2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Ground
[x] Cancel search: GroundPage 898 of 2643
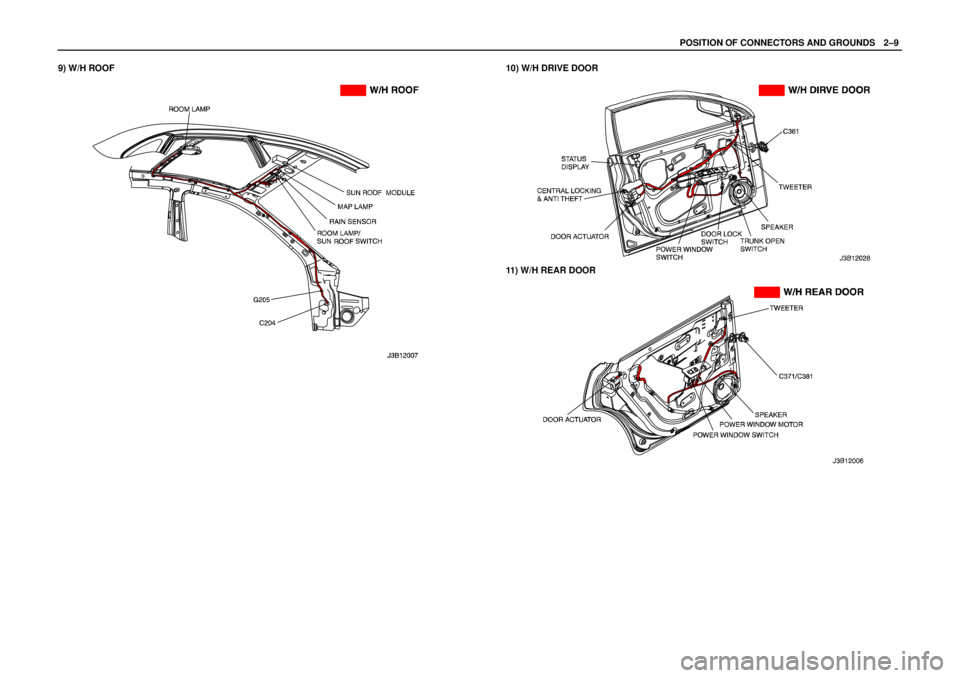
POSITION OF CONNECTORS AND GROUNDSW2–9
9) W/H ROOF10) W/H DRIVE DOOR
11) W/H REAR DOOR
Page 899 of 2643

2–10WPOSITION OF CONNECTORS AND GROUNDS
12) W/H TRUNK (N/B)
13) W/H TRUNK (H/B)
V3B1P000
14) W/H TRUNK LID
15) W/H TAIL GATE
Page 900 of 2643

POSITION OF CONNECTORS AND GROUNDSW2–11
16) W/H AIR BAG
17) SPLICE PACK
S101 (BLACK) : MR–140
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
ECT Sensor ”2” Ter
TP Sensor ”1” Ter
Knock Sensor ”2” TerIAT Sensor ”1” TerLEGR ”2” Ter ECM ”M48” Ter
ECM ”M51” Ter ECM ”M35” Ter ECM ”M64” TerMAP Sensor ”3” Ter
ECM ”M1” Ter B
B
B
B
GW GW
GWOrB
OrB
OrB
EI System ”3” Ter
EI System ”1” TerSb Sb Sb
ECM ”M33” Ter
J3B1S001
S101 (BLACK) : HV–240
S202 (BLACK)
S203 (RED)
Page 901 of 2643
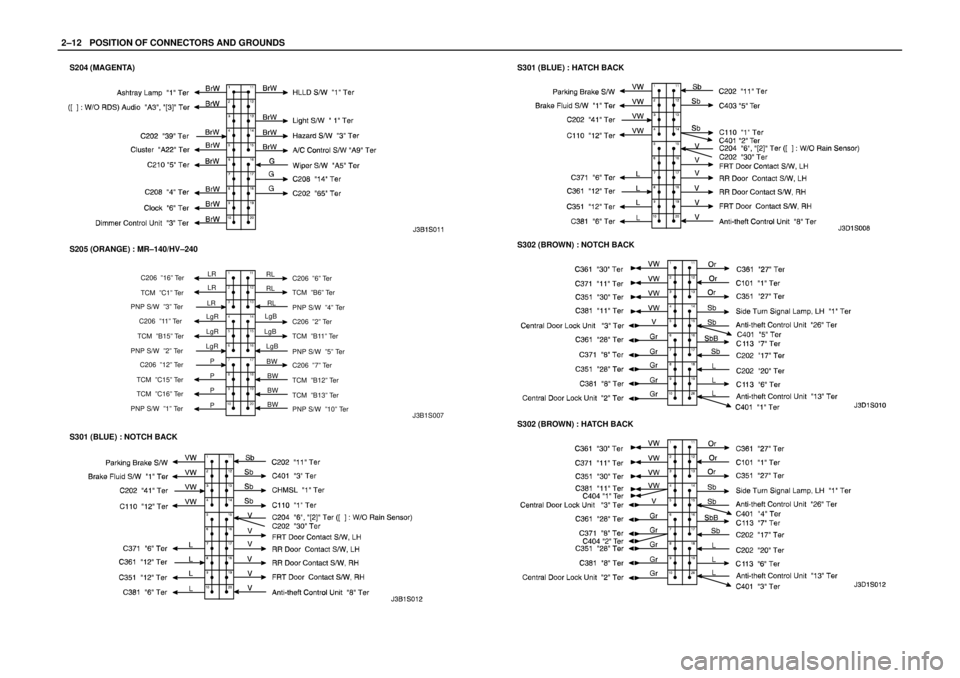
2–12WPOSITION OF CONNECTORS AND GROUNDS
S204 (MAGENTA)
S205 (ORANGE) : MR–140/HV–240
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
TCM ”B15” TerC206 ”11” TerTCM ”B6” Ter
PNP S/W ”3” Ter
C206 ”2” Ter
PNP S/W ”5” Ter
BW BW BW BW
PNP S/W ”4” Ter
LgB
LgB
LgB
PNP S/W ”10” Ter
TCM ”B13” Ter
TCM ”B12” Ter
C206 ”6” Ter RL
RL
RL
PNP S/W ”2” Ter
PNP S/W ”1” Ter
C206 ”12” Ter
TCM ”C15” Ter
TCM ”C16” Ter
P P P P LgRLgR LgRLRLR LR
TCM ”B11” Ter
C206 ”7” Ter C206 ”16” Ter
TCM ”C1” Ter
J3B1S007
S301 (BLUE) : NOTCH BACK
S301 (BLUE) : HATCH BACK
S302 (BROWN) : NOTCH BACK
S302 (BROWN) : HATCH BACK
Page 942 of 2643

