Page 1173 of 1500
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-8
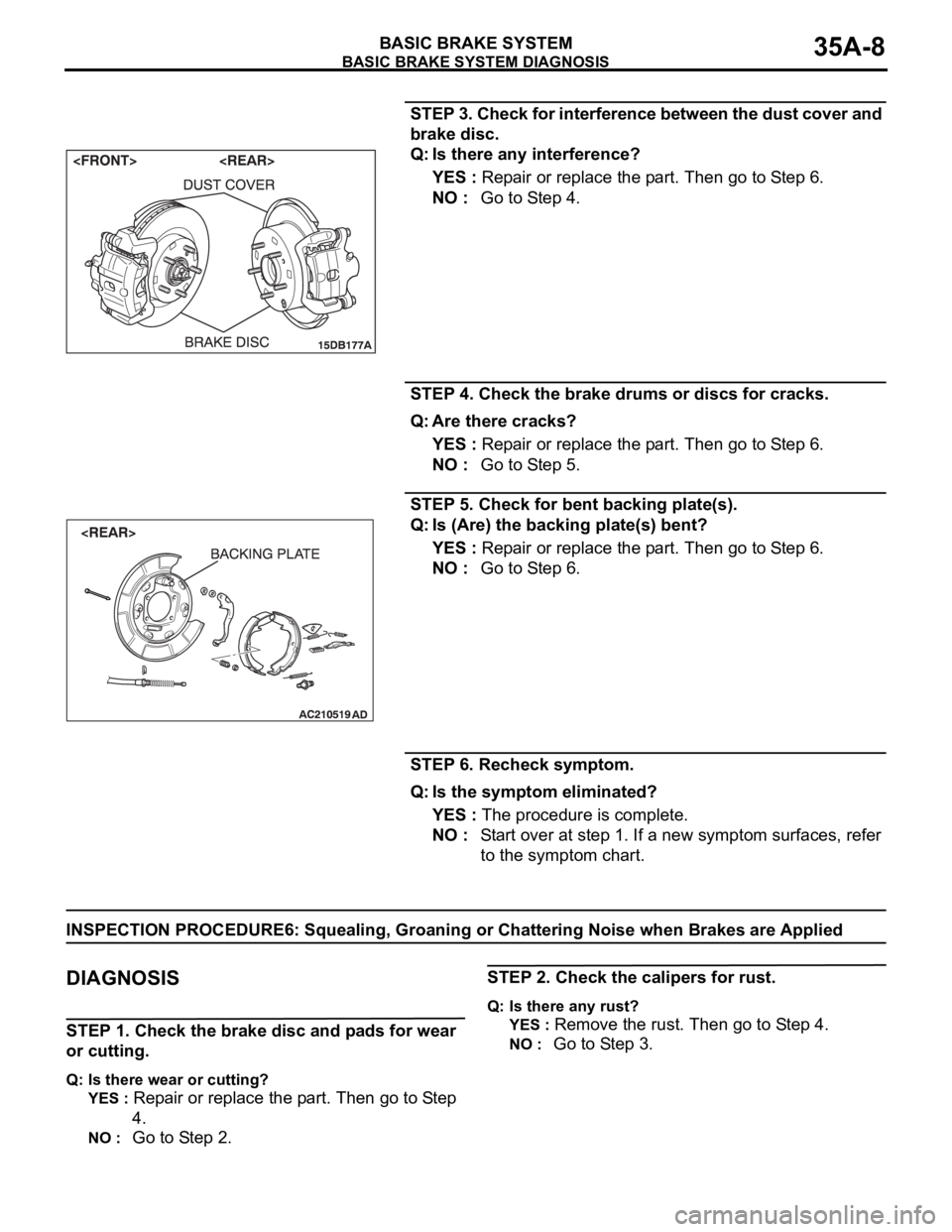
STEP 3. Check for interference between the dust cover and
brake disc.
Q: Is there any interference?
YES : Repair or replace the part. Then go to Step 6.
NO : Go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Check the brake drums or discs for cracks.
Q: Are there cracks?
