2003 PONTIAC BONNEVILLE spare tire
[x] Cancel search: spare tirePage 261 of 418
Section 5 Service and Appearance Care
Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement ............. 5-61
Tires .............................................................. 5.62
Inflation
.. Tire Pressure ................................ 5.62
Check Tire Pressure System
.......................... 5.64
Tire Inspection and Rotation
........................... 5.65
When It
Is Time for New Tires ....................... 5-67
Buying New Tires
........................................ 5-67
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
.......................... 5.68
Wheel Replacement
...................................... 5.69
Tire Chains
.................................................. 5-71
Accessory Inflator
......................................... 5.72
If a Tire Goes Flat ........................................ 5.72
Changing a Flat Tire
..................................... 5.73
Compact Spare Tire
..................................... 5-81
Appearance Care ............................................ 5.82
Wheel
Alignment and Tire Balance
.................. 5-69
Cleaning the Inside of Your Vehicle
................. 5-82
Care of Safety Belts
...................................... 5-85
Weatherstrips ............................................... 5.85
Cleaning the Outside of Your Vehicle .............. 5-85
Sheet Metal Damage
..................................... 5.87
Finish Damage
............................................. 5.87
Underbody Maintenance
................... ...... 5.87
Chemical Paint Spotting
................................. 5.88
Vehicle Identification ..................................... 5-90
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
...... ., ...... 5-90
Service Parts Identification Label
........ ...... 5-90
Electrical System ............................... ...... 5-91
Add-on Electrical Equipment
................ , ...... 5-91
Headlamp Wiring
.......................................... 5-91
Windshield Wiper Fuses
................................ 5-91
Power Windows and Other Power Options
....... 5-91
Fuses and Circuit Breakers
............................ 5-92
Removing the Rear Seat Cushion
................... 5-95
Capacities and Specifications ........................ 5-100
Normal Maintenance Replacement Parts ......... 5-101
GM Vehicle Care/Appearance Materials .......... 5.88
5-2
Page 322 of 418

See the example below. When you end this high-speed
driving, return to the cold inflation pressure shown on
the Tire-Loading Information label.
Example:
You’ll find maximum load and inflation pressure molded
on the tire’s sidewall, in small letters near the rim
flange. It will read something like this: Maximum load
690
kg (1521 Ibs) @ 300 kPa (44 psi) Max. Press.
For this example, you would set the inflation pressure
for high-speed driving at
35 psi (244 kPa).
Notice: Don’t let anyone tell you that underinflation
or overinflation
is all right. It’s not. If your tires
don’t have enough air (underinflation), you can get
the following:
Too much flexing
Too much heat
Tire overloading
Bad wear
Bad handling
Bad fuel economy
If your tires have too much air (overinflation), you
can get the following:
Unusual wear
Bad handling
Rough ride
Needless damage from road hazards
When to Check
Check your tires once a month or more.
Don’t forget your compact spare tire. It should be at
60 psi (420 kPa).
How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type gage to check tire
pressure. You can’t tell
if your tires are properly inflated
simply by looking at them. Radial tires may look
properly inflated even when they’re underinflated.
Be sure to put the valve caps back
on the valve stems.
They help prevent leaks by keenin9 out dirt and
moisture.
5-63
Page 323 of 418