FRONT SUSPENSION 2C – 25
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
FRONT SUSPENSION
The front suspension for this vehicle is a combination of
a strut assembly and a knuckle assembly. The strut as-
sembly combines a strut dampener and spring mounted
to the body of the vehicle. The upper end of the strut is iso-
lated by a rubber mount and contains a bearing to allow the
strut to turn. The knuckle is attached to the strut assembly
and pivots on a ball joint bolted to the control arm. The con-
trol arms pivot from the body using rubber bushings.
The ball joint is fastened to the steering knuckle with a
pinch bolt and nut, and to the lower control arm with rivets.
The stabilizer bar interconnects both strut assemblies ofthe vehicle through the stabilizer link and is attached to the
front suspension crossmember. Jounce and rebound
movements affecting one wheel are partially transmitted
to the opposite wheel of the vehicle to stabilize body roll.
When servicing the control arm–to–body attachment and
the stabilizer shaft–to–body insulators, make sure the at-
taching bolts are loose until the control arms are moved to
the trim height, which is curb height. Trim height is the nor-
mal position to which the control arms move when the ve-
hicle is sitting on the ground. Refer to ”General Specifica-
tions” in this section.
The springs in the front suspension of engine family II are
stronger and the strut dampeners heavier than are the
springs and strut dampeners found in the front suspension
of engine family I.
