ASSY.
2. Remove the radiator support upper insulator mounting bolts from
the chassis (2 places).engine sideengine side
engine mount stopper
rear of chassis>
front of chassis>
MZ203830 or MZ203831
slide bracket (HI)
front of
chassis
joint (90)
(MB991930)
foot (standard) (MB991932)
slide bracket (HI)
Page 40 of 364
ENGINE – ENGINE ASSY11-34
� �
D� �
Fitting the O-ring and the fuel high pressure hose
1. Apply a little fresh engine oil to the O-ring.
Caution
Ensure that no engine oil gets inside the deliver pipe.
2. Without damaging the O-ring, fit the fuel high pressure hose to
the delivery pipe by twisting it from left to right. Ensure that the
hose is twisted smoothly.
3. If the hose cannot be twisted smoothly, there is a possibility that
it may be biting into the O-ring, so remove the fuel high pressure
hose, and check for any damage to the O-ring. If the O-ring is
undamaged, reinsert it into the delivery pipe and check once
more whether the hose can be turned smoothly.
4. Tighten the mounting bolts for the fuel high pressure hose, to
the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 5.0 ± 1.0 N•m.
Page 41 of 364

MPI – GENERAL
13A-1
SECTION 13A
MPI (Multi-point Fuel Injection)
CONTENTS
General ..................................................................... 2
Servicing standards .................................................3
Special tools ............................................................3
Troubleshooting ......................................................5Servicing the vehicle ............................................29
1. Adjusting specified revolutions when idling.....29
2. MPI system components layout diagram ........29
3. Checking the air temperature sensor..............29
4. Checking the oil feeder control valve..............30
GENERAL
Servicing guidelines have been changed because of the changes listed below.
•Avariable valve timing control system (V.V.T.) has been adopted. Because of this, an oil feeder control valve and an intake
cam position sensor have been added.
•Amanifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor has been added.
•An air temperature sensor has been added.
Page 42 of 364
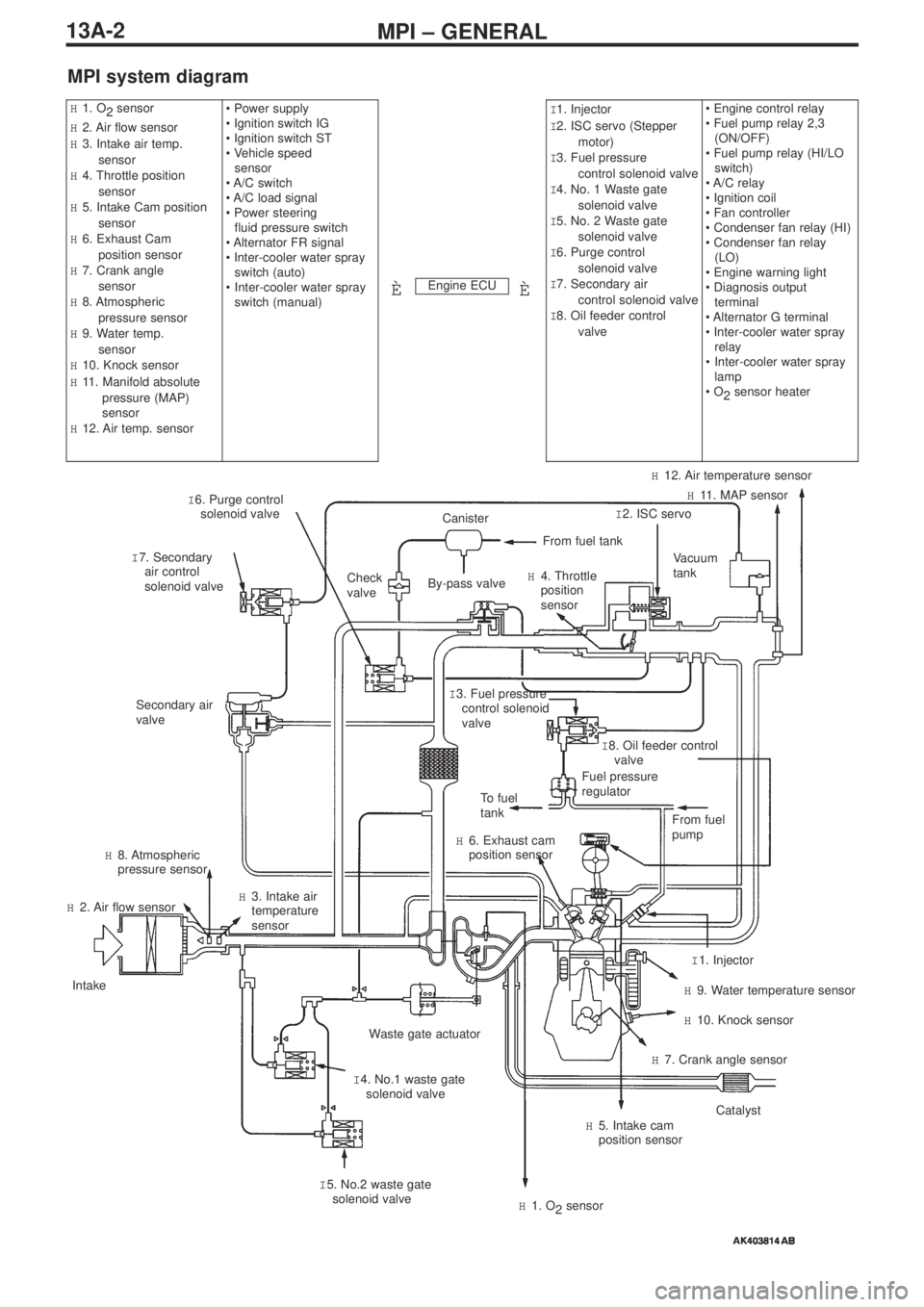
MPI – GENERAL13A-2
MPI system diagram
Engine ECU
H1. O
2 sensor
H2. Air flow sensor
H3. Intake air temp.
sensor
H4. Throttle position
sensor