YES : Repair or replace the part. Then go to Step 6.
NO : Go to Step 5.
STEP 5. Check for bent backing plate(s).
Q: Is (Are) the backing plate(s) bent?
YES : Repair or replace the part. Then go to Step 6.
NO : Go to Step 6.
STEP 6. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES : The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom surfaces, refer
to the symptom chart.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE6: Squealing, Groaning or Chattering Noise when Brakes are Applied
.
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check the brake disc and pads for wear
or cutting.
Q: Is there wear or cutting?
YES :
Repair or replace the part. Then go to Step
4.
NO : Go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check the calipers for rust.
Q: Is there any rust?
YES :
Remove the rust. Then go to Step 4.
NO : Go to Step 3.
Page 1174 of 1500

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-9
STEP 3. Adjust the brake pedal or brake booster
pushrod.
Refer to P.35A-13 or P.35A-26.
Q: Are the brake pedal and the brake booster pushrod
adjusted correctly?
YES :
Go to Step 4.
NO : Adjust the brake pedal or the brake booster
pushrod. Then go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES :
The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom
surfaces, refer to the symptom chart.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 7: Squealing Noise when Brakes are not Applied
DIAGNOSIS
.
STEP 1. Check whether the backing plate is bent or loose
and interfering with the drum.
Q: Is there a fault?
YES : Replace the part. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check whether the drum is damaged due to
interference with the backing plate or shoe.
Q: Is there any damage?
YES : Replace the part. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 3.
STEP 3. Check the brake drum for wear and the shoe
spring for damage.
Q: Is there any wear or damage?
YES : Replace the part. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Check the brake discs for rust.
Q: Are the brake discs rusted?
YES : Remove the rust by using sand paper. If still rusted,
turn the rotors with an on-the-car brake lathe. Then go
to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 5.
STEP 5. Check the brake pads for correct installation.
Q: Are the pads installed incorrectly?
YES : Repair the pads. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 6.
STEP 6. Check the calipers for correct installation.
Q: Are the calipers installed incorrectly?
YES : Repair the calipers. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 7.
Page 1175 of 1500

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-10
STEP 7. Check the wheel bearings for end play.
(1) Remove the brake discs.
(2) Place a dial gauge as shown, and measure the end play
while moving the hub in the axial direction.
Limit: 0.05 mm (0.002 inch)
Q: Does the measured end play exceed the limit?
YES : Replace the faulty hub assembly. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 8.
STEP 8. Check whether the brake booster or master
cylinder return is insufficient.
Q: Is the brake booster or master cylinder return
insufficient?
YES : Replace the part. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 9.
STEP 9. Adjust the brake pedal or brake booster pushrod.
Refer to P.35A-13 or P.35A-26.
Q: Are the brake pedal and the brake booster pushrod
adjusted correctly?
YES : Go to Step 10.
NO : Adjust the brake pedal or the brake booster pushrod.
Then go to Step 10.
STEP 10. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES : The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom surfaces, refer
to the symptom chart.
Page 1177 of 1500
SPECIAL TOOLS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-12
STEP 4. Check the wheel bearings for end play.
(1) Remove the brake discs.
(2) Place a dial gauge as shown, and measure the end play
while moving the hub in the axial direction.
Limit: 0.05 mm (0.002 inch)
Q: Does the measured end play exceed the limit?
YES : Replace the faulty hub assembly. Then go to Step 5.
NO : Go to Step 5.
STEP 5. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES : The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom surfaces, refer
to the symptom chart.
SPECIAL TOOLSM1351000600360
TOOL TOOL NUMBER AND
NAMESUPERSESSION APPLICATION
MB991568
Push rod adjusting socketGeneral service
toolAdjustment of the brake booster
push rod protrusion amount
MB990964
Brake tool set
A: MB990520
Disc brake piston expanderMB990620-01 or
general service
toolPushing-in of the disc brake
piston
Page 1179 of 1500
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-14
BRAKE PEDAL FREE PLAY
1. Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position, and
depress the brake pedal two or three times. After eliminating
the vacuum in the brake booster, press the pedal down by
hand, and confirm that the amount of movement before
resistance is met (free play) is within the standard value
range.