Page 972 of 2643

2E – 10ITIRES AND WHEELS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
turers of tire chains have a specific chain size for each tire
size to ensure a proper fit when the chain is installed. Be
sure to purchase the correct chains for the tires on which
they are to be used. Use rubber adjusters to take up any
slack or clearance in loose chains.
Use of chains may adversely affect vehicle handling.
When tire chains are installed, follow these precautions:
S Adjust speed to road conditions.
S Avoid sharp turns.
S Avoid locked–wheel braking.
To prevent chain damage to the vehicle, install the chains
on the front tires as tightly as possible. Tighten them again
after driving 0.4 to 0.8 kilometer (0.3 to 0.5 mile). The use
of chains on the rear tires is not recommended because
they may contact the vehicle and possibly damage it. If
chains must be used on the rear tires, be sure there is suffi-
cient clearance between the chains and the body. Do not
exceed 70 km/h (45 mph) or the chain manufacturer’s
speed limit, if lower. Avoid large bumps, potholes, severe
turns and any other maneuvers which could cause the
tires to bounce. Follow any other instructions of the chain
manufacturer which do not disagree with the above in-
structions.
REPLACEMENT TIRES
A tire performance criteria (TPC) specification number is
molded in the sidewall near the tire size of all original
equipment tires. This specification number assures that
the tire meets performance standards for traction, endur-
ance, dimensions, noise, handling and rolling resis–tance.
Usually a specific TPC number is assigned to each tire
size.
CAUTION : Do not mix different types of tires on the
same vehicle such as radial, bias and bias–belted
tires except in emergencies, because vehicle han-
dling may be seriously affected and may result in loss
of control.
Use only replacement tires with the same size, load range,
and construction as the original. The use of any other tire
size or construction type may seriously affect ride, han-
dling, speedometer/odometer calibration, vehicle ground
clearance, and tire clearance to the body and the chassis.
This does not apply to the spare tire furnished with the ve-
hicle.
It is recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on
the same axle.
If it is necessary to replace only one tire, pair it with the tire
having the most tread to equalize the braking action.
Although they may appear different in tread design, tires
built by different manufacturers with identical TPC specifi-
cations may be used on the same vehicle.
ALL SEASON TIRES
Most vehicles are now equipped with steel–belted all sea-
son radial tires as standard equipment. These tires qualify
as snow tires, with a 37 percent higher average rating for
snow traction than the non–all season radial tires pre-
viously used. Other performance areas, such as wet trac-
tion, rolling resistance, tread life, and air retention, have
also been improved. This was done by improvements in
both tread design and tread compounds. These tires are
identified by an ”M + S” molded in the tire sidewall following
the size number. The suffix ”MS” is also molded in the side-
wall after the TPC specification number.
The optional handling tires used on some vehicles are not
all season tires. These will not have the ”MS” marking after
the tire size or the TPC specification number.
PASSENGER METRIC SIZED TIRES
All Daewoo vehicles now use Passenger (P) metric sized
tires. P–metric tires are available in two load ranges: stan-
dard load (35 psi maximum) and extra load (41 psi maxi-
mum). Most passenger vehicle tires are standard load.
Most P–metric tire sizes do not have exact corresponding
alphanumeric tire sizes. For example, a P175/70R13 is
not exactly equal in size and load–carrying capacity to an
FR70–13. For this reason, replacement tires should be of
the same TPC specification number as the originals. If P–
metric tires must be replaced with other sizes, consult a
tire dealer. Tire companies can best recommend the clos-
est match of alphanumeric to P–metric sizes within their
own tire lines.
The metric term for measuring tire inflation pressure is the
kilopascal (kPa). Tire pressure may be printed in both kPa
and psi. One psi equals 6.895 kPa.
See the tire label or refer to ”Tire Size and Pressure Speci-
fications” in this section for tire inflation pressures.
TIRE LABEL
The tire label is permanently located on the rear face of the
driver’s door and should be referred to for tire information.
It lists the maximum vehicle load, the tire size (including
the spare tire), and the cold inflation pressure (including
the spare tire).
SPARE TIRE
The notchback and the wagon come equipped with a full–
sized tire on a steel wheel. The hatchback comes
equipped with a reduced–sized temporary tire on a steel
wheel.
