2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Ground
[x] Cancel search: GroundPage 805 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 559
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
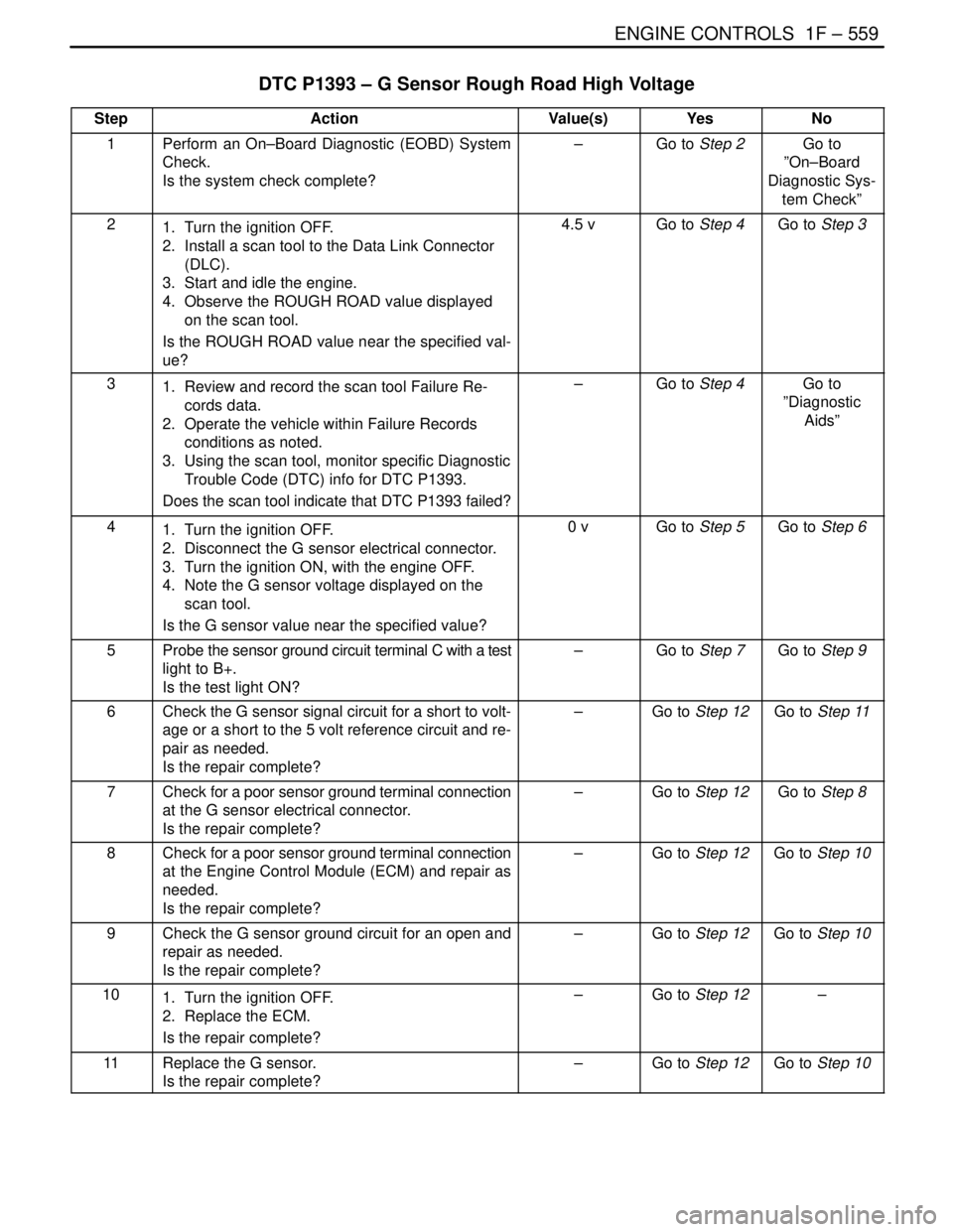
DTC P1393 – G Sensor Rough Road High Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
3. Start and idle the engine.
4. Observe the ROUGH ROAD value displayed
on the scan tool.
Is the ROUGH ROAD value near the specified val-
ue?4.5 vGo to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Review and record the scan tool Failure Re-
cords data.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using the scan tool, monitor specific Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) info for DTC P1393.
Does the scan tool indicate that DTC P1393 failed?–Go to Step 4Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids”
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the G sensor electrical connector.
3. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
4. Note the G sensor voltage displayed on the
scan tool.
Is the G sensor value near the specified value?0 vGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Probe the sensor ground circuit terminal C with a test
light to B+.
Is the test light ON?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 9
6Check the G sensor signal circuit for a short to volt-
age or a short to the 5 volt reference circuit and re-
pair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 11
7Check for a poor sensor ground terminal connection
at the G sensor electrical connector.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 8
8Check for a poor sensor ground terminal connection
at the Engine Control Module (ECM) and repair as
needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 10
9Check the G sensor ground circuit for an open and
repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 10
101. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 12–
11Replace the G sensor.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 10
Page 811 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 565
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1404
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION CLOSED VALVE
PINTLE ERROR
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber.When the air/fuelmixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced.
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with an En-
gine Control Module (ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM
controls the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle
Position (TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sen-
sors. The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate
when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through
the ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the De-
sired EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-
back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR Position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
Position.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Difference between current and learned low posi-
tion is greater than 10%.S Desired EGR position is equal to 0.
S Engine is running.
S Ignition voltage is between 11.7 and 16 volts.
S Intake Air Temperature (IAT) is greater than 3°C
(37.4°F).
S DTCs P0112, P0113, P0405, P0406, and P0502
are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
S EGR is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after three consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 80 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Due to moisture associated with exhaust systems, the
EGR valve may freeze and stick in cold weather. After the
vehicle is brought into a warm shop for repairs, the valve
warms and the problem disappears. By watching the Actu-
al EGR and Desired EGR Positions on a cold vehicle with
a scan tool, the fault can be easily verified. Check the
Page 812 of 2643
1F – 566IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
freeze frame data to determine if the DTC set when the ve-
hicle was cold by viewing the Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT).
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Commanding the EGR valve open determines
whether the EGR system can control the EGR
valve accurately and if the fault is present.
3. When the EGR valve electrical connector is discon-
nected, the scan tool should display the Actual
EGR Position as 0%. If it does not, the fault lies
either in the EGR signal circuit or the ECM.
5. If the ERG valve 5 volt reference is shorted to volt-
age, the Digital Voltmeter (DVM) will read battery
voltage and additional DTCs may be set and engine
performance will be poor.6. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
10. An open or poor connection condition may have
caused this DTC to set. Be sure to check the termi-
nals for being backed out, improperly formed or
damaged, and for poor tension.
11. All circuits to the EGR valve are OK at this point.
The fault lies internally in the EGR valve and there-
fore must be replaced. Be sure all gasket material
is removed from the EGR mounting surface. Even
a small amount of material may cause a DTC
P0401 to set.
12. Check the terminals for being backed out, improp-
erly formed or damaged, and for poor tension.
13. Clearing DTCs is a very important step for this
diagnostic. The clearing function allows the EGR
valve to relearn a new pintle position as the old
pintle position was inaccurate due to the failure that
caused the DTC. The DTC must be cleared with
the ignition ON, engine OFF or when the engine is
idling. If the ECM sees a EGR command, the new
pintle will not be learned.
14. If no malfunctions have been found at this point and
no additional DTCs were set, refer to ”Diagnostic
Aids” in this section for additional checks and infor-
mation.
