2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Section 6
[x] Cancel search: Section 6Page 278 of 2643

1F – 32IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ON–BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (EOBD) SYSTEM CHECK
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) system check is the
starting point for any driveability complaint diagnosis. Be-
fore using this procedure, perform a careful visual/physi-
cal check of the engine control module (ECM) and the en-
gine grounds for cleanliness and tightness.
The EOBD system check is an organized approach to
identifying a problem created by an electronic engine con-
trol system malfunction.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for poor connections or a damaged har-
ness. Inspect the ECM harness and connections for im-
proper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or dam-
aged terminals, poor terminal–to–wire connection, and
damaged harness.Test Description
Numbers below refer to the step number on the Diagnostic
Chart:
1. The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) should be
ON steady with the ignition ON and the engine
OFF. If not, go to ”Diagnostic Aids”.
2. Checks the Class 2 data circuit and ensures that
the ECM is able to transmit serial data.
3. This test ensures that the ECM is capable of con-
trolling the MIL and the MIL driver circuit is not
shorted to ground.
4. If the engine will not start, refer to ”Engine Cranks
But Will Not Run” in this section.
7. A scan tool parameter which is not within the typical
range may help to isolate the area which is causing
the problem.
10. This vehicle is equipped with a ECM which utilizes
an Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory (EEPROM). The replacement ECM must
be programmed. Refer to the latest Techline proce-
dure for ECM reprogramming.
Page 280 of 2643

1F – 34IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ON–BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (EOBD) SYSTEM CHECK
(1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) system check is the
starting point for any driveability complaint diagnosis. Be-
fore using this procedure, perform a careful visual/physi-
cal check of the engine control module (ECM) and the en-
gine grounds for cleanliness and tightness.
The EOBD system check is an organized approach to
identifying a problem created by an electronic engine con-
trol system malfunction.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for poor connections or a damaged har-
ness. Inspect the ECM harness and connections for im-
proper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or dam-
aged terminals, poor terminal–to–wire connection, and
damaged harness.Test Description