WHEELS
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have
excessive lateral or radial runout, leak air through welds,
have elongated bolt holes, or if the wheel bolts won’t stay
tight or are heavily rusted. Wheels with excessive runout
may cause vehicle vibration. Replacement wheels must
be equivalent to the original equipment wheels in load ca-
Page 973 of 2643

TIRES AND WHEELS 2E – 11
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
pacity, diameter, rim width, offset, and mounting configu-
ration. A wheel of improper size or type may affect wheel
and bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer/odometer
calibration, vehicle ground clearance, and tire clearance
to the body and the chassis. The wheel offset is 49 ± 1 mm
(1.93 ± 0.04 inches). Steel wheels may be identified by a
two– or three–letter code stamped into the rim near the
valve stem. Alloy wheels should have the code, the part
number, and the manufacturer ID cast into the back side.
INFLATION O TIRES
The pressure recommended for any vehicle line is careful-
ly calculated to give a satisfactory ride, handling, tread life,
and load–carrying capacity.
Tire pressure should be checked monthly or before any
extended trip. Check the tires when they are cold, after the
vehicle has sat for 3 hours or more, or has been driven less
than 1 mile. Set the tire pressure to the specifications on
the tire label located on the rear face of the driver’s door.
Tire inflation pressure is also given under ”Tire Size and
Pressure Specifications” in this section.
Valve caps or extensions should be on the valves to keep
dust and water out.
For sustained driving at speeds up to 140 km/h (85 mph),
inflate the tires to the pressure recommended on the tire.
Sustained driving at speeds faster than 140 km/h (85mph), even if permitted by law, is not advised unless the
vehicle has special high–speed tires available from many
tire dealers. Tire pressures may increase as much as 41
kPa (6 psi) when the tires are hot.
Higher than recommended tire pressure can cause
S Hard ride.
S Tire bruising or damage.
S Rapid tread wear at the center of the tire.
Lower than recommended pressure can cause
S Tire squeal on turns.
S Hard steering.
S Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread.