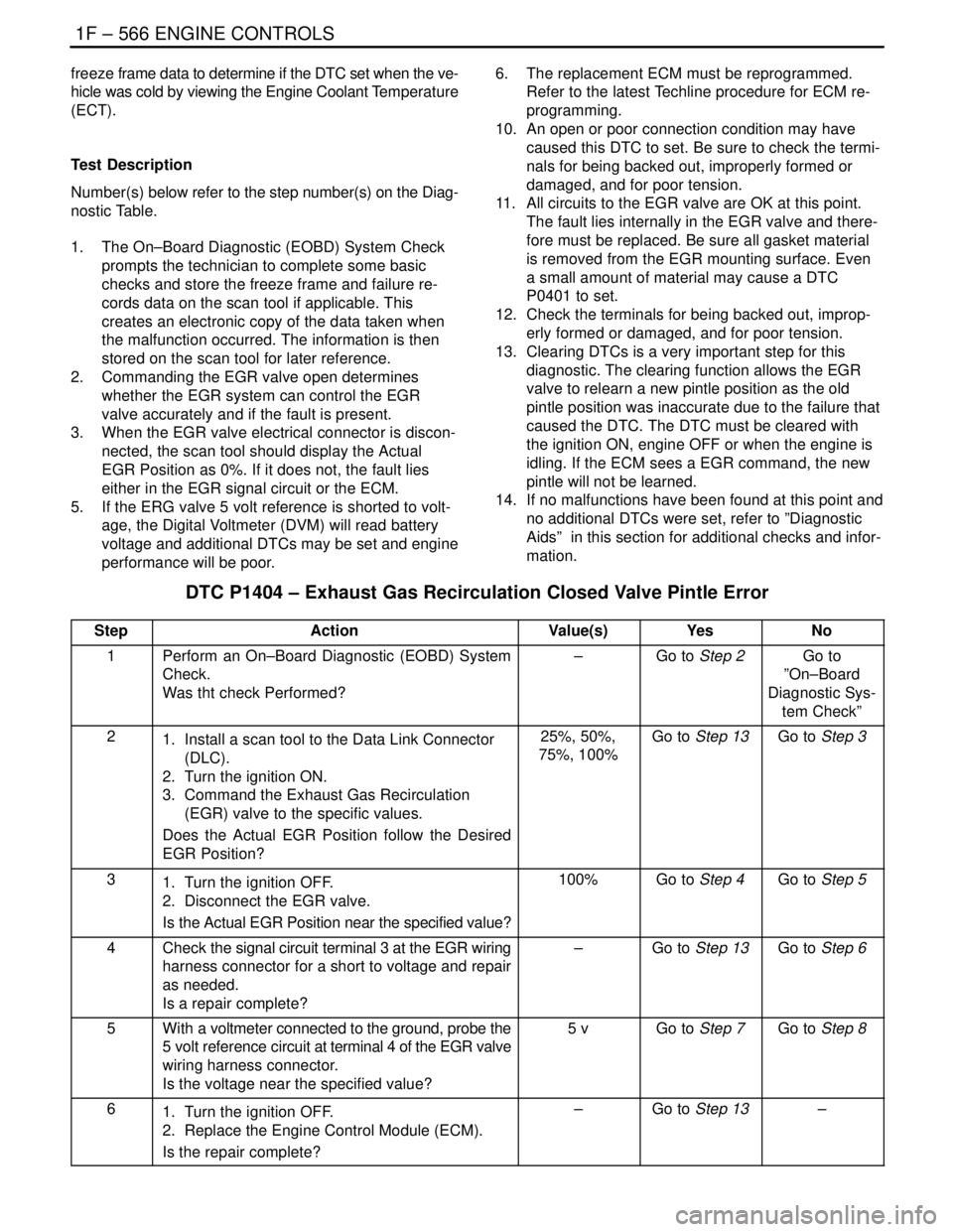
DTC P1404 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Closed Valve Pintle Error
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was tht check Performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Command the Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve to the specific values.
Does the Actual EGR Position follow the Desired
EGR Position?25%, 50%,
75%, 100%Go to Step 13Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the EGR valve.
Is the Actual EGR Position near the specified value?100%Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Check the signal circuit terminal 3 at the EGR wiring
harness connector for a short to voltage and repair
as needed.
Is a repair complete?–Go to Step 13Go to Step 6
5With a voltmeter connected to the ground, probe the
5 volt reference circuit at terminal 4 of the EGR valve
wiring harness connector.