Standard value: 3
8 mm (0.12 0.31 inch)
2. If the brake pedal play is not within the standard value,
check the following, and adjust or replace if necessary:
Excessive play between the brake pedal and the clevis pin,
or between the clevis pin and the brake booster operating
rod
Brake pedal height
Installation position of the stop light switch, etc.
CLEARANCE BETWEEN BRAKE PEDAL AND
DASH PANEL
1. Turn up the carpet, etc. under the brake pedal.
2. Start the engine, depress the brake pedal with
approximately 500 N (112 pounds) of force, and measure
the clearance between the brake pedal and the dash panel.
Standard value: 110 mm (4.33 inches) or more [From
the surface of dash panel to the face of pedal pad]
3. If the clearance is outside the standard value, check for air
trapped in the brake line and check the thickness of the disc
brake pad. Andjust and replace defective parts as required.
4. Return the carpet etc. to its original position.
BRAKE BOOSTER OPERATING TESTM1351001000372
1. For simple checking of the brake booster operation, carry
out the following tests:
(1) Run the engine for one or two minutes, and then stop it. If
the pedal depresses fully the first time but gradually
becomes higher when depressed succeeding times, the
booster is operating properly. If the pedal height remains
unchanged, the booster is defective. Go to step 2.
Page 1180 of 1500
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-15
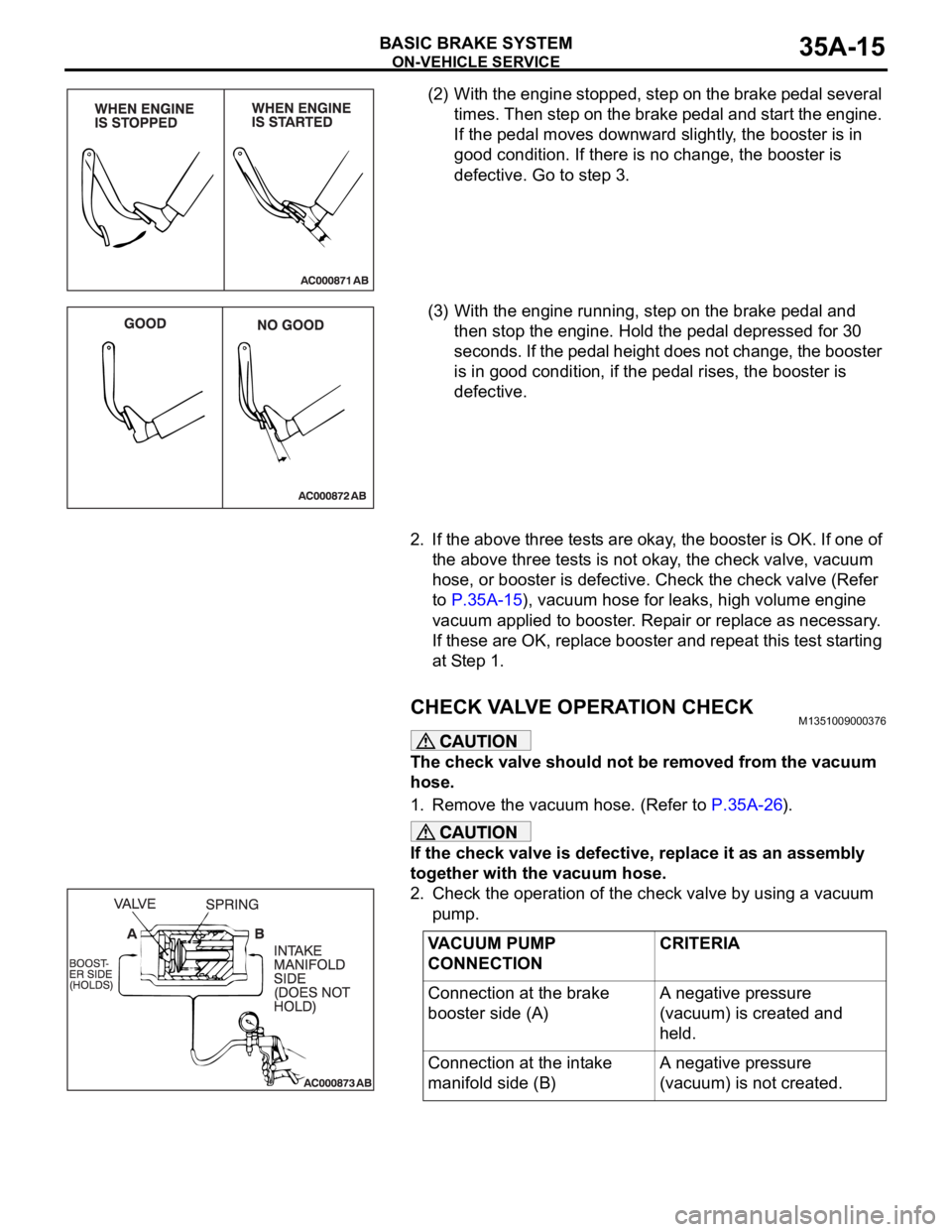
(2) With the engine stopped, step on the brake pedal several
times. Then step on the brake pedal and start the engine.
If the pedal moves downward slightly, the booster is in
good condition. If there is no change, the booster is
defective. Go to step 3.
(3) With the engine running, step on the brake pedal and
then stop the engine. Hold the pedal depressed for 30
seconds. If the pedal height does not change, the booster
is in good condition, if the pedal rises, the booster is