S Tire rim bruises and rupture.
S Tire cord breakage.
S High tire temperatures.
Unequal tire pressures on same axle can cause
S Uneven braking.
S Steering lead.
S Reduced handling.
S Swerve on acceleration.
S Torque steer.
Page 1022 of 2643
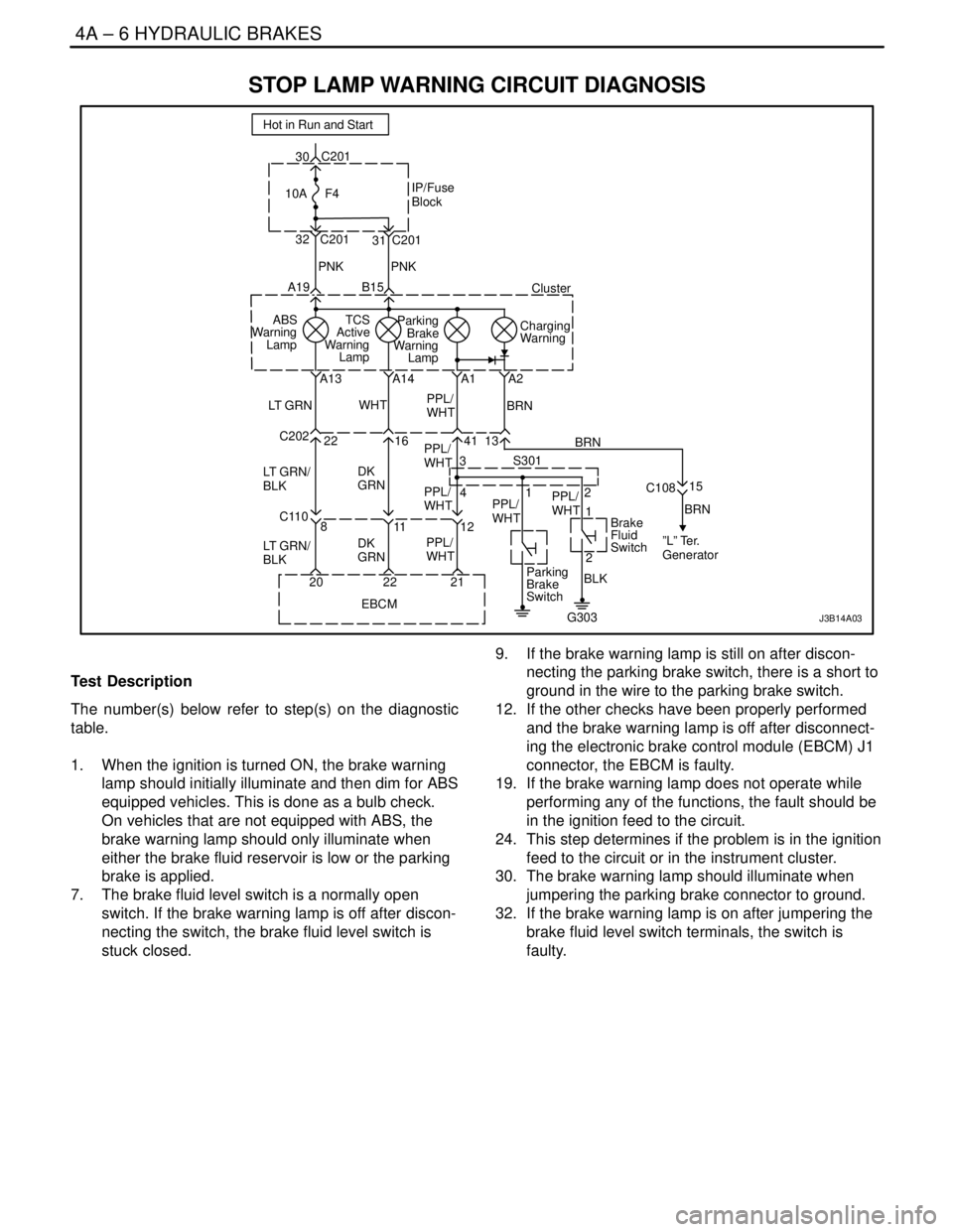
4A – 6IHYDRAULIC BRAKES
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
STOP LAMP WARNING CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS
J3B14A03
10A30
F4
32
A19
A13 A14 A1 A2B15 C201
31C201IP/Fuse
Block C201
C202
C110C108 S301 WHT
BRN
BRN
Parking
Brake
SwitchBrake
Fluid
Switch
BLKBRN LT GRN
DK
GRN
DK
GRN LT GRN/
BLK
LT GRN/
BLKPPL/
WHT
PPL/
WHT
PPL/
WHTPPL/
WHT PPL/
WHT
PPL/
WHT ABS
Warning
Lamp TCS
Active
Warning
Lamp Parking
Brake
Warning
Lamp Charging
Warning
Hot in Run and Start
PNK
Cluster PNK
EBCM”L” Ter.
Generator 1 12
2
20 2222 16 41 13
3
4
11 1 215
8
21
G303
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. When the ignition is turned ON, the brake warning
lamp should initially illuminate and then dim for ABS
equipped vehicles. This is done as a bulb check.
On vehicles that are not equipped with ABS, the
brake warning lamp should only illuminate when
either the brake fluid reservoir is low or the parking
brake is applied.
7. The brake fluid level switch is a normally open
switch. If the brake warning lamp is off after discon-
necting the switch, the brake fluid level switch is
stuck closed.9. If the brake warning lamp is still on after discon-
necting the parking brake switch, there is a short to
ground in the wire to the parking brake switch.
12. If the other checks have been properly performed
and the brake warning lamp is off after disconnect-
ing the electronic brake control module (EBCM) J1
connector, the EBCM is faulty.
19. If the brake warning lamp does not operate while
performing any of the functions, the fault should be
in the ignition feed to the circuit.
24. This step determines if the problem is in the ignition
feed to the circuit or in the instrument cluster.
30. The brake warning lamp should illuminate when
jumpering the parking brake connector to ground.
32. If the brake warning lamp is on after jumpering the
brake fluid level switch terminals, the switch is
faulty.