Check Tire Pressure System
The check tire pressure system can alert you to a large
change in the pressure of one tire. The system won’t
alert you before you drive that a tire is low or flat.
You must begin driving before the system will work
properly.
The CHECK TIRE PRESSURE message will appear on
the Driver Information Center (DIC) or the system
monitor TIRE PRESS light will come on
if pressure
difference (low pressure) is detected in one tire.
The check tire pressure system may not alert you
if:
more than one tire is low,
the vehicle is moving faster than 65 mph (105 km/h),
the system is not yet calibrated,
the compact spare tire is installed,
the tire treadwear is uneven,
tire chains are being used, or
the vehicle is being driven on a rough or
frozen road. If
the anti-lock brake system warning light comes on,
the check tire pressure system may not be working
properly. See your dealer for service. Also, see
Anti-Lock Brake System Warning Light on page 3-43.
The check tire pressure system detects differences
in tire rotation speeds that are caused by changes in tire
pressure. The system can alert you about a low
tire
- but it doesn’t replace normal tire maintenance.
See
Tires on page 5-62.
When the CHECK TIRE PRESSURE message appears
on the Driver Information Center (DIC) or the systems
monitor TIRE PRESS light comes on, you should
stop as soon as you can and check all your tires for
damage. If a tire is flat, see
If a Tire Goes Flat on
page
5-72. Also check the tire pressure in all four tires
as soon as you can. See
Inflation -- Tire Pressure
on page
5-62.
Any time you adjust a tire’s pressure or have one or more
tires repaired or replaced, you’ll need to reset (calibrate)
the check tire pressure system. You’ll also need to reset
the system whenever you rotate the tires, buy new tires
and install or remove the compact spare.
Don’t reset the check tire pressure system without first
correcting the cause of the problem and checking
and adjusting the pressure in all four tires.
If you reset
the system when the tire pressures are incorrect,
the check tire pressure system will not work properly
and may not alert you when a tire is low
or high.
5-64
Page 325 of 418
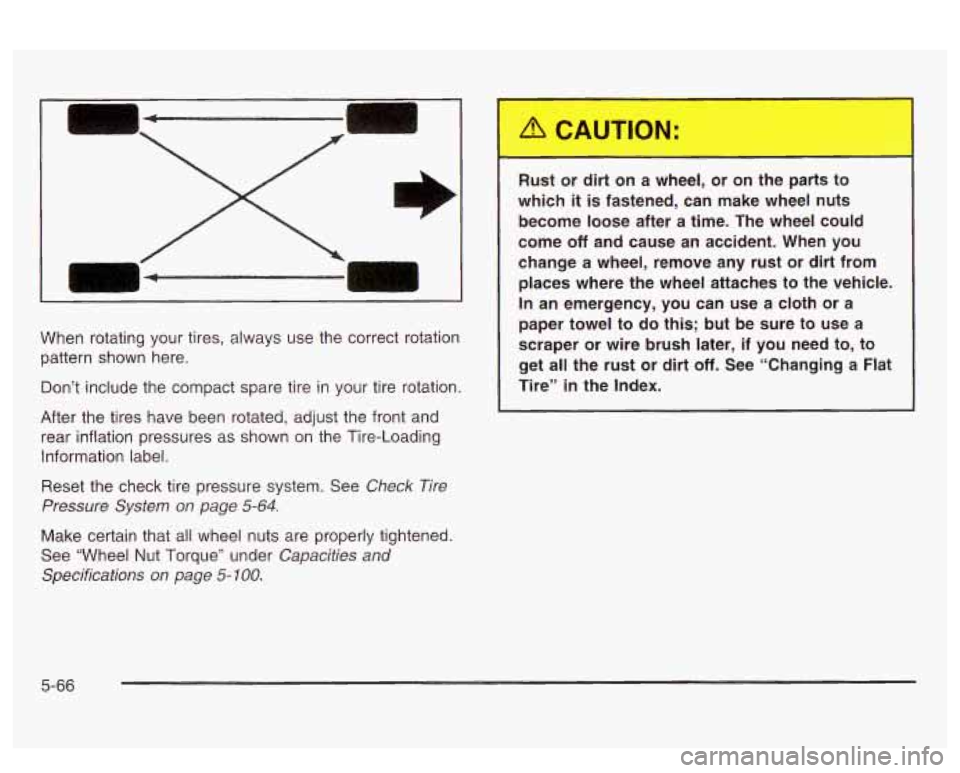
When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
Don’t include the compact spare tire in your tire rotation.
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and
rear inflation pressures as shown on the Tire-Loading
Information label.
Reset the check tire pressure system. See
Check Tire
Pressure System on page
5-64.
Make certain that all wheel nuts are properly tightened.
See “Wheel Nut Torque” under
Capacities and
Specifications on page
5- 100.
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to
which
it is fastened, can make wheel nuts
become loose after a time. The wheel could
come
off and cause an accident. When you
change a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from
places where the wheel attaches to
the vehicle.
In an emergency, you can use a cloth or a
paper towel to do this; but be sure to use a
scraper or wire brush later, if you need
to, to
get all the rust or dirt
off. See “Changing a Flat
Tire”
in the Index.
5-66
Page 327 of 418
Mixing tires couh :ause you to lose control
while driving. If you mix tires of different sizes
or types (radial and bias-belted tires), the
vehicle may not handle properly, and you
could have a crash. Using tires of different
sizes may also cause damage to your vehicle.
Be sure to use the same size and type tires on
all wheels. It’s all right to drive with your
compact spare, though.
It was developed for
use on your vehicle.
I
If you use bias-ply tires on your vehicle, the
wheel rim flanges could develop cracks after many miles of driving.
A tire and/or wheel
could fail suddenly, causing a crash. Use only
radial-ply tires with the wheels on your vehicle.
5-68
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
Quality grades can be found where applicable on the
tire sidewall between tread shoulder and maximum
section width. For example:
Treadwear 200 Traction AA Temperature A
The following information relates to the system
developed by the United States National Highway
Traffic Safety Administration, which grades tires by
treadwear, traction and temperature performance.
(This applies only
to vehicles sold in the United States.)
The grades are molded on the sidewalls of most
passenger car tires. The Uniform Tire Quality Grading
system does not apply to deep tread, winter-type
snow tires, space-saver or temporary use spare tires,
tires with nominal rim diameters
of 10 to 12 inches
(25
to 30 cm), or to some limited-production tires.
While the tires available on General Motors passenger
cars and light trucks may vary with respect to these
grades, they must also conform
to federal safety
requirements and additional General Motors Tire
Performance Criteria (TPC) standards.
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on
the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled
conditions on a specified government test course.
For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and
a half (1.5) times as well on the government course as
Page 333 of 418