defective.
2. If the above three tests are okay, the booster is OK. If one of
the above three tests is not okay, the check valve, vacuum
hose, or booster is defective. Check the check valve (Refer
to P.35A-15), vacuum hose for leaks, high volume engine
vacuum applied to booster. Repair or replace as necessary.
If these are OK, replace booster and repeat this test starting
at Step 1.
CHECK VALVE OPERATION CHECKM1351009000376
The check valve should not be removed from the vacuum
hose.
1. Remove the vacuum hose. (Refer to P.35A-26).
If the check valve is defective, replace it as an assembly
together with the vacuum hose.
2. Check the operation of the check valve by using a vacuum
pump.
VACUUM PUMP
CONNECTIONCRITERIA
Connection at the brake
booster side (A)A negative pressure
(vacuum) is created and
held.
Connection at the intake
manifold side (B)A negative pressure
(vacuum) is not created.
Page 1181 of 1500
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-16
BLEEDINGM1351001400455
Use only brake fluid DOT 3 or DOT 4. Never mix the speci-
fied brake fluid with other fluid as it will influence the brak-
ing performance significantly.
.
MASTER CYLINDER BLEEDING
The master cylinder used has no check valve, so if bleeding is
carried out by the following procedure, bleeding of air from the
brake pipeline will become easier. (When brake fluid is not con-
tained in the master cylinder).
1. Fill the reserve tank with brake fluid.
2. Keep the brake pedal depressed.
3. Have another person cover the master cylinder outlet with a
finger.
4. With the outlet still closed, release the brake pedal.
5. Repeat steps 2
4 three or four times to fill the inside of the
master cylinder with brake fluid.
.
BRAKE LINE BLEEDING
Start the engine and bleed the air in the sequence shown in the
figure.
Page 1196 of 1500
DISC BRAKE ASSEMBLY
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-31
INSTALLATION SERVICE POINT
.