H5. Intake Cam position
sensor
H6. Exhaust Cam
position sensor
H7. Crank angle
sensor
H8. Atmospheric
pressure sensor
H9. Water temp.
sensor
H10. Knock sensor
H11. Manifold absolute
pressure (MAP)
sensor
H12. Air temp. sensor• Power supply
• Ignition switch IG
• Ignition switch ST
• Vehicle speed
sensor
• A/C switch
• A/C load signal
• Power steering
fluid pressure switch
• Alternator FR signal
• Inter-cooler water spray
switch (auto)
•Inter-cooler water spray
switch (manual)I1. Injector
I2. ISC servo (Stepper
motor)
I3. Fuel pressure
control solenoid valve
I4. No. 1 Waste gate
solenoid valve
I5. No. 2 Waste gate
solenoid valve
I6. Purge control
solenoid valve
I7. Secondary air
control solenoid valve
I8. Oil feeder control
valve• Engine control relay
• Fuel pump relay 2,3
(ON/OFF)
• Fuel pump relay (HI/LO
switch)
• A/C relay
• Ignition coil
• Fan controller
• Condenser fan relay (HI)
• Condenser fan relay
(LO)
• Engine warning light
• Diagnosis output
terminal
• Alternator G terminal
• Inter-cooler water spray
relay
•Inter-cooler water spray
lamp
• O
2sensor heater
ÈÈ
I 6. Purge control
solenoid valve
I 7. Secondary
air control
solenoid valveCheck
valve
Secondary air
valve
To fuel
tank
H 6. Exhaust cam
position sensor
H 8. Atmospheric
pressure sensor
H 2. Air flow sensor
Intake
Waste gate actuator
I 4. No.1 waste gate
solenoid valve H 3. Intake air
temperature
sensor
I 5. No.2 waste gate
solenoid valve
H 1. O
2sensor
H 5. Intake cam
position sensorCatalyst
H 7. Crank angle sensor
H 10. Knock sensor
H 9. Water temperature sensor
I 1. Injector From fuel
pump
Fuel pressure
regulatorI 8. Oil feeder control
valve I 3. Fuel pressure
control solenoid
valve
Vacuum
tank
I 2. ISC servoH 11. MAP sensor
H 12. Air temperature sensor
H 4. Throttle
position
sensor
From fuel tank
Canister
By-pass valve
Page 43 of 364
MPI – SERVICING STANDARDS, SPECIAL TOOLS
13A-3
Servicing standards
Special tools
ItemStandard level
Revolutions when idling r/min800 ± 50
Air temperature sensor resistance kΩat -20 ºC13~18
at 0 ºC5.1~6.9
at 20 ºC2.0~3.0
at 40 ºC0.9~1.5
at 60 ºC0.40~0.78
at 80 ºC0.23~0.42
Oil feeder control valve resistance (at 20 ºC) Ω6.9~7.9
ToolNumberNameFunction
MB991502MUT-II sub ASSYChecking the MPI system
MB991955
A:MB991824
B:MB991827
C:MB991910
D:MB991911
E:MB991825
F:MB991826MUT-III sub ASSY
A: Vehicle Communication
Interface (V.C.I..)