Is the voltage near the specified value?5 vGo to Step 7Go to Step 8
61. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 13–
Page 813 of 2643
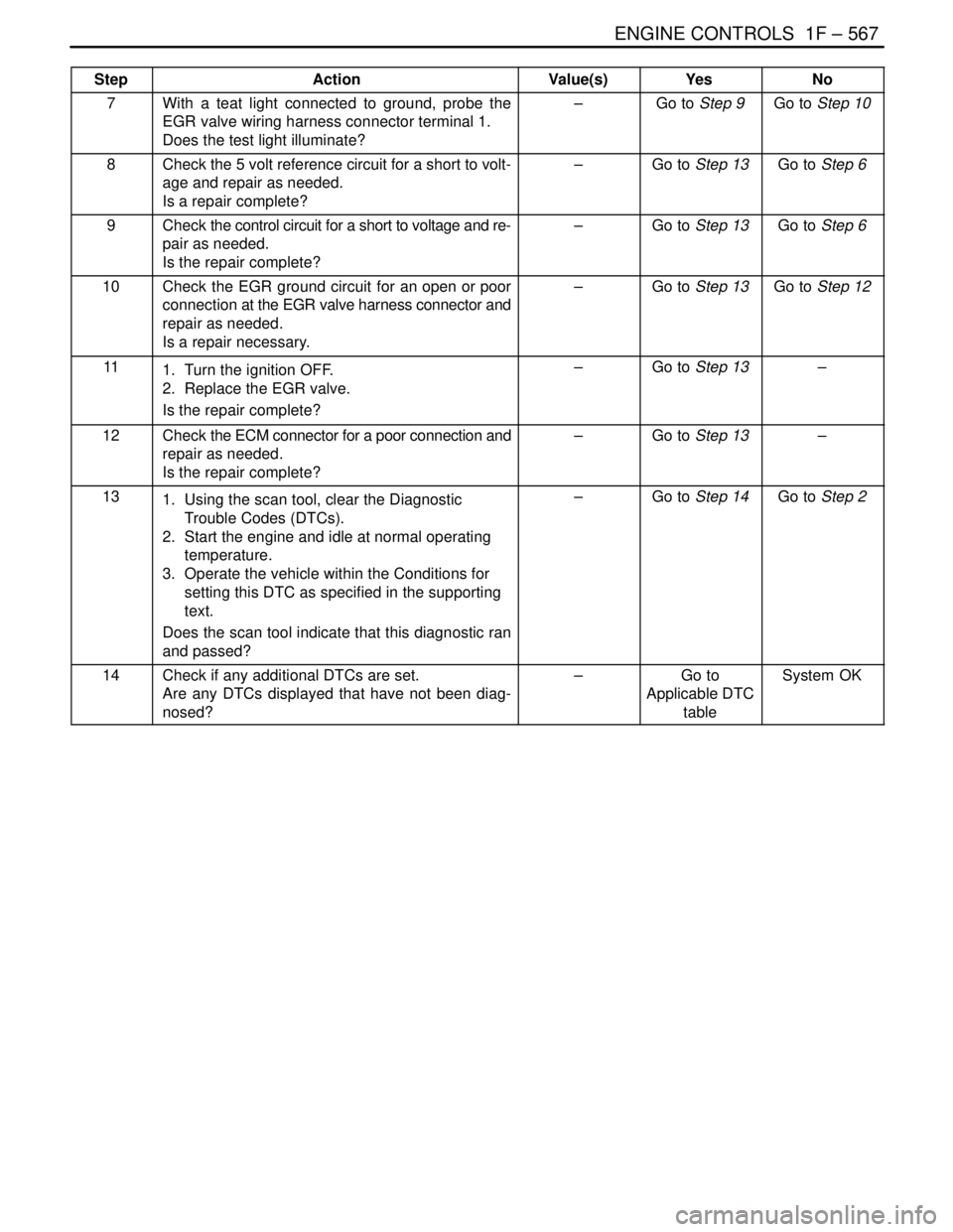
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 567
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
7With a teat light connected to ground, probe the
EGR valve wiring harness connector terminal 1.
Does the test light illuminate?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 10
8Check the 5 volt reference circuit for a short to volt-
age and repair as needed.
Is a repair complete?–Go to Step 13Go to Step 6
9Check the control circuit for a short to voltage and re-
pair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 13Go to Step 6
10Check the EGR ground circuit for an open or poor
connection at the EGR valve harness connector and
repair as needed.