Numbers below refer to the step number on the Diagnostic
Chart:
1. The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) should be
ON steady with the ignition ON and the engine
OFF. If not, go to”Diagnostic Aids”.
2. Checks the Class 2 data circuit and ensures that
the ECM is able to transmit serial data.
3. This test ensures that the ECM is capable of con-
trolling the MIL and the MIL driver circuit is not
shorted to ground.
4. If the engine will not start, refer to ”Engine Cranks
But Will Not Run” in this section.
7. A scan tool parameter which is not within the typical
range may help to isolate the area which is causing
the problem.
10. This vehicle is equipped with a ECM which utilizes
an Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory (EEPROM). The replacement ECM must
be programmed. Refer to the latest Techline proce-
dure for ECM reprogramming.
Page 307 of 2643
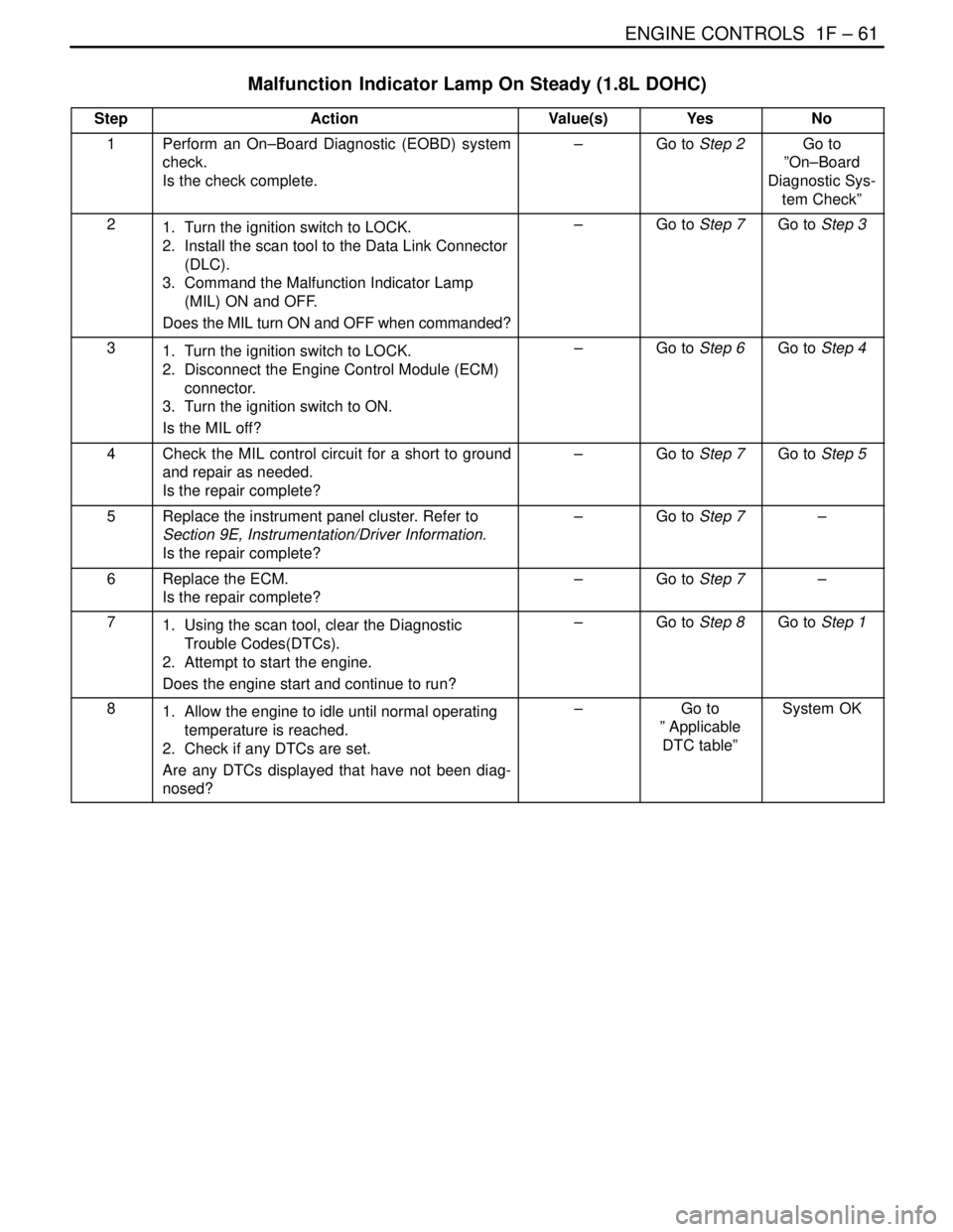
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 61
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Malfunction Indicator Lamp On Steady (1.8L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) system
check.
Is the check complete.–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Install the scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
3. Command the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) ON and OFF.
Does the MIL turn ON and OFF when commanded?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module (ECM)
connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Is the MIL off?–Go to Step 6Go to Step 4
4Check the MIL control circuit for a short to ground
and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 5
5Replace the instrument panel cluster. Refer to
Section 9E, Instrumentation/Driver Information.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7–
6Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7–
71. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes(DTCs).
2. Attempt to start the engine.
Does the engine start and continue to run?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 1
81. Allow the engine to idle until normal operating
temperature is reached.
2. Check if any DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
” Applicable
DTC table”System OK
Page 361 of 2643
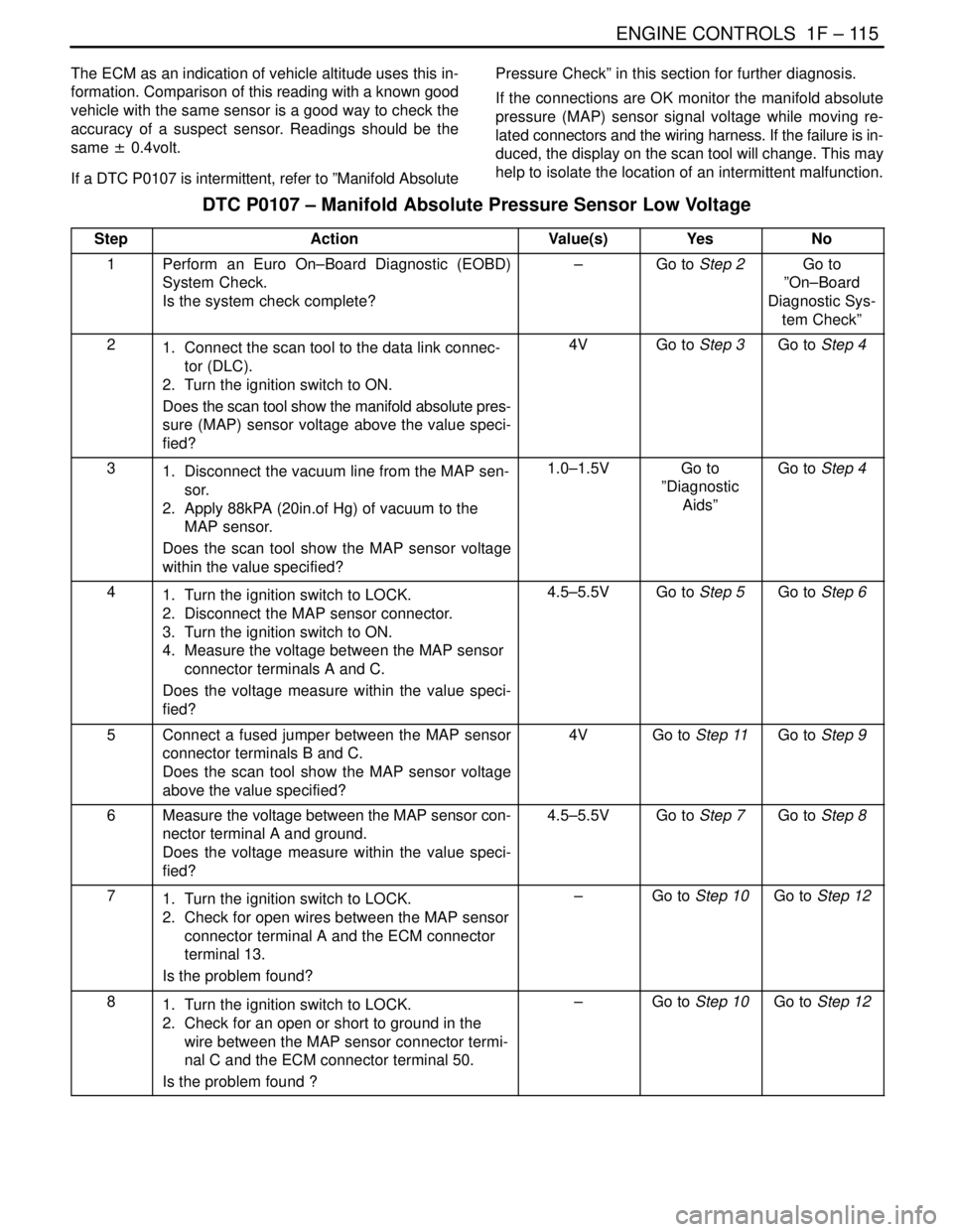
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 115
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
The ECM as an indication of vehicle altitude uses this in-
formation. Comparison of this reading with a known good
vehicle with the same sensor is a good way to check the
accuracy of a suspect sensor. Readings should be the
same ± 0.4volt.
