2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Ground
[x] Cancel search: GroundPage 790 of 2643

1F – 544IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
A malfunction in the HO2S1 ignition feed or ground circuit
may cause a DTC P1134 to set. Check HO2S1 circuitry for
intermittent faults or poor connections. If connections and
wiring are OK and DTC P1134 continues to set, replace
the HO2S1.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how open
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Chart.
3. A condition that affects pre–converter and post–
converter oxygen sensors indicates probable con-
tamination. To avoid damaging replacement sen-
sors, correct the condition which caused the
contamination before replacing the affected sen-
sors.
5. This step checks for conditions which may cause
the oxygen sensor to appear faulty. Correct any of
the described conditions if present.
8. To avoid damaging replacement sensors, correct
the condition which caused the contamination be-
fore replacing the affected sensors
DTC P1134 – Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) Transition
Ratio
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
2Important : If any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
are set, refer to those DTCs before processing with
this diagnostic chart.
1. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the engine within parameters specified
under Conditions for Setting the DTC.
4. Using a scan tool, monitor specific DTC info for
DTC P1134 until the DTC P1134 test runs.
5. Note the test result.
Does the scan tool indicate DTC P1134 failed this
ignition?–Go to Step 3Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids”
3Perform an exhaust system leak test.
If an exhaust leak is found, repair as needed.
The exhaust leak isolated?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 4
4Visually/physically inspect for the following items:
S Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) is se-
curely installed.
S Corrosion on the terminals.
S Terminal tension.
S HO2S1 wiring harness for poor terminal con-
nection or damaged wiring.
Is a problem found in any of the above areas?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 5
Page 791 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 545
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
51. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the HO2S1 connector.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. Using a voltmeter, measure the voltage be-
tween following terminals.
5. Terminal 4 of Engine Control Module (ECM)
side HO2S1 connector and ground.
6. Terminal 3 of ECM side HO2S1 connector and
ground.
Are both voltages in the specified value?3–5 vGo to Step 6Go to Step 8
61. With the HO2S1 disconnected, jumper the
ECM side HO2S1 connector terminals 4 and 3.
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Using a scan tool, monitor the HO2S1 voltage.
Does the scan tool indicates less than 10 millivolts
and immediately return to about 450 millivolts when
the jumper is removed?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 9
7Repair conditions as needed.
Is the action complete?–Go to Step 14–
8Check for faulty ECM connections or terminal dam-
ages and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 9
9Repair open, short, or grounded signal circuit.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Step 11
10Remove the HO2S1 and examine it for sign of:
S Fuel contamination.
S Improper room temperature vulcanizing sealant
(white powdery coating on the sensor)
S Engine oil/coolant consumption.
Are sign of contamination observed?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 13
111. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 13
12Determine and correct the cause of contamination.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14
13Replace the HO2S1.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14–
141. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 15Go to Step 2
15Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 798 of 2643

1F – 552IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1391
G SENSOR ROUGH ROAD RATIONALITY
Circuit Description
TThe Gravity Sensing Rough Road (G) sensor is a vertical
low g–acceleration sensor. By sensing vertical accelera-
tion caused by bumps or potholes in the road, the Engine
Control Module (ECM) can determine if the changes in
crankshaft speed are due to engine misfire or are driveline
induced. If the G sensor detects a rough road condition,
the ECM misfire detection diagnostic will be de–activated.
The G sensor at rest output should be between 2.35–2.65
volts (+1G). During a rough road condition, the voltage
output can vary between 0.5 (–1G) and 4.5 volts (+3G).
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Engine is running.
S Vehicle speed is less than or equal to 5 km/h (3.1
mph).
S G sensor output at idle indicates below –0.39 volts
or above 2.21 volts.
OR
S Engine is running more than 10 seconds and ve-
hicle speed is between 30 mph (50 km/h) and 70
mph (112 km/h).
S G sensor signal changes less than 0.00024 volts
while driving.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles without a
fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
S Poor connection at the ECM – Inspect the harness
connections for backed–out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or dam-
aged terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connec-
tion.
S Damaged harness –– Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe
the G sensor display on the scan tool while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sen-
sor. A change in the display will indicate the loca-
tion of the fault.
Since the G sensor shares the ECM 5 volt reference and
ground terminals with the A/C Pressure Sensor, a dam-
aged A/C Pressure Sensor harness or sensor could cause
a G sensor DTC to set. Refer to ”Multiple ECM Information
Sensor DTCs Set” in this section. in this section.
The G sensor will give correct voltages only if it is level and
mounted securely to its bracket.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the con
Page 799 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 553
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Checkprompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
DTC P1391 – G Sensor Rough Road Rationality
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition ON, with engine OFF.
2. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
3. Review and record the scan tool Failure Re-
cords data.
4. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
5. Using the scan tool, monitor specific Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) info for DTC P1391.
Does the scan tool indicate that DTC P1391 failed?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
3Check for the following conditions and repair as
needed:
S G sensor seal missing or damaged.
S G sensor mounting flanges cracked, missing,
or incorrectly installed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids”
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the G sensor electrical connector.
3. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
4. Observe the G sensor value displayed on the
scan tool.
Is the G sensor value near the specified value?0 vGo to Step 5Go to Step 12
51. Jumper the 5 volt reference circuit, terminal A
and the G sensor signal circuit, terminal B to-
gether at the G sensor harness connector.
2. Observe the G sensor value displayed on the
scan tool.
Is the G sensor value near the specified value?4.95 vGo to Step 6Go to Step 7
61. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module (ECM)
and check the sensor ground circuit for high
resistance, an open between the ECM and the
G sensor, or for a poor connection at the termi-
nal k34 of the ECM and repair as needed.
3. f the problem is found, repair as necessary.
Is a problem found?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 10
7Check the 5 volt reference circuit for high resistance,
an open between the ECM and the G sensor, or a
poor connection at the terminal k50 of the ECM and
repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 8
Page 800 of 2643

1F – 554IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
81. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM and check the G sensor
signal circuit for high resistance, an open, a
short to ground, or a short to the sensor ground
circuit and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 9
9Check the G sensor signal circuit for a poor connec-
tion at the ECM and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 13
10Check for a poor connection at terminal C of the G
sensor and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?Go to Step 14Go to Step 11
11Replace the G sensor.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14–
121. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. Check the G sensor signal circuit for a short to
voltage or a short to the 5 volt reference circuit
and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 13
131. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14–
141. Using the scan tool, clear the DTCs.
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran
and passed?–Go to Step 15Go to Step 2
15Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 801 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 555
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1392
G SENSOR ROUGH ROAD LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Gravity Sensing Rough Road (G) sensor is a vertical
low g–acceleration sensor. By sensing vertical accelera-
tion caused by bumps or potholes in the road, the Engine
Control Module (ECM) can determine if the changes in
crankshaft speed are due to engine misfire or are driveline
induced. If the G sensor detects a rough road condition,
the ECM misfire detection diagnostic will be de–activated.
The G sensor at rest output should be between 2.35–2.65
volts (+1G). During a rough road condition, the voltage
output can vary between 0.5 (–1G) and 4.5 volts (+3G).
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S G sensor output is less than 2%.
S Engine is running more than or equal to 10 sec-
onds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles without a
fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:S Poor connection at the ECM – Inspect the harness
connections for backed–out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or dam-
aged terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connec-
tion.
S Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe
the G sensor display on the scan tool while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sen-
sor. A change in the display will indicate the loca-
tion of the fault.
Since the G sensor shares the ECM 5 volt reference and