Is a repair necessary.–Go to Step 13Go to Step 12
111. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the EGR valve.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 13–
12Check the ECM connector for a poor connection and
repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 13–
131. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran
and passed?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 2
14Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 820 of 2643
1F – 574IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
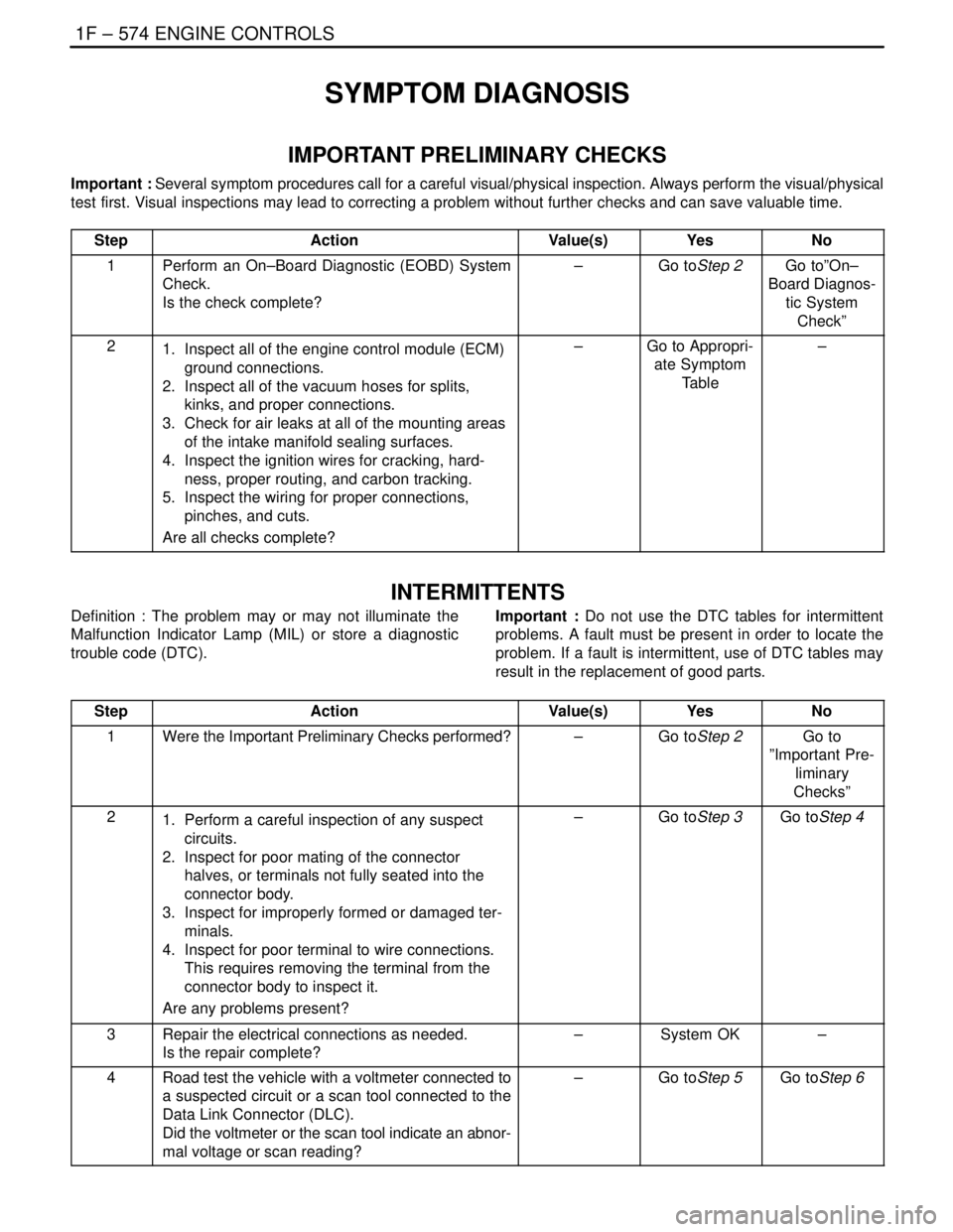
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
IMPORTANT PRELIMINARY CHECKS
Important : Several symptom procedures call for a careful visual/physical inspection. Always perform the visual/physical
test first. Visual inspections may lead to correcting a problem without further checks and can save valuable time.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the check complete?–Go toStep 2Go to”On–
Board Diagnos-
tic System
Check”
21. Inspect all of the engine control module (ECM)
ground connections.
2. Inspect all of the vacuum hoses for splits,
kinks, and proper connections.
3. Check for air leaks at all of the mounting areas
of the intake manifold sealing surfaces.
4. Inspect the ignition wires for cracking, hard-
ness, proper routing, and carbon tracking.
5. Inspect the wiring for proper connections,
pinches, and cuts.
Are all checks complete?–Go to Appropri-
ate Symptom
Table–
INTERMITTENTS
Definition : The problem may or may not illuminate the
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) or store a diagnostic
trouble code (DTC).Important : Do not use the DTC tables for intermittent
problems. A fault must be present in order to locate the
problem. If a fault is intermittent, use of DTC tables may
result in the replacement of good parts.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Were the Important Preliminary Checks performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”Important Pre-
liminary
Checks”
21. Perform a careful inspection of any suspect
circuits.