If a DTC P0107 is intermittent, refer to ”Manifold AbsolutePressure Check” in this section for further diagnosis.
If the connections are OK monitor the manifold absolute
pressure (MAP) sensor signal voltage while moving re-
lated connectors and the wiring harness. If the failure is in-
duced, the display on the scan tool will change. This may
help to isolate the location of an intermittent malfunction.
DTC P0107 – Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Low Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Connect the scan tool to the data link connec-
tor (DLC).
2. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Does the scan tool show the manifold absolute pres-
sure (MAP) sensor voltage above the value speci-
fied?4VGo to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Disconnect the vacuum line from the MAP sen-
sor.
2. Apply 88kPA (20in.of Hg) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor.
Does the scan tool show the MAP sensor voltage
within the value specified?1.0–1.5VGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 4
41. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the MAP sensor connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
4. Measure the voltage between the MAP sensor
connector terminals A and C.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?4.5–5.5VGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Connect a fused jumper between the MAP sensor
connector terminals B and C.
Does the scan tool show the MAP sensor voltage
above the value specified?4VGo to Step 11Go to Step 9
6Measure the voltage between the MAP sensor con-
nector terminal A and ground.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?4.5–5.5VGo to Step 7Go to Step 8
71. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Check for open wires between the MAP sensor
connector terminal A and the ECM connector
terminal 13.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 12
81. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Check for an open or short to ground in the
wire between the MAP sensor connector termi-
nal C and the ECM connector terminal 50.
Is the problem found ?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 12
Page 363 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 117
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0108
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses the Manifold Ab-
solute Pressure (MAP) sensor to control the fuel delivery
and the ignition timing. The MAP sensor measures the
changes in the intake manifold pressure, which results
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and the rpm
changes; and converts these into voltage outputs. The
ECM sends a 5 volt–reference voltage to the MAP sensor.