Removing the Spare Tire and Tools 5. Remove the wheel wrench, jack and the spare tire
from the trunk.
The equipment you’ll need is in the trunk.
1. Pull the carpeting from the floor of the trunk.
2. Remove the retainer, then lift and remove the cover.
3. Remove the compact spare tire. See Compact
Spare Tire on page 5-81 for more information
about the compact spare tire.
4. Unscrew the wing nuts to remove the container that
holds the wrench and jack. The
tools you’ll be using include the jack
(A) and wheel
wrench
(B).
Removing the Wheel Covers and
Wheel Nut Caps
If your vehicle has aluminum wheels and a center cover
hides the wheel nuts, remove the center cover by
using the flat end
of the wrench to pry it off. Do not drop
the cover or lay it face down,
as it could become
scratched or damaged.
Do not use a hammer or mallet
on this type of cover.
5-74
Page 334 of 418

Removing the Flat Tire and Installing
the Spare Tire 2. The jack has a bolt at the end. Attach the wheel
wrench to the bolt to create a jack handle.
1. Use the wheel wrench to loosen the wheel nuts, but
don't remove them.
3. Turn the wheel wrench counterclockwise to lower
the jack
lift head until it fits under the vehicle.
5-75
Page 336 of 418

5. Raise the vehicle by turning the wheel wrench
clockwise. Raise the vehicle far enough
off the
ground
so there is enough room for the compact
spare tire to fit under the wheel well.
6. Remove all the wheel nuts and take off the flat tire.
7. Remove any rust or dirt
from the wheel bolts,
mounting surfaces
and spare wheel.
r
Rust or dirt on the wheel, or on the parts to
which
it is fastened, can make the wheel nuts
become loose after a time. The wheel could
come
off and cause an accident. When you
change a wheel, remove any rust
or dirt from
the places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle.
In an emergency, you can use a cloth
or a paper towel to do this; but be sure to use
a scraper or wire brush later,
if you need to, to
get all the rust or dirt
off.
5-77