B: USB cable
C: MUT-III Main harness A
(For vehicles fitted with
CAN)
D: MUT-III Main harness B
(For vehicles not fitted with
CAN)
E: Adaptor
F: Trigger harnessNote
If a MUT-III main harness A is connected to
a vehicle not fitted with CAN, there is a
chance that a pulse signal will be entered
in the simulated vehicle speed line, when
the MUT-III is activated. Therefore, use a
MUT-III main harness B with vehicles not
fitted with CAN.
DO NOT USE
Page 45 of 364

MPI – TROUBLESHOOTING
13A-5
TROUBLESHOOTING
1. Diagnosis Functions
1-1 Engine warning light (Check engine lamp)
Changes have been made to engine warning lights.
Checklist for engine warning lights.
1-2 Checking of freeze frame data
Additions have been made to the freeze frame data tables.
Checklist for data tables
1-3 Failsafe and back-up functions
If one of the diagnosis functions detects that one of the main sensors is malfunctioning, it will ensure that the car can be driven
safely, in accordance with the pre-set control logic.
Engine ECU
Air flow sensor (AFS)
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor system
Intake air temperature sensor
Throttle position sensor (TPS)
Water temperature sensor
Crank angle sensor
Exhaust cam position sensor
Injector
Ignition coil (with built-in power transistor)
Atmospheric pressure sensor
O
2sensor
O
2sensor heater
Fuel system malfunction
Knock sensor
Intake cam position sensor system
Oil feeder control valve system
Item numberType of data Units/condition
95MAP sensorkPa
Malfunctioning itemControl measures taken when a malfunction occurs
Air temperature sensorRegulation of the intake air temperature at 25ºC.
Exhaust cam position sensor(1) Simultaneous flushing out of all fuel pipes.
(But only if the No. 1 cylinder has not been detected in the
TDC position after the ignition switch has been turned "ON".)
(2) Cutting off the fuel 4 seconds after the malfunction has been
detected.
(But only if the No. 1 cylinder has not been detected in the
TDC position after the ignition switch has been turned "ON".)
Intake cam position sensorThe oil feeder control valve should be switched "OFF", and the
angle of the cam should be in the reset position.
Page 46 of 364
MPI- TROUBLESHOOTING13A-6
Code No.Diagnosis itemPage
P0105MAP sensor13A-7
P0340Exhaust cam position sensor system13A-9
P1012Intake cam position sensor system13A-11
P1021Oil feeder control valve system13A-13
P2226Atmospheric pressure system13A-14
2. Diagnosis code classification table
Page 53 of 364

13A-13MPI – TROUBLESHOOTING
Replace the engine ECU
Check connectors B-19X & C-23
Check connector B-134
Check connectors B-19 & C-23
Check connector C-49
Check that the problem has been
solved
Inspect the oil feeder control
valve by itself (Ref: P13A-30)
Inspect the harness between the
engine control relay and the oil
feeder control valve, repair if
necessary
•Check for damage to the power
supply wire
Inspect the harness between the
engine control relay and the oil
feeder control valve, repair if
necessary
•Check if the power supply wire
is cut or has short circuited
Check connectorC-49
Inspect the harness between the
engine ECU and the oil feeder
control valve, repair if necessary
•Check if the output wire is cut or
has short circuited
Temporary malfunction (Ref
Section 00: Dealing with
temporary malfunctions)
Replace the oil feeder control
valve
A-134 Measurement of the oil
feeder control valve
•Measure using a harness
connected to the connector
•Ignition switch: ON
•Voltage across earth at 1
OK:battery voltage
C-49 Measurement of engine
ECU
•Undo the connector and
measure on the harness side
•Ignition switch: ON
•Voltage across earth at 32
OK:battery voltage
Inspect the harness between the
engine ECU and the oil feeder
control valve
•Check for damage to the output
wire
OK
NG
OKOK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
NG
NG
NG
NG
NG
NG
NG
NG
NG
NG
OK
OK
Repair
Repair
Repair
Repair
Repair
Repair
Repair
Code No.P1021 Oil feeder control valve systemProbable cause of the malfunction
Conditions for inspection
•Oil feeder control valve: OFF
Evaluation conditions
•Operational terminal voltage of the oil feeder control valve in the ECU is
abnormal for 4 seconds•Malfunction of the oil feeder control
valve
•Broken circuit or short circuit in the oil
feeder control valve circuit, or poor
connector contact
•Malfunction of engine ECU