As the manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of
the MAP sensor also changes. By monitoring the MAP
sensor output voltage, the ECM knows the manifold pres-
sure. A low–pressure (low voltage) output voltage will be
about 1.0 to 1.5 volts at idle, while higher pressure (high
voltage) output voltage will be about 4.5 to 4.8 at wide
open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is metric pressure,
allowing the ECM to make adjustments for different alti-
tudes.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S This DTC can be stored in ”key–on” status.
S When the engine idling.
S Engine speed is greater than 700rpm.
S No throttle position sensor (TPS) fail conditions
present.
S The MAP is greater than 95kPA.
S A high voltage condition exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
S The ECM will substitutes a fixed MAP value and
use TP to control the fuel delivery (the scan tool will
not show defaulted)
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the engine stopped, the manifold
pressure is equal to atmosphere pressure and the signal
voltage will be high.
The ECM as an indication of vehicle altitude uses this in-
formation. Comparison of this reading with a known good
vehicle with the same sensor is a good way to check the
accuracy of a suspect sensor. Readings should be the
same ±0.4volt.
If a DTC P0108 is intermittent, refer to ”Manifold Absolute
Pressure Check” in this section for further diagnosis.
If the connections are OK monitor the manifold absolute
pressure(MAP) sensor signal voltage while moving re-
lated connectors and the wiring harness. If the failure is in-
duced, the display on the scan tool will change. This may
help to isolate the location of an intermittent malfunction.
Page 366 of 2643

1F – 120IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B11F51
BRNORN
/BLK
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0112
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor uses a thermis-
tor to control the signal voltage to the engine control mod-
ule (ECM). The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage
and a ground to the sensor. When the air is cold, the resist-
ance is high ; therefore IAT sensor signal voltage will be
high. If the intake air is warm, resistance is low ; therefore
the IAT sensor signal voltage will be low.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S IAT voltage is less than 0.01V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.S The ECM will default to 605C(1405F) for intake air
temperature. The scan tool will not show the de-
faulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
If the vehicle is at ambient temperature, compare the IAT
sensor to the engine coolant temperature(ECT) sensor.
The IAT sensor and the ECT sensor should be relatively
close to each other. Use the temperature vs. Resistance
Values table to evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor.
Refer to ”Temperature vs. Resistance” in this section.
Page 368 of 2643

1F – 122IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B11F51
BRNORN
/BLK
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0113
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR HIGH VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor uses a thermis-
tor to control the signal voltage to the engine control mod-
ule (ECM). The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage
and a ground to the sensor . when the air is cold, the resist-
ance is high ; therefore IAT sensor signal voltage will be
high. If the intake air is warm, resistance is low ; therefore
the IAT sensor signal voltage will be low.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S IAT voltage is less than 4.99V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.S The ECM will default to 605C(1405F) for intake air
temperature. The scan tool will not show the de-
faulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
S If the vehicle is at ambient temperature, compare
the IAT sensor to the engine coolant temperature
(ECT) sensor. The IAT sensor and the ECT sensor
should be relatively close to each other.
S Use the temperature vs. Resistance Values table to
evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor. Refer
to ”Temperature vs. Resistance” in this section.
Page 371 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 125
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0117
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Engine Coolant Temperature sensor (ECT) uses a
thermistor to control the signal voltage to the engine con-
trol module (ECM).
The ECM supplies a voltage on the signal circuit to the
sensor. When the engine coolant is cold, the resistance is
high; therefore the ECT signal voltage will be high.
As the engine warms, the sensor resistance becomes
less, and the voltage drops. At normal engine operating
temperature, the voltage will be between 1.5 and 2.0 volts
at the ECT signal terminal.
The ECT sensor is used to the following items:
S Fuel delivery.
S Lock Up Clutch (LUC).
S Ignition.
S Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge
Valve.
S Electric cooling fan.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S ECT voltage is less than 0.03V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will default to 20°C (68°F) for the first 60
seconds of the engine run time, and then 92 °C
(198 °F).
S The scan tool will not show the defaulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
After the engine has started, the ECT should rise steadily
to about 90°C (194°F) then stabilize when the thermostat
opens.
Use the temperature vs. Resistance values table to evalu-
ate the possibility of a skewed sensor. Refer to ”Tempera-
ture vs. Resistance” in this section.