ground terminals with the A/C Pressure Sensor, a dam-
aged A/C Pressure Sensor harness or sensor could cause
a G sensor DTC to set. Refer to ”Multiple ECM Information
Sensor DTCs Set” in this section.
The G sensor will give correct voltages only if it is level and
mounted securely to its bracket.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
Page 802 of 2643
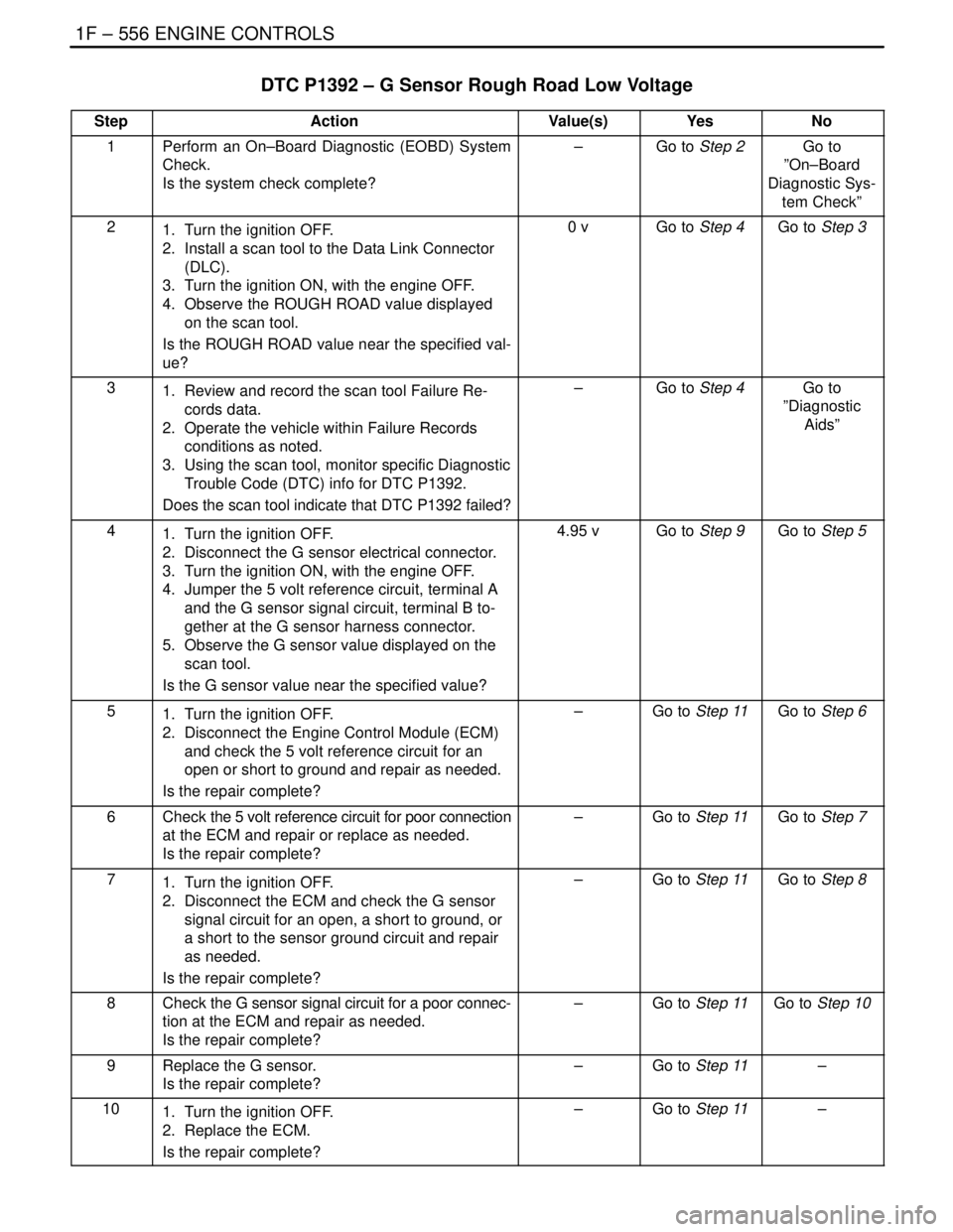
1F – 556IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P1392 – G Sensor Rough Road Low Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
3. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
4. Observe the ROUGH ROAD value displayed
on the scan tool.
Is the ROUGH ROAD value near the specified val-
ue?0 vGo to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Review and record the scan tool Failure Re-
cords data.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using the scan tool, monitor specific Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) info for DTC P1392.
Does the scan tool indicate that DTC P1392 failed?–Go to Step 4Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids”
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the G sensor electrical connector.
3. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
4. Jumper the 5 volt reference circuit, terminal A
and the G sensor signal circuit, terminal B to-
gether at the G sensor harness connector.
5. Observe the G sensor value displayed on the
scan tool.
Is the G sensor value near the specified value?4.95 vGo to Step 9Go to Step 5
51. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module (ECM)
and check the 5 volt reference circuit for an
open or short to ground and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 11Go to Step 6
6Check the 5 volt reference circuit for poor connection
at the ECM and repair or replace as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 11Go to Step 7
71. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM and check the G sensor
signal circuit for an open, a short to ground, or
a short to the sensor ground circuit and repair
as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 11Go to Step 8
8Check the G sensor signal circuit for a poor connec-
tion at the ECM and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 11Go to Step 10
9Replace the G sensor.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 11–
101. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 11–
Page 804 of 2643

1F – 558IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1393
G SENSOR ROUGH ROAD HIGH VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Rough Road (G) sensor is a vertical low g–accelera-
tion sensor. By sensing vertical acceleration caused by
bumps or potholes in the road, the Engine Control Module
(ECM) can determine if the changes in crankshaft speed
are due to engine misfire or are driveline induced. If the G
sensor detects a rough road condition, the ECM misfire
detection diagnostic will be de–activated. The G sensor at
rest output should be between 2.35–2.65 volts (+1G). Dur-
ing a rough road condition, the voltage output can vary be-
tween 0.5 (–1G) and 4.5 volts (+3G).
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S G sensor output is greater than 98%.
S Engine is running more than or equal to 10 sec-
onds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles without a
fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:S Poor connection at the ECM – Inspect the harness
connections for backed–out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or dam-
aged terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connec-
tion.
S Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe
the G sensor display on the scan tool while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sen-
sor. A change in the display will indicate the loca-
tion of the fault.
Since the G sensor shares the ECM 5 volt reference and
ground terminals with the A/C Pressure Sensor, a dam-
aged A/C Pressure Sensor harness or sensor could cause
a G sensor DTC to set. Refer to”Multiple ECM Information
Sensor DTCs Set” in this section.
The G sensor will give correct voltages only if it is level and
mounted securely to its bracket.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.