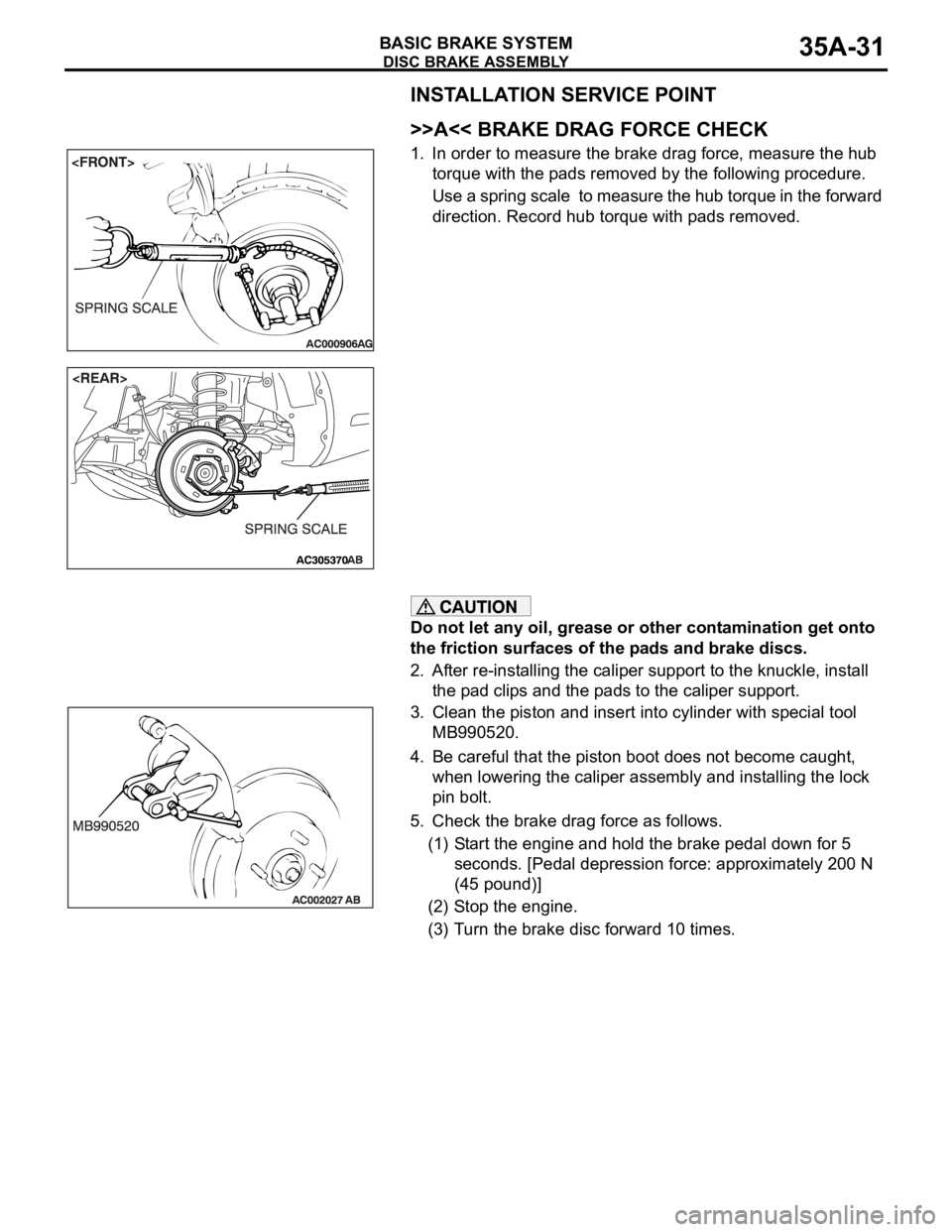
>>A<< BRAKE DRAG FORCE CHECK
1. In order to measure the brake drag force, measure the hub
torque with the pads removed by the following procedure.
Use a spring scale to measure the hub torque in the forward
direction. Record hub torque with pads removed.
Do not let any oil, grease or other contamination get onto
the friction surfaces of the pads and brake discs.
2. After re-installing the caliper support to the knuckle, install
the pad clips and the pads to the caliper support.
3. Clean the piston and insert into cylinder with special tool
MB990520.
4. Be careful that the piston boot does not become caught,
when lowering the caliper assembly and installing the lock
pin bolt.
5. Check the brake drag force as follows.
(1) Start the engine and hold the brake pedal down for 5
seconds. [Pedal depression force: approximately 200 N
(45 pound)]
(2) Stop the engine.
(3) Turn the brake disc forward 10 times.