2. Inspect for poor mating of the connector
halves, or terminals not fully seated into the
connector body.
3. Inspect for improperly formed or damaged ter-
minals.
4. Inspect for poor terminal to wire connections.
This requires removing the terminal from the
connector body to inspect it.
Are any problems present?–Go toStep 3Go toStep 4
3Repair the electrical connections as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
4Road test the vehicle with a voltmeter connected to
a suspected circuit or a scan tool connected to the
Data Link Connector (DLC).
Did the voltmeter or the scan tool indicate an abnor-
mal voltage or scan reading?–Go toStep 5Go toStep 6
Page 821 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 575
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
5Replace the sensor in the affected circuit, if a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) was stored for this circuit
(except for the DTCs P0171 and P0172.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
6Does an intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) or DTC occur?–Go toStep 7Go toStep 8
71. Check for a faulty relay, electronic control mod-
ule (ECM) driven solenoid, or switch.
2. Check for improper installation of electrical de-
vices, such as lights, two–way radios, electric
motors, etc.
3. Inspect the ignition control wires for proper
routing (away from ignition wires, ignition sys-
tem components, and the generator).
4. Check for a short–to–ground in the MIL circuit
or the DLC ”test” terminal.
5. Inspect the ECM ground connections.
6. Correct or repair the affected circuits as need-
ed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
81. Check for a loss of DTC memory.
2. 2. Disconnect the Throttle Position Sensor.
3. Run the engine at idle until the MIL comes on.
4. Turn the ignition OFF.
Is DTC P0122 stored in memory?–Go toStep 10Go toStep 9
9Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
10Does the vehicle stall while driving?–Go toStep 11Go toStep 12
11Monitor the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1)
and the injector base pulse width with the scan tool.
Does the scan tool display a steady low voltage
(about 0 mv) for the HO2S1 sensor with the control
module commanding an injector base pulse width of
the value specified?8 msGo toStep 9Go toStep 12
121. Check for an open diode across the A/C clutch
and for other open diodes.
2. Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 823 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 577
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
101. Check the fuel injector driver circuit.
2. Disconnect all of the fuel injector harness con-
nectors at the fuel injectors.
3. Connect an injector test light between the har-
ness terminals of each fuel injector connector.
4. Note the test light while cranking the engine.
Does the test light blink at all connectors?–Go toStep 13Go toStep 11
11Check the fuel injector driver wiring harness, the
connectors, and the connector terminals for the
proper connections.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 12Go toStep 30
12Repair the wiring harness, the connector, or the con-
nector terminal as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK
13Measure the resistance of each fuel injector at 68°F
(20°C). The resistance will increase slightly at high-
er temperatures.
Is the fuel injector resistance within the value speci-
fied?11.6–12.4 ΩGo toStep 15Go toStep 14
14Replace any fuel injector with a resistance that is out
of specifications.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
15Perform an injector balance test.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 16Go toStep 17
16Replace any restricted or leaking fuel injectors as
needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
171. Check for the proper ignition voltage output for
each cylinder with a spark tester.
2. Inspect the spark plugs for cracks, wear, im-
proper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy de-
posits.
3. Inspect the ignition wires for short conditions.
4. Inspect all of the ignition grounds for loose con-
nections.
5. Inspect the powertrain control module
(PCM)/engine control module (ECM) for the
proper operation.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 18Go toStep 19
18Correct or replace any faulty ignition components.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
19Does the engine misfire or cut out under load or at
idle?Go to
”Ignition Sys-
tem Check”Go toStep 20
20Does the engine start, but then immediately stall?–Go toStep 21Go toStep 23
211. Remove the Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor.
2. Inspect for faulty connections and repair as
needed.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 22Go toStep 25
22Repair the faulty connections as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 826 of 2643

1F – 580IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
121. Inspect the engine control module (ECM)
grounds to make sure they are clean, tight, and
in their proper locations.
2. Inspect the vacuum lines for kinks or leaks.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 13Go toStep 14
13Repair the electrical connections or the vacuum
lines as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
14Check the generator output voltage.
Is the generator voltage within the value specified?12–16 vGo toStep 16Go toStep 15
15Repair the generator.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
161. Check for intermittent Exhaust Gas Recircula-
tion (EGR) valve operation.
2. Check Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) opera-
tion.
3. Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
17Repair the fuel system as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
18Replace the fuel filter.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
19Replace the leaking or restricted fuel